Abstract
In the process of applying plant protection sprays, the atomisation process of complex pesticide components such as emulsion pesticides is different from that of water. Indeed, emulsion is often used as an additive to spray to reduce drift. Therefore, this study investigated the different morphological characteristics that occur between emulsions and water during atomisation at different pressures through visualisation experiments and interpreting the formation of structural differences between the two fragmentation mechanisms. The effect of liquid sheet structure on droplet size distribution was analysed in three-dimensional space, not only from one spatial perspective, but how it alters the morphological structures of liquid sheet leading to different potential droplet drift characteristics. It was found that the smaller the liquid sheet disturbance, the more concentrated the droplet size distribution, the more intense the liquid sheet disturbance, the more dispersed the droplet size distribution. The addition of 0.02% emulsion significantly reduced the proportion of V100 (the ratio of volume with drops smaller than 100 μm to the total volume of all droplets) from 21.33% to 10.24%, and the higher the emulsion concentration, the smaller the V100. The ability of the emulsion to increase V400 decreased with increasing pressure.
1. Introduction
Pesticide spraying is an important part of modern agriculture and one of the most important ways to control weeds, crop diseases and insect pests. The focus of research has for many years been on how to improve the effective utilisation of pesticides, and reduce pesticide drift, and increase deposition [1,2]. The use of an emulsion could significantly reduce the generation of fine droplets that have the potential drift during the spraying process [3,4].
The research on the atomisation of water and similar low viscosity Newtonian liquids has been relatively well explored. Due to Kelvin-Helmholtz instability, wave motions occur in the liquid sheet formed after leaving the nozzle outlet. Then, these liquid sheets break into droplets due to the Rayleigh instability driven by surface tension. In addition, bags of liquid break into droplets [5]. In the application of pesticide spray, the use of emulsions could lead to another fragmentation mechanism, for example the formation of holes in placid sheets. During emulsion atomisation, oil droplets first enter the air/water interface, and then diffuse on the interface and perforations are generated on the liquid sheet [6]. The holes in the liquid sheet grow until they merge to form net structure and breaks-up into droplets [7]. Emulsion formulations lead to earlier rupture and coarser droplet spectra [8]. A power law relationship between sheet thickness and droplet size was noted [9]. Small liquid sheet areas correspond to thick liquid sheets, resulting in coarser droplet sizes [10]. Many researchers have studied the mechanism of hole formation in liquid sheets. One mechanism considers that, considering the mutual flow between the disperse oil phase and the continuous water phase, sub-phase flow generated by oil droplets entering the water/air interface may can increase the formation of perforation [11]. Another mechanism considers that, when oil droplets enter the water/air interface, they diffuse and form a weak point, which finally form holes. Mathematical description of the formation of holes in emulsion sprays have been achieved using the entry coefficient. The growth and fragmentation of two holes was predicted by a hole dynamics model. With the increase of hole spacing and the decrease of the initial distance from the nozzle, the droplet diameter increased and the proportion of driftable fine spray decreased [12].
Based on the literature available, the perforation mechanism of emulsion fragmentation produces larger droplet size than water [13,14]. The holes structure of perforation mechanism would reduce the fine droplet [15]. However, due to the complexity of influencing factors, attempts to link droplet size and spray drift results with the characteristics of spray liquid are challenged. Yet, the narrow droplet size spectrum or volume median diameter is often used as the index to quantify the decrease of small droplet size, resulting in the lacking of quantitative detailed description of the effect of perforation on droplet size distribution. How the holes structure affects the divergence and spatial distribution of droplet size remains to be further explored [16].
In this study, the atomisation process and droplet size distribution of different physical and chemical properties, different pressures and different spatial positions were explored. A high-speed camera was used to visualise the process of spray atomisation process and the spray structure was quantitatively analysed by image post-processing. Furthermore, V100 and V400 were used as the standards to describe in detail how different atomisation disturbance structures affect the droplet size distribution. The effects of different spray structures on droplet size divergence were studied. This study serves as a resource for subsequent research on adjusting pesticide formulations to reduce droplet drift and pesticide waste.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
The morphology structures of water atomisation and emulsion pesticide butachlor (Lulilai, China) atomisation were captured by the spray image acquisition system shown in Figure 1. Butachlor is a typical emulsion herbicide that the CAS Number is 23184-66-9. Fragmentation perforation mechanism was studied by using butachlor as an oil in water emulsion, which could cause hole structure. The method of pendant drop was used to measure the surface tension of emulsion pesticide butachlor and water by an automated tensiometer, CAM 101 (KSV, Espoo, Finland). The pendant drop method uses Laplace-Young fitting to fit the outline of the droplet to obtain surface tension. Three concentrations of butachlor were considered, which are 0.02%, 0.1% and 0.5%. The water used in the experiment is tap water with surface tension of 0.071153 N/m. All chemicals were used as obtained without further purification. The pressure of the spray system is provided by the air compressor and combined with a tank for pressure stabilisation to provide a more stable pressure output than a pump, which was adjusted by a gas regulator valve with measurement range of 0.1 MPa to 0.5 MPa. This pressure range could satisfy the requirements of spraying water and pesticide in plant protection operations. Atomised flat fan sheet was produced with a commercially available flat fan ST-110-01 nozzle (Lechler GmbH, Metzingen, Germany), which has a design of an elliptical cross section at the orifice. The flat fan nozzle was mounted on a rotating mechanism to realise the function of capturing the spray characteristics in any circumferential direction. This provides flexibility in spraying at three-dimensional spatial scale evolution of liquid sheet and the spatial distribution characteristics of droplets under the disturbance mechanism and hole-breaking mechanism of water spray. For a more intuitive description of this three-dimensional evolution, as shown in Figure 2, the following spray spatial coordinates are set. The nozzle outlet was set as the coordinate origin (0, 0, 0), the Y-axis along the direction of spray flow, which formed vertically downward, the X-axis along the spreading direction of the liquid sheet and the z-axis perpendicular to the spreading direction of the liquid sheet.
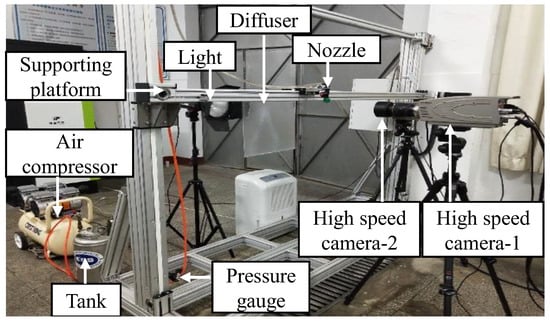
Figure 1.
Image acquisition system based on two high speed camera and spray camera.
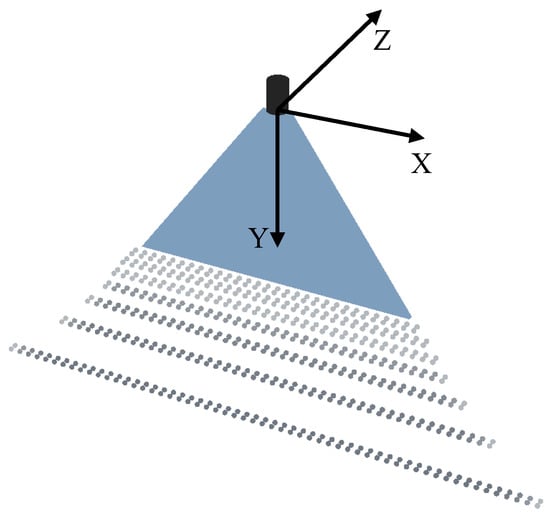
Figure 2.
Geometrical orientation of the system.
2.2. Spray Visualisation
The fragmentation evolution process was taken by the high-speed camera, i-SPEED (OLYMPUS, Essex, UK), which introduces the fixed mode noise (FPN) into the image through the image sensor and photoreceptor captures the light and converts it into the electronic copy of the optical image. Then the video image of various directions as XY plane and YZ plane was stored. The high-speed camera was set to 10,000 frames/s. For getting various spray structures, hundreds of atomisation image in different operating conditions were measured through image processing software of Image-Pro Plus (Meyer instruments, Houston, TX, USA). To ensure the accuracy of the data, five sets of averages were measured for each value. The breakup length was defined as the distance of the pieces of the sheet rupture from the main sheet to form ligaments. The diffusion angle was determined as the angle formed by the boundary of liquid sheet in the direction of the side view. Diffusion angle was measured through flexible two-point method through an image processing software [17].
2.3. Droplet Size Measurement
The laser diffusion particle size analyser (OMEC, Zhuhai, China) realises the measurement of the droplet size according to the Fraunhofer diffraction principle and the typical parallel light path design. The test range is 0.5–1500 μm, and the error is less than 3%. The differences of droplet size distribution of water and emulsion spray in different spatial positions were measured. Three sets of droplet size data at different spatial locations were measured in the spatial coordinates. Single measurement time is 5 s, and average value for each of the three groups was obtained. In the flow direction, droplet size change from Y = 30 mm to Y = 500 mm was measured. In the horizontal direction, when Y = 500 mm (the distance from the nozzle outlet to the crop is usually set at 500 mm), where the droplet size and shape are stable, one value was measured every 20 mm in the horizontal direction until droplet size data cannot be detected. When Y = 50 mm (the liquid sheet has just broken into droplets), where the droplet size has a narrow distribution, one value was measured every 10 mm.
The droplet size of spray droplets was calibrated by Dv50, V100 and V400. Dv50 means the droplets with diameters less than that accounted for 50% of the total volume of liquid droplets [18]. V100 and V400 are the ratio of volume with drops smaller than 100 μm and 400 μm to total volume of all droplets.
2.4. Dimensionless Analysis
The dimensional analysis method is used to analyse the obtained data, and the dimensionless numbers can be used to describe the relevant physical changes in the liquid sheet atomisation and crushing [19]. The addition of a small amount of emulsion pesticide could significantly reduce the surface tension of spray solution. Therefore, this study mainly involves two related dimensionless numbers with significant effects, Weber number and dimensionless angle.
The dimensionless liquid surface tension uses the Weber number, which is the ratio of the kinetic energy of the liquid flow to the surface tension. To compare the effects of physicochemical properties of spray and pressure on the two fragmentation mechanisms, that is, to investigate the competition between fluid inertia and surface tension when liquid sheet breaks into droplets, the values obtained of Weber number were varied with nine pressures (0.1 MPa to 0.5 MPa) and two solutions including water and 0.1% concentration of butachlor. The Weber number (We) for the flat fan nozzle with elliptical outlet is defined as [20]:
where ρ is the liquid density (kg/m3), v is the characteristic velocity (m/s), σ is the surface tension (N/m), and l is the characteristic length (m).
Another dimensionless number we discussed in detail from the perspective of atomisation mechanism is diffusion angle, θ, which is already non-dimensional and thus can serve as its own non-dimensional group.
3. Results
3.1. Rheological Behaviours
Butachlor is a hydrophobic solution as the dispersed phase creates an inhomogeneous formulation which alters the mechanism in the atomisation process. Droplet formation is due to competition between fluid inertia and surface tension whose surface tension is 10−4 times of the inertial force and the effect of viscosity can be negligible below 2 × 10−3 Pa∙s [21]. The correlation between the viscosity of dispersed phase and spray coarsening effect is very weak, so the viscosity seems not to be a key parameter for perforation initiation. Therefore, we expect to have surface tension to describe the effect of the composition of the emulsion type pesticide on the fragmentation mechanism. The surface tension of butachlor was measured for the different concentrations. The data on the relationship between concentration and surface tension in Figure 3 indicate that there seems to be a critical concentration which is about 0.8%. When the solution concentration exceeds this critical concentration, the surface tension tends to stabilise at about 0.032 N/m, and after reaching this concentration, the decrease of surface tension is not obvious with the increase of concentration.
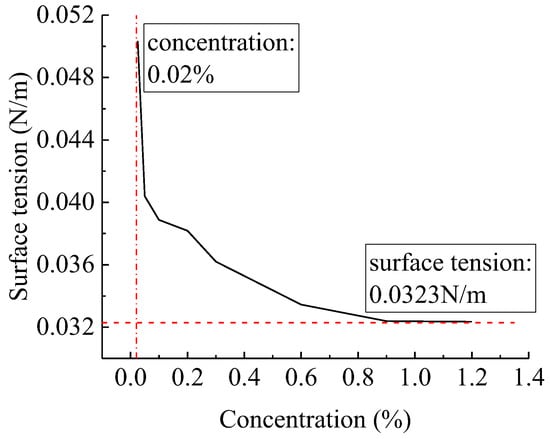
Figure 3.
Surface tension changes with butachlor concentration.
3.2. Atomisation Process and Spray Structure
3.2.1. Fragmentation Process and Breakup Length in XY Plane
As many researchers have studied, the spray evolution of water and emulsion have different characteristics in morphology. It can be seen from Figure 4 that from the shape of the disintegrate droplets that the fragmentation method of water atomisation and emulsion atomisation is obviously different. There are also different structures between the liquid sheet rim of water and emulsion [22].
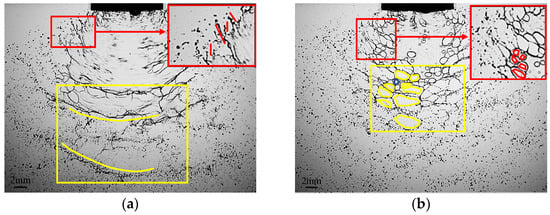
Figure 4.
Water (a) and emulsion (b) atomisation process and rim recession in XY plane. The difference between the two liquid sheet atomisation processes is marked by yellow frame; the difference between two rim recessions is marked by red frame.
The fragmentation mechanism of water is the process of that liquid sheet broken into liquid ligaments under oscillation disturbance and then the liquid ligament is broken into droplets. In the mechanism of water spray, the liquid is deformed in the nozzle due to the action of shear force and corrugated during the contraction process. On the liquid sheet formed by water spray, there are obvious corrugated structures. Due to Rayleigh-Taylor instability, with the increase in disturbance on the liquid sheet, the wavy structure on the liquid sheet gradually tears into liquid ligaments. Droplets are formed under the action of surface tension through these liquid ligaments. The shape of the broken liquid droplets is distributed in a ligament shape, and gradually spreads around.
The addition of emulsion resulted in a more complicated fragmentation mechanism. The morphology of the crushing process is obviously changed. Fragmentation of the emulsion takes place resulting in the formation of a hole structure on the liquid sheet. The holes gather to form a grid, and the droplets are distributed to form the grid. The droplet size formed by emulsion spray could be seen from the image, which is coarser than the droplets generated by water [23].
Figure 5 shows the evolution of hole structure with time during emulsion atomisation. When there are oil droplets of sufficient size or hydrophobicity on the liquid sheet, hole structures are formed, and the single hole combines with the surrounding holes, gradually expanding to form a grid structure [24,25]. The grid structure continues to break into droplets. The process of hole formation to complete fragmentation to droplet formation is about 0.6 ms when the breakup mechanism is perforation mechanism. In the 0.7–0.8 ms, the fragmented droplet population remains in the shape of the elliptical holes because of the inertial force. The initial stage of broken holes is close to circular shape, then the shape of the hole changes into elliptical shape with time.
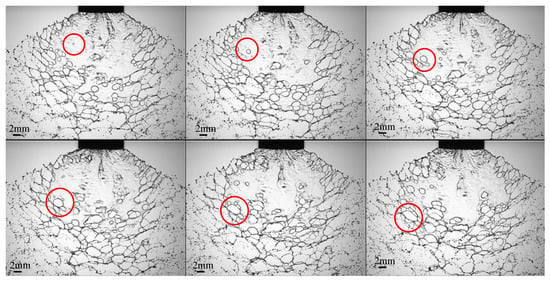
Figure 5.
Time scale evolution process of perforation. One hole formation and fragmentation structure is marked by red circles.
The variation of liquid sheet breakup length as one of the essential parameters of fragmentation on time scale was further studied. Liquid sheet breakup length takes a period of 0.3–0.6 ms from the initial liquid sheet gradually elongated to the formation of ligaments or network structure. The time for the emulsion spray to complete such a period is 0.2 ms, less than that of water. It can be seen that perforation mechanism shortens atomisation period and advances 33% fragmentation process time. The reason for this phenomenon is the alteration of atomisation process with the addition of emulsion. The mechanism of emulsion atomisation is hole breaking. While the atomisation mechanism of water is usually due to the development of unstable disturbance waves on the liquid sheet surface and the enhancement of surface tension by ambient air, resulting in Rayleigh regime and breakup into droplets [26]. The addition of emulsion made the liquid sheet instable and weakened the liquid sheet disturbance during atomisation process. The unstable waves on the liquid sheet are curved or sinusoidal, then it forms liquid ligaments and finally disintegrated into droplets [27]. Because of the early occurrence of the liquid sheet instability caused by the emulsion, the droplet size formed by the instability and fragmentation of the liquid sheet would be affected.
The fragmentation characteristics of liquid sheet formed under different pressure were further quantitatively analysed. Changes in breakup length of liquid sheet with water as spray liquid are usually studied. However, under the breaking mechanism of perforation mechanism, the liquid sheet length shows another change with pressure. Comparing the change of liquid sheet breakup length of water and emulsion as shown in Figure 6a, it could be seen that the discrepancy of the breakup length between two liquids decreases with the increase of pressure. The breakup length of water decreases with pressure, alternately, the breakup length of emulsion increases with pressure. Variation in the breakup length of water shows a more obvious fluctuation, in contrast, the breakup length of emulsion shows a more stable growth trend shown in Figure 6b. This observation may be due to the difference caused by the change of liquid sheet stability.
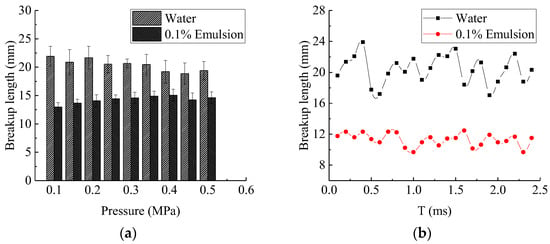
Figure 6.
(a) The variation of liquid sheet breakup length under different spray pressures. (b) The variation of liquid sheet breakup length with Time (T) caused by different fragmentation mechanisms.
Because the surface tension of emulsion is less than that of water, the stability of the liquid sheet during spraying is reduced, resulting in the formation of liquid ligaments closer to the nozzle, and the formation of droplets earlier. The liquid sheet breakup length of emulsion is less than that of water. Compared with emulsion and water, it will be broken in advance to prove each other. Spray instability was the effect of surface tension. The smaller the surface tension is, the shorter the liquid sheet breakup length is, and the faster the droplet formed.
3.2.2. Liquid Sheet Disturbance and Diffusion Angle in YZ Plane
The different morphological characteristics of the atomisation of water and emulsion also had been captured from the side view, that is, from the YZ plane. The morphology of liquid sheet in YZ plane shows the disturbance movement of liquid sheet intuitively.
It can be seen from Figure 7 that liquid sheet flapping behaviour is different in water atomisation and emulsion atomisation captured by high-speed camera in the YZ plane, although the flapping structure can be observed in both water atomisation and emulsion atomisation. The flapping structure of water atomisation is more obvious than that of emulsion. Compared with water, the flapping degree of emulsion atomisation is significantly reduced, and indicated that the perforation atomisation mechanism of emulsion spray significantly inhibits the flapping of liquid sheet. With the increase of the distance from the nozzle outlet, the flapping degree of the liquid sheet becomes more obvious, the wave peak of liquid sheet flapping increases gradually, and the instability increases. While the wave peak of emulsion liquid sheet disturbance structure did not change significantly with the distance increase from the nozzle outlet. This indicates that the perforation mechanism of emulsion atomisation obviously destroys the disturbance of liquid sheet, making the perforation mechanism replace the disturbance mechanism of water spray as the dominant mechanism in the atomisation process. The result shows that the disturbance of water is more obvious and the greater the flapping degree is, the flapping degree of emulsion disturbance is less obvious. The weaker the disturbance flapping, the thicker the liquid sheet would be stretched, resulting in larger droplet size, which may have a positive effect on reducing the drift during spray [28].

Figure 7.
The morphological characteristics of water (a) and emulsion (b) in the YZ plane. The liquid sheet flapping degree from side view is indicated by red lines; and the partial enlarged detail is marked by red frame.
Very few measurements of diffusion angle were reported in the literature, using diffusion angle as an index to quantify the degree of liquid sheet disturbance. The disturbance of the unstable waves on the liquid sheet leads to a decrease in diffusion angle, therefore the diffusion angle of emulsion is smaller than that of water.
It can be seen from Figure 8a that the diffusion angle increases with the increase of pressure for both water and emulsion atomisation, and the growth rate of water liquid tends to be constant while the growth rate of emulsion decreases gradually. The diffusion angle varies greatly under different pressures. It can be increased from 5° to more than 15° of water while from 4° to more than 10° of emulsion atomisation. The diffusion angle of emulsion is obviously smaller than that of water. Figure 8b shows the variation of diffusion angle with Weber number that the slope of diffusion angle with the Weber number is extremely small. Diffusion angle increases extraordinarily slightly with the increase of Weber number. The diffusion angle of water is slightly larger than that of emulsion. This is consistent with the morphological features that the longer the length of the liquid sheet and the more obvious the liquid sheet flapping, the smaller the droplet size is.
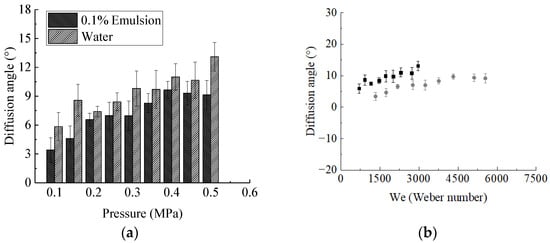
Figure 8.
(a) Diffusion angle of two fragmentation mechanisms varies with pressure. (b) Diffusion angle varies with Weber number. The concentration of emulsion is 0.1%. The black symbols are diffusion angles under high surface tension and the grey symbols for low surface tension.
3.3. Droplet Size Distribution Spatially and Drift Characteristics
Emulsions increase the droplet size compared to water spray through a conventional nozzle which corresponds to the structural features of liquid sheet fragmentation captured by high-speed cameras.
3.3.1. Effect of Emulsion Pesticide on Droplet Size at Different Positions in Three-Dimensional Space
Conventionally, for the factors to measure the atomisation quality, the droplet size is usually only considered at 500 mm from the nozzle outlet, and the spatial distribution of the droplet size is rarely considered. The effect of perforation mechanism caused by emulsion on the spatial distribution of droplet size is a problem worthy of discussion. Since the liquid sheet formed by the flat fan nozzle is symmetrical, the droplet size along the positive direction of X-axis from the centre position of the liquid sheet to the rim of the liquid sheet is discussed in this study.
In the position range near the nozzle outlet, the size of droplet decreases with the increase of flow direction distance, then this trend of inverse proportions becomes diminishing with the increase of flow direction distance, and finally remains unchanged [29]. No matter when the liquid is water atomised dominated by Rayleigh mechanism, or the liquid is emulsion dominated by perforation mechanism all show a similar trend like this. It can be seen from Figure 9a that the reason for this droplet size change along the jet direction is not due to the different surface tensions. From the data, the droplet size is obviously affected by the distance from the target height, however, the size of droplet should not change after the droplet breakup from the formation mechanism of droplets. The reason for this phenomenon may be due to droplets continue to evaporate, deform, collide and fragment as they leave the nozzle outlet in the atomisation process until 200–500 mm away from the outlet and gradually tended to be stable. Because the droplet is stable at 500 mm away from the target, the number of droplets measured at different heights is not completely consistent, this may also be one of the reasons for this phenomenon.
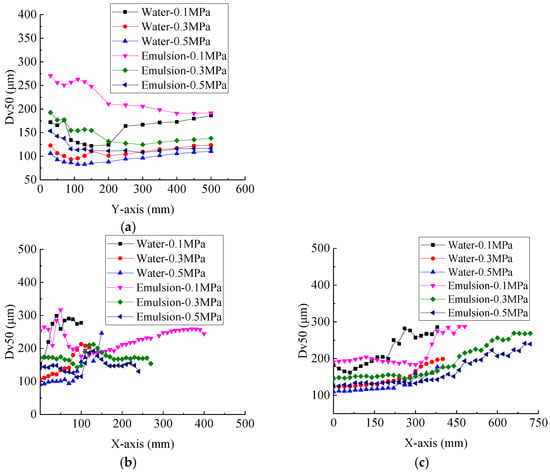
Figure 9.
(a) Droplet size varieties with different distance nozzle outlet along Y-axis. (b) Droplet size varieties with different positions along X-axis at 50 mm distance from nozzle outlet. (c) Droplet size varieties with different positions along X-axis at 500 mm distance from nozzle outlet. The concentration of emulsion is 0.1%.
However, it is noteworthy that when the pressure is low, droplet size shows larger instability in the flow direction. When hydraulic pressure is low, Rayleigh regime generate main impact, ambient gas has little effect on liquid breakup, which leads liquids to break up into larger droplets. As the pressure increases, the liquid velocity increases, liquid atomisation enters the first wind-induced atomisation regime, consequently causing the effect of ambient air to be enhanced, resulting in smaller droplets.
Figure 9b shows the droplet sizes at different spanwise positions at 50 mm from the nozzle outlet. The volume median of water was smaller than that of butachlor with the change of lateral position, near the nozzle outlet. The droplet size of the emulsion near the nozzle outlet is larger than that of the water because of the different ways of breaking caused by different physicochemical properties of different spray liquids [30]. The closer the water is to the rim, the larger the droplet size is, because the rim fragmentation mechanism is another mechanism. However, the droplet size of butachlor fluctuates around a certain value, which is due to the formation of holes in the atomisation of emulsion, resulting in a more uniform trend in the final droplet size. The volume median diameter of butachlor may be sinusoidal and the amplitude was small. Significant differences were observed between butachlor and water at shorter target distances.
The data in Figure 9c show the droplets size at 500 mm from the nozzle outlet changes along with the X-axis indicating that no matter what the solution is, water or emulsion, the droplet size formed by atomisation is smaller and more stable at the position of 500 mm from the nozzle outlet than at the position of 50 mm. The droplet size of the emulsion is larger than that of water near the middle of the nozzle. With the increase of displacement in X-axis direction, the droplet size of water is larger than that of oil due to the change of water spray rim atomisation mode. Water atomisation reaches the boundary range at about X = 400 mm, while the droplet size of oil atomisation continues to increase until X = 750 mm. At the distance of 500 mm from the nozzle outlet, the droplet size distribution is U-shaped in both water and oil for the whole complete flat fan spray. When the distance from the nozzle outlet increases from 50 mm to 500 mm, the droplet size distribution is more uniform and stable in the horizontal direction. Study on the spatial distribution of droplet size has application significance for target distance setting.
3.3.2. Influence of Emulsion Pesticide on Droplet Drift and Deposition
Another representation of droplet size is that the number, surface area, volume, or mass of all droplets under a certain diameter account for the percentage of the total number, total surface area, total volume or total mass of droplets (Vc (%)), which is called the cumulative distribution of droplet size [31]. Droplet drift would occur when the droplet size is less than 100 μm, that is, V100 is less than 100 μm [32,33]. While the droplet size is greater than 400 μm, the droplet is prone to bounce when it reaches the surface of the leaves surface, which affects the droplet deposition effect. Therefore, the study on the cumulative distribution of droplet size has considerable practical application value, especially for V100 and V400.
It can be clearly seen from Figure 10a that there are obvious size differences between the coarse droplets and the fine droplets when the water is atomised. When butachlor was atomised, the size difference between the coarse droplets and the fine droplets was significantly reduced. Especially, with the increase of butachlor concentration, the uniformity of the droplets was significantly improved. This may be because the atomisation process of water is that the liquid sheet is broken into liquid cylinder, and finally the liquid cylinder is broken into droplets, while the emulsion spray is that the liquid sheet forms a network of filaments structure and finally breaks into droplets. The difference between the structural changes in the atomisation process can also be seen from the photograph.
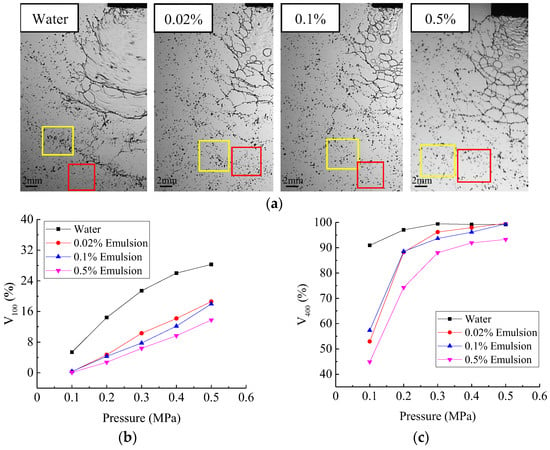
Figure 10.
(a) Comparison of coarse droplets and fine droplets formed by atomisation of water and different concentrations of emulsion, in which coarse droplets are marked by yellow frames and fine droplets by red frames. (b) The effect of emulsion spray on droplet size proportion of V100 under different pressures. (c) The effect of emulsion spray on droplet size proportion of V400 under different pressures.
V100 and V400 could well characterize the proportion of coarse droplets and fine droplets in agriculture. In order to reduce drift and increase deposition, usually smaller values of V100 and V400 are required. Consideration from reducing drift, it is obvious from Figure 10b,c that adding emulsion of only 0.02% concentration could significantly reduce the proportion of V100 of droplets formed in the atomisation fragmentation to 10.24% from 21.33% of water and the higher the concentration of emulsion, the smaller the V100.
Consideration from increasing deposition, the addition of emulsion would increase the proportion of V400 in spray, but this ability weakens as pressure increases. The proportion of V400 in water spray was 0.55%, while after adding 0.02% emulsion, the proportion of V400 increased to 4.25%. The increase in the proportion of V400 may be due to the global increase of droplet size spectrum caused by the change of atomisation mechanism of the emulsion spray relative to the water spray.
3.4. Theoretical Analysis of Perforation Effects on Droplet Characteristics
For hydraulic spray, studies have shown that one of the main reasons for spray fragmentation is affected by surface tension. Hydrophobic emulsion droplets disperse in water by surfactant as another phase that distinguishes them from water. The local surfactant concentration on the surface of the emulsion drops decreases due to the deformation of emulsion drops under shearing action, resulting in the contact between hydrophobic emulsion drops and water, which leads to the formation of holes [34,35].
The change of droplet size caused by holes is related to the pressure difference on both sides of the liquid sheet. The coupling of low-pressure region and high-pressure region on both sides of the liquid sheet is the main reason for the flapping dynamic characteristics [36]. Liquid sheet formed by water spray and emulsion pesticide spray all have disturbance wave structure. The greater the bending degree of the wave structure on the liquid sheet, the greater the pressure difference. The smaller the bending degree of the wave structure on the liquid sheet, the smaller the pressure difference. The disturbance of the liquid sheet produced by the emulsion atomisation is not obvious, and the pressure difference on both sides of the liquid sheet is small. The liquid sheet receives a more gentle and uniform deformation caused by the pressure difference. More stable liquid sheet thickness will produce more uniform droplet size. A thicker liquid sheet wound generate a larger and uniform droplet size. The greater the pressure difference, the thinner the liquid sheet will be stretched. The thinner the sheet thickness, the smaller the droplet size. The atomisation droplet size of water with more obvious disturbance is smaller. The stronger the disturbance is, the more different pressure differences will be produced at different locations, resulting in the liquid sheet being stretched to varying degrees, resulting in more different liquid film thickness and wider droplet size distribution. Furthermore, water spray is mainly caused by Kelvin–Helmholtz instability fluctuation broken form droplets, but the rim fragmentation of water spray is a finger-like structure broken. While in the emulsion spray, no matter the main fragmentation mechanism or the rim fragmentation are all the hole fragmentation mechanism. That may also be one of the reasons for the more uniform droplet size distribution formed by the emulsion spray.
4. Discussion
Emulsion could alter the atomisation mechanism and affect the droplet size distribution characteristics in the atomisation process. Improving pesticide utilisation efficiency can significantly improve pesticide atomisation quality, reduce pesticide drift and minimise environmental pollution. Research on pesticide formulation is an effective way to reduce pesticide waste and environmental pollution. In the future research, it is necessary to further study the effect of different agricultural machinery in different operating scenarios by adding emulsifiable concentrate to improve pesticide drift. Especially UAV spraying, due to its high operating speed and high operating height, it is easy to produce pesticide drift and pesticide waste. For the high-speed and low-altitude operation scenario of UAV pesticide spraying, how the use of emulsion in pesticide formulations can provide the best effect of pesticide spraying is a very meaningful research direction in the following research.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the morphology characteristics of liquid sheet were quantitatively described by the influence of pressure and surface tension of spray, including liquid sheet breakup length and diffusion angle. The influence of emulsion on droplet size distribution is analysed in a three-dimensional space. V100 and V400 were used as indicators to quantitatively analyse the drift and deposition performance of coarse droplets fine droplets. Reasons for emulsion perforation effect on droplet size characteristics was further investigated.
The surface tension affects the stability of the spray, the length of the liquid sheet and the urgency of fragmentation: the smaller the surface tension, the more unstable the liquid sheet, the smaller the liquid sheet length, and the faster the droplet formation. Emulsion not only changes the surface tension, but also causes the surface free energy between emulsion droplets and water, resulting in the formation of perforation. Perforation inhibits the disturbance of liquid sheet and changes the pressure difference at the interface, resulting in less fine droplets and more uniform droplet size distribution. Droplet size produced by emulsion spray is more uniform in horizontal direction than that of water; smaller Dv50 at 500 mm from nozzle outlet and more stable in horizontal direction than that of water; adding 0.02% butachlor reduces V100 from 21.33% to 10.24%, whereas V400 only increased from 0.55% to 4.25%.
Author Contributions
W.Y., W.J. and M.O. conceived research idea and designed the experiments; W.Y. and W.Z. performed the experiments; W.Y. analysed the data and wrote the paper; W.J., M.O., L.J. and X.W. reviewed and revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Project of Faculty of Agricultural Equipment of Jiangsu University (grant number NZXB20200204); the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region science and technology key R&D project (Grant No. 2018BBF02020); the Jiangsu Agriculture Science and Technology In-novation Fund (JASTIF) (CX (20)3065).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Faculty of Agricultural Equipment of Jiangsu University for its facilities and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X. Study on Spray Drift and Anti-Drift Method. Master’s Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Appah, S.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Wang, P.; Asante, E.A. Analysis of potential impaction and phytotoxicity of surfactant-plant surface interaction in pesticide application. Crop Prot. 2020, 127, 104961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilz, E.; Vermeer, A.W.P.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Leermakers, F.A.M. Mechanism of perforation based on spreading properties of emulsified oils. At. Sprays 2012, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Li, D.; Kang, C.; Wang, Y. Visualisation of the evolution of perforations in oil-based emulsion sheets formed by flat-fan spray nozzles. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 207, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgarian, A.; Heinrich, M.; Schwarz, R.; Bussmann, M.; Chattopadhyay, K. Experiments and Modeling of the Breakup Mechanisms of an Attenuating Liquid Sheet. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2020, 130, 103347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernay, C.; Ramos, L.; Würger, A.; Ligoure, C. Playing with Emulsion Formulation to Control, the Perforation of a Freely Expanding Liquid Sheet. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2017, 33, 3458–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avulapati, M.M.; Megaritis, T.; Xia, J.; Ganippa, L. Experimental understanding on the dynamics of micro-explosion and puffing in ternary emulsion droplets. Fuel 2019, 239, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryer, S.A.; Altieri, A.L.; Schmucker, A.L.; Schmucker, A.L.; Day, K.M. Minimising atomisation drift potential by exploring the break-up of liquid sheets using multiphase methylated soybean and silicon oil emulsions. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 202, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbaglah, G. Breakup of thin liquid sheets through hole–hole and hole–rim merging. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 911, A23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Kang, C.; Jia, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, Y. The effect of spray structure of oil-based emulsion spray on the droplet characteristics. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 198, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Yi, R.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.J. Theoretical breakup model in the planar liquid sheets exposed to high-speed gas and droplet size prediction. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2018, 98, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, A.L.; Cryer, S.A. Break-up of sprayed emulsions from flat-fan nozzles using a hole kinematics model. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 169, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.K.; Antuniassi, U.R.; Chechetto, R.G.; Mota, A.A.B.; de Jesus, M.G.; de Carvalho, L.R. Viscosity, surface tension and droplet size of sprays of different formulations of insecticides and fungicides. Crop Prot. 2017, 101, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Li, D.Y.; Kang, C. Visualization of the evolution of bubbles in the spray sheet discharged from the air-induction nozzle. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franc, A.J.A.L.; da Cunha, J.P.A.R.; Antuniassiu, U.R. Spectrum, velocity and drift of droplets sprayed by nozzles with and without air induction and mineral oil. Eng. Agric. 2017, 37, 502–509. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiong, L. Effect of adjuvants on the spray droplet size of pesticide dilute emulsion—ScienceDirect. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619, 126557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Rodriguez, I.; Pos, R.; Megaritis, T.; Ganippa, L.C. Investigation of Spray Angle Measurement Techniques. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 22276–22289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.L.; Silva, H.J.P.; Almeida, D.P.; Ferreira, M.D.C.; Pontes, N.D.C. Droplet spectra and surface tension of spray solutions by biological insecticide and adjuvants. Eng. Agrícola 2017, 37, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altieri, A.; Cryer, S.; Acharya, L. Mechanisms, experiment, and theory of liquid sheet breakup and drop size from agricultural nozzles. At. Sprays 2014, 24, 695–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnogrodzki, A. Theoretical prediction of the critical weber number. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1993, 19, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooij, S.; Sijs, R.; Denn, M.M.; Villermaux, E.; Bonn, D. What Determines the Drop Size in Sprays. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 031019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Néel, B.; Lhuissier, H.; Villermaux, E. ‘Fines’ from the collision of liquid rims. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 893, A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.C.; Tuck, C.R. How adjuvants influence spray formation with different hydraulic nozzles. Crop Prot. 1999, 18, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryer, S.A.; Altieri, A.L. Role of large inhomogeneities in initiating liquid sheet breakup in agricultural atomisation. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 163, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurkar, S.Y.; Yadav, G.; Mishra, D.P. Visualizations of sheet breakup of non-Newtonian gels loaded with nanoparticles. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2017, 100, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, S.L.; Hewitt, A.J. Flat-Fan Spray Atomization Model. Trans. ASABE 2018, 61, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negeed, E.R.; Hidaka, S.; Kohno, M.; Takata, Y. Experimental and analytical investigation of liquid sheet breakup characteristics. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2011, 32, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Qiao, R.; Mu, K.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, R.X.; Si, T. Manipulation of jet breakup length and droplet size in axisymmetric flow focusing upon actuation. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 91702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.S.; Kruger, G.R.; da Cunha, J.P.A.R. Spray drift and droplet spectrum from dicamba sprayed alone or mixed with adjuvants using air-induction nozzles. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2018, 53, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, B.C.; Alves, G.S.; Carvalho, F.K.; Da Cunha, J.P.A.; Antuniassi, U.R.; Kruger, G.R. Influence of Airspeed and Adjuvants on Droplet Size Distribution in Aerial Applications of Glyphosate. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2018, 34, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianming, C. Liquid Sprays; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, P.A.; Miller, P.; Walklate, P.J.; Tuck, C.R.; Western, N.M. Spray Drift from Hydraulic Spray Nozzles: The Use of a Computer Simulation Model to Examine Factors Influencing Drift. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1993, 54, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P. The measurement of spray drift. Pestic. Outlook 2003, 14, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, R.W. The effect of fluid properties on the spray quality from a flat fan nozzle. ASTM Spec. Technol. Publ. 2001, 1400, 27–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dombrowski, N.; Fraser, R.P. A photographic investigation into the disintegration of liquid sheets. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1954, 247, 101–130. [Google Scholar]
- Odier, N.; Balarac, G.; Corre, C.; Moureau, V. Numerical study of a flapping liquid sheet sheared by a high-speed stream. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 77, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).