Comparative Fruit Morphology and Anatomy of Wild Relatives of Carrot (Daucus, Apiaceae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Fruit Morphology
2.3. Fruit Anatomy
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fruit Morphology
3.2. Fruit Anatomy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plunkett, G.M.; Pimenov, M.G.; Reduron, J.-P.; Kljuykov, E.V.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Ostroumova, T.A.; Henwood, M.J.; Tilney, P.M.; Spalik, K.; Watson, M.F.; et al. Flowering Plants. Eudicots. The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants; Kadereit, J., Bittrich, V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 15, pp. 9–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubatzky, V.E.; Quiros, C.F.; Simon, P.W. Carrots and Related Vegetable Umbelliferae; CABI: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–294. [Google Scholar]
- Heinonen, M.I. Carotenoids and provitamin A activity of carrot (Daucus carota L.) cultivars. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1990, 38, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H.-E.; Prasad, K.N.; Kong, K.-W.; Jiang, Y.; Ismail, A. Carotenoids and their isomers: Color pigments in fruits and vegetables. Molecules 2011, 16, 1710–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáenz Lain, C. Research on Daucus L. (Umbelliferae). An. Jard. Bot. Madrid 1981, 37, 481–533. [Google Scholar]
- Spalik, K.; Downie, S.R. Intercontinental disjunctions in Cryptotaenia (Apiaceae, Oenantheae): An appraisal using molecular data. J. Biogeogr. 2007, 34, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Downie, S.R.; Peng, H. Towards a more robust molecular phylogeny of Chinese Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae: Additional evidence from nrDNA ITS and cpDNA intron (rpl16 and rps16) sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2009, 53, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.; Rojas, P.; Bonierbale, M.; Mueller, L.A.; Srivastav, M.; Senalik, D.; Simon, P. Molecular phylogeny of Daucus (Apiaceae). Syst. Bot. 2013, 38, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizu, C.; Ruess, H.; Senalik, D.; Simon, P.W.; Spooner, D.M. Phylogenomics of the carrot genus (Daucus, Apiaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1666–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizu, C.I.; Ellison, S.L.; Senalik, D.; Simon, P.W.; Spooner, D.M. Genotyping-by-sequencing provides the discriminating power to investigate the subspecies of Daucus carota (Apiaceae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banasiak, Ł.; Wojewódzka, A.; Baczyński, J.; Reduron, J.P.; Piwczyński, M.; Kurzyna-Młynik, R.; Gutaker, R.; Czarnocka-Cieciura, A.; Kosmala-Grzechnik, S.; Spalik, K. Phylogeny of Apiaceae subtribe Daucinae and the taxonomic delineation of its genera. Taxon 2016, 65, 563–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M.; Ruess, H.; Iorizzo, M.; Senalik, D.; Simon, P. Entire plastid phylogeny of the carrot genus (Daucus, Apiaceae): Concordance with nuclear data and mitochondrial and nuclear DNA insertion to the plastid. Am. J. Bot. 2017, 104, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M.; Ruess, H.; Ellison, S.; Senalik, D.; Simon, P. What is truth: Consensus and discordance in next-generation phylogenetic analyses of Daucus. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzebelus, D.; Baranski, R.; Spalik, K.; Allender, C.; Simon, P.W. Daucus. In Wild Crop Relatives: Genomic and Breeding Resources. Vegetables; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M. Daucus: Taxonomy, phylogeny, distribution. In The Carrot Genome. Compendium of Plant Genomes; Simon, P., Iorizzo, M., Grzebelus, D., Baranski, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankiewicz, K.E.; Oskolski, A.; Banasiak, Ł.; Fernandes, F.; Reduron, J.-P.; Reyes-Betancort, J.-A.; Szczeparska, L.; Alsarraf, M.; Baczyński, J.; Spalik, K. Parallel evolution of arborescent carrots (Daucus) in Macaronesia. Am. J. Bot. 2020, 107, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iovene, M.; Grzebelus, E.; Carputo, D.; Jiang, J.; Simon, P.W. Major cytogenetic landmarks and karyotype analysis in Daucus carota and other Apiaceae. Am. J. Bot. 2008, 95, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, A.; Glick, L.; Abadi, S.; Einhorn, M.; Kopelman, N.M.; Salman-Minkov, A.; Mayzel, J.; Chay, O.; Mayrose, I. The chromosome counts database (CCDB)—A community resource of plant chromosome numbers. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, A.; Sliwinska, E.; Grzebelus, D.; Baranski, R.; Simon, P.W.; Nothnagel, T.; Grzebelus, E. Nuclear DNA content variation within the genus Daucus (Apiaceae) determined by flow cytometry. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 209, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxo, G.; Moura, M.; Talhinhas, P.; Costa, J.C.; Silva, L.; Vasconcelos, R.; Menezes de Sequeira, M.; Romeiras, M.M. Diversity and cytogenomic characterization of wild carrots in the Macaronesian islands. Plants 2021, 10, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadluczka, D.; Sliwinska, E.; Grzebelus, E. Combining genome size and pollen morphology data to study species relationships in the genus Daucus (Apiaceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljuykov, E.V.; Liu, M.; Ostroumova, T.A.; Pimenov, M.G.; Tilney, P.M.; van Wyk, B.-E.; van Staden, J. Towards a standardised terminology for taxonomically important morphological characters in the Umbelliferae. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2004, 70, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kljuykov, E.V.; Zakharova, E.A.; Ostroumova, T.A.; Tilney, P.M. Most important carpological anatomical characters in the taxonomy of Apiaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, 195, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenov, M.G.; Leonov, M.V. The Genera of the Umbelliferae: A Nomenclator; Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: Richmond, UK, 1993; pp. 1–156. [Google Scholar]
- Spalik, K.; Wojewódzka, A.; Downie, S.R. The evolution of fruit in Scandiceae subtribe Scandicinae (Apiaceae). Can. J. Bot. 2001, 79, 1358–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.M. The taxonomic value of fruit structure in the subfamily Saniculoideae and related African genera (Apiaceae). Taxon 2003, 52, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Plunkett, G.M.; Lowry, P.P.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.M. The taxonomic value of fruit wing types in the order Apiales. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.M.; Plunkett, G.M.; Lowry, P.P. Evidence from fruit structure supports in general the circumscription of Apiaceae subfamily Azorelloideae. Plant Syst. Evol. 2009, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajepiri, M.; Ghahremaninejad, F.; Mozaffarian, V. Fruit anatomy of the genus Pimpinella L. (Apiaceae) in Iran. Flora 2010, 205, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalın Uruşak, E. Fruit anatomy of some Ferulago (Apiaceae) species in Turkey. Turk. J. Bot. 2013, 37, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalın, E.; Yeşil, Y.; Akpulat, A. Fruit anatomy of the Turkish Pimpinella species. Flora 2016, 223, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Downie, S.R. The phylogenetic significance of fruit anatomical and micromorphological structures in Chinese Heracleum species and related taxa (Apiaceae). Syst. Bot. 2017, 42, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizu, C.I.; Simon, P.W.; Martínez-Flores, F.; Ruess, H.; Crespo, M.B.; Spooner, D.M. Integrated molecular and morphological studies of the Daucus guttatus complex (Apiaceae). Syst. Bot. 2016, 41, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, N.; Zaouali, I.; Bel Amri, W.; Rouz, S.; Simon, P.W.; Hannachi, C.; Ghrabi, Z.; Neffati, M.; Bouzbida, B.; Spooner, D.M. Fruit morphological descriptors as a tool for discrimination of Daucus L. germplasm. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2014, 61, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojewódzka, A.; Baczyński, J.; Banasiak, Ł.; Downie, S.R.; Czarnocka-Cieciura, A.; Gierek, M.; Frankiewicz, K.; Spalik, K. Evolutionary shifts in fruit dispersal syndromes in Apiaceae tribe Scandiceae. Plant Syst. Evol. 2019, 305, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brozynska, M.; Furtado, A.; Henry, R.J. Genomics of crop wild relatives: Expanding the gene pool for crop improvement. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1070–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempewolf, H.; Baute, G.; Anderson, J.; Kilian, B.; Smith, C.; Guarino, L. Past and future use of wild relatives in crop breeding. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prohens, J.; Gramazio, P.; Plazas, M.; Dempewolf, H.; Kilian, B.; Díez, M.J.; Fita, A.; Herraiz, F.J.; Rodríguez-Burruezo, A.; Soler, S.; et al. Introgressiomics: A new approach for using crop wild relatives in breeding for adaptation to climate change. Euphytica 2017, 213, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadluczka, D.; Grzebelus, E. Using carrot centromeric repeats to study karyotype relationships in the genus Daucus (Apiaceae). BMC Genomics 2021, 22, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Darshetkar, A.M.; Choudhary, R.K.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Choi, S. Mericarp morphology of the tribe Selineae (Apiaceae, Apioideae) and its taxonomic implications in Korea. Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 2018, 25, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafina, F.U.; Lee, H.; Sharipova, V.K.; Lee, A.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, M.N.; Jang, J.W.; Kim, Y.-S. Comparative fruit morphology and its systematic significance in Ferula (Apiaceae) species from different growth habitats. Flora 2021, 283, 151899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearn, W.T. Botanical Latin. History, Grammar, Syntax, Terminology and Vocabulary, 3rd ed.; David & Charles: New Abbot, UK, 1983; pp. 506–507. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroumova, T.A. Fruit micromorphology in the Umbelliferae of the Russian Far East. Bot. Pac. 2018, 7, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piwczyński, M.; Puchałka, R.; Spalik, K. The infrageneric taxonomy of Chaerophyllum (Apiaceae) revisited: New evidence from nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS sequences and fruit anatomy. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 178, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.P.; Esler, K.J. Phenotypic plasticity among Echium plantagineum populations in different habitats of Western Cape, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2008, 74, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotra, A.B.; Atkin, O.K.; Bonser, S.P.; Davidson, A.M.; Finnegan, E.J.; Mathesius, U.; Poot, P.; Purugganan, M.D.; Richards, C.L.; Valladares, F.; et al. Plant phenotypic plasticity in a changing climate. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurahman, M.; Sabirhazi, G.; Liu, B.; Yin, L.; Pan, B. Comparison of five Calligonum species in Tarim Basin based on morphological and molecular data. EXCLI J. 2012, 11, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feist, M.A.E.; Downie, S.R.; Magee, A.R.; Liu, M.R. Revised generic delimitations for Oxypolis and Ptilimnium (Apiaceae) based on leaf morphology, comparative fruit anatomy, and phylogenetic analysis of nuclear rDNA ITS and cpDNA trnQ–trnK intergenic spacer sequence data. Taxon 2012, 61, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Downie, S.R.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, B. New insights into the phylogeny of Angelica and its allies (Apiaceae) with emphasis on East Asian species, inferred from nrDNA, cpDNA, and morphological evidence. Syst. Bot. 2013, 38, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyskov, D.; Degtjareva, G.; Samigullin, T.; Pimenov, M. Systematic placement of the Turkish endemic genus Ekimia (Apiaceae) based on morphological and molecular data. Turk. J. Bot. 2015, 39, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yembaturova, E.Y.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.M.; Winter, P.J.D. The taxonomic significance of fruit morphology and anatomy in the genus Alepidea Delaroche (Apiaceae, subfamily Saniculoideae). Plant Divers. Evol. 2010, 128, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeşil, Y.; Akalın, E.; Akpulat, A.; Vural, C. Fruit morphology of the genus Pimpinella (Apiaceae) in Turkey. An. Jard. Bot. Madr. 2018, 75, e072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bani, B.; Karakaya, M.A.; Çeter, T. Fruit micromorphological characters of the genus Grammosciadium DC. (Apiaceae) in Turkey. Phytotaxa 2016, 246, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostroumova, T.A.; Kljuykov, E.V. Fruit structure and microsculpture in the annual species of the genus Bupleurum, section Perfoliata (Umbelliferae). Phytol. Balc. 2015, 21, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum, M.R. Evolution of specialization in insect-umbellifer associations. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronse, A.C.; Popper, Z.A.; Preston, J.C.; Watson, M.F. Taxonomic revision of European Apium L. s.l.: Helosciadium W.D.J.Koch restored. Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 287, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.; Plunkett, G.M.; Lowry, P.P.; Magee, A.R. The phylogenetic significance of fruit structural variation in the tribe Heteromorpheae (Apiaceae). Pak. J. Bot. 2016, 48, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.M. A revision of the genus Choritaenia (Apiaceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2007, 73, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magee, A.R.; van Wyk, B.-E.; Tilney, P.M.; Downie, S.R. Phylogenetic position of African and Malagasy Pimpinella species and related genera (Apiaceae, Pimpinelleae). Plant Syst. Evol. 2010, 288, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miranda, R.M.; Dias, D.C.F.D.; Picoli, E.A.D.; da Silva, P.P.; Nascimento, W.M. Physiological quality, anatomy and histochemistry during the development of carrot seeds (Daucus carota L.). Ciênc. Agrotec. 2017, 41, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Taxon | Length (L; mm) | Width (W; mm) | L/W | Shape | 100 Fruit Weight (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | Mean ± SE | Min–Max | Mean ± SE | Mean ± SE | |||
| DaucusI subclade | |||||||
| D. aureus | 2.5–4.4 | 3.3 ± 0.06 h | 1.2–2.1 | 1.5 ± 0.03 de | 2.2 | NE | 0.136 ± 0.002 f–h |
| D. carota subsp. capillifolius | 4.0–6.5 | 4.9 ± 0.07 g | 1.1–1.7 | 1.4 ± 0.02 d–f | 3.6 | OB | 0.206 ± 0.002 f |
| D. carota subsp. sativus (DH) | 2.3–3.4 | 2.8 ± 0.04 i | 1.5–1.7 | 1.6 ± 0.01 d | 1.7 | E | 0.117 ± 0.003 f–h |
| D. carota subsp. sativus (‘Dolanka’) | 1.6–2.8 | 2.1 ± 0.04 k | 0.9–1.7 | 1.3 ± 0.02 fg | 1.7 | E | 0.139 ± 0.005 f–h |
| D. muricatus | 4.5–8.4 | 6.5 ± 0.12 e | 2.1–4.0 | 2.6 ± 0.05 c | 2.5 | NE | 1.076 ± 0.020 d |
| D. rouyi | 6.8–12.1 | 8.4 ± 0.13 c | 5.6–10.9 | 7.7 ± 0.15 a | 1.1 | OV | 1.349 ± 0.012 c |
| D. sahariensis | 2.0–3.8 | 2.7 ± 0.05 i | 0.9–1.6 | 1.3 ± 0.03 e–g | 2.1 | NE | 0.098 ± 0.002 gh |
| D. syrticus | 1.9–3.7 | 2.7 ± 0.06 i | 0.9–1.7 | 1.2 ± 0.03 fg | 2.2 | NE | 0.080 ± 0.002 h |
| DaucusII subclade | |||||||
| D. conchitae | 1.9–3.7 | 2.5 ± 0.05 i–k | 0.8–1.5 | 1.1 ± 0.03 fg | 2.2 | NE | 0.106 ± 0.003 gh |
| D. glochidiatus | 1.8–3.0 | 2.2 ± 0.04 jk | 0.9–1.5 | 1.2 ± 0.02 fg | 1.9 | E | 0.079 ± 0.004 h |
| D. guttatus | 2.2–3.8 | 2.8 ± 0.05 i | 1.1–1.8 | 1.4 ± 0.03 d–f | 2.1 | NE | 0.109 ± 0.001 f–h |
| D. involucratus | 2.5–3.4 | 2.9 ± 0.03 i | 0.9–1.6 | 1.1 ± 0.02 g | 2.6 | OB | 0.098 ± 0.002 gh |
| D. littoralis | 4.8–6.7 | 5.7 ± 0.07 f | 2.1–3.3 | 2.6 ± 0.04 c | 2.3 | NE | 0.596 ± 0.011 e |
| D. pusillus | 2.0–2.9 | 2.5 ± 0.03 ij | 1.1–1.6 | 1.3 ± 0.02 e–g | 2.0 | NE | 0.091 ± 0.002 gh |
| Outgroup | |||||||
| Caucalis platycarpos | 5.8–8.2 | 7.1 ± 0.07 d | 2.3–3.5 | 2.8 ± 0.03 c | 2.6 | OB | 1.664 ± 0.023 b |
| Orlaya daucoides | 8.7–14.0 | 11.4 ± 0.18 a | 4.2–8.1 | 5.8 ± 0.11 b | 2.0 | NE | 3.407 ± 0.061 a |
| O. daucorlaya | 6.8–12.5 | 10.1 ± 0.18 b | 3.8–7.3 | 5.8 ± 0.09 b | 1.8 | E | 3.451 ± 0.035 a |
| Torilis arvensis | 2.2–3.6 | 2.7 ± 0.03 i | 1.2–1.8 | 1.4 ± 0.02 d–g | 2.0 | NE | 0.178 ± 0.005 fg |
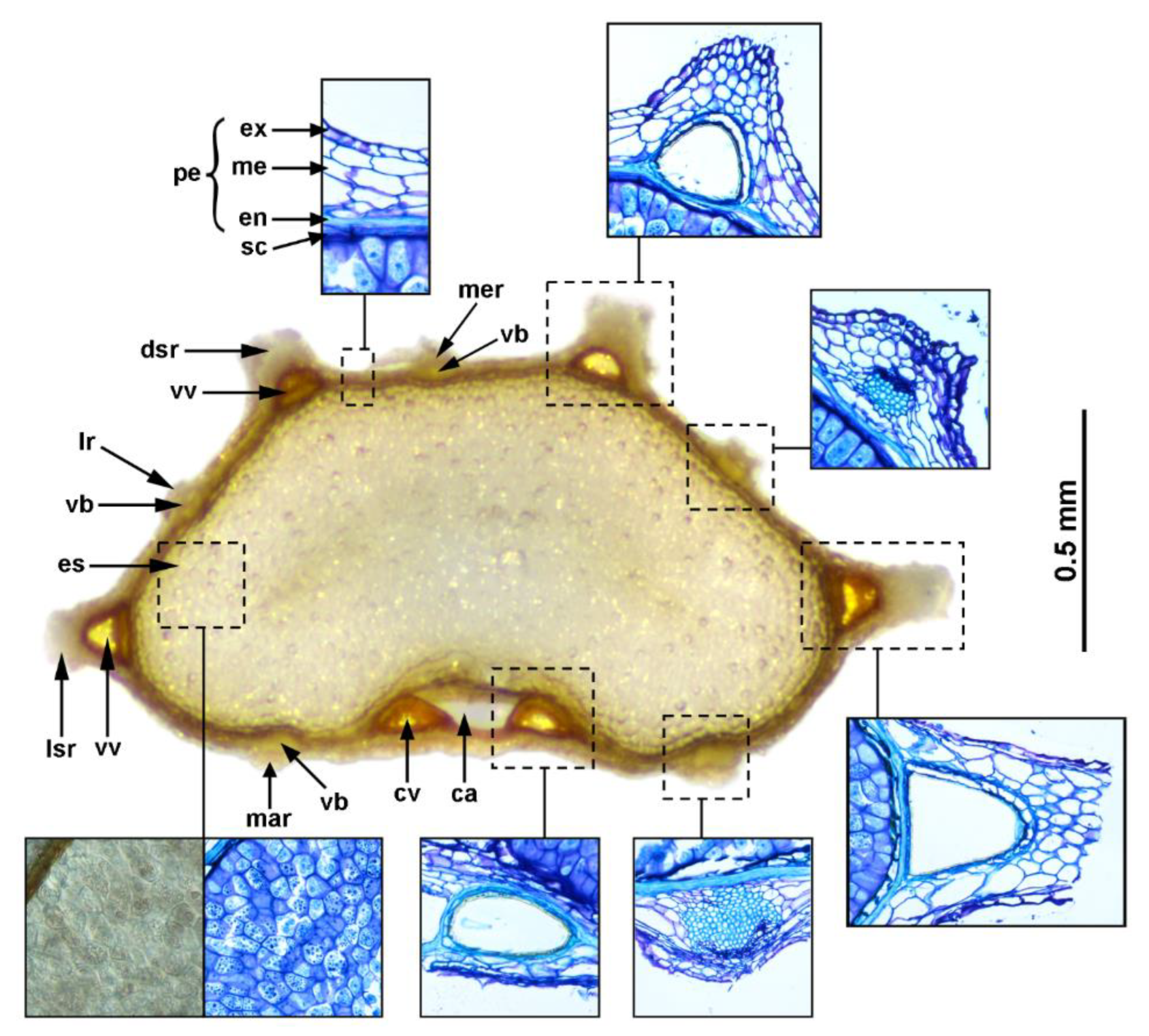
| Taxon | Width (µm) | Pericarp Thickness (µm) | Mericarp Outline a | Exocarp b | Hypendocarp | Endosperm c | Surface Micromorphology | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VV | CV | |||||||
| DaucusI subclade | ||||||||
| D. aureus | absent | absent | 51 ± 5 c–e | SCD | T | – | F/C | Tuberculate |
| D. carota subsp. capillifolius | 139 ± 6 bc | 181 ± 16 cd | 28 ± 1 e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| D. carota subsp. sativus (DH) | 91 ± 4 ef | 115 ± 6 e–g | 38 ± 1 e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| D. carota subsp. sativus (‘Dolanka’) | 82 ± 8 fg | 78 ± 3 f–h | 32 ± 3 e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| D. muricatus | 33 ± 2 i | 83 ± 6 f–h | 108 ± 7 ab | SCD | – | – | F/C | Tuberculate |
| D. rouyi | 168 ± 7 a | 200 ± 7 c | 132 ± 9 a | SCD | – | – | F/C | Ribbed–striate |
| D. sahariensis | 75 ± 4 f–h | 122 ± 5 e–g | 42 ± 5 e | SCD | A | – | F/C | Rugose |
| D. syrticus | 70 ± 3 f–h | 144 ± 14 de | 48 ± 4 de | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| DaucusII subclade | ||||||||
| D. conchitae | 64 ± 3 gh | 71 ± 5 gh | 35 ± 2 e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| D. glochidiatus | 53 ± 3 hi | 53 ± 3 h | 34 ± 6 e | SCD | A | – | F/C | N/A |
| D. guttatus | 87 ± 4 e–g | 108 ± 8 e–g | 51 ± 4 c–e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose–tuberculate |
| D. involucratus | 75 ± 2 f–h | 81 ± 2 f–h | 31 ± 2 e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| D. littoralis | 110 ± 5 de | 127 ± 8 ef | 80 ± 5 bc | SCD | – | – | F/C | Lineolate–tuberculate |
| D. pusillus | 85 ± 2 e–g | 125 ± 5 ef | 38 ± 5 e | SCD | – | – | F/C | Rugose |
| Outgroup | ||||||||
| Caucalis platycarpos | 93 ± 2 ef | 87 ± 3 f–h | 117 ± 7 a | SCL | – | – | MG | Smooth |
| Orlaya daucoides | 125 ± 5 cd | 273 ± 17 b | 129 ± 6 a | SCD | – | + | F/C | Undulate |
| O. daucorlaya | 150 ± 12 ab | 329 ± 26 a | 118 ± 13 a | SCD | – | + | F/C | Undulate |
| Torilis arvensis | 81 ± 3 fg | 106 ± 7 e–g | 77 ± 6 cd | SCD | T | – | MG | Tuberculate |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kadluczka, D.; Grzebelus, E. Comparative Fruit Morphology and Anatomy of Wild Relatives of Carrot (Daucus, Apiaceae). Agriculture 2022, 12, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122104
Kadluczka D, Grzebelus E. Comparative Fruit Morphology and Anatomy of Wild Relatives of Carrot (Daucus, Apiaceae). Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKadluczka, Dariusz, and Ewa Grzebelus. 2022. "Comparative Fruit Morphology and Anatomy of Wild Relatives of Carrot (Daucus, Apiaceae)" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122104
APA StyleKadluczka, D., & Grzebelus, E. (2022). Comparative Fruit Morphology and Anatomy of Wild Relatives of Carrot (Daucus, Apiaceae). Agriculture, 12(12), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122104









