Automatic Fruit Harvesting Device Based on Visual Feedback Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
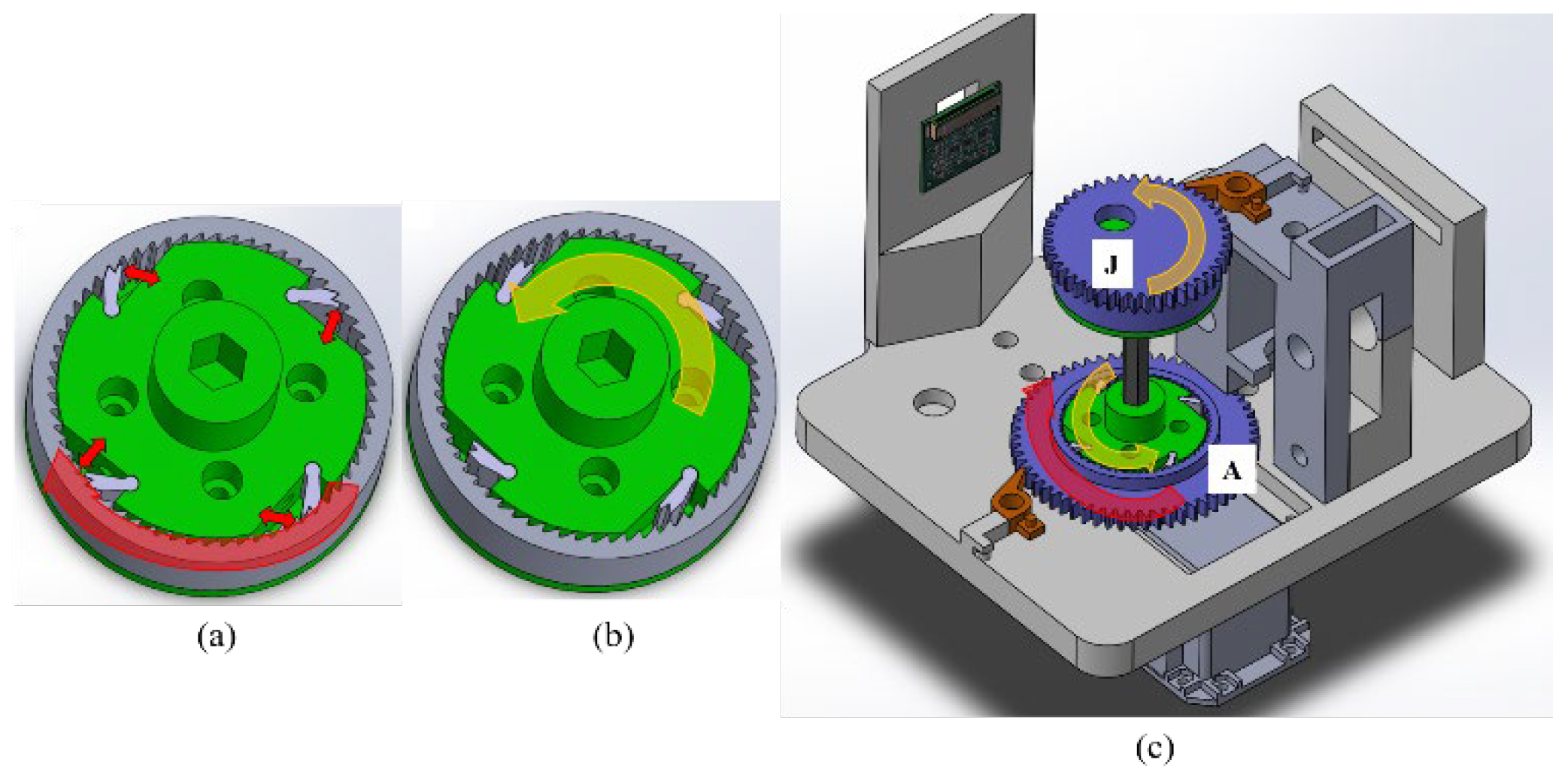
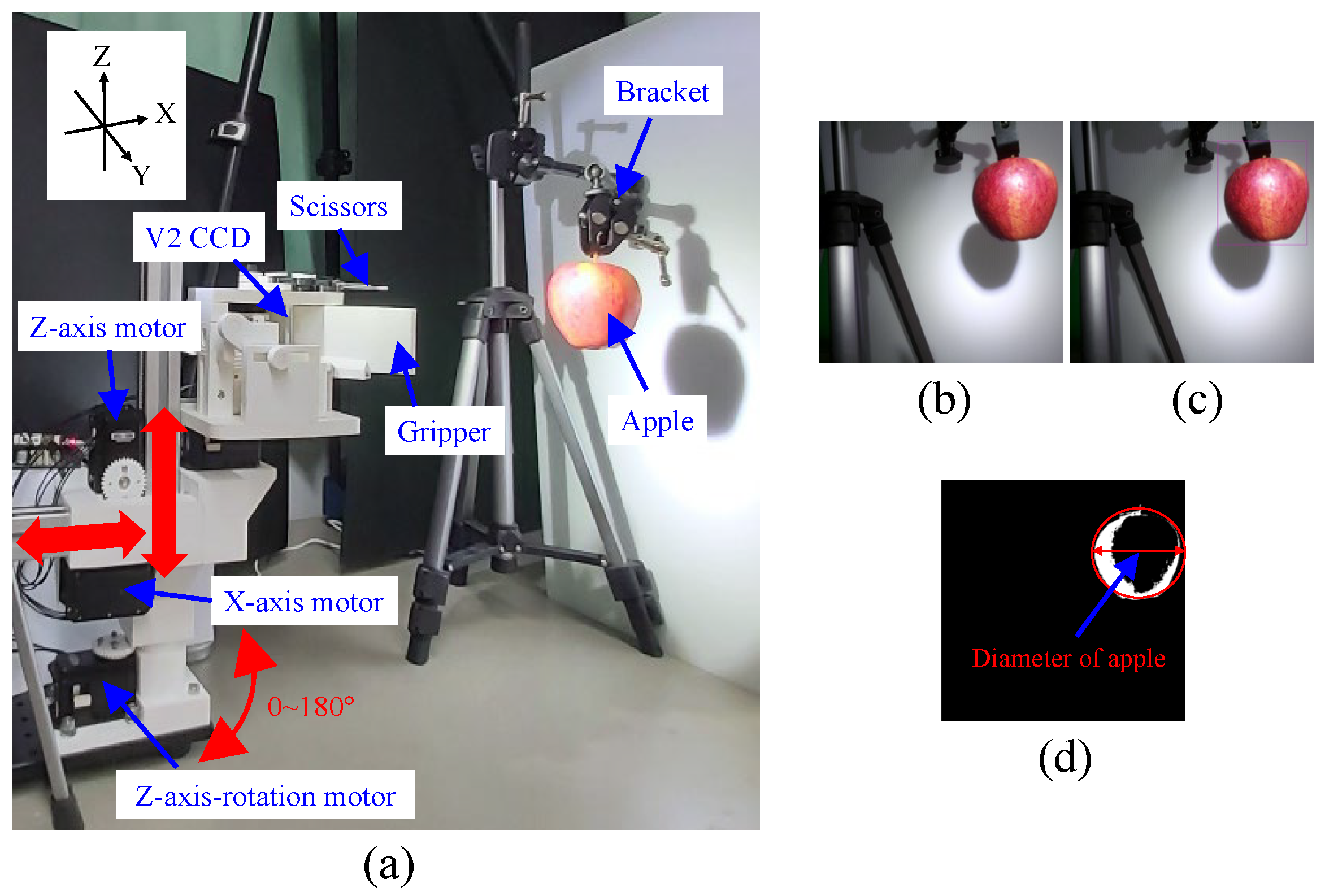
2. Design of the Harvesting Device
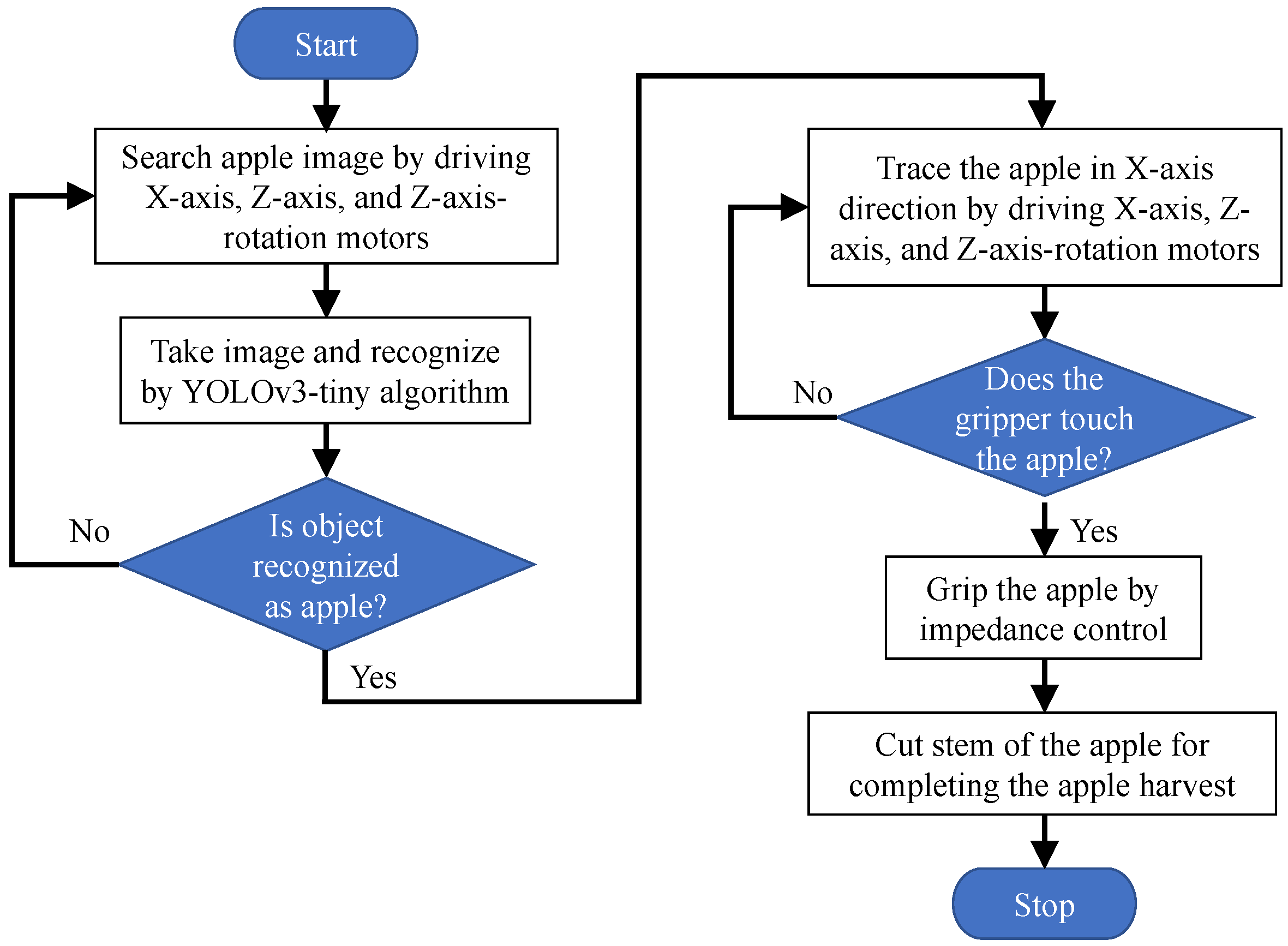
3. Visual Feedback Control
3.1. Visual Position
3.2. Cut and Grip control of Harvesting Device
4. Experiment and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Growers: Far Too Few Workers—Fruit Growers News. Available online: https://fruitgrowersnews.com/article/growers-far-too-few-workers/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Zhang, Z.; Igathinathane, C.; Li, J.; Cen, H.; Lu, Y.; Flores, P. Technology progress in mechanical harvest of fresh market apples. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Chai, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, G.; Sun, T. Multi-level feature fusion for fruit bearing branch keypoint detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 191, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, J.; Donné, K.; Boedrij, S.; Beckers, W.; Claesen, E. Autonomous Fruit Picking Machine: A Robotic Apple Harvester; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 531–539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.A.; Jidong, L.; Wei, J.; Ying, Z.; Yu, C. Design and control of an apple harvesting robot. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Knee, M. (Ed.) Fruit Quality and Its Biological Basis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, K.; Feng, T. Characterizing apple picking patterns for robotic harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.H.; Chiu, C.H.; Chen, T.L.; Pai, T.Y.; Chen, Y.; Hsu, M.C. A Soft Robotic Gripper Module with 3D Printed Compliant Fingers for Grasping Fruits. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Auckland, New Zealand, 9–12 July 2018; pp. 736–741. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.J.; Liu, T.S. Flexible-characteristics Inspection System for Flexible Substrates by Using Image Feedback Control. Displays 2011, 32, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang-Chen, H.; Li-Ming, C.; Wang, Z.K.; Tsao, S.C. Position control and novel application of SCARA robot with vision system. Adv. Technol. Innov. 2017, 2, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.J.; Syu, K.C.; Kao, C.H. Dynamic Proportional-Fuzzy Grip Control for Robot Arm by Two-dimensional Vision Sensing Method. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thotapalli, P.K.; Kumar, C.R.V.; Reddy, B.C.M. A New Approach to Control the Position of Joint Arm Robot Using Image Background Subtraction Technique. In Advances in Simulation, Product Design and Development; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 845–854. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Hu, J.; Yun, J.; Liu, Y. Manipulator grabbing position detection with information fusion of color image and depth image using deep learning. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 10809–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, Z.; Lin, R.; Bu, R.; He, Z.; Yang, Z.; Liang, C. Green grape detection and picking-point calculation in a night-time natural environment using a charge-coupled device (CCD) vision sensor with artificial illumination. Sensors 2018, 18, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ringdahl, O.; Kurtser, P.; Edan, Y. Evaluation of approach strategies for harvesting robots: Case study of sweet pepper harvesting. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2019, 95, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Tang, C.; Zhao, D. Grasping mode analysis and adaptive impedance control for apple harvesting robotic grippers. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 186, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Shigematsu, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Kohno, Y.; Kamata, J.; Kurita, M. Evaluation of a strawberry-harvesting robot in a field test. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 105, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, E.; Liang, Z. Apple detection during different growth stages in orchards using the improved YOLO-V3 model. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Nouaze, J.C.; Touko Mbouembe, P.L.; Kim, J.H. YOLO-tomato: A robust algorithm for tomato detection based on YOLOv3. Sensors 2020, 20, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Z. Multi-Scale Safety Helmet Detection Based on SAS-YOLOv3-Tiny. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3652. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, B.-J.; Chang, C.-R.; Lan, C.-W.; Zheng, Y.-C. Magnus-Forces Analysis of Pitched-Baseball Trajectories Using YOLOv3-Tiny Deep Learning Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraji, H.; Colbaugh, R. Force tracking in impedance control. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1997, 16, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Gan, Y.; Chen, M.; Dai, X. Adaptive variable impedance control for dynamic contact force tracking in uncertain environment. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 102, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roveda, L.; Piga, D. Robust state dependent riccati equation variable impedance control for robotic force-tracking tasks. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2020, 4, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.R.; Hamrock, B.J.; Jacobson, B.O. Fundamentals of Machine Elements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tree Fruit Overview. Available online: https://extension.wsu.edu/chelan-douglas/agriculture/treefruit/horticulture/tree_fruit_overview/ (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Our Standards: Washington Apple Commission. Available online: https://waapple.org/standards/ (accessed on 19 November 2022).
- Yang, M.S.; Sinaga, K.P. A feature-reduction multi-view k-means clustering algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 114472–114486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderstrom, T.; Stoica, P. Instrumental variable methods for system identification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2002, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badadal Raghavendra, R.; Naik, S.B. Experimental Determination of Cutting Force Required for Severing Fruit Stalks. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Puchalski, C.; Brusewitz, G.H.; Slipek, Z. Coefficients of friction for apple on various surfaces as affected by velocity. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2003, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]














Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, B.-J.; Yeh, C.-C. Automatic Fruit Harvesting Device Based on Visual Feedback Control. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122050
Wen B-J, Yeh C-C. Automatic Fruit Harvesting Device Based on Visual Feedback Control. Agriculture. 2022; 12(12):2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122050
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Bor-Jiunn, and Che-Chih Yeh. 2022. "Automatic Fruit Harvesting Device Based on Visual Feedback Control" Agriculture 12, no. 12: 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122050
APA StyleWen, B.-J., & Yeh, C.-C. (2022). Automatic Fruit Harvesting Device Based on Visual Feedback Control. Agriculture, 12(12), 2050. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122050








