Abstract
Horses working with humans for recreational purposes are subjected to a variety of external factors that can have a negative impact on their well-being. There is an urgent need for unequivocal evidence from scientific studies to unify methods of welfare verification of working animals. The testosterone/cortisol ratio has recently been proposed as a marker of the propensity for social aggression as one of the stress reactions. In this study, we analyzed testosterone and cortisol blood concentration and ratio to evaluate the stress susceptibility of horses used for recreational purposes. The blood samples were collected from eleven (n = 11) standardbred horses (age 6–10; geldings–mares = 6:5) during the intense leisure exploitation and after the rest season. The cortisol concentration remained unchanged, whereas, despite the small study population, we observed higher testosterone levels during the horses’ intensive exploitation compared to the resting season (p > 0.09). Thus, the testosterone/cortisol ratio was increased during intensive exploitation. We conclude that recreational horseback riding is not an overly stressful activity for horses; however, it may lead to some behavioral abnormalities connected with high testosterone levels. However, more research is needed.
1. Introduction
Animal welfare is defined as “the physical and emotional state of an animal in relation to the conditions in which it lives and dies” by the World Organization for Animal Health (“Animal Welfare” n.d.). Since short-term positive feelings can occur during disturbed care states and since it is conceivable to be in a good nurturing state while still experiencing chronic dread or pain, it is important to distinguish between good as a chronic state and transitory states. The idea of animal welfare has evolved over time and is piquing the public interest, where oftentimes, it is discussed in a highly subjective and emotional manner. Since it was first introduced, the idea of well-being includes both good health and the general maintenance required to keep it [1,2]. The availability of feed, hydration, shelter, and medical care used to be considered the full picture of equine welfare; only recently, the behavioral aspect and, by extension, animal sensitivity, anxiety, pain, or discomfort have also received attention and entered the equation [3,4]. To define and evaluate animal well-being, scientists have established several concepts. According to behavioral techniques, animals should act naturally and be able to carry out all required actions without resistance or deprivation. In addition, welfare strongly influences the animal’s health status [3,4,5]. It is well established that physical exercise needs cardiovascular, respiratory, metabolic responses and musculoskeletal adaptations in athletes in order to restore homeostasis [3].
Some objective indicators are examined to determine animal welfare, including hematological parameters. It may be possible to identify chronic disorders by counting white blood cells (WBC), and thus, it may reveal whether the animal has experienced persistently stressful circumstances [3]. The ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes (N/L) has been shown to be inversely connected to equine welfare, as N/L ratios were higher in horses with lower well-being scores [3,6]. Another approach analyzes the prospective changes in well-being using heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV), which were initially proposed to evaluate emotional stimuli [4,7]. However, there are several limitations. For example, in comparison to their non-stereotyped counterparts, the stereotyped horses’ HR and HRV were either lower or identical [4]. Thus, other tests, such as hormonal response, started dominating the most recent research. As a matter of fact, cardiovascular parameters are the most studied as they represent good indices of fitness level and of workload effort [8]. The HR may indicate the animal’s internal physiological state; indeed, the rise in HR is not only caused by an increase in physical activity but also reflects heightened emotional reactivity [9]. Several studies investigated hormone tests to aid the assessment of equine welfare. The level of cortisol is the most commonly studied parameter (the so-called “stress hormone”) [6]. According to recent reports, blood, stool, hair samples, and saliva are used for testing [6,10,11,12]. Because of the rapid release following stimulation, plasma cortisol levels can successfully be used to assess the effects of acute stressors, as well as the long-term. In most cases, plasma cortisol levels in horses show potential for welfare disorders, chronic diseases, and chronic stress. Pawluski et al. [6] discovered that horses in poor welfare conditions had lower fecal cortisol levels, but there were no differences between horses with SB/ARB (stereotypic or abnormal repetitive behaviors) and their healthy counterparts or between socially isolated horses and their healthy counterparts [4]. Another hormone that can be used in evaluating animal and human well-being is testosterone, which is an endogenous anabolic steroid and one of the sex hormones. In most vertebrates, testosterone is secreted primarily by the testes of males and, to a lesser extent, by the ovaries of females. Changes in testosterone and cortisol levels were proven to regulate well-being and emotional feelings. Mehta’s hypothesis about the dual hormone indicates hormone interaction and mutual correlation influencing the individual’s physiological state [13]. However, in equine medicine, there is a lack of studies exploring the stress reaction during intense leisure exploitation based on hormonal response, and thus, no objective well-being indicator is used in the day-to-day life of the working equines.
Horses fulfill human socio-economic demands in many aspects. However, the increase in the popularity of recreational activities makes this segment the largest in the equine industry. Unlike athlete horses, where physical performance is essential, leisure horses are expected to fulfill high psychological needs, often literally, when they play a role of a supporting therapist (ex., in autism spectrum disorder) [14]. Increased stress may be the cause of undesired behavior, expressed either actively or passively [15]. Not so long ago, researchers started to raise ontological and ethical questions about equine exploitation for human pleasure [16]. A highly profitable business that recreational horseback riding has become and anthropocentrism have induced apprehension about the horse’s prosperity being neglected in favor of human joy and effort reduction. According to scientific papers, horse owners, caretakers, and trainers do not always have enough knowledge about the needs of horses, contributing to the unintentional deterioration of their welfare [5,17]. Lack of expertise in handling procedures, natural needs, and physiology of the animal’s behavior could unintentionally lead to putting the animal under chronic stress and consequently worsening welfare. Caretakers and trainers are still directed by a presumptive system of breeding and training based on their personal ideas and subjective feelings despite the growing corpus of knowledge on equine behavior and welfare. Such overly reactive animals are troublesome for handlers, leading to the elimination of individuals from particular activities (working with children or inexperienced riders). An accessible stress marker would allow not only optimize reasonable training but also provide a simple tool to prove animal cruelty and exploitation in closely related tourism, where occasional deaths from the exhaustion of animals involved are reported. This is important, especially in countries where tourism and equestrianism are not seasonal. Long-term stress itself is correlated with various illnesses [18], and the testosterone/cortisol (T/C) ratio, when measured regularly in athletes, was found to be a good indicator of the breaking point when catabolism takes over anabolism and induces proneness to soft tissue or bone damage [19]. Considering the above-mentioned threats, general horse welfare status should be the priority for handlers. However, it is still unclear if leisure riding is a strong stressor for horses, and there is a lack of reliable and universal welfare indicators.
Thus, the study aimed to evaluate the stress response based on hormonal reactions during the intense exploitation of leisure horses. The hypothesis is that the intense exploitation of leisure horses influences horses’ hormonal responses.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Procedure
For this study, eleven (n = 11) 6–10 years old private-owned healthy Standardbred horses (+/−500 kg) were selected (5 mares and 6 geldings) that were used for at least 2 years for this type of activity. The blood samples were collected during two time points: (1) the intense leisure season (beginning of July), namely recreational riding ~3–4 h per day, 6 days per week, and (2) after the rest (end of November) riding ~1–2 h a day, 5 days per week. Males were castrated at least 3 years before the experiment. Each horse had been already used for this type of work for not less than 2 years. The riding was not always performed by the same individuals with the same horse during the five-month experiment, as it is impossible in this type of horse riding. They were fed with the standard diet designed for horses (oats 5.0 kg/horse, meadow hay 7.5 kg/horse). All horses were clinically healthy based on veterinary examination (heart and breath rate, no visible lameness, mucous membranes (color and moisture), capillary refill time, and dehydration measured as the time it takes for a pinched skin to fold over the point of the shoulder to flatten). There were also no visible signs of heat in the mares. The blood samples were collected at rest at a similar hour in the morning before feeding. It was performed as a part of standard veterinary diagnostic procedures. Thus, no approval of the Local Commission for Ethics in Animal Experiments was required, according to the Polish legal regulations [20] and the European directive EU/2010/6. Peripheral blood was gathered from the jugular vein into sterile dry tubes for serum analyses using the BD Vacutainer system (BD, Warsaw, Poland). Tubes were centrifuged (500× g, 5 min), and serum was isolated and stored at −80 °C for further analyses.
2.2. Hormone Analysis
To determine cortisol and testosterone concentration, the available immunoenzymatic commercial assay dedicated to equine species was used (ELISA, ELK Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China). Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV% < 8%; inter-assay precision (Precision between assays): CV% < 10%. The absorbance was measured by Multiscan Reader (Labsystem, Helsinki, Finland) using a Genesis V3.00 software program. All analyses were performed based on manufacturer instructions.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
For statistical analysis, the OriginPro 2022 statistics package (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA) was used. All data were normally distributed (Shapiro-Wilk test). Comparison of cortisol, testosterone, and their ratio values of the experimental horse group measured at two points of time were analyzed using paired sample t-test. A p value < 0.09 is to be considered as close to significant. A higher p-value was used due to the small size of the studied population.
3. Results
Data of 11 horses’ cortisol and testosterone blood level were compared in two periods of their different extent of activity. There was no influence of sex on the level of hormones measured. Three horses (two mares and one gelding) were excluded from the analysis since the sample from the seasonal interlude (rest) was impossible to obtain. There was no significant difference in cortisol concentration in the blood between the two performed measurements (p > 0.09). Serum blood testosterone level was observed to drop significantly at the time of the resting season (~3-fold) (Figure 1).
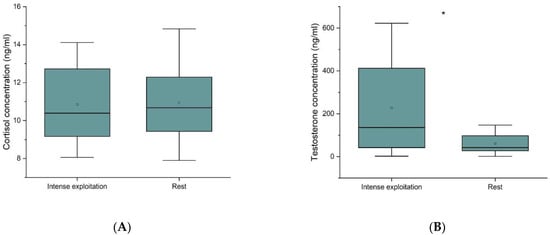
Figure 1.
Comparison of serum cortisol (A) and testosterone (B) concentration measured during the intense leisure exploitation in July and in November, when the horses rested. The box plot presents data distribution (mean, median, and interquartile range) among samples of horses included in the analysis (n = 8) p < 0.09. * p < 0.09.
A comparison of the testosterone-to-cortisol ratio (T/C) indicates a decrease in this index at the time that the horses rested (Figure 2).
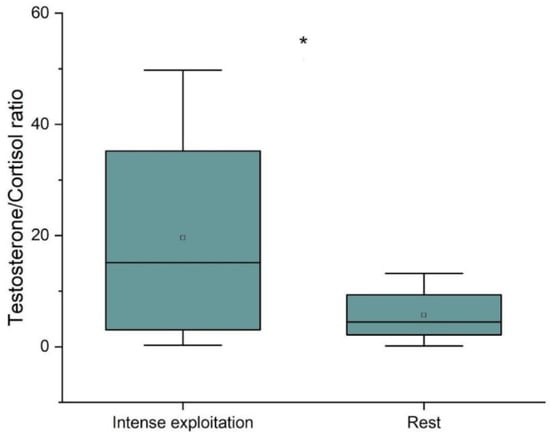
Figure 2.
Testosterone/cortisol ratio in two measured points of time. The box plot presents data distribution (mean, median, and interquartile range) among samples of horses included in the analysis (n = 8). p < 0.09. * p < 0.09.
4. Discussion
This is the first study evaluating the stress response in leisure horses during intense ride exploration. The physiological response to acute stress in equines is manifested mostly by a cortisol spike in about ten minutes, which makes it a widely used parameter to assess equine well-being [12]. However, it was documented that also changes in the basal level of cortisol may indicate stress reactions in humans and horses [10,21]. In humans, elevated basal cortisol levels were strongly correlated with impaired stress recovery [21], and it was more informative than stress-induced cortisol rise. In addition, disorders in functioning the HPA-axis are connected with stress-related psychopathology, which may also be reflected by changes in basal cortisol concentrations [22]. High cortisol levels have been linked to anxiety and social avoidance, while low levels have been attributed to reduced stress and social attitudes [23]. Horses kept in groups and on pastures had higher cortisol levels after stimulation than horses kept in solitary [24]. In contrast, hormone levels do not significantly alter for variables including gender, season, or coat color, according to a study that examined cortisol measures taken from horse hair samples. However, it was discovered that horses over the age of 15 had much greater cortisol levels than the younger ones [25].
Cortisol is a hormone commonly measured in exercising horses as their exposure to stress is connected with competitions and strenuous training is very high. According to research, well-trained horses have lower basal cortisol levels, indicating that they are less stressed during exercise than untrained horses [10,26]. Additionally, there are differences in cortisol concentrations between race and endurance horses during horse racing. Cortisol levels rose after both training and competition, but the growth was more intense after the competition in both groups. However, the basal level of cortisol during the competition was higher in endurance horses, which was probably connected to transportation [10]. Transportation is considered a stressful stimulus [27]; however, sometimes, changes in cortisol levels are difficult to detect because of a quick return to baseline [5]. Cortisol levels fluctuate depending on the type of stressor and the duration of the animal’s exposure. According to studies, horse transportation as a stressor causes peak concentrations to be 4–5-fold higher than participation in equestrian competitions [7]. According to the researchers, the change in hormone levels may indicate that interference during training was frustrating and stressful for the horses [28]. There is a study that confirms that cortisol levels increased in a group of horses who were exposed to talking and walking humans who were observers of a training session in progress. Thus, cortisol concentration is correlated with race, the number of riders, time spent in the pasture, and socialization with other horses [28]. In leisure horses, several studies are reporting no change in horse stress levels. Activities such as therapeutic horseback riding or hunt seat riding did not significantly impact the elevation of cortisol in comparison to recreational riding [29,30]. The observation of a slightly increased plasma cortisol level throughout lasting activity was implicated with normal, “good stress” that is well known to be the short-termed response to intense exercise [10]. Our data lead to a conclusion consistent with the predecessors. There was no significant difference in cortisol levels upon the change in the activity mode, so it can be concluded that horses included in our studies did not experience unduly stress.
In our study, we also measured testosterone levels. There is an established, strong correlation between testosterone levels and aggression in humans and animals, and it is extensively researched in psychiatry. According to the “challenge hypothesis”, dominant behavior related to social status and maintenance is linked with the testosterone level in primates and non-primates. Human studies reports facilitate aggressive response correlated with high testosterone concentration in the face of the competitive opportunity to preserve hierarchy status [31]. The supportive studies of non-primates are also consistent with it. It has been observed that the administration of testosterone to lambs and tropical birds selectively increases aggressive dominance behaviors when the status hierarchy is unstable [32,33]. According to some studies, testosterone rises in response to social stimulus in Przewalski horses as well [34]. However, there are some opposite ideas, suggesting that the change in testosterone concentration in the blood can be influenced only by environmental stressors [34]. In our study, we observed an increase in testosterone levels during the intense leisure season. Thus, the leisure activity season might be more socially challenging for horses and provoke dominant behaviors. However, during our study, the social factors remain unchanged. In addition, we observed that horses were more difficult to handle during the intense leisure season, which may be connected with aggression intensification.
Hormone research is typically conducted independently of one another, but cortisol has been shown to inhibit testosterone secretion, which may indirectly block testosterone’s effect. However, we decided to measure cortisol and testosterone together because they are the end products secreted in two neural axes, the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) and hypothalamus–pituitary–gonadal (HPG). In response to cognitive, and emotional arousal, the axes are top-down regulated by the brain, and the cortisol and testosterone release have various and widespread consequences on the whole organism. The triggered action of hormones also involves the bottom-up regulation of the endocrine cascade that is manifested by inter- and intra-axis feedback [35]. Such pathway coupling is known to be relevant in the development of stress and social stimuli response [36,37]. Moreover, the parallel activation of HPA and HPG axes and their further co-modulation has been proven to be the molecular regulator of the “fight and flight” response [35,38].
In addition, testosterone has been shown to directly inhibit the function of the HPA, which regulates cortisol secretion [36]. According to research, (T/C) ratio is related to the feeling and expression of anger. High testosterone levels and low cortisol levels indicate a proclivity for violence [37]. Some authors have argued that these axes are relatively slow as an isolated apparatus (where genomic pathways at each level take at least 10 min) compared to the changes in T/C ratio in experimental conditions, granted the effect of a stressor on one’s cognition is almost immediate. It was proposed that the axes are supported by shifts in metabolic clearance and hemoconcentration of both hormones and catecholamines released as a result of sympathetic stimulation [38]. The bigger picture of stress response possibly involves oxytocin [39], which has been found to decrease risk-taking behavior, and through the reduction of cortisol levels, acts as an anxiolytic [40]. The T/C ratio has recently been proposed as a marker of the propensity for social aggression and pathological criminal behavior in human studies [35,37]. High testosterone/low cortisol ratios seem to predict approach motivation/reward sensitivity in humans, and thus, in these motivational stances, individuals are more likely to confront threats, which could result in aggressive behavior [37]. However, there is a lack of such research on horses. In our study, there was a ~3-fold increase in the T/C ratio during intense leisure exploitation. Thus, it may influence the predisposition to aggressive behavior in these animals, especially when abnormal aggressive behavior is one of the signs of poor horse management and welfare [41]. Overall, the aforementioned findings fall into place with the fact that at the blood drawing during leisure exploitation, the subjects of this study were much more dominant with pronounced aggression compared to the procedure during rest, where they followed the human lead peacefully. It was documented that there is a correlation between chronic discomfort/potential pain and aggression [42,43]. Thus, in our research, the levels of cortisol and testosterone were monitored simultaneously. The T/C ratio is believed to be a more accurate indicator of chronic stress due to the common biochemical precursor and molecular interdependence of the two hormones [44,45]. We speculate that in the case of chronic stress, the aforementioned axes might be much more independent from the metabolic changes than in cases of acute stressors. Furthermore, T and C levels should be double-analyzed to obtain more plausible results and the ability to make conclusions. The practical application of the T/C ratio transferred from humans to mares and geldings in the future may help with a more precise evaluation of the feeling and expression of anger in horses.
The main limitation of the study is the small sample size, and hence, the findings should be considered preliminary. Further research is needed to replicate these findings in a larger group. Another one is that the samples were obtained during a standard veterinary procedure; thus, it was not possible to collect the blood at other time points, and the behavioral evaluation was not performed. In addition, blood sampling may be considered another stressor, and salivary samples may be more accurate [10,46,47,48]. However, several studies confirm that there may be high variability in salivary cortisol concentration [11,49]. In addition, it should be taken into consideration that the point of the year may influence hormonal response [50]. However, mainly the differences were obtained in stallions, not in mares [50,51] thus, in our study, we used geldings and mares only. In addition, it was postulated that the year season mostly influences cortisol responsiveness during ACTH stimulation [51].
5. Conclusions
The high season of horse exploitation might affect horses’ daily routine; however, it should not be considered a stressor. According to our study, leisure activity season might be more socially challenging for horses, expressed by increased serum testosterone concentration. At the same time, the level of cortisol is low and remains at the same level during the resting season, which may be evidence of proper stress balance. However, leisure exploitation may influence aggression and stress-related behavior while mishandled. Thus, a balanced work effort and varied and attractive exercises that prevent animal boredom might be an important factor in preserving horses’ mental health. However, additional behavioral studies are still needed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.W.-P.; methodology, O.W.-P.; formal analysis, I.D., J.G., K.M. and O.W.-P.; investigation, O.W.-P.; resources, K.M., J.M. and B.P.; data curation, I.D. and J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, I.D., J.G., K.M. and O.W.-P.; writing—review and editing, O.W.-P.; visualization, I.D. and J.G.; supervision, O.W.-P.; funding acquisition, B.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All samplings were a part of standard veterinary diagnostic procedures, and according to the Polish legal regulations and the European directive EU/2010/63, approval of the Local Commission for Ethics in Animal Experiments was not required. However, ethical standards for animal research were high caring about animal welfare.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all owners for agreeing to use excessive amounts of blood after examination during the standard veterinary procedure.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Arfuso, F.; Rizzo, M.; Giannetto, C.; Giudice, E.; Cirincione, R.; Cassata, G.; Cicero, L.; Piccione, G. Oxidant and Antioxidant Parameters’ Assessment Together with Homocysteine and Muscle Enzymes in Racehorses: Evaluation of Positive Effects of Exercise. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfuso, F.; Assenza, A.; Fazio, F.; Rizzo, M.; Giannetto, C.; Piccione, G. Dynamic Change of Serum Levels of Some Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Tryptophan in Athletic Horses After Different Physical Exercises. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2019, 77, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manteca Vilanova, X.; Beaver, B.; Uldahl, M.; Turner, P.V. Recommendations for Ensuring Good Welfare of Horses Used for Industrial Blood, Serum, or Urine Production. Animals 2021, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesimple, C. Indicators of Horse Welfare: State-of-the-Art. Animals 2020, 10, E294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausberger, M.; Lesimple, C.; Henry, S. Detecting Welfare in a Non-Verbal Species: Social/Cultural Biases and Difficulties in Horse Welfare Assessment. Animals 2021, 11, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawluski, J.; Jego, P.; Henry, S.; Bruchet, A.; Palme, R.; Coste, C.; Hausberger, M. Low plasma cortisol and fecal cortisol metabolite measures as indicators of compromised welfare in domestic horses (Equus caballus). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Birck, M.; Schmidt, A.; Lasarzik, J.; Aurich, J.; Möstl, E.; Aurich, C. Cortisol release and heart rate variability in sport horses participating in equestrian competitions. J. Vet. Behav. 2013, 8, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, M.; Giudice, E.; Rizzo, M.; Congiu, F.; Zumbo, A.; Arfuso, F.; Di Pietro, S.; Bruschetta, D.; Piccione, G. Application of a combined global positioning and heart rate monitoring system in jumper horses during an official competition—A preliminary study. Acta Vet. Hung. 2016, 64, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfuso, F.; Giannetto, C.; Giudice, E.; Fazio, F.; Panzera, M.; Piccione, G. Peripheral Modulators of the Central Fatigue Development and Their Relationship with Athletic Performance in Jumper Horses. Animals 2021, 11, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska-Piłaszewicz, O.; Grzędzicka, J.; Seń, J.; Czopowicz, M.; Żmigrodzka, M.; Winnicka, A.; Cywińska, A.; Carter, C. Stress response after race and endurance training sessions and competitions in Arabian horses. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 188, 105265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.P.; Viljanto, M.; Bright, J.; Pearce, C.; Maynard, S. Investigations into the feasibility of routine ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of equine hair samples for detecting the misuse of anabolic steroids, anabolic steroid esters, and related compounds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljanto, M.; Scarth, J.; Hincks, P.; Hillyer, L.; Cawley, A.; Suann, C.; Noble, G.; Walker, C.J.; Kicman, A.T.; Parkin, M.C. Application of testosterone to epitestosterone ratio to horse urine—A complementary approach to detect the administration of testosterone and its pro-drugs in Thoroughbred geldings. Drug Test Anal. 2017, 9, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.; Sulon, J.; Beckers, J.F.; Ledoux, D.; Vandenheede, M. Comparison between blood serum and salivary cortisol concentrations in horses using an adrenocorticotropic hormone challenge. Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiley-Worthington, M. Ecological, ethological, and ethically sound environments for animals: Toward symbiosis. J. Agric. Ethics 1989, 2, 323–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.M.; Cavagnino, D.T.; Bhat, A.N. Effects of Equine Therapy on Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Rev. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 5, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Creighton, E.; Smith, T.; Hosie, C. A novel scale of behavioural indicators of stress for use with domestic horses. Appl Anim. Behav. Sci. 2012, 140, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E. Posthumanism and tourism. Tour. Rev. 2019, 74, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, M.; Hiney, K.; Croney, C.; Waite, K.; Borron, A.; Brady, C. Show Horse Welfare: The Viewpoints of Judges, Stewards, and Show Managers. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2016, 19, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman, J.H.; Ferlazzo, A. Physiological responses to stress in the horse. Pferdeheilkunde 1996, 12, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, M.; Mullis, P.E.; Vogt, M.; Ventura, N.; Hoppeler, H. Training modalities: Over-reaching andover-training in athletes, includinga study of the role of hormones. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 17, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive Dz.U.2018.0.1207. n.d., Ustawa Z dnia 15 Stycznia 2015 r. o Ochronie Zwierząt Wykorzystywanych do celów Naukowych lub Edukacyjnych. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20150000266 (accessed on 26 July 2022).
- Laceulle, O.M.; Nederhof, E.; van Aken, M.A.; Ormel, J. Adolescent personality: Associations with basal, awakening, and stress-induced cortisol responses. J. Personal. 2015, 83, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, J. Cortisol and depression: Three questions for psychiatry. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.H.; Josephs, R.A. Testosterone and cortisol jointly regulate dominance: Evidence for a dual-hormone hypothesis. Horm. Behav. 2010, 58, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, F.J.; Hermann, M.; Ramseyer, A.; Burger, D.; Riemer, S.; Gerber, V. Effects of breed, management and personality on cortisol reactivity in sport horses. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzola, S.; Colombani, C.; Pizzamiglio, G.; Cannas, S.; Palestrini, C.; Costa, E.; Gazzonis, A.; Bionda, A.; Crepaldi, P. Do You Think I Am Living Well? A Four-Season Hair Cortisol Analysis on Leisure Horses in Different Housing and Management Conditions. Animals 2021, 11, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayado, P.; Munoz-Escassi, B.; Dominguez, C.; Manley, W.; Olabarri, B.; Sanchez de la Muela, M.; Castejon, F.; Maranon, G.; Vara, E. Hormone response to training and competition in athletic horses. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 2006, 36, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Medica, P.; Cravana, C.; Ferlazzo, A.A. Pituitary-adrenocortical adjustments to transport stress in horses with previous different handling and transport conditions. Veter-World 2016, 9, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczarek, I.; Wilk, I.; Stachurska, A.; Krakowski, L.; Liss, M. Cardiac activity and salivary cortisol concentration of leisure horses in response to the presence of an audience in the arena. J. Vet. Behav. 2019, 29, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Medica, P.; Cravana, C.; Ferlazzo, A. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responses of horses to therapeutic riding program: Effects of different riders. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 118, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, C.; Mueller, M.K.; Frank, N. Effects of Therapeutic Riding on Measures of Stress in Horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.A.; Uceda, S.; Oliveira, T.F.; Fernandes, A.C.; Garcia-Marques, T.; Oliveira, R.F. Testosterone response to competition in males is unrelated to opponent familiarity or threat appraisal. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-de-la-torre, J.L.; Manteca, X. Effects of testosterone on aggressive behaviour after social mixing in male lambs. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 68, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfield, R.; Collias, N.; Tarvyd, E. Testosterone versus psychological castration in the expression of dominance, territoriality and breeding behavior by male village weavers (Ploceus cucullatus). Behaviour 2002, 139, 801–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorleuchter, D.; Herberz, S.; Van den Poel, D. Mining Social Behavior Ideas of Przewalski Horses. In Advances in Computer, Communication, Control and Automation; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Wu, Y., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 649–656. [Google Scholar]
- Dismukes, A.R.; Johnson, M.M.; Vitacco, M.J.; Iturri, F.; Shirtcliff, E.A. Coupling of the HPA and HPG axes in the context of early life adversity in incarcerated male adolescents. Dev. Psychobiol. 2015, 57, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.L.; Christian, C.B.; Morales, P.J.; Harbaugh, W.T.; Mayr, U.; Mehta, P.H. Exogenous testosterone enhances cortisol and affective responses to social-evaluative stress in dominant men. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 85, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terburg, D.; Morgan, B.; van Honk, J. The testosterone–cortisol ratio: A hormonal marker for proneness to social aggression. Int. J. Law Psychiatry 2009, 32, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casto, K.V.; Edwards, D.A. Testosterone, cortisol, and human competition. Horm. Behav. 2016, 82, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berends, Y.R.; Tulen, J.H.M.; Wierdsma, A.I.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Kushner, S.A.; van Marle, H.J.C. Oxytocin moderates the association between testosterone-cortisol ratio and trustworthiness: A randomized placebo-controlled study. Compr. Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021, 8, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkaki, I.; Cima, M.; Granic, I. The role of trauma in the hormonal interplay of cortisol, testosterone, and oxytocin in adolescent aggression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 88, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, B.; Roy, B.; Dwivedi, Y. Role of HPA and the HPG-axis interaction in testosterone-mediated learned helpless behavior. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczak, K.; Klocek, C. A Review of Aggressive Bahavior In Horses. Ad. Alta. J. Interdiscip. Res. 2014, 4, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Fureix, C.; Menguy, H.; Hausberger, M. Partners with Bad Temper: Reject or Cure? A Study of Chronic Pain and Aggression in Horses. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Martínez, A.; González-Bono, E.; Lila, M.; Moya-Albiol, L. Testosterone/cortisol ratio in response to acute stress: A possible marker of risk for marital violence. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-M.; Colangelo, L.A.; Schwartz, J.E.; Yano, Y.; Siscovick, D.S.; Seeman, T.; Schreiner, P.J.; Liu, K.J.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Greenland, P. Associations of cortisol/testosterone and cortisol/sex hormone-binding globulin ratios with atherosclerosis in middle-age women. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelec, K.; Kędzierski, W.; Bereznowski, A.; Janczarek, I.; Bocian, K.; Radosz, M. Salivary Cortisol Levels in Horses and their Riders During Three-Day-Events. J. Veter Res. 2013, 57, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaesser, F.; Klobasa, F.; Ellendorff, F. ACTH stimulation test for the determination of salivary cortisol and of cortisol responses as markers of the training status/fitness of warm-blooded sports horses. DTW Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2001, 108, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Strzelec, K.; Kankofer, M.; Pietrzak, S. Cortisol concentration in the saliva of horses subjected to different kinds of exercise. Acta Vet. Brno 2011, 80, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Maneu, S.; Carbajal, A.; Gardela, J.; Lopez-Bejar, M. Hair Cortisol, Testosterone, Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate and Their Ratios in Stallions as a Retrospective Measure of Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal and Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal Axes Activity: Exploring the Influence of Seasonality. Animals 2021, 11, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinsaat, C.; Under, A.G.; Sulu, N.; Ergun, A. Seasonal variations in serum concentrations of melatonin, testosterone, and progesterone in Arabian horse. Ankara Üniv. Vet Fak. Derg. 2009, 56, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).