Content of Trace Elements in Soil Fertilized with Potassium and Nitrogen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodological Design
2.2. Methods of Laboratory and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrzeba, M.; Rusinowski, S.Z.; Sitko, K.; Krzyżak, J.; Skalska, A.; Małkowski, E.; Ciszek, D.; Werle, S.; McCalmont, J.P.; Mos, M.; et al. Relationships between soil parameters and physiological status of Miscanthus x giganteus cultivated on soil contaminated with trace elements under NPK fertilisation vs. microbial inoculation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, J.R.; Zhang, H.; Schroder, J.L.; Hattey, J.A.; Raun, W.R.; Payton, M.E. Micronutrient availability as affected by the long-term application of phosphorus fertilizer and organic amendments. Soil Fertil. Plant Nutr. 2011, 75, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belon, E.; Boisson, M.; Deportes, I.Z.; Eglin, T.K.; Feix, I.; Bispo, A.O.; Galsomies, L.; Leblond, S.; Guellier, C.R. An inventory of trace elements inputs to French agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 439, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latifi, Z.; Jalali, M. Trace element contaminants in mineral fertilizers used in Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 31917–31928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortvedt, J.J. Heavy metal contaminants in inorganic and organic fertilizers. Fert. Res. 1995, 43, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Disla, J.M.; Gómez, I.; Navarro-Pedreño, J.; Lag-Brotons, A. Evaluation of single chemical extractants for the prediction of heavy metal uptake by barley in soils amended with polluted sewage sludge. Plant Soil 2010, 327, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehoczky, É.; Debreczeni, K.; Szalai, T. Available micronutrient contents of soils in long-term fertilization experiments in Hungary. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; p. 403. Available online: http://base.dnsgb.com.ua/files/book/Agriculture/Soil/Trace-Elements-in-Soils-and-Plants.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Gray, C.; McLaren, R.; Roberts, A.; Condron, L.M. The effect of long-term phosphatic fertiliser applications on the amounts and forms of cadmium in soils under pasture in New Zealand. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1999, 54, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejcman, M.; Szaková, J.; Schellberg, J.; Šrek, P.; Tlustoš, P. The Rengen Grassland Experiment: Soil contamination by trace elements after 65 years of Ca, N, P and K fertiliser application. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 83, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losak, T.; Hlusek, J.; Martinec, J.; Jandak, J.; Szostkova, M.; Filipcik, R.; Manasek, J.; Prokes, K.; Peterka, J.; Varga, L.; et al. Nitrogen fertilization does not affect micronutrient uptake in grain maize (Zea mays L.). Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2011, 61, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husted, S.; Thomsen, M.U.; Mattsson, M.; Schjoerring, J. Influence of nitrogen and sulphur form on manganese acquisition by barley (Hordeum vulgare). Plant Soil 2005, 268, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, S.E.; Hamon, R.E.; Mcgrath, S.P.; Holm, P.E.; Christensen, T.H. Applications of fertilizer cations affect cadmium and zinc concentrations in soil solutions and uptake by plants. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1994, 45, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Chen, W.; Chang, A.C.; Page, A.L. Environmental risks of trace elements associated with long-term phosphate fertilizers applications: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 168, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference base for soil resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps; WRB: London, UK, 2014; Volume 106, p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 October 2003 relating to fertilizers. Off. J. L 2003, 304, 1–194.
- US-EPA Method 3051A. Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediment, Sludges, Soils and Oils; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; p. 30. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3051a.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2020).
- Ostrowska, A.; Gawliński, S.; Szczubiałka, Z. Methods for Analysis and Evaluation of Soil and Plant Properties; IOŚ: Warszawa, Poland, 1991; pp. 1–334. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- PN-R-04032. Soil and Mineral Materials—Sampling and Determination of Particle Size Distribution; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warszawa, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10390. Soil Quality—Determination of Ph; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shimadzu, C. Shimadzu Analytical and Measuring Instruments. Shimadzu Corporation, Japan. 2019. Available online: https://solutions.shimadzu.co.jp/an/n/en/etc/jpz19014.pdf?_ga=2.50821161.1231336941.1597769507-1298426863.1597769507 (accessed on 18 August 2020).
- ISO 11261. Soil Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Modified Kjeldahl Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Egner, H.; Riehm, H.; Domingo, W.R. Untersuchun-gen über die chemische Bodenanalyse als Grundlage für die Beurteilung des Nährstoffzustandes der Böden. II. Chemische Extractionsmethoden zur Phospor- und Kaliumbestimmung. Ann. R. Agric. Coll. Sweden 1960, 26, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichting, E.; Blume, H.P.; Stahr, K. Bodenkundliches Praktikum; Pareys Studientexte 81; Blackwell Wissenschafts-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1995; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Boratyński, K.; Grom, A.; Ziętecka, M. Research on the content of sulfur in soil. Part I. Rocz. Gleboz. 1975, 3, 121–139. [Google Scholar]
- Dell Inc. Dell Statistica (Data Analysis Software System), Version 13. 2016. Available online: http://software.dell.com (accessed on 24 July 2020).
- Ni, R.; Ma, Y. Current inventory and changes of the input/output balance of trace elements in farmland across China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, N.U.; Anake, W.U.; Etesin, U.M. Trace metals levels in inorganic fertilizers commercially available in Nigeria. J. Sci. Res. Rep. 2014, 3, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atafar, Z.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Nouri, J.; Homaee, M.; Yunesian, M.; Ahmadimoghaddam, M.; Mahvi, A.H. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 160, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Jin, J. Status of heavy metals in agricultural soils as affected by different patterns of land use. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 139, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, Z.; Mazur, T. The influence of long-term fertilization with slurry, manure and NPK on the soil content of trace elements. J. Elem. 2016, 21, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, D.; Hejcman, M.; Száková, J.; Kunzová, E.; Tlustoš, P. Concentration of trace elements in arable soil after long-term application of organic and inorganic fertilizers. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2009, 85, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnecki, S.; Düring, R.A. Influence of long-term mineral fertilization on metal contents and properties of soil samples taken from different locations in Hesse, Germany. Soil 2015, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ding, W.; Chen, Z.; Ziadi, N. Thirty-year amendment of horse manure and chemical fertilizer on the availability of micronutrients at the aggregate scale in black soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 19, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Sosulski, T.; Stępień, W. Soil micronutrient availability to crops affected by long-term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Agrawal, M.; Marshall, F.M. The role of organic vs. inorganic fertilizers in reducing phytoavailability of heavy metals in a wastewater-irrigated area. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y.; Zhou, D.M.; Cang, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Fan, X.H.; Qin, S.W. Soil micronutrient availability to crops as affected by long-term inorganic and organic fertilizer applications. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 96, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, P.J.; Rietra, J.; Heinen, M.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Bindraban, P.S. Effects of nutrient antagonism and synergism on yield and fertilizer use efficiency. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1895–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, B.; Szulc, W.; Łabętowicz, J. Influence of soil fertilization on concentration of microelements in soil solution of sandy soil. J. Elem. 2009, 14, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symanowicz, B.; Kalembasa, S.; Jaremko, D.; Niedbała, M. Effect of nitrogen application and year on concentration of Cu, Zn, Ni, Cr, Pb and Cd in herbage of Galega orientalis Lam. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation. Regulation of Minister of the Environment of 1 September 2016 on the procedures for the assessment of land surface contamination. J. Laws 2016, 1395. [Google Scholar]
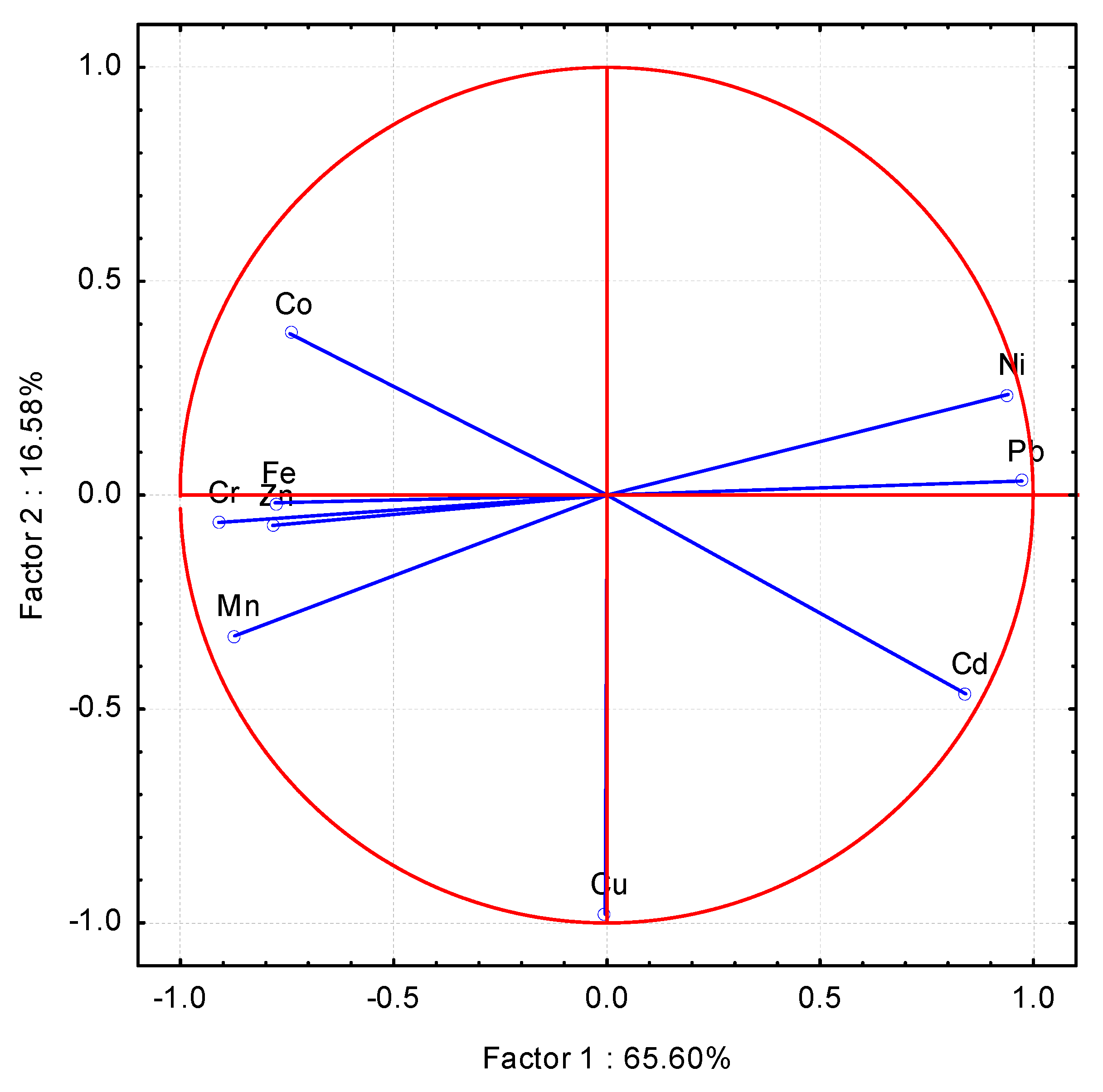
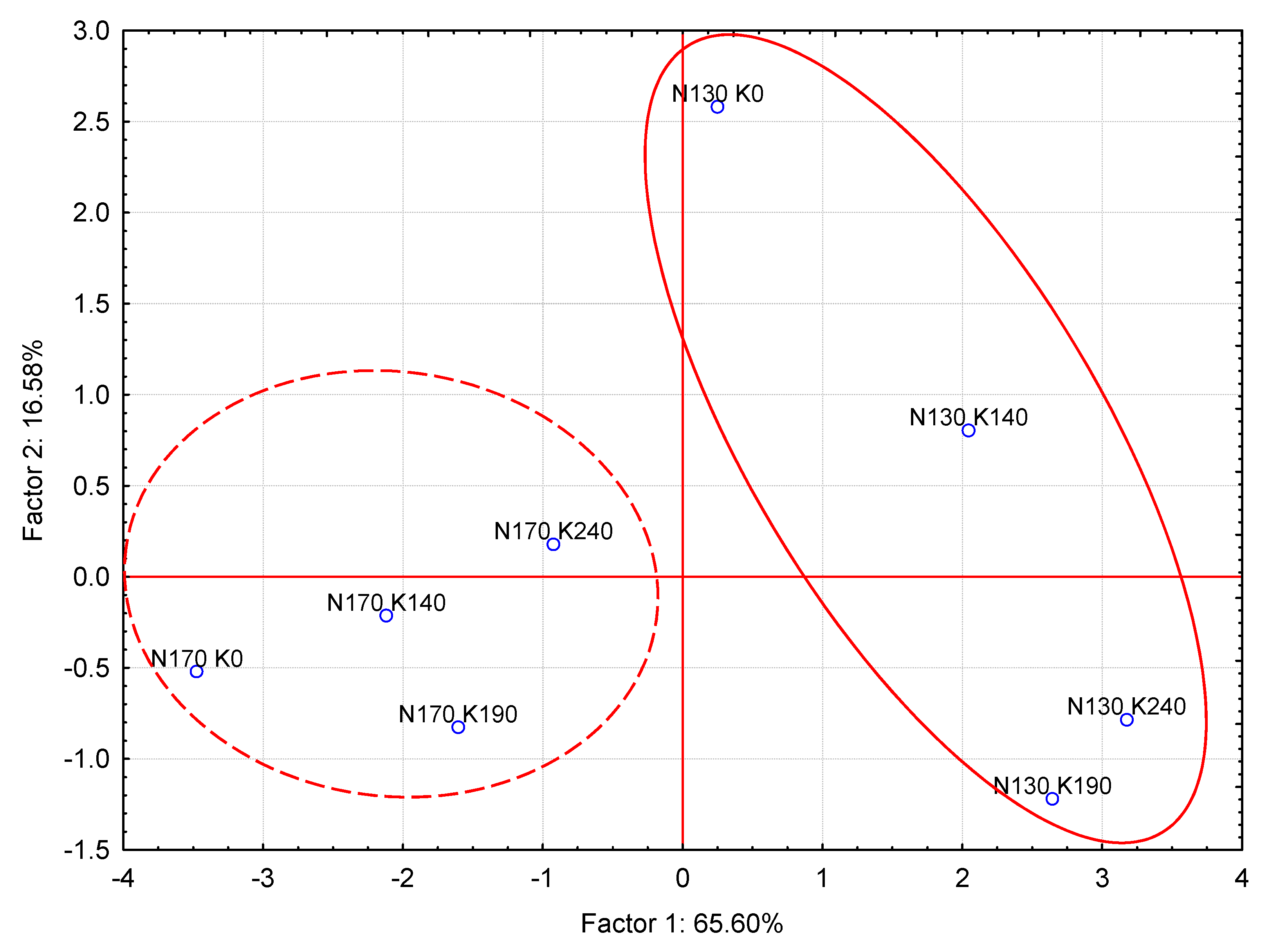
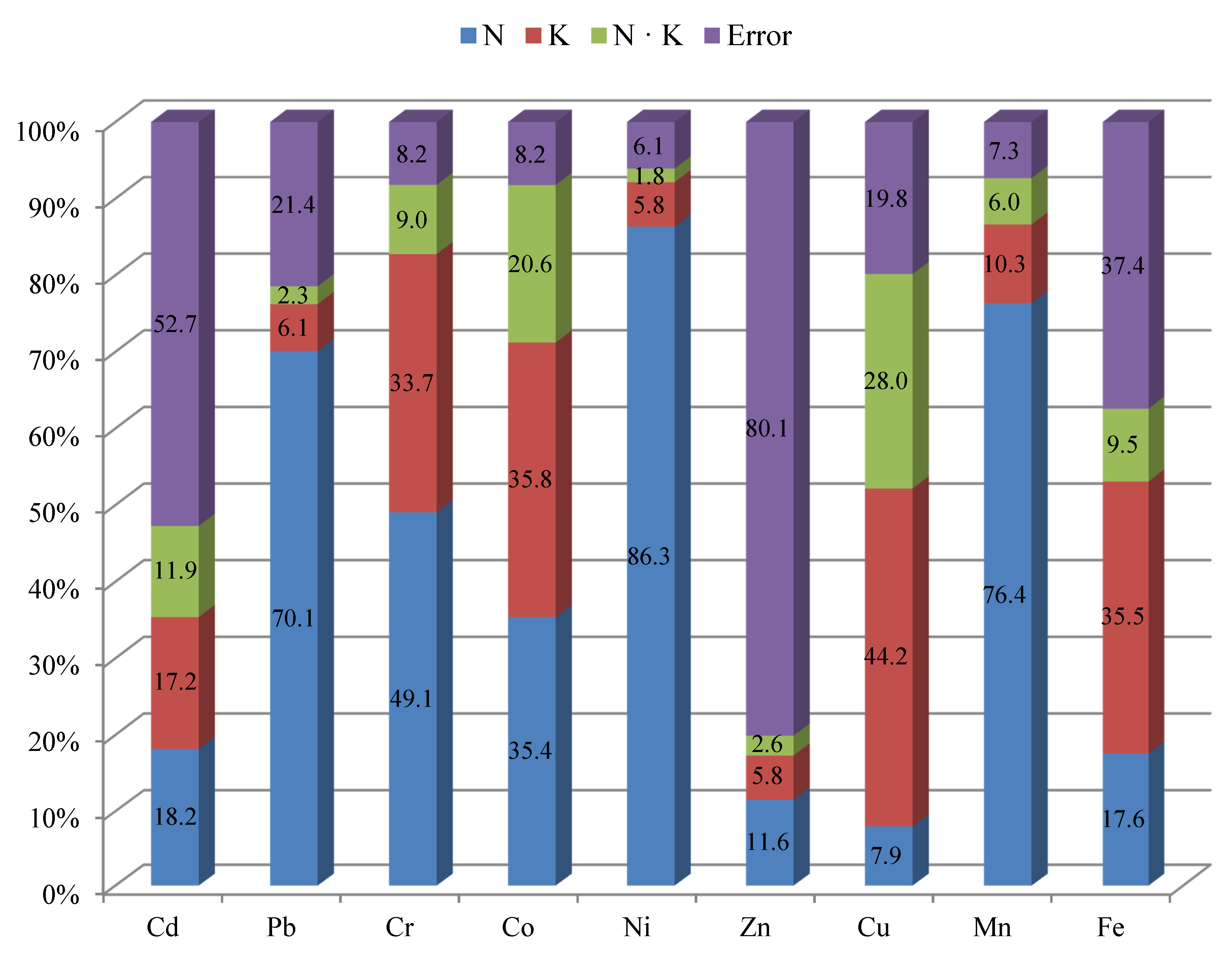
| Parameter | Soil |
|---|---|
| Granulometric composition | sand |
| Sand > 0.05 mm (%) | 90.28 |
| Silt 0.002–0.05 mm (%) | 7.86 |
| Clay < 0.002 mm (%) | 1.86 |
| pH value in 1 M KCl/dm3 | 6.02 |
| Hydrolytic acidity—HAC (mM(+)/kg DM) | 16.00 |
| Total exchangeable bases—TEB (mM(+)/kg DM) | 41,25 |
| Cation exchange capacity—CEC (mM(+)/kg DM) | 57.75 |
| Base saturation—BS (%) | 71.43 |
| Total organic carbon—TOC (g/kg DM) | 3.304 |
| Total nitrogen (g/kg DM) | 0.620 |
| Available phosphorus (mg P/kg DM) | 14.20 |
| Available potassium (mg K/kg DM) | 98.00 |
| Available magnesium (mg Mg/kg DM) | 38.56 |
| Sulphur (mg S-SO4/kg DM) | 18.56 |
| Cadmium (mg Cd/kg DM) | 0.142 |
| Lead (mg Pb/kg DM) | 13.12 |
| Chromium (mg Cr/kg DM) | 58.65 |
| Cobalt (mg Co/kg DM) | 5.741 |
| Nickel (mg Ni/kg DM) | 16.31 |
| Copper (mg Cu/kg DM) | 4.142 |
| Zinc (mg Zn/kg DM) | 32.78 |
| Manganese (mg Mn/kg DM) | 143.6 |
| Iron (mg Fe/kg DM) | 11,209 |
| K Dose in mg/kg of Soil | Content of Trace Elements in mg/kg DM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | Cr | Co | |
| 130 mg N/kg of soil | ||||
| 0 | 0.121 | 13.43 | 56.96 | 4.966 |
| 140 | 0.196 | 17.17 | 55.68 | 5.360 |
| 190 | 0.208 | 17.36 | 53.45 | 1.796 |
| 240 | 0.221 | 17.79 | 51.47 | 1.710 |
| Average | 0.187 | 16.44 | 54.39 | 3.458 |
| r | 0.984 ** | 0.961 ** | −0.928 ** | −0.765 ** |
| 170 mg N/kg of soil | ||||
| 0 | 0.138 | 8.39 | 71.21 | 4.995 |
| 140 | 0.142 | 8.98 | 60.68 | 6.465 |
| 190 | 0.142 | 9.24 | 60.43 | 5.773 |
| 240 | 0.150 | 9.67 | 58.28 | 4.813 |
| Average | 0.143 | 9.07 | 62.65 | 5.512 |
| r | 0.865 ** | 0.986 ** | −0.969 ** | 0.066 |
| Average | ||||
| 0 | 0.130 | 10.91 | 64.09 | 4.981 |
| 140 | 0.169 | 13.08 | 58.18 | 5.913 |
| 190 | 0.175 | 13.30 | 56.94 | 3.785 |
| 240 | 0.186 | 13.73 | 54.88 | 3.262 |
| Average | 0.165 | 12.75 | 58.52 | 4.485 |
| r | 0.991 ** | 0.981 ** | −0.997 ** | −0.613 * |
| LSD for: | ||||
| N dose | n.s. | 3.32 ** | 2.76 ** | 0.808 ** |
| K dose | n.s. | n.s. | 3.90 ** | 1.143 ** |
| interaction | n.s. | n.s. | 5.51 * | 1.616 ** |
| K Dose in mg/kg of Soil | Content of Trace Elements in mg/kg DM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Zn | Cu | Mn | Fe | |
| 130 mg N/kg of soil | |||||
| 0 | 15.63 | 31.65 | 3.905 | 140.4 | 11063 |
| 140 | 17.04 | 30.42 | 5.281 | 140.3 | 11125 |
| 190 | 16.31 | 31.09 | 6.496 | 140.0 | 11003 |
| 240 | 16.16 | 31.40 | 5.956 | 138.1 | 10686 |
| Average | 16.29 | 31.14 | 5.410 | 139.7 | 10969 |
| r | 0.446 | −0.290 | 0.920 ** | −0.725 ** | −0.656 * |
| 170 mg N/kg of soil | |||||
| 0 | 11.23 | 32.56 | 5.779 | 157.9 | 11726 |
| 140 | 12.37 | 32.18 | 5.936 | 157.9 | 11266 |
| 190 | 13.05 | 31.50 | 6.398 | 164.0 | 11129 |
| 240 | 12.56 | 32.39 | 5.453 | 148.4 | 10942 |
| Average | 12.30 | 32.16 | 5.892 | 157.1 | 11266 |
| r | 0.893 ** | −0.457 | −0.023 | −0.318 | −0.999 ** |
| Average | |||||
| 0 | 13.43 | 32.11 | 4.842 | 149.2 | 11395 |
| 140 | 14.71 | 31.30 | 5.609 | 149.1 | 11196 |
| 190 | 14.68 | 31.30 | 6.447 | 152.0 | 11066 |
| 240 | 14.36 | 31.90 | 5.705 | 143.3 | 10814 |
| Average | 14.29 | 31.65 | 5.651 | 148.4 | 11118 |
| r | 0.793 ** | −0.443 | 0.778 ** | −0.386 | −0.950 ** |
| LSD for: | |||||
| N dose | 0.86 ** | n.s. | n.s. | 4.4 ** | 353 * |
| K dose | 1.22 ** | n.s. | 0.879 ** | 6.2 ** | 499 * |
| interaction | 1.73 * | n.s. | 1.242 * | 8.8 * | n.s. |
| Factor | Content of Trace Elements in Soil | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Pb | Cr | Co | Ni | Zn | Cu | Mn | |
| Pb | 0.543 ** | |||||||
| Cr | −0.287 | −0.611 ** | ||||||
| Co | −0.562 ** | −0.622 ** | 0.507 ** | |||||
| Ni | 0.354 | 0.868 ** | −0.795 ** | −0.535 ** | ||||
| Zn | −0.059 | −0.178 | 0.376 | −0.008 | −0.291 | |||
| Cu | 0.290 | −0.022 | 0.032 | −0.200 | −0.192 | 0.079 | ||
| Mn | −0.479 * | −0.689 ** | 0.695 ** | 0.602 ** | −0.767 ** | 0.291 | 0.287 | |
| Fe | −0.567 ** | −0.306 | 0.707 ** | 0.414 * | −0.428 * | 0.195 | 0.018 | 0.561 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wyszkowski, M.; Brodowska, M.S. Content of Trace Elements in Soil Fertilized with Potassium and Nitrogen. Agriculture 2020, 10, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10090398
Wyszkowski M, Brodowska MS. Content of Trace Elements in Soil Fertilized with Potassium and Nitrogen. Agriculture. 2020; 10(9):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10090398
Chicago/Turabian StyleWyszkowski, Mirosław, and Marzena S. Brodowska. 2020. "Content of Trace Elements in Soil Fertilized with Potassium and Nitrogen" Agriculture 10, no. 9: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10090398
APA StyleWyszkowski, M., & Brodowska, M. S. (2020). Content of Trace Elements in Soil Fertilized with Potassium and Nitrogen. Agriculture, 10(9), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture10090398





