Accurate Blood-Based Diagnostic Biosignatures for Alzheimer’s Disease via Automated Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Construction of Biosignatures/Models via AutoML
2.3. Correlation of Selected Features to AD
3. Results
3.1. Datasets
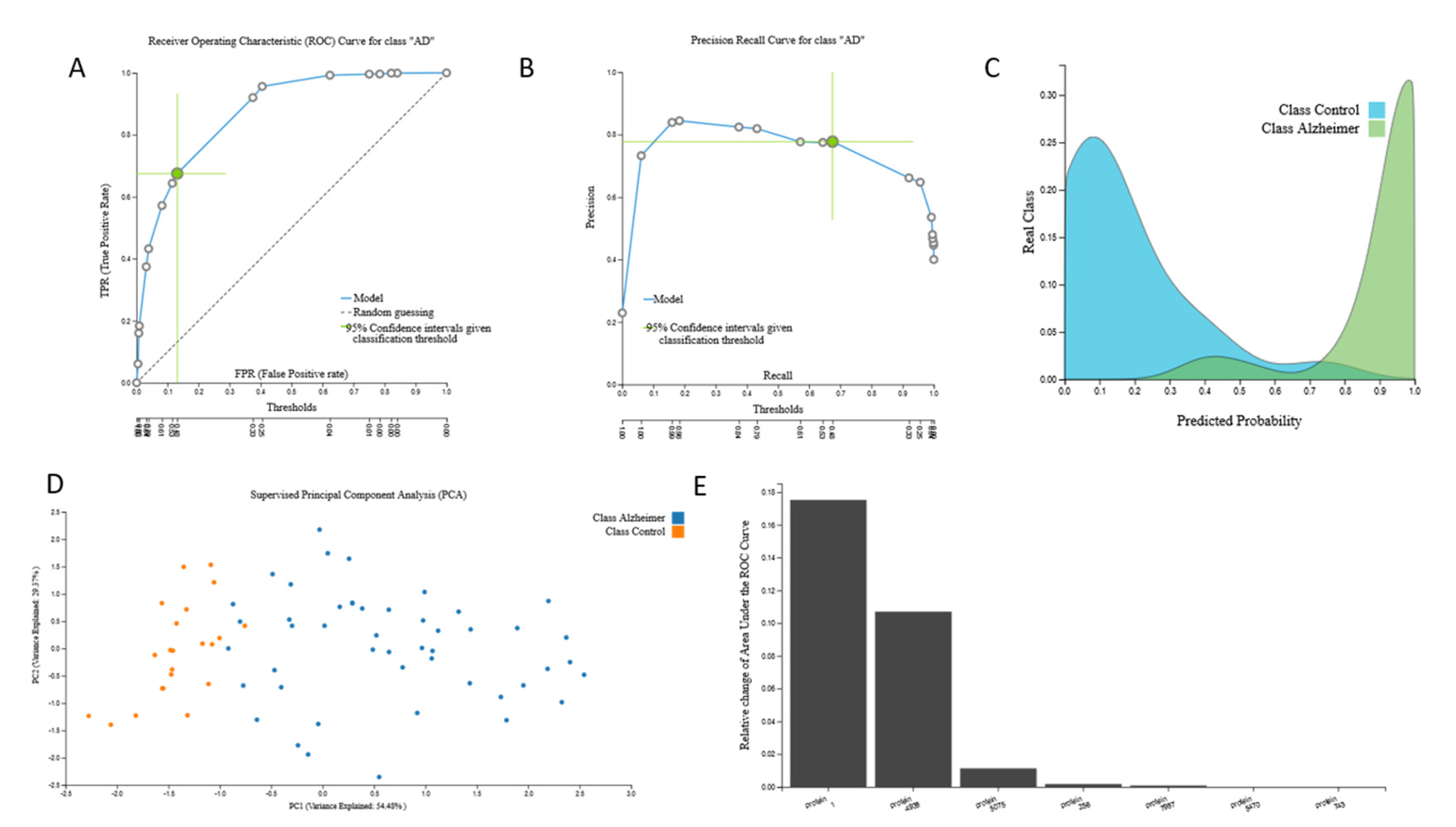
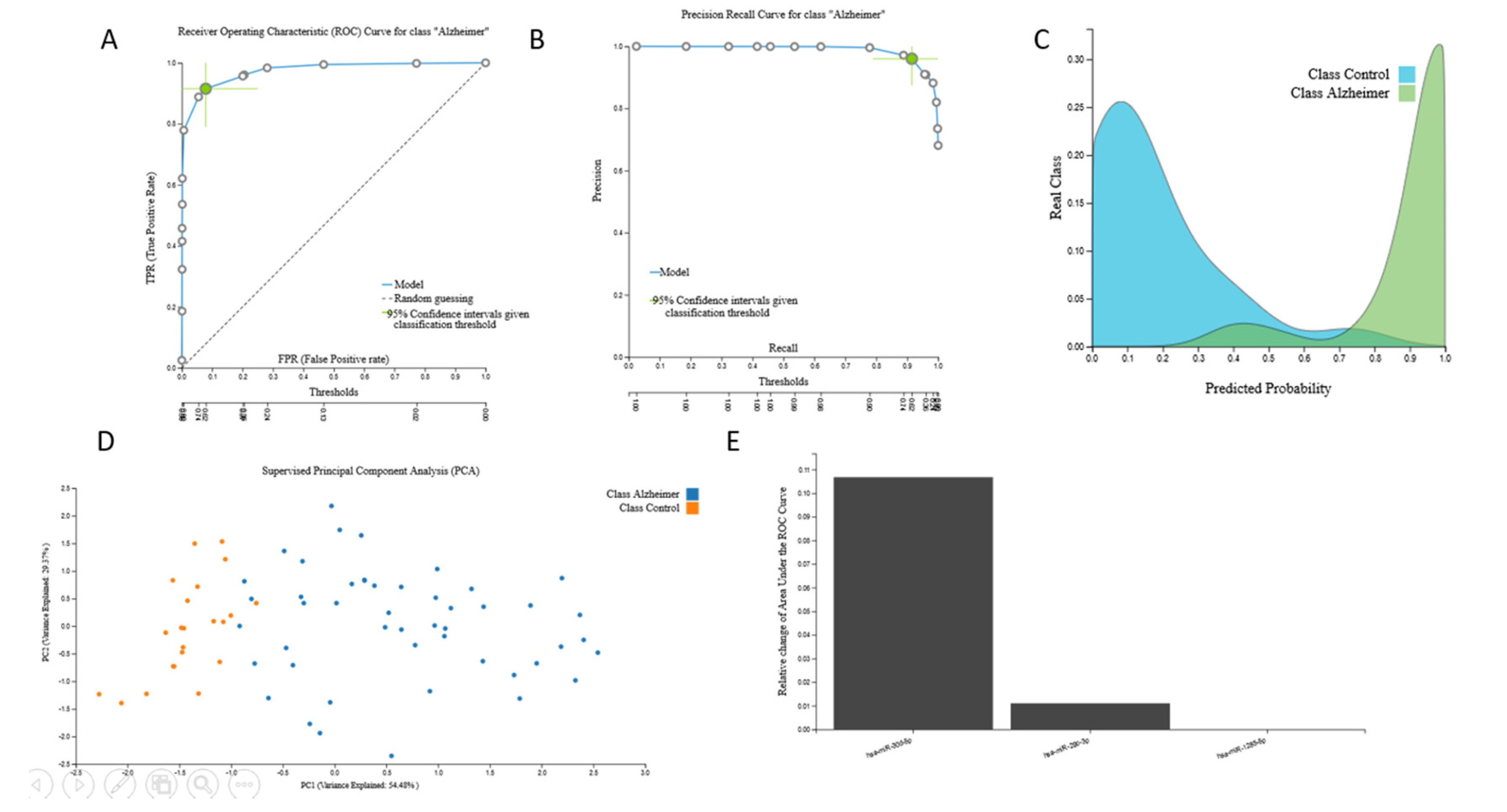
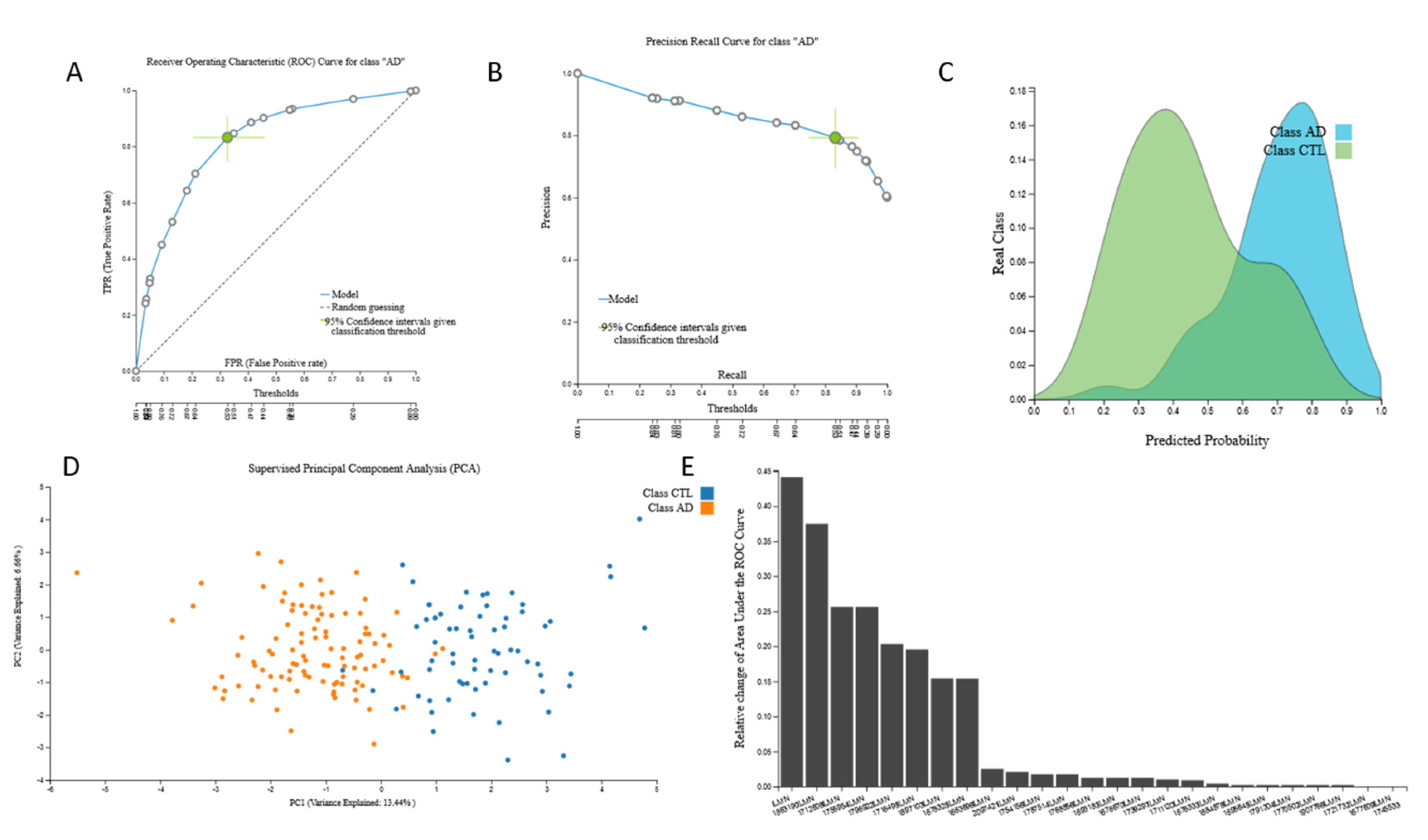
3.2. Biosignatures
3.2.1. Proteomic Biosignature
3.2.2. miRNA Biosignatures
3.2.3. mRNA Biosignatures
3.2.4. Metabolomic Biosignatures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winblad, B.; Amouyel, P.; Andrieu, S.; Ballard, C.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Dubois, B.; Edvardsson, D.; Feldman, H.H.; et al. Defeating Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: A priority for European science and society. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 455–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, E.; Szoeke, C.E.; Vollset, S.E.; Abbasi, N.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Aichour, M.T.E.; Akinyemi, R.O.; Alahdab, F.; Asgedom, S.W.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galasko, D. Expanding the Repertoire of Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease: Targeted and Non-targeted Approaches. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zverova, M. Alzheimer’s disease and blood-based biomarkers—Potential contexts of use. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zetterberg, H. Applying fluid biomarkers to Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2017, 313, C3–C10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsamardinos, I.; Charonyktakis, P.; Lakiotaki, K.; Borboudakis, G.; Zenklusen, J.C.; Juhl, H.; Chatzaki, E.; Lagani, V. Just Add Data: Automated Predictive Modeling and BioSignature Discovery. Biorxiv. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesanto, A.; D’Aquila, P.; Lagani, V.; Paparazzo, E.; Geracitano, S.; Formentini, L.; Giacconi, R.; Cardelli, M.; Provinciali, M.; Bellizzi, D.; et al. A New Robust Epigenetic Model for Forensic Age Prediction. J. Forensic Sci. 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulou, M.; Karaglani, M.; Balgkouranidou, I.; Biziota, E.; Koukaki, T.; Karamitrousis, E.; Nena, E.; Tsamardinos, I.; Kolios, G.; Lianidou, E.; et al. Circulating cell-free DNA in breast cancer: Size profiling, levels, and methylation patterns lead to prognostic and predictive classifiers. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3387–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanoudaki, G.; Markaki, M.; Chatzi, K.; Tsamardinos, I.; Economou, A. MatureP: Prediction of secreted proteins with exclusive information from their mature regions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borboudakis, G.; Stergiannakos, T.; Frysali, M.; Klontzas, E.; Tsamardinos, I.; Froudakis, G.E. Chemically intuited, large-scale screening of MOFs by machine learning techniques. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamou, M.; Antoniou, G.; Greasidou, E.; Lagani, V.; Charonyktakis, P.; Tsamardinos, I.; Doyle, M. Toward Automatic Risk Assessment to Support Suicide Prevention. Crisis 2019, 40, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagani, V.; Athineou, G.; Farcomeni, A.; Tsagris, M.; Tsamardinos, I. Feature Selection with the R Package MXM: Discovering Statistically Equivalent Feature Subsets. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsamardinos, I.; Greasidou, E.; Borboudakis, G. Bootstrapping the out-of-sample predictions for efficient and accurate cross-validation. Mach. Learn. 2018, 107, 1895–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lakiotaki, K.; Vorniotakis, N.; Tsagris, M.; Georgakopoulos, G.; Tsamardinos, I. BioDataome: A collection of uniformly preprocessed and automatically annotated datasets for data-driven biology. Database (Oxford) 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Azam, K.; Vadivelu, I.; Burant, C.F.; Edison, A.S.; Fiehn, O.; Higashi, R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Metabolomics Workbench: An international repository for metabolomics data and metadata, metabolite standards, protocols, tutorials and training, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D463–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collado-Torres, L.; Nellore, A.; Kammers, K.; Ellis, S.E.; Taub, M.A.; Hansen, K.D.; Jaffe, A.E.; Langmead, B.; Leek, J.T. Reproducible RNA-seq analysis using recount2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagele, E.P.; Han, M.; Acharya, N.K.; DeMarshall, C.; Kosciuk, M.C.; Nagele, R.G. Natural IgG autoantibodies are abundant and ubiquitous in human sera, and their number is influenced by age, gender, and disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagele, E.; Han, M.; Demarshall, C.; Belinka, B.; Nagele, R. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease based on disease-specific autoantibody profiles in human sera. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidinger, P.; Backes, C.; Deutscher, S.; Schmitt, K.; Mueller, S.C.; Frese, K.; Haas, J.; Ruprecht, K.; Paul, F.; Stähler, C.; et al. A blood based 12-miRNA signature of Alzheimer disease patients. Genome Boil. 2013, 14, R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shigemizu, D.; Akiyama, S.; Asanomi, Y.; Boroevich, K.A.; Sharma, A.; Tsunoda, T.; Matsukuma, K.; Ichikawa, M.; Sudo, H.; Takizawa, S.; et al. Risk prediction models for dementia constructed by supervised principal component analysis using miRNA expression data. Commun. Boil. 2019, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sood, S.; Gallagher, I.J.; Lunnon, K.; Rullman, E.; Keohane, A.; Crossland, H.; Phillips, B.; Cederholm, T.; Jensen, T.; Van Loon, L.J.C.; et al. A novel multi-tissue RNA diagnostic of healthy ageing relates to cognitive health status. Genome Boil. 2015, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerkentzes, K.; Lagani, V.; Tsamardinos, I.; Vyberg, M.; Røe, O.D. Hidden Treasures in “Ancient” Microarrays: Gene-Expression Portrays Biology and Potential Resistance Pathways of Major Lung Cancer Subtypes and Normal Tissue. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hampel, H.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Zetterberg, H.; Masters, C.L.; Lista, S.; Kiddle, S.J.; Batrla, R.; Blennow, K. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer disease: Mapping the road to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Kang, J.; Svetnik, V.; Warden, D.; Wilcock, G.; Smith, A.D.; Savage, M.J.; Laterza, O.F. A Machine Learning Approach to Identify a Circulating MicroRNA Signature for Alzheimer Disease. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2019, 5, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Iniesta, R.; Stahl, D.; Dobson, R.J.B.; Newhouse, S.J. Working Towards a Blood-Derived Gene Expression Biomarker Specific for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 74, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, H. Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease using blood gene expression data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Long, J.; Pan, G.; He, T.; Anichtchik, O.; Belshaw, R.; Albani, D.; Edison, P.; Green, E.K.; et al. Systematic Analysis and Biomarker Study for Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez Ravetti, M.; Moscato, P. Identification of a 5-Protein Biomarker Molecular Signature for Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamate, D.; Kim, M.; Proitsi, P.; Westwood, S.; Baird, A.; Nevado-Holgado, A.; Hye, A.; Bos, I.; Vos, S.J.; Vandenberghe, R.; et al. A metabolite-based machine learning approach to diagnose Alzheimer-type dementia in blood: Results from the European Medical Information Framework for Alzheimer disease biomarker discovery cohort. Alzheimer’s Dement. (New York, NY) 2019, 5, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, R.; Du, W.; Briller, M.; Gaujoux, R.; Starosvetsky, E.; Ziv-Kenet, A.; Shalev-Malul, G.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Shen-Orr, S.S. Found In Translation: A machine learning model for mouse-to-human inference. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzaki, E.; Tsamardinos, I. Somatic copy number aberrations detected in circulating tumor DNA can hold diagnostic value for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2020, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Dataset | Data Type | Alzheimer’s Disease Samples | Cognitively Healthy Samples | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolomic 1 | Metabolites profiles | 15 | 15 | 3734 |
| Metabolomic 2 | Sphingolipid and fatty acid profiles | 18 | 21 | 25 |
| Proteomic | Protein profiles | 25 | 37 | 9483 |
| Transcriptomic 1 | miRNA profiles | 48 | 22 | 506 |
| Transcriptomic 2 | miRNA profiles | 300 | 289 | 2566 |
| Transcriptomic 3 | mRNA profiles | 134 | 100 | 38,327 |
| Transcriptomic 4 | mRNA profiles | 126 | 131 | 32,053 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karaglani, M.; Gourlia, K.; Tsamardinos, I.; Chatzaki, E. Accurate Blood-Based Diagnostic Biosignatures for Alzheimer’s Disease via Automated Machine Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093016
Karaglani M, Gourlia K, Tsamardinos I, Chatzaki E. Accurate Blood-Based Diagnostic Biosignatures for Alzheimer’s Disease via Automated Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093016
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaraglani, Makrina, Krystallia Gourlia, Ioannis Tsamardinos, and Ekaterini Chatzaki. 2020. "Accurate Blood-Based Diagnostic Biosignatures for Alzheimer’s Disease via Automated Machine Learning" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093016
APA StyleKaraglani, M., Gourlia, K., Tsamardinos, I., & Chatzaki, E. (2020). Accurate Blood-Based Diagnostic Biosignatures for Alzheimer’s Disease via Automated Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 3016. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9093016








