Analysis of miR-29 Serum Levels in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors—Results from an Exploratory Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Study and Patient Cohort
2.2. miRNA Isolation from Serum
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
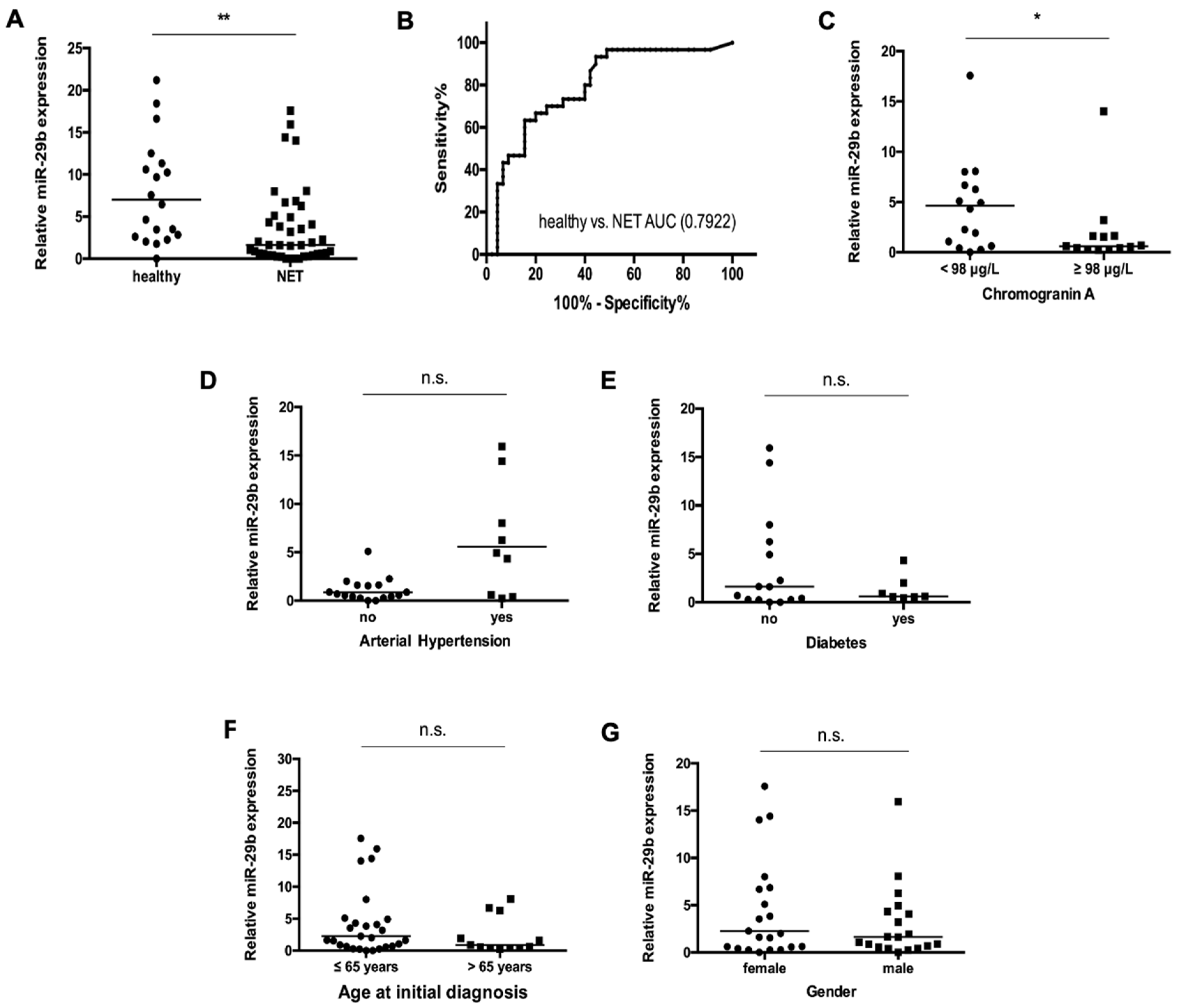
3.2. Levels of Circulating miR-29b in NET Patients
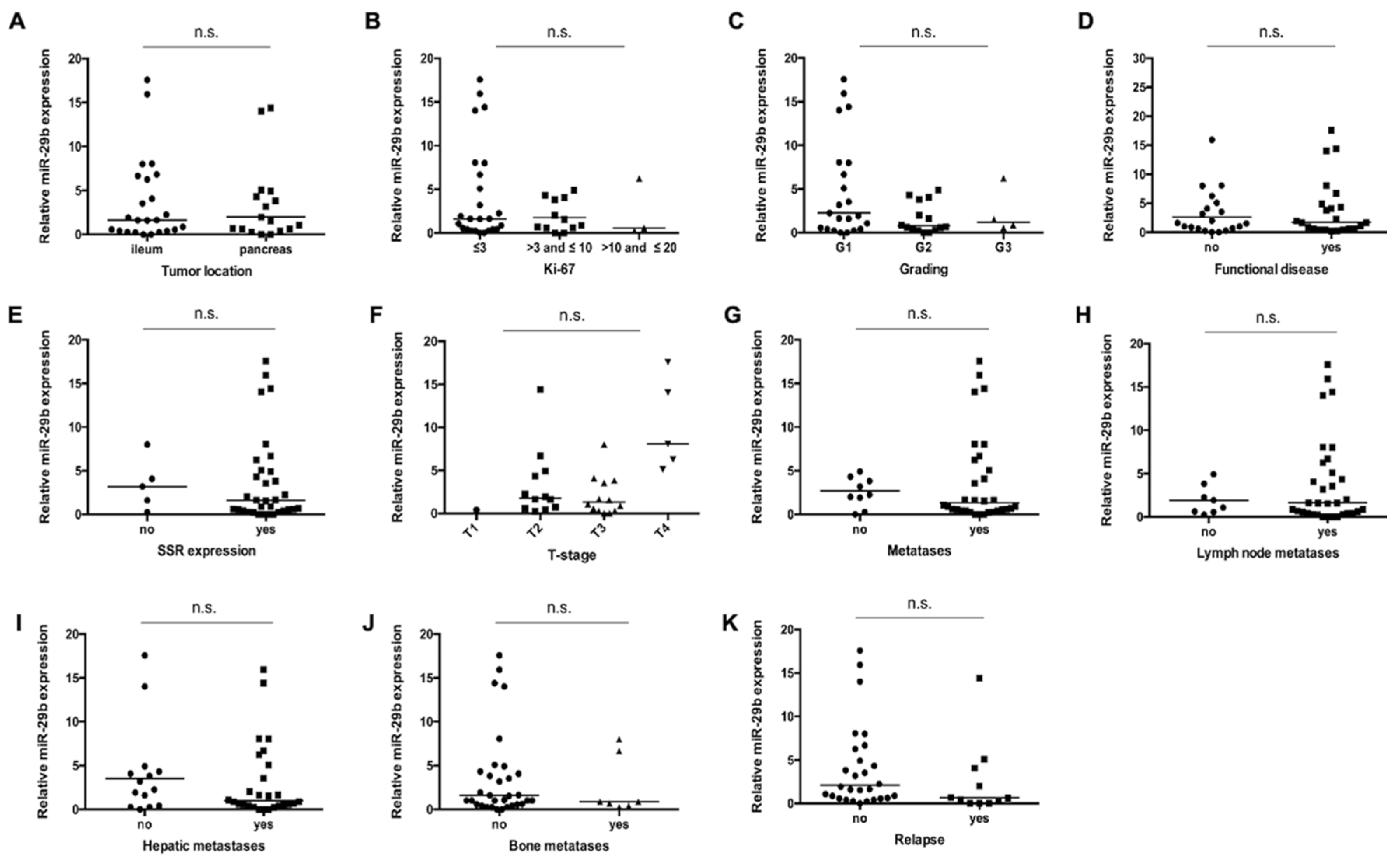
3.3. miR-29b Serum Concentrations Are Not Associated with Disease Characteristics in Patients with NET
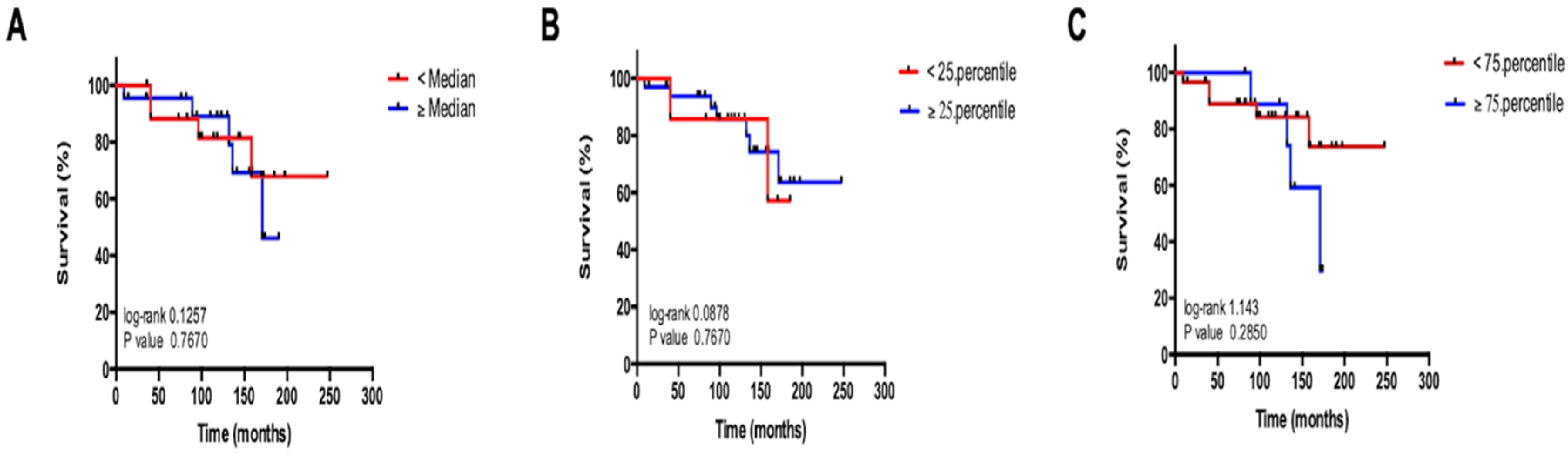
3.4. Circulating miR-29b Levels Do Not Reflect Overall Survival in Patients with NET
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Arbitrary units | (AU) |
| Area under the curve | (AUC) |
| Cholangiocellular carcinoma | (CCA) |
| Chromogranin A | (CgA) |
| Epithelial-mesenchymal transition | (EMT) |
| MicroRNAs | (miRNAs) |
| Neuroendocrine carcinoma | (NEC) |
| Neuroendocrine neoplasia | (NEN) |
| Neuroendocrine tumor | (NET) |
| Receiver operating characteristic | (ROC) |
| Room temperature | (RT) |
| Somatostatin analogue | (SSA) |
| Somatostatin receptor | (SSR) |
References
- Schuetz, P.; Chiappa, V.; Briel, M.; Greenwald, J.L. Procalcitonin algorithms for antibiotic therapy decisions: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials and recommendations for clinical algorithms. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, V.; Zatelli, M.C.; Sciammarella, C.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Bondanelli, M.; Colao, A.; Faggiano, A. Chromogranin A as circulating marker for diagnosis and management of neuroendocrine neoplasms: More flaws than fame. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, R11–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubimova, N.V.; Churikova, T.K.; Kushlinskii, N.E. Chromogranin as a biochemical marker of neuroendocrine tumors. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 160, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, G.; Wiedenmann, B. Neuroendocrine neoplasia goes molecular-time for a change. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.T.; Bodei, L.; Capdevila, J.; Couvelard, A.; Falconi, M.; Glasberg, S.; Kloppel, G.; Lamberts, S.; Peeters, M.; Rindi, G.; et al. Unmet needs in functional and nonfunctional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Neuroendocrinology 2019, 108, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofland, J.; Zandee, W.T.; de Herder, W.W. Role of biomarker tests for diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumours. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knnole, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schueller, F.; Roy, S.; Vucur, M.; Trautwein, C.; Luedde, T.; Roderburg, C. The role of miRNAs in the pathophysiology of liver diseases and toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNA identification in plasma and serum: A new tool to diagnose and monitor diseases. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malczewska, A.; Frampton, A.E.; Mato Prado, M.; Ameri, S.; Dabrowska, A.F.; Zagorac, S.; Clift, A.K.; Kos-Kudta, B.; Faiz, O.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in small-bowel neuroendocrine tumors: A potential tool for diagnosis and assessment of effectiveness of surgical resection. Ann. Surg. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.J.; Factora, T.D.; Dey, S.; Kota, J. A Systematic Review of miR-29 in Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2018, 12, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, M.; Safarzadeh, A.; Beyranvand, F.; Ahmadpour, F.; Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Baradaran, B. The potential role of miR-29 in health and cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 19280–19297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slusarz, A.; Pulakat, L. The two faces of miR-29. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015, 16, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Motoi, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Nagano, H.; Ushijima, M.; Matsuura, M.; Okumura, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Fukuyama, M.; Ishikawa, Y. Pulmonary carcinoids and low-grade gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors show common microRNA expression profiles, different from adenocarcinomas and small cell carcinomas. Neuroendocrinology 2018, 106, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, M.; Zhou, C.W.; Zhang, S.; Brais, L.; Rossi, A.; Naudin, L.; Thiagalingam, A.; Sicinska, E.; Kulke, M.H. Profiling of metastatic small intestine neuroendocrine tumors reveals characteristic miRNAs detectable in plasma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 54331–54344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Luedde, M.; Vargas Cardenas, D.; Vucur, M.; Scholten, D.; Frey, N.; Koch, A.; Trautwein, C.; Tacke, F.; Luedde, T. Circulating microRNA-150 serum levels predict survival in patients with critical illness and sepsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampoka, K.; Muangpaisarn, P.; Khongnomnan, K.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Payungporn, S. Serum miR-29a and miR-122 as potential biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Microrna 2018, 7, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loosen, S.H.; Lurje, G.; Wiltberger, G.; Vucur, M.; Koch, A.; Kather, J.N.; Paffenholz, P.; Tacke, F.; Ulmer, F.T.; Trautwein, C.; et al. Serum levels of miR-29, miR-122, miR-155 and miR-192 are elevated in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vienberg, S.; Geiger, J.; Madsen, S.; Dalgaard, L.T. MicroRNAs in metabolism. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsmans, M.; Holvoet, P. MicroRNA-containing microvesicles regulating inflammation in association with atherosclerotic disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 100, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Fang, J.; Pang, Y.; Zheng, J. Prognostic value of the microRNA-29 family in patients with primary osteosarcomas. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, G.; Qu, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Identification and validation of reference genes for the detection of serum microRNAs by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction in patients with bladder cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayyad-Kazan, M.; Eidirani, R.; Hamade, E.; El Majzoub, R.; Akl, H.; Bitar, N.; Fayyad-Kazan, H.; Badran, B. Circulating miR-29c, miR-30c, miR-193a-5p and miR-885-5p: Novel potential biomarkers for HTLV-1 infection diagnosis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 74, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Mollnow, T.; Bongaerts, B.; Elfimova, N.; Vargas Cardenas, D.; Berger, K.; Zimmermann, H.; Koch, A.; Vucur, M.; Luedde, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling in human serum reveals compartment-specific roles of miR-571 and miR-652 in liver cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilsiz, N. Role of exosomes and exosomal microRNAs in cancer. Future Sci. OA 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Trautwein, C. Cell-specific functions of miRNA in the liver. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairinger, F.D.; Ting, S.; Werner, R.; Walter, R.F.H.; Hager, T.; Vollbrecht, C.; Christoph, D.; Worm, K.; Mairinger, T.; Sheu-Grabellus, S.-Y.; et al. Different micro-RNA expression profiles distinguish subtypes of neuroendocrine tumors of the lung: Results of a profiling study. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1632–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, L.; Qiu, Y. MicroRNA-29a inhibits growth, migration and invasion of melanoma A375 cells in vitro by directly targeting BMI1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, M.P.; Kopetz, S.; Ajani, J.A.; Calin, G.A. Non-coding RNAs in GI cancers: From cancer hallmarks to clinical utility. Gut 2020, 69, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinke, A.; Gress, T.M. Neuroendocrine cancer, therapeutic strategies in G3 cancers. Digestion 2017, 95, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippa, S.; Partelli, S.; Belfiori, G.; Palucci, M.; Muffatti, F.; Adamenko, O.; Cardinali, L.; Doglioni, C.; Zamboni, G.; Falconi, M. Management of neuroendocrine carcinomas of the pancreas (WHO G3): A tailored approach between proliferation and morphology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9944–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinke, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; Auernhammer, C.; Bartenstein, P.; Bartsch, D.K.; Begum, N.; Faiss, S.; Fottner, C.; Gebauer, B.; Goretzki, P.; et al. [Practice guideline neuroendocrine tumors-AWMF-Reg. 021-27]. Z. Gastroenterol. 2018, 56, 583–681. [Google Scholar]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özdirik, B.; Stueven, A.K.; Mohr, R.; Geisler, L.; Wree, A.; Knorr, J.; Demir, M.; Vucur, M.; Loosen, S.H.; Benz, F.; et al. Analysis of miR-29 Serum Levels in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors—Results from an Exploratory Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092881
Özdirik B, Stueven AK, Mohr R, Geisler L, Wree A, Knorr J, Demir M, Vucur M, Loosen SH, Benz F, et al. Analysis of miR-29 Serum Levels in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors—Results from an Exploratory Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(9):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092881
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzdirik, Burcin, Anna K. Stueven, Raphael Mohr, Lukas Geisler, Alexander Wree, Jana Knorr, Münevver Demir, Mihael Vucur, Sven H. Loosen, Fabian Benz, and et al. 2020. "Analysis of miR-29 Serum Levels in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors—Results from an Exploratory Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 9: 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092881
APA StyleÖzdirik, B., Stueven, A. K., Mohr, R., Geisler, L., Wree, A., Knorr, J., Demir, M., Vucur, M., Loosen, S. H., Benz, F., Reiss, M., Wiedenmann, B., Tacke, F., Jann, H., Hellberg, T., & Roderburg, C. (2020). Analysis of miR-29 Serum Levels in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumors—Results from an Exploratory Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9092881






