Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
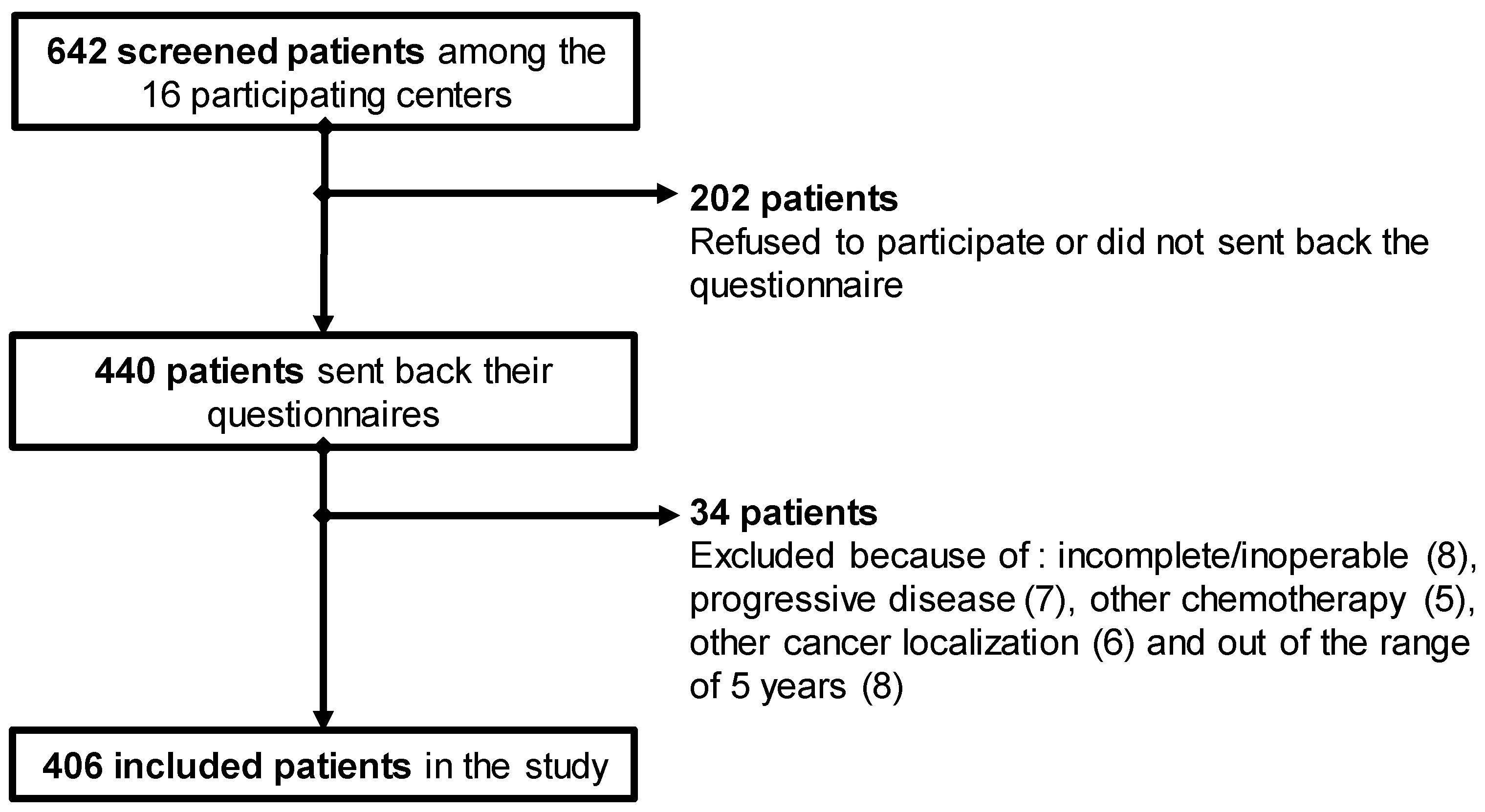
2.3. Participants
2.4. Variables
2.5. Data Sources and Measurements
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Population
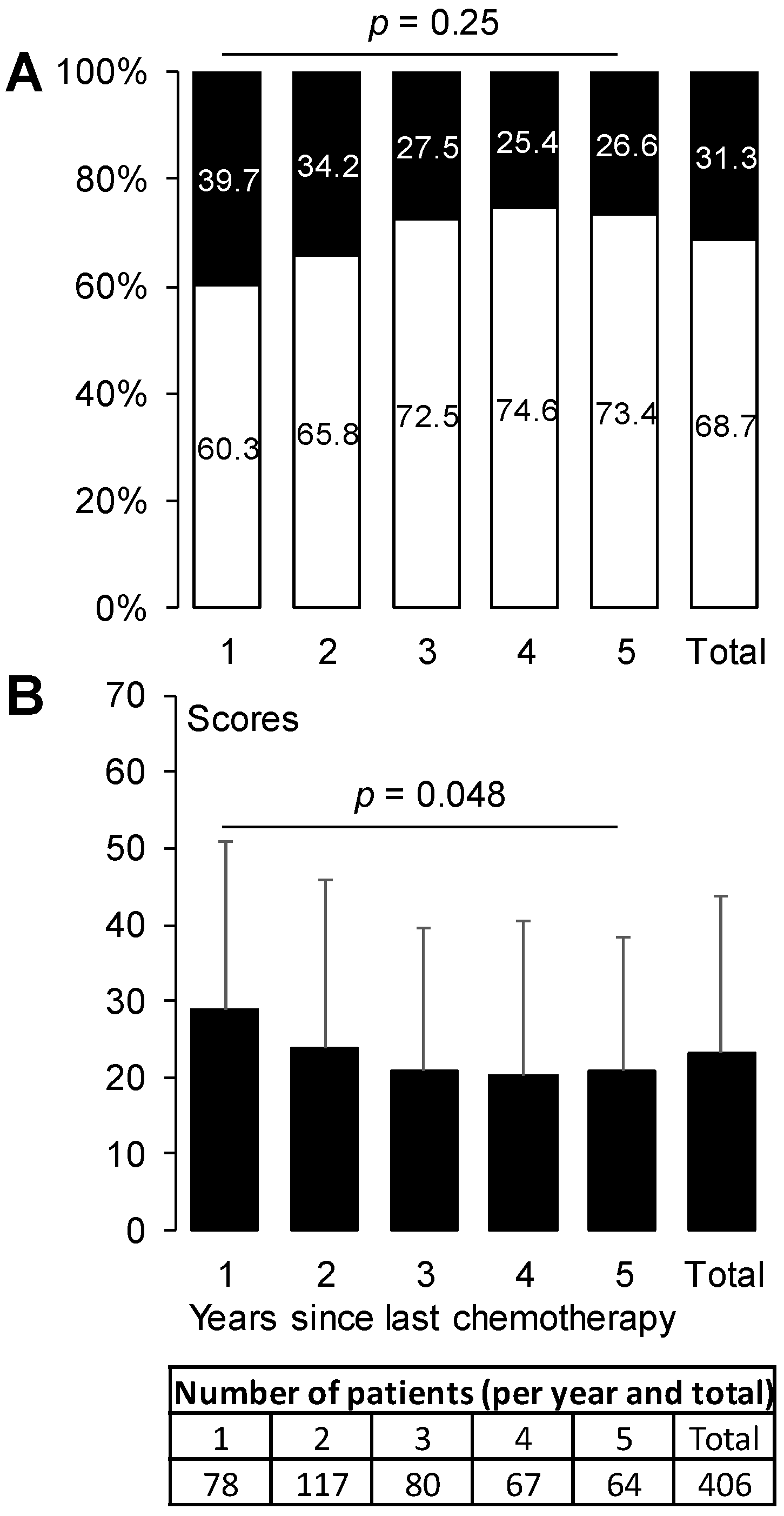
3.2. Prevalence of Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
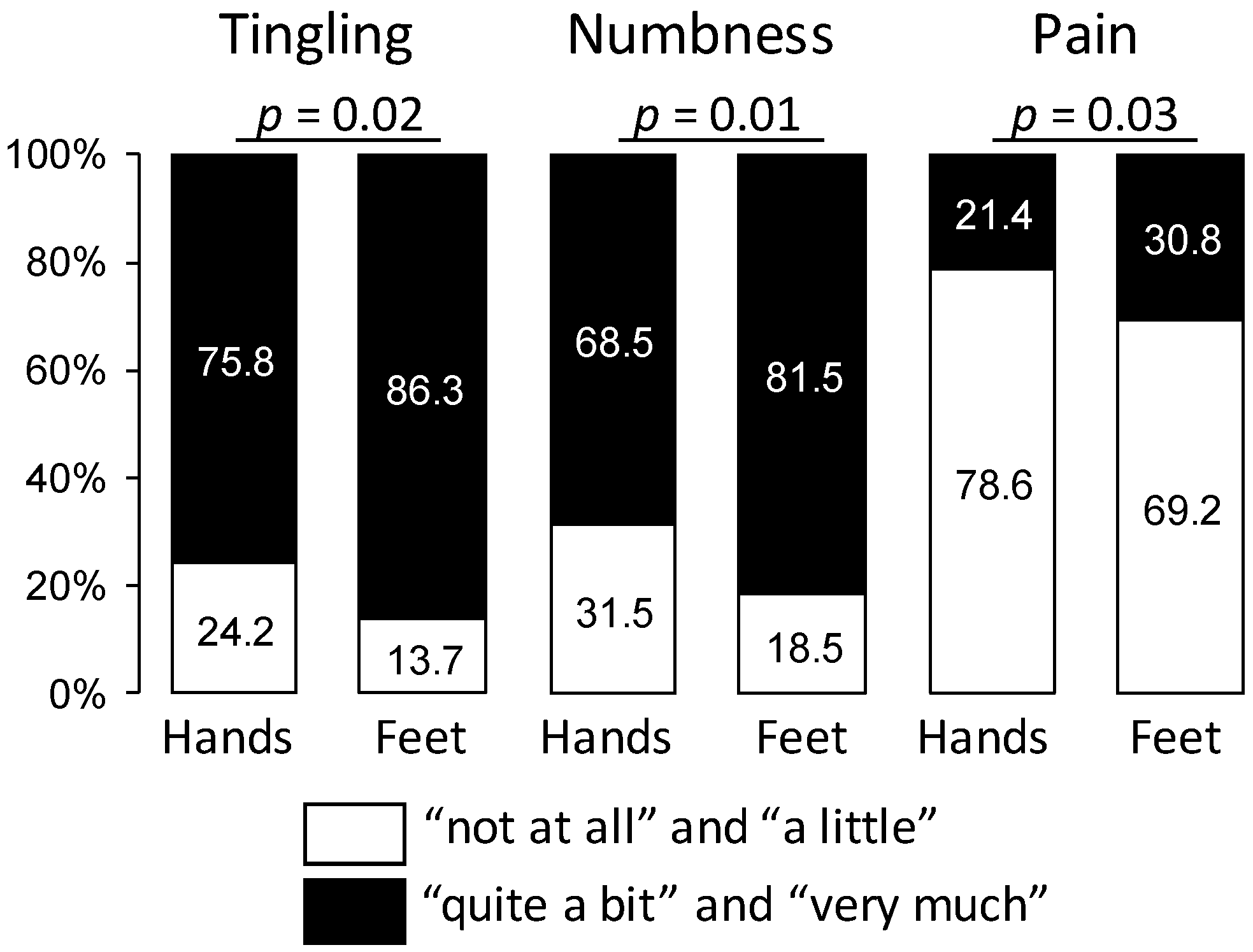
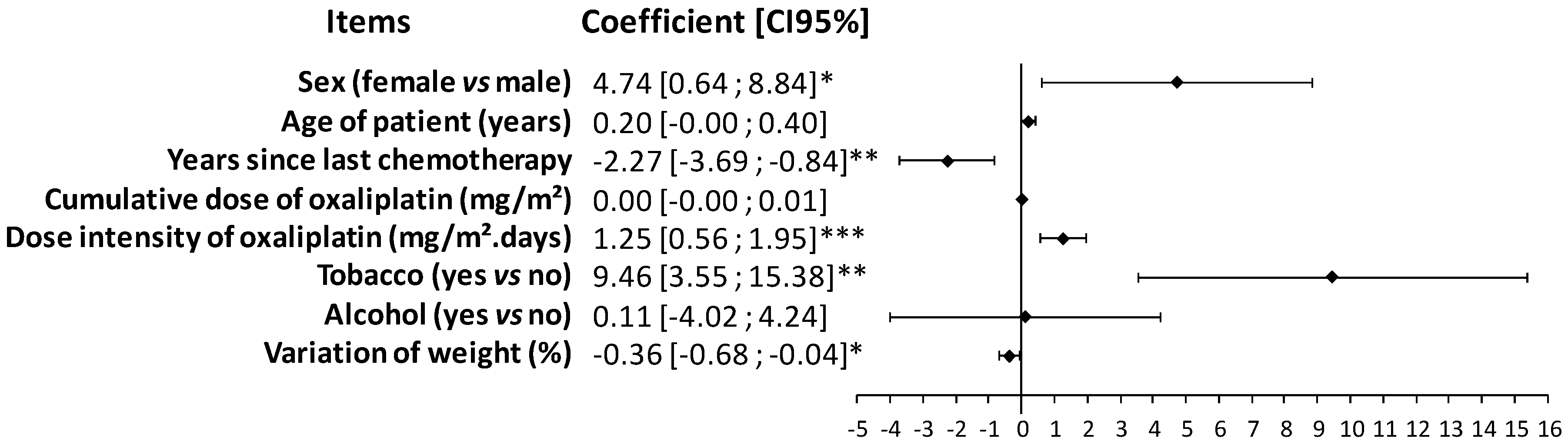
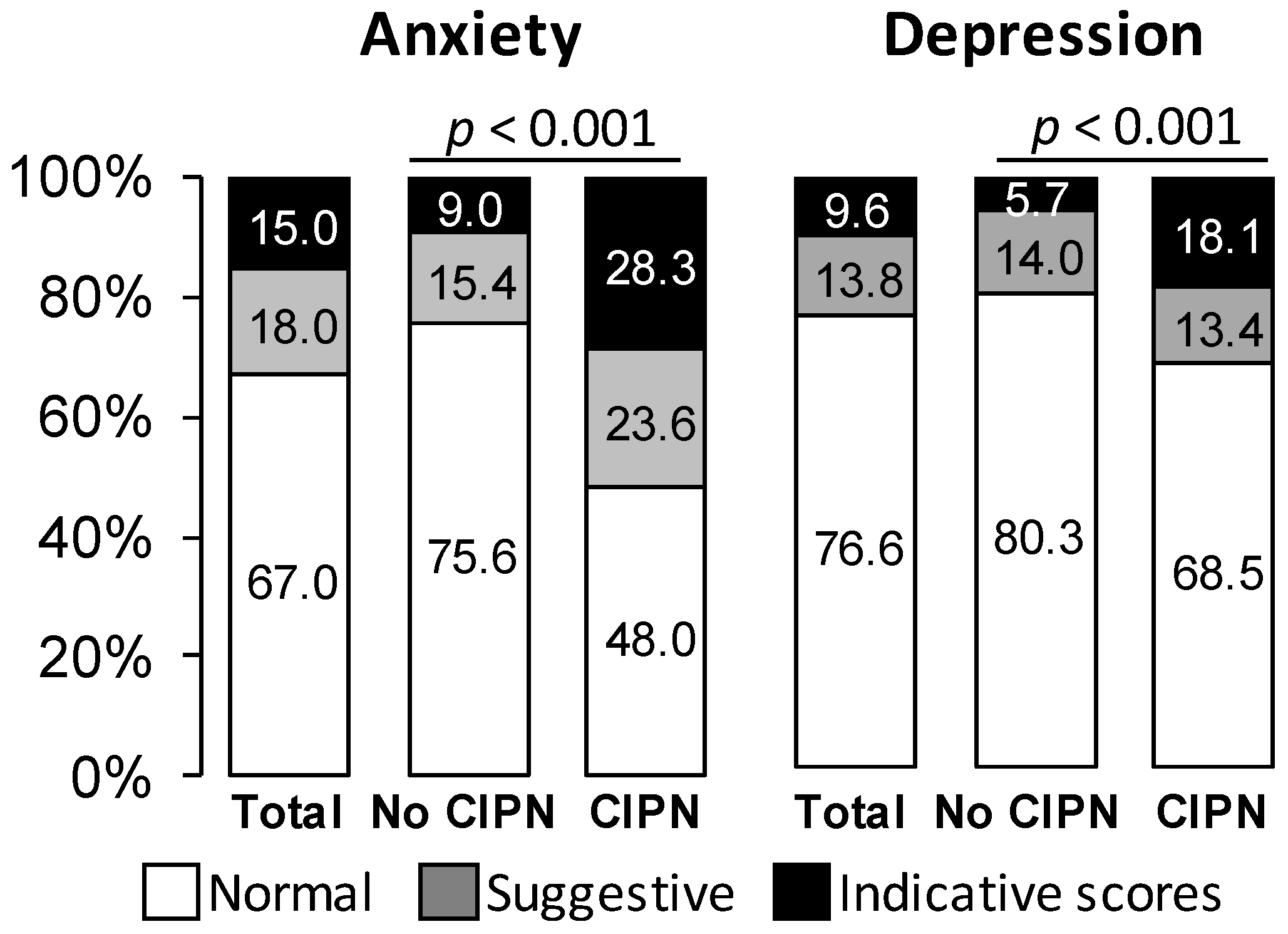
3.3. Impact of Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmoll, H.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Stein, A.; Valentini, V.; Glimelius, B.; Haustermans, K.; Nordlinger, B.; van de Velde, C.J.; Balmana, J.; Regula, J.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2479–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhove, N.; Collin, A.; Condé, S.; Chaleteix, C.; Pezet, D.; Balayssac, D. Long-term effects, pathophysiological mechanisms, and risk factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: A comprehensive literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N.; Bouhassira, D.; Gautron, M.; Vaillant, J.N.; Mitry, E.; Lepère, C.; Rougier, P.; Guirimand, F. Thermal hyperalgesia as a marker of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity: A prospective quantified sensory assessment study. Pain 2009, 144, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijers, A.J.M.; Mols, F.; Vreugdenhil, G. A systematic review on chronic oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy and the relation with oxaliplatin administration. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijers, A.J.M.; Mols, F.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.G.; Faber, C.G.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Vreugdenhil, G. Peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer survivors: The influence of oxaliplatin administration. Results from the population-based PROFILES registry. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventzel, L.; Jensen, A.B.; Jensen, A.R.; Jensen, T.S.; Finnerup, N.B. Chemotherapy-induced pain and neuropathy: A prospective study in patients treated with adjuvant oxaliplatin or docetaxel. Pain 2016, 157, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, B.; Frezza, A.M.; Schiavon, G.; Spoto, C.; Addeo, R.; Catalano, V.; Graziano, F.; Santini, D.; Tonini, G. Identification of clinical predictive factors of oxaliplatin-induced chronic peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients treated with adjuvant Folfox IV. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palugulla, S.; Thakkar, D.N.; Kayal, S.; Narayan, S.K.; Dkhar, S.A. Association of voltage-gated sodium channel genetic polymorphisms with oxaliplatin-induced chronic peripheral neuropathy in south indian cancer patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2017, 18, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palugulla, S.; Devaraju, P.; Kayal, S.; Narayan, S.K.; Mathaiyan, J. Genetic polymorphisms in cyclin H gene are associated with oxaliplatin-induced acute peripheral neuropathy in South Indian digestive tract cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 82, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereno, M.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, G.; Rubio, J.M.; Apellániz-Ruiz, M.; Sánchez-Barroso, L.; Casado, E.; Falagan, S.; López-Gómez, M.; Merino, M.; Gómez-Raposo, C.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of SCN9A are associated with oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershman, D.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Dworkin, R.H.; Lavoie Smith, E.M.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Gavin, P.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1941–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dault, R.; Rousseau, M.P.; Beaudoin, A.; Frenette, M.A.; Lemay, F.; Beauchesne, M.F. Impact of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer: A prospective evaluation at a single institution. Curr. Oncol. 2016, 23, e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibaudel, B.; Maindrault-Goebel, F.; Lledo, G.; Mineur, L.; André, T.; Bennamoun, M.; Mabro, M.; Artru, P.; Carola, E.; Flesch, M.; et al. Can chemotherapy be discontinued in unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer? The GERCOR OPTIMOX2 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5727–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molassiotis, A.; Cheng, H.L.; Lopez, V.; Au, J.S.K.; Chan, A.; Bandla, A.; Leung, K.T.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, K.H.; Suen, L.K.P.; et al. Are we mis-estimating chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy? Analysis of assessment methodologies from a prospective, multinational, longitudinal cohort study of patients receiving neurotoxic chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatandoust, S.; Joshi, R.; Pittman, K.B.; Esterman, A.; Broadbridge, V.; Adams, J.; Singhal, N.; Yeend, S.; Price, T.J. A descriptive study of persistent oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Lin, C.S.Y.; Krishnan, A.V.; Goldstein, D.; Friedlander, M.L.; Kiernan, M.C. Long-term neuropathy after oxaliplatin treatment: Challenging the dictum of reversibility. Oncology 2011, 16, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, P.A. Why and how to study the fate of cancer survivors: Observations from the clinic and the research laboratory. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Strobe initiative strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (strobe) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, T.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Heimans, J.J.; Muller, M.J.; Hildebrand, J.G.; Delattre, J.Y.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Grant, R.; Huddart, R.; et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: The QLQ-CIPN20. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, P.; Rossi, E.; Cornblath, D.R.; Merkies, I.S.J.; Postma, T.J.; Frigeni, B.; Bruna, J.; Velasco, R.; Argyriou, A.A.; Kalofonos, H.P.; et al. Physician-assessed and patient-reported outcome measures in chemotherapy-induced sensory peripheral neurotoxicity: Two sides of the same coin. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhassira, D.; Attal, N.; Alchaar, H.; Boureau, F.; Brochet, B.; Bruxelle, J.; Cunin, G.; Fermanian, J.; Ginies, P.; Grun-Overdyking, A.; et al. Comparison of pain syndromes associated with nervous or somatic lesions and development of a new neuropathic pain diagnostic questionnaire (DN4). Pain 2005, 114, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaronson, N.K.; Ahmedzai, S.; Bergman, B.; Bullinger, M.; Cull, A.; Duez, N.J.; Filiberti, A.; Flechtner, H.; Fleishman, S.B.; de Haes, J.C. The european organization for research and treatment of cancer QLQ-C30: A quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; L. Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988; ISBN 0-8058-0283-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, K.J. No adjustments are needed for multiple comparisons. Epidemiology 1990, 1, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feise, R.J. Do multiple outcome measures require p-value adjustment? BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2002, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.; Lange, S. Adjusting for multiple testing—When and how? J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretny, M.; Currie, G.L.; Sena, E.S.; Ramnarine, S.; Grant, R.; MacLeod, M.R.; Colvin, L.A.; Fallon, M. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soveri, L.M.; Lamminmäki, A.; Hänninen, U.A.; Karhunen, M.; Bono, P.; Osterlund, P. Long-term neuropathy and quality of life in colorectal cancer patients treated with oxaliplatin containing adjuvant chemotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2019, 58, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, T.; Boni, C.; Navarro, M.; Tabernero, J.; Hickish, T.; Topham, C.; Bonetti, A.; Clingan, P.; Bridgewater, J.; Rivera, F.; et al. Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yothers, G.; O’Connell, M.J.; Allegra, C.J.; Kuebler, J.P.; Colangelo, L.H.; Petrelli, N.J.; Wolmark, N. Oxaliplatin as adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: Updated results of NSABP C-07 trial, including survival and subset analyses. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3768–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Satoh, A.; Yamada, T.; Aisu, N.; Matsuoka, T.; Koganemaru, T.; Kajitani, R.; Munechika, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nagano, H.; et al. The relationship between evaluation methods for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho Barbosa, M.; Kosturakis, A.K.; Eng, C.; Wendelschafer-Crabb, G.; Kennedy, W.R.; Simone, D.A.; Wang, X.S.; Cleeland, C.S.; Dougherty, P.M. A quantitative sensory analysis of peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer and its exacerbation by oxaliplatin chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5955–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhove, N.; Pereira, B.; Pezet, D.; Balayssac, D. Clinical assessment of new antineuropathic strategies for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Pain should not be the principal endpoint. Pain 2017, 158, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandro, L.M.; Behrendt, C.E.; Chen, K.; Openshaw, H.; Shibata, S. Predicting acute and persistent neuropathy associated with oxaliplatin. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 36, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Barnett, C.; Katzberg, H.D.; Lovblom, L.E.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V. Sex differences in neuropathic pain intensity in diabetes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 388, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, A.J.; Lissounov, A.; Knezevic, I.; Candido, K.D.; Knezevic, N.N. Pain and sex hormones: A review of current understanding. Pain Manag. 2016, 6, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Tunoda, T.; Takiguchi, T.; Shibata, K.; Ohtani, T.; Kizu, J.; Nishio, M.; Horai, T.; Hama, T.; Taguchi, K. Factors exacerbating peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel plus carboplatin in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2012, 20, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRowe, L.R.; Ditre, J.W. Pain, nicotine, and tobacco smoking: Current state of the science. Pain 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Reddy, A.; Hui, D.; Tanco, K.; Liu, D.; Park, M.; Williams, J.; Carmack, C.; Bruera, E. Association between tobacco use, pain expression, and coping strategies among patients with advanced cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Timmins, H.C.; King, T.; Kiernan, M.C.; Goldstein, D.; Park, S.B. Characteristics and risk factors of bortezomib induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review of phase III trials. Hematol. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, D.L.; Kidwell, K.M.; Vangipuram, K.; Li, F.; Pai, M.P.; Burness, M.; Griggs, J.J.; Schott, A.F.; Van Poznak, C.; Hayes, D.F.; et al. Paclitaxel plasma concentration after the first infusion predicts treatment-limiting peripheral neuropathy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3602–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhof, C.S.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Vissers, P.A.J.; Wasowicz, D.K.; Wegdam, J.A.; Révész, D.; Vreugdenhil, G.; Mols, F. Anxiety and depression mediate the association between chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and fatigue: Results from the population-based profiles registry. Psycho-Oncology 2019, 28, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofthagen, C.; Donovan, K.A.; Morgan, M.A.; Shibata, D.; Yeh, Y. Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy’s effects on health-related quality of life of colorectal cancer survivors. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 3307–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Mori, M.; Tamura, K. Effects of the publication of clinical guidelines for the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy on the administration preferences of oncology specialists: Japanese association of supportive care in cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvy, M.; Cuménal, M.; Kerckhove, N.; Courteix, C.; Busserolles, J.; Balayssac, D. The safety of medications used to treat peripheral neuropathic pain, part 1 (antidepressants and antiepileptics): Review of double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trials. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, L.A. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Where are we now? Pain 2019, 160, S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Rademacher, J.; Kanwar, R.; Seisler, D.; Pachman, D.R.; Qin, R.; Abyzov, A.; Ruddy, K.J.; Banck, M.S.; Lavoie Smith, E.M.; Dorsey, S.G.; et al. Patient-reported (EORTC QLQ-CIPN20) versus physician-reported (CTCAE) quantification of oxaliplatin- and paclitaxel/carboplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in NCCTG/Alliance clinical trials. Support. Care Cancer 2017, 25, 3537–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molassiotis, A.; Cheng, H.L.; Leung, K.T.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, K.H.; Au, J.S.K.; Sundar, R.; Chan, A.; Ng, T.R.D.; Suen, L.K.P.; et al. Risk factors for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving taxane- and platinum-based chemotherapy. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | All the Patients n = 406 | No Sensory CIPN n = 279 | Sensory CIPN n = 127 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 54.2 (220) | 56.6 (158) | 48.8 (62) |
| Female | 45.8 (186) | 43.4 (121) | 51.2 (65) |
| Age (year) | 66.3 ± 9.7 | 66.0 ± 10.0 | 67.0 ± 8.9 |
| Min: 31.1; Max: 89.3 | Min: 31.1; Max: 89.3 | Min: 34.5; Max: 84.7 | |
| Height (cm) | 168.1 ± 9.5 | 168.4 ± 8.9 | 167.4 ± 10.6 |
| Weight (Kg) | |||
| 1st cycle | 71.8 ± 16.3 | 72.2 ± 15.8 | 70.7 ± 17.4 |
| Last cycle | 72.0 ± 16.5 | 72.8 ± 15.9 | 70.4 ± 17.6 |
| Percentage variance | 0.7 ± 6.2 | 1.1 ± 6.3 | −0.03 ± 5.9 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | |||
| 1st cycle | 25.3 ± 5.0 | 25.4 ± 5.0 | 25.1 ± 5.1 |
| Last cycle | 25.4 ± 4.9 | 25.6 ± 4.9 | 24.9 ± 4.8 |
| Percentage variance | 0.7 ± 6.2 | 1.1 ± 6.3 | −0.03 ± 5.9 |
| Body surface area (m2) | |||
| 1st cycle | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 |
| Last cycle | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 |
| Percentage variance | 0.4 ± 2.7 | 0.5 ± 2.8 | 0.03 ± 2.6 |
| Tobacco use | 12.4 (50) | 10.4 (29) | 16.7 (21) |
| Alcohol use | 66.3 (269) | 67.4 (188) | 63.8 (81) |
| Hazardous alcohol use (males: ≥21 units/week) | 14.4 (23) | 13.7 (16) | 16.3 (7) |
| Hazardous alcohol use (females: ≥14 units/week) | 12.3 (13) | 11.3 (8) | 14.3 (5) |
| Years since last chemotherapy | 2.4 ± 1.6 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 2.2 ± 1.6 * |
| 1 year | 19.2 (78) | 16.9 (47) | 24.4 (31) |
| 2 years | 28.8 (117) | 27.6 (77) | 31.5 (40) |
| 3 years | 19.7 (80) | 20.8 (58) | 17.3 (22) |
| 4 years | 16.5 (67) | 17.9 (50) | 13.4 (17) |
| 5 years | 15.8 (64) | 16.9 (47) | 13.4 (17) |
| Oxaliplatin chemotherapy | |||
| Cumulative dose (mg/m2) | 1220.8 ± 455.6 | 1201.6 ± 472.6 | 1263.0 ± 418.1 |
| Number of cycles | 9.7 ± 2.7 | 9.6 ± 2.8 | 9.9 ± 2.6 |
| Dose intensity (mg/m2/weeks) | 62.3 ± 20.9 | 60.9 ± 21.6 | 65.4 ± 18.9 |
| Mean percentage of cycles with a dose reduction | 44.8 ± 34.3 | 45.1 ± 35.5 | 44.2 ± 31.7 |
| Drug Name | All Patients n = 406 % (Number) | Sensory CIPN n = 127 % (Number) | Neuropathic Pain n = 62 % (Number) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol | 26.9 (109) | 29.9 (38) | 37.1 (23) |
| Aspirin | 4.2 (17) | 4.7 (6) | 6.5 (4) |
| Tramadol | 3.5 (14) | 4.7 (6) | 6.5 (4) |
| Ibuprofen | 3.2 (13) | 3.9 (5) | 4.8 (3) |
| Codeine + paracetamol | 3.0 (12) | 4.7 (6) | 8.1 (5) |
| Tramadol + paracetamol | 3.0 (12) | 3.9 (5) | 6.5 (4) |
| Opium + caffeine + paracetamol | 1.7 (7) | 1.6 (2) | 6.5 (4) |
| Pregabalin | 1.7 (7) | 3.2 (4) | 4.8 (3) |
| Gabapentin | 1.0 (4) | 1.6 (2) | 4.8 (3) |
| Amitriptyline | 1.0 (4) | 1.6 (2) | 3.2 (2) |
| Codeine | 0.7 (3) | 0.8 (1) | 1.6 (1) |
| Morphine | 0.7 (3) | 0.8 (1) | 1.6 (1) |
| NSAIDs other | 0.7 (3) | 0 (0) | 1.6 (1) |
| Triptans | 0.5 (2) | 0 (0) | 1.6 (1) |
| Opium + paracetamol | 0.3 (1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Dihydrocodeine | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Duloxetine | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Imipramine | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Oxycodone | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Dimensions | QLQ-C30 Scores | QLQ-C30 Scores According to Sensory CIPN | Correlations QLQ-C30 and Sensory Scores | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Sensory CIPN | Sensory CIPN | Effect Size (95% CI) | |||
| Global health status | 69.2 ± 20.5 | 71.6 ± 20.1 | 63.7 ± 20.4 *** | −0.39 (−0.61, −0.18) | −0.28 # |
| Physical functioning | 81.7 ± 19.7 | 84.7 ± 17.8 | 75.0 ± 22.1 *** | −0.50 (−0.71, −0.29) | −0.32 # |
| Role functioning | 79.1 ± 28.2 | 84.2 ± 24.5 | 67.9 ± 32.3 *** | −0.60 (−0.81, −0.38) | −0.38 # |
| Emotional functioning | 74.6 ± 25.1 | 78.8 ± 22.5 | 65.2 ± 27.8 *** | −0.56 (−0.77, −0.34) | −0.32 # |
| Cognitive functioning | 77.6 ± 23.5 | 80.7 ± 21.0 | 70.7 ± 27.2 *** | −0.43 (−0.64, −0.22) | −0.22 # |
| Social functioning | 74.3 ± 30.5 | 78.6 ± 28.2 | 64.5 ± 33.1 *** | −0.47 (−0.69, −0.26) | −0.28 # |
| Fatigue | 33.7 ± 27.2 | 28.3 ± 24.6 | 45.5 ± 29.0 *** | 0.66 (0.44, 0.87) | 0.36 # |
| Nausea and vomiting | 6.5 ± 15.7 | 5.7 ± 14.8 | 8.4 ± 17.4 | 0.17 (0.04, 0.38) | 0.17 # |
| Pain | 20.5 ± 26.0 | 14.0 ± 22.2 | 34.6 ± 28.1 *** | 0.85 (0.63, 1.07) | 0.42 # |
| Dyspnea | 23.2 ± 28.1 | 21.0 ± 26.6 | 28.0 ± 30.8 * | 0.25 (0.04, 0.46) | 0.18 # |
| Insomnia | 34.8 ± 35.4 | 29.1 ± 33.4 | 47.4 ± 36.4 *** | 0.53 (0.32, 0.74) | 0.28 # |
| Appetite loss | 11.2 ± 23.6 | 8.9 ± 20.6 | 16.4 ± 28.5 ** | 0.32 (0.11, 0.53) | 0.21 # |
| Constipation | 19.3 ± 28.2 | 17.1 ± 26.8 | 24.1 ± 30.9 * | 0.25 (0.04, 0.46) | 0.14 # |
| Diarrhea | 24.2 ± 31.9 | 20.7 ± 29.5 | 31.7 ± 35.5 ** | 0.35 (0.14, 0.56) | 0.23 # |
| Financial difficulties | 9.9 ± 22.2 | 6.9 ± 17.0 | 16.5 ± 29.8 ** | 0.44 (0.23, 0.65) | 0.20 # |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selvy, M.; Pereira, B.; Kerckhove, N.; Gonneau, C.; Feydel, G.; Pétorin, C.; Vimal-Baguet, A.; Melnikov, S.; Kullab, S.; Hebbar, M.; et al. Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082400
Selvy M, Pereira B, Kerckhove N, Gonneau C, Feydel G, Pétorin C, Vimal-Baguet A, Melnikov S, Kullab S, Hebbar M, et al. Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(8):2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082400
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelvy, Marie, Bruno Pereira, Nicolas Kerckhove, Coralie Gonneau, Gabrielle Feydel, Caroline Pétorin, Agnès Vimal-Baguet, Sergey Melnikov, Sharif Kullab, Mohamed Hebbar, and et al. 2020. "Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 8: 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082400
APA StyleSelvy, M., Pereira, B., Kerckhove, N., Gonneau, C., Feydel, G., Pétorin, C., Vimal-Baguet, A., Melnikov, S., Kullab, S., Hebbar, M., Bouché, O., Slimano, F., Bourgeois, V., Lebrun-Ly, V., Thuillier, F., Mazard, T., Tavan, D., Benmammar, K. E., Monange, B., ... Balayssac, D. (2020). Long-Term Prevalence of Sensory Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy for 5 Years after Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy to Treat Colorectal Cancer: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(8), 2400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9082400







