Anti-atherogenic Modification of Serum Lipoprotein Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment, a Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Disease Activity
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Cholesterol Loading Capacity (CLC) Measurement
2.5. Cholesterol Efflux Capacity (CEC) Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Laboratory Parameters
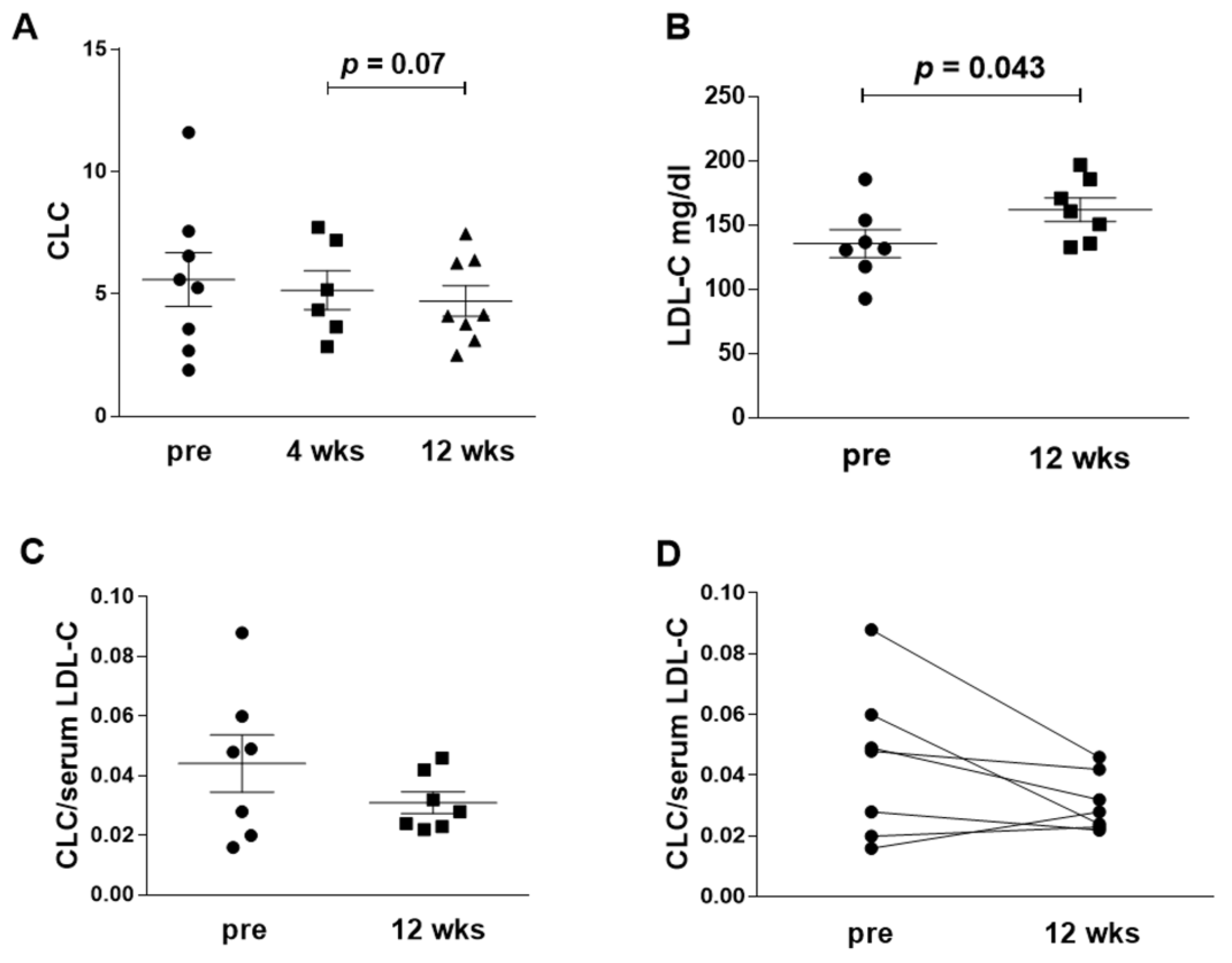
3.2. Serum CLC
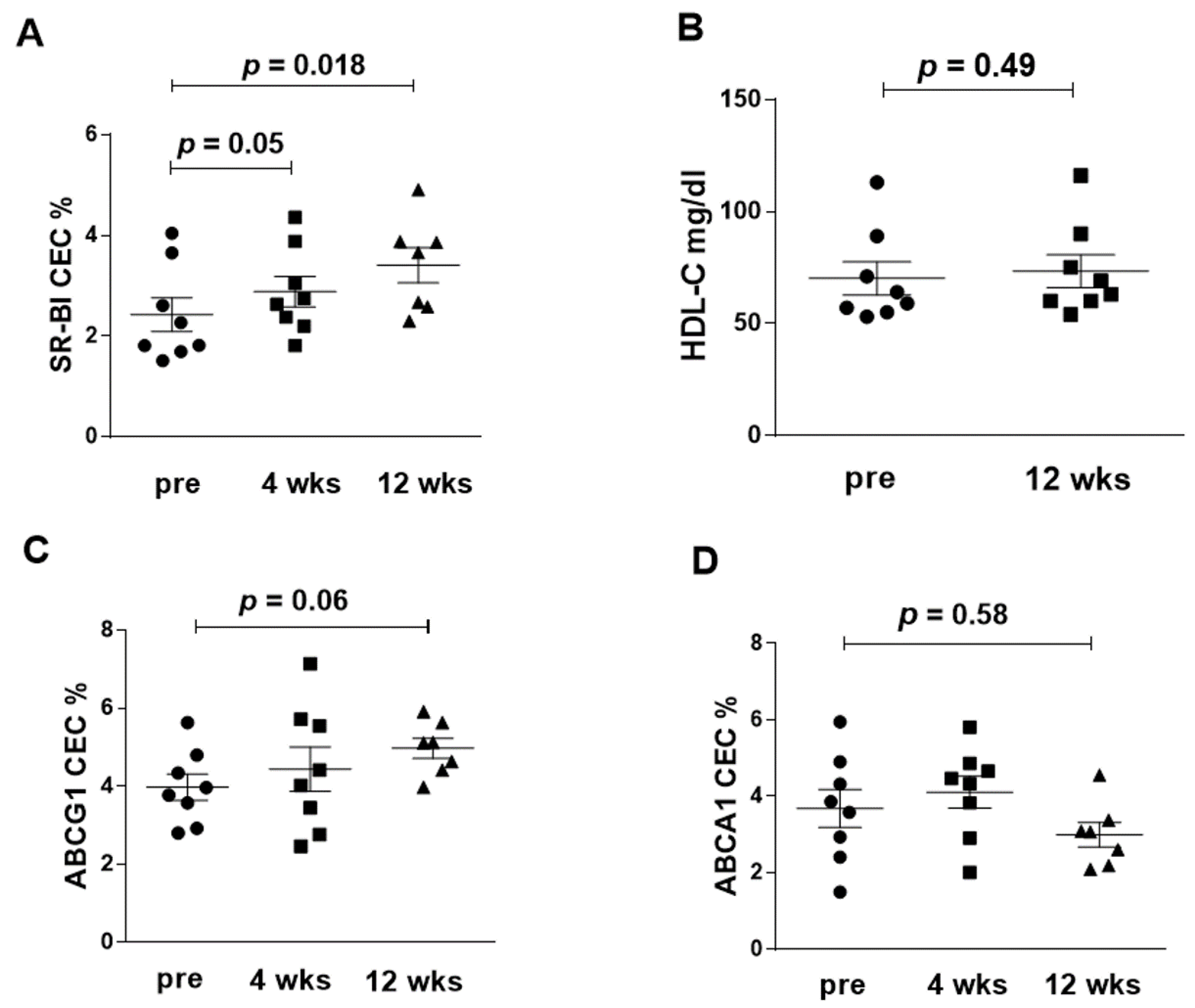
3.3. Serum CEC
3.4. Sample Size Estimate for a Larger Study
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danesh, J.; Kaptoge, S.; Mann, A.G.; Sarwar, N.; Wood, A.; Angleman, S.B.; Wensley, F.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Lennon, L.; Eiriksdottir, G.; et al. Long-term interleukin-6 levels and subsequent risk of coronary heart disease: Two new prospective studies and a systematic review. PLoS Med 2008, 5, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Beaulieu, A.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Ramos-Remus, C.; Rovensky, J.; Alecock, E.; Woodworth, T.; Alten, R. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2008, 371, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Fumery, M.; Singh, A.G.; Singh, N.; Prokop, L.J.; Dulai, P.S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Curtis, J.R. Comparative Risk of Cardiovascular Events with Biologic and Synthetic Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2019, 72, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagne, B.; Viprey, M.; Martin, J.; Schott, A.M.; Cucherat, M.; Soubrier, M. Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuchel, M.; Rader, D.J. Macrophage reverse cholesterol transport: Key to the regression of atherosclerosis? Circulation 2006, 113, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohatgi, A.; Khera, A.; Berry, J.D.; Givens, E.G.; Ayers, C.R.; Wedin, K.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Rader, D.R.; de Lemos, J.A.; et al. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and incident cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2383–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleheen, D.; Scott, R.; Javad, S.; Zhao, W.; Rodrigues, A.; Picataggi, A.; Lukmanova, D.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Luben, R.; Billheimer, J.; et al. Association of HDL cholesterol efflux capacity with incident coronary heart disease events: A prospective case-control study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, D.J.; Alexander, E.T.; Weibel, G.L.; Billheimer, J.; Rothblat, G.H. The role of reverse cholesterol transport in animals and humans and relationship to atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S189–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Cuchel, M.; de la Llera-Moya, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Burke, M.F.; Jafri, K.; French, B.C.; Phillips, J.A.; Mucksavage, M.L.; Wilensky, R.L.; et al. Cholesterol efflux capacity, high-density lipoprotein function, and atherosclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Tang, W.H.; Mosior, M.K.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Matter, W.; Gao, V.; Schmitt, D.; DiDonato, J.A.; Fisher, E.A.; et al. Paradoxical association of enhanced cholesterol efflux with increased incident cardiovascular risks. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, K.; Hui, C. The level of malondialdehyde-modified LDL and LDL immune complexes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, E.; Kobayashi, K.; Tabuchi, M.; Lopez, L.R. Oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein and immune regulation of atherosclerosis. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 466–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronda, N.; Favari, E.; Borghi, M.O.; Ingegnoli, F.; Gerosa, M.; Chighizola, C.; Zimetti1, F.; Adorni1, M.P.; Bernini1, F.; Meroni, P.L. Impaired serum cholesterol efflux capacity in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham III, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevoo, M.L.; van ’t Hof, M.A.; Kuper, H.H.; van Leeuwen, M.A.; van de Putte, L.B.; van Riel, P.L. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995, 38, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, N.; Greco, D.; Adorni, M.P.; Zimetti, F.; Favari, E.; Hjeltnes, G.; Mikkelsen, K.; Borghi, M.O.; Favalli, E.G.; Gatti, R.; et al. Newly identified antiatherosclerotic activity of methotrexate and adalimumab: Complementary effects on lipoprotein function and macrophage cholesterol metabolism. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, K. Determination of DNA concentration with diphenylamine. Methods Enzymol. 1968, 12, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Hollan, I.; Dessein, P.H.; Ronda, N.; Wasko, M.C.; Svenungsson, E.; Agewall, S.; Cohen-Tervaert, J.W.; Maki-Petaja, K.; Grundtvig, M.; Karpouzas, G.A.; et al. Prevention of cardiovascular disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 952–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Porter, D.; Sattar, N.; Packard, C.J.; Caslake, M.; McInnes, I.; McCarey, D. Interleukin-6 blockade raises LDL via reduced catabolism rather than via increased synthesis: A cytokine-specific mechanism for cholesterol changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youyou, Y.; Dandan, S.; Junduo, W.; Junnan, W. Long Non-Coding RNAs link oxidized low-density lipoprotein with the inflammatory response of macrophages in atherogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 30, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Brilakis, E.S.; Lennon, R.J.; Miller, E.R.; Witztum, J.L.; McConnell, J.P.; Kornman, K.S.; Berger, P.B. Relationship of IgG and IgM autoantibodies to oxidized low density lipoprotein with coronary artery disease and cardiovascular events. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Mun, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, Y.R.; Sheen, D.H.; Ihm, C.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, H.-G. Proteomics Analysis for Verification of Rheumatoid Arthritis Biomarker Candidates Using Multiple Reaction Monitoring. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, e1800011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strang, A.C.; Bisoendial, R.J.; Kootte, R.S.; Schulte, D.M.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; Levels, J.H.; Kok, M.; Vos, K.; Tas, S.W.; Tietg, U.J.F.; et al. Pro-atherogenic lipid changes and decreased hepatic LDL receptor expression by tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Atherosclerosis 2013, 229, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Hernandez-Hernandez, M.V.; Tejera-Segura, B.; Delgado-Frias, E.; Macia-Diaz, M.; Machado, J.D.; Diaz-González, F. Effect of IL-6 Receptor Blockade on Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type-9 and Cholesterol Efflux Capacity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtierotti, R.; Ingegnoli, F.; Griffini, S.; Grovetti, E.; Meroni, P.L.; Cugno, M. Prothrombotic biomarkers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The beneficial effect of IL-6 receptor blockade. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2016, 34, 451–458. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Limon, P.; Ortega, R.; Arias de la Rosa, I.; Abalos-Aguilera, M.D.C.; Perez-Sanchez, C.; Jimenez-Gomez, Y.; Peralbo-Santaella, E.; Font, P.; Ruiz-Vilches, D.; Ferrin, G.; et al. Tocilizumab improves the proatherothrombotic profile of rheumatoid arthritis patients modulating endothelial dysfunction, NETosis, and inflammation. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirao, M.; Yamasaki, N.; Oze, H.; Ebina, K.; Nampei, A.; Kawato, Y.; Shi, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Nishimoto, N.; Hashimoto, J. Serum level of oxidative stress marker is dramatically low in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 4041–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, E.; Rahat, M.A.; Feld, J.; Elias, M.; Rosner, I.; Kaly, L.; Lavie, I.; Gazitt, T.; Zisman, D. Effects of Tocilizumab, an Anti-Interleukin-6 Receptor Antibody, on Serum Lipid and Adipokine Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimetti, F.; De Vuono, S.; Gomaraschi, M.; Adorni, M.P.; Favari, E.; Ronda, N.; Ricci, M.A.; Veglia, F.; Calabresi, L.; Lupattelli, G. Plasma cholesterol homeostasis, HDL remodeling and function during the acute phase reaction. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2051–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chapman, M.J.; Piraino, P.; Lamerz, J.; Schindler, T.; Cutler, P.; Dernick, G. Remodeling of plasma lipoproteins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Interleukin-6 receptor-alpha inhibition with tocilizumab. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline | After 4 Weeks | After 12 Weeks | Median Difference Baseline vs. 12 Weeks [95% CI] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLC(IQR) | 5.4 [2.9, 7.1] | 4.7 [3.4, 7.3] | 4.1 [3.3, 6.4] # | −0.95 [−2.61, 0.4] |
| SR-BI(IQR) | 2.0 [1.7, 3.4] | 2.7 [2.2, 3.7] * | 3.7 [2.6, 3.9] ** | 0.87 [0.48, 1.62] |
| ABCG1 (IQR) | 3.9 [3.1, 4.7] | 4.2 [2.9, 5.7] | 5.1 [4.4, 5.6] | 0.92 [−0.05, 2.32] |
| ABCA1 (IQR) | 4.0 [2.7, 5.1] | 4.7 [3.4, 5.2] | 3.3 [2.8, 3.6] | −0.34 [−1.33, 0.97] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greco, D.; Gualtierotti, R.; Agosti, P.; Adorni, M.P.; Ingegnoli, F.; Rota, M.; Bernini, F.; Meroni, P.L.; Ronda, N. Anti-atherogenic Modification of Serum Lipoprotein Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment, a Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072157
Greco D, Gualtierotti R, Agosti P, Adorni MP, Ingegnoli F, Rota M, Bernini F, Meroni PL, Ronda N. Anti-atherogenic Modification of Serum Lipoprotein Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment, a Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072157
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreco, Daniela, Roberta Gualtierotti, Pasquale Agosti, Maria Pia Adorni, Francesca Ingegnoli, Matteo Rota, Franco Bernini, Pier Luigi Meroni, and Nicoletta Ronda. 2020. "Anti-atherogenic Modification of Serum Lipoprotein Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment, a Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072157
APA StyleGreco, D., Gualtierotti, R., Agosti, P., Adorni, M. P., Ingegnoli, F., Rota, M., Bernini, F., Meroni, P. L., & Ronda, N. (2020). Anti-atherogenic Modification of Serum Lipoprotein Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis after Tocilizumab Treatment, a Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072157







