Diet: A Specific Part of the Western Lifestyle Pack in the Asthma Epidemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diet and the Parallel Epidemics of Obesity and Asthma
2.1. Role of Micronutrients and Macronutrients
2.2. Role of Food Groups and Dietary Patterns
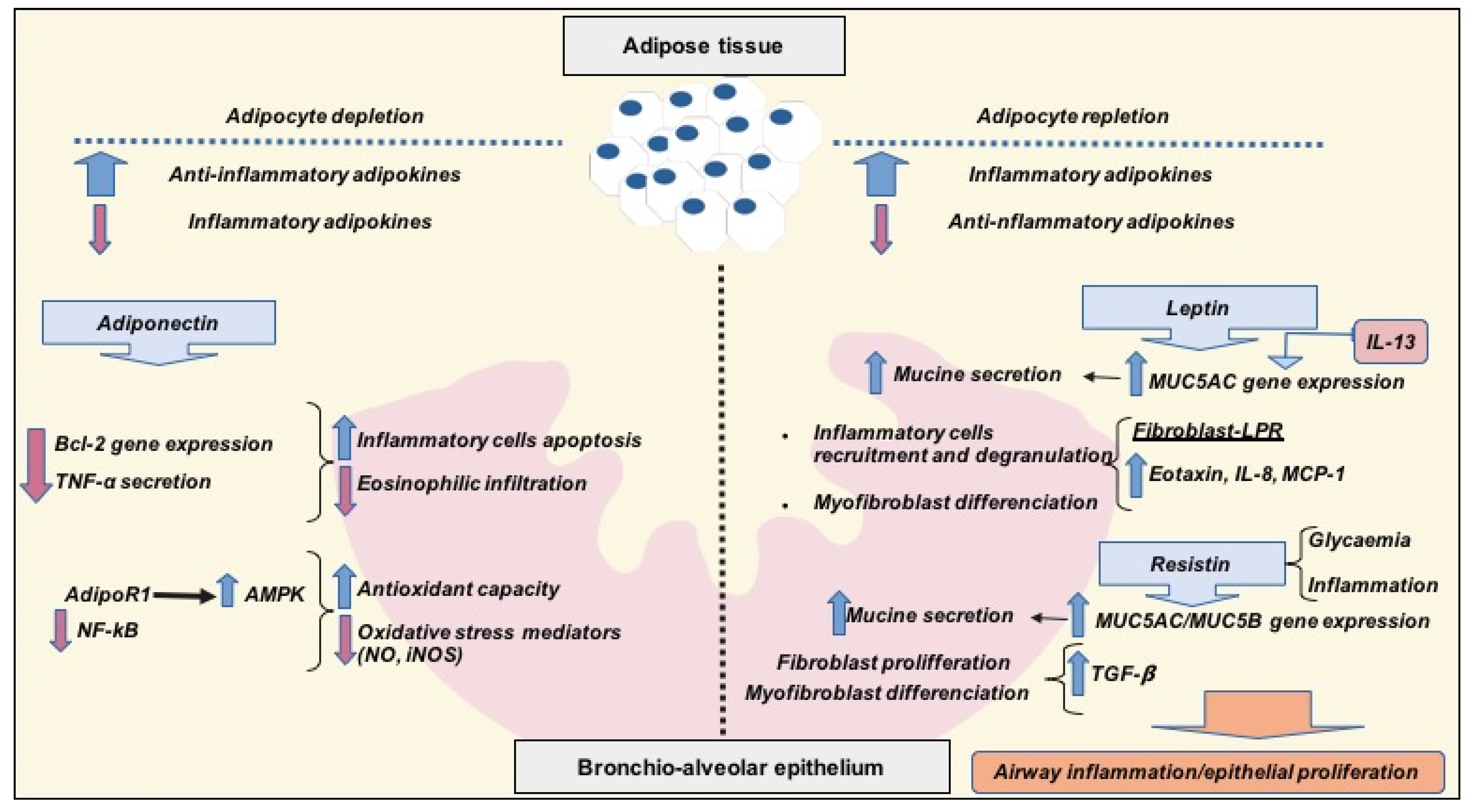
3. Obesity-Related Asthma and Interrelations with Diet, Inflammation and Adipose Tissue
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Adipokines: Adiponectin
3.2. Pro-Inflammatory Adipokines: Leptin and Resistin
4. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christ, A.; Latz, E. The Western lifestyle has lasting effects on metaflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 267–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyalil, H.A.; Wood, L.G.; Wright, T.A.; Karihaloo, C.; Starkey, M.R.; Miu, A.S.; Baines, K.J.; Hansbro, P.M.; Gibson, P.G. Obese asthmatics are characterized by altered adipose tissue macrophage activation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sin, D.D.; Sutherland, E.R. Obesity and the lung: 4. Obesity and asthma. Thorax 2008, 63, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, E.C.; Yan, M.R. Evolution not Revolution: Nutrition and Obesity. Nutrients 2017, 9, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braback, L.; Hjern, A.; Rasmussen, F. Trends in asthma, allergic rhinitis and eczema among Swedish conscripts from farming and non-farming environments. A nationwide study over three decades. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haahtela, T.; Lindholm, H.; Bjorksten, F.; Koskenvuo, K.; Laitinen, L.A. Prevalence of asthma in Finnish young men. BMJ 1990, 301, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, W.; Ege, M.J.; von Mutius, E. The asthma epidemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2226–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Marcos, L.; Quiros, A.B.; Hernández, G.G.; Guillen-Grima, F.; Díaz, C.G.; Ureña, I.C.; Peña, A.A.; Monge, R.B.; Suarez-Varela, M.M.; Varela, A.L.; et al. Stabilization of asthma prevalence among adolescents and increase among schoolchildren (ISAAC phases I and III) in Spain. Allergy 2004, 59, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, M.I.; Montefort, S.; Bjorksten, B.; Lai, C.K.; Strachan, D.P.; Weiland, S.K.; Williams, H. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet 2006, 368, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.M.; Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Freedman, D.S.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity and Severe Obesity Prevalence in US Youth and Adults by Sex and Age, 2007–2008 to 2015–2016. JAMA 2018, 319, 1723–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, C.L.; Fryar, C.D.; Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Aoki, Y.; Freedman, D.S. Differences in Obesity Prevalence by Demographics and Urbanization in US Children and Adolescents, 2013–2016. JAMA 2018, 319, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallstrand, T.S.; Fischer, M.E.; Wurfel, M.M.; Afari, N.; Buchwald, D.; Goldberg, J. Genetic pleiotropy between asthma and obesity in a community-based sample of twins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 116, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thomsen, S.F.; Ulrik, C.S.; Kyvik, K.O.; Sørensen, T.I.; Posthyma, D.; Skadhauge, L.R.; Steffensen, I.; Backer, V. Association between obesity and asthma in a twin cohort. Allergy 2007, 62, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Marcos, L.; Canflanca, I.M.; Garrido, J.B.; Varela, A.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, G.; Guillen-Grima, F.; Gonzalez-Diaz, C.; Carbajal-Ureña, I.; Arnedo-Peña, A.; Busquets-Monge, R.M.; et al. Relationship of asthma and rhinoconjunctivitis with obesity, exercise and Mediterranean diet in Spanish schoolchildren. Thorax 2007, 62, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Marcos, L.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A.; Weinmayer, G.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Priftis, K.N.; Nagel, G. Influence of Mediterranean diet on asthma in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 24, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwood, P.; Asher, M.I.; Garcia-Marcos, L.; Williams, H.; Keil, U.; Robertson, C.; Nagel, G. Do fast foods cause asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema? Global findings from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC) phase three. Thorax 2013, 68, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Hatziagorou, E.; Antonogeorgos, G.; Matziou, V.N.; Tsanakas, J.N.; Gratziou, C.; Tsabouri, S.; Priftis, K.N. Antioxidant foods consumption and childhood asthma and other allergic diseases: The Greek cohorts of the ISAAC II survey. Allergol. Immunopathol. (Madr) 2015, 43, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, U.M.; Birben, E.; Erzurum, S.; Sackesen, C.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress in asthma: Part of the puzzle. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, C.R.; Stewart, A.W.; Hancox, R.J.; Murphy, R.; Braithwaite, I.; Beasley, R.; Mitchell, E.A. Association between frequency counsumption of fruit, vegetables, nuts and pulses and BMI: Alayses of the International study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood. Nutrients 2018, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, F.; Hassounah, S.; Swaka, A. The Impact of Mediterranean Dietary Patterns During Pregnancy on Maternal and Offspring Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forno, E.; Young, O.M.; Kumar, R.; Simhan, H.; Celedon, J.C. Maternal obesity in pregnancy, gestional weight gain and risk of childhood asthma. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e535–e546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, H.T.; Xia, Y.Y.; Zeng, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, C.L.; Guo, J.J.; Zhao, Y. Risk of childhood overweight or obesity associated with excessive weight gain during pregnancy: A meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 289, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, G.; Weinmayr, G.; Kleiner, A.; García-Marcos, L.; Strachan, D.P. Effect of diet on asthma and allergic sensitization in the International Studies on Allergies and Asthma in Childhood (ISAAC) Phase Two. Thorax 2010, 65, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwarith, J.; Kahleova, H.; Crosby, L.; Brooks, A.; Brandon, L.; Levin, S.M.; Barnard, N.D. The role of nutrition in asthma prevention and treatment. Nutr. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Fung, T.T.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Forouhi, N.H. Food based dietary patterns and chronic disease prevention. BMJ 2018, 361, k2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younas, H.; Vieira, M.; Gu, C.; Lee, R.; Shin, M.K.; Berger, S.; Loube, J.; Nelson, A.; Bevans-Fonti, S.; Zhong, Q.; et al. Caloric restriction prevents the development of airway hyperresponsiveness in mice on a high fat diet. Sci. Rep. 2019, 22, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Rodríguez, J.A.; Garcia Marcos, L. What is the effect of a Mediterranean diet on allergies and asthma in children? Front. Pediatr. 2017, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandhorst, S.; Longo, V.D. Dietary restrictions and nutrition in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Guarnido, O.; Urquiza, N.; Saiz, M.; Lozano, D.; Rodrigo, L.; Pascual, M.; Lorente, J.A.; Alvarez-Cubero, M.J.; Rivas, A. Bioactive compounds of the Mediterranean diet and prostate cancer. Aging Male 2018, 21, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, E.P.; Kolahdooz, F.; Hansel, N.; Breysse, P.N.; Davis, M.; Sharma, S.; Matsui, E.C.; Diette, G.; McCormack, M.C. Association between Western diet pattern and adult asthma: A focused review. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Subar, A.F.; Hollenbeck, A.; Schatzkin, A. Dietary fiber intake and mortality in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Nutrition or pharmacology? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.J.; Fernandez, M.L. Dietary strategies to reduce metabolic syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2013, 14, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, H.V.; Lee, H.; Jauhiainen, M.; Joensuu, A.; Borodulin, K.; Männistö, S.; Jin, Z.; Terwilliger, J.D.; Isola, V.; Ahtiainen, P.; et al. Substantial fat mass loss reduces low-grade inflammation and induces positive alteration in cardiometabolic factors in normal-weight individuals. Nat. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duwaerts, C.C.; Maher, J.J. Macronutrients and the adipose-liver axis in obesity and fatty liver. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khazáai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggini, S.; Pierre, A.; Calder, P.C. Inmune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.K.; Koh-Banerjee, P.; Franz, M.; Sampson, L.; Gronbaek, M.; Rimm, E.B. Whole grains, bran and germ in relation to homocysteine and markers of glycemic control, lipids and inflammation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulangé, C.L.; Neves, A.L.; Chilloux, J.; Nicholson, J.K.; Dumas, M.E. Impact of the gut microbiota, obesity, and metabolic disease. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeChristopher, L.R.; Tucker, K.L. Excess of free fructose, high-fructose corn syrup and adult asthma: The Framingham Offspring Cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botchlett, R.; Chaodong, W. Diet composition for the management of obesity and obesity-related disorders. J. Diabetes Mellit. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 3, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, S.G.; Baffi, C.; Holguin, F. Fatty acids, inflammation and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Inmunol. 2014, 133, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureda, A.; Bibiloni, M.M.; Julibert, A.; Bouzas, C.; Argelich, E.; Llompart, I.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and inflammatory markers. Nutrients 2018, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.G.; Li, Q.; Scott, H.A.; Rutting, S.; Berthon, B.S.; Gibson, P.G.; Hansbro, P.M.; Williams, E.; Horvat, J.; Simpson, J.L.; et al. Saturated fatty acids, obesity, and the nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Inmunol. 2019, 143, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.G.; Shivappa, N.; Berthon, B.S.; Gibson, P.G.; Hebert, J.R. Dietary inflammatory index is related to asthma risk, lung function and systemic inflammation in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Elwood, P.E.; Asher, M.I. Diet and asthma: Looking back, moving forward. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Ghanim, H.; Chaudhuri, A.; Dhindsa, S.; Kim, S.S. Macronutrient intake induces oxidative and inflammatory stress: Potential relevance to atherosclerosis and insulin resistance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, F.; Macchi, C.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Mediterranean diet and health. Biofactors 2013, 39, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Morenga, L.; Montez, J.M. Health effects of saturated and trans-fatty acid intake in children and adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, K.; Lawrence, M.; Naika, A.; Baker, P. Processed foods and nutrition transition in the Pacific: Regional trends, patterns and food system drivers. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Essential Nutrition Actions: Mainstreaming Nutrition throughout the Life-Course; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-92-4-151585-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Rava, M.; Bédard, A.; Dumas, O.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Leynaert, B.; Pison, C.; Le Moual, N.; Romieu, I.; Siroux, V.; et al. Cured meat intake is associated with worsening asthma symptoms. Thorax 2017, 72, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brathwaite, N.; Fraser, H.S.; Modeste, N.; Broome, H.; King, R. Obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and vegetarian status among Seventh-Day Adventists in Barbados: Preliminary results. Ethn. Dis. 2003, 13, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Andrianasolo, R.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Moufidath, A.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Varraso, R. Association between cured meat intake and asthma symptoms. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 52, PA1149. [Google Scholar]
- Statovci, D.; Aguilera, M.; MacSharry, J.; Melgar, S. The impact of Western diet and nutrients on the microbiota and immune response at mucosal interfaces. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, P.E.; Hawrylowicz, C.M. Vitamin D in asthma. Mechanisms of action and considerations for clinical trials. CHEST 2018, 153, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, H.A.; Gibson, P.G.; Garg, M.L.; Wood, L.G. Airway inflammation is augmented by obesity and fatty acids in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, D.T. Mechanisms by which obesity impacts upon asthma. Thorax 2017, 72, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, A.; Vilariño-García, T.; Fernández-Riejos, P.; Martín-González, J.; Segura-Egea, J.J.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of leptin as a link between metabolism and the immune system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017, 35, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.A.; Gibson, P.G.; Garg, M.L.; Pretto, J.J.; Morgan, P.J.; Callister, R.; Wood, L.G. Relationship between body composition, inflammation and lung function in overweight and obese asthma. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.A.; Poynter, M.E. Mechanisms of asthma in obesity: Pleiotropic aspects of obesity produce distinct asthma phenotypes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 54, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frati, F.; Salvatori, C.; Incorvaia, C.; Bellucci, A.; Di Cara, G.; Marcucci, F.; Esposito, S. The role of the microbiome in asthma: The gut-lung axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, P.; Malireddi, S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Food for training- Western diet and inflammatory memory. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wood, I.S. Adipokines: Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, P. The role of adipokines in chronic inflammation. Immunotargets Ther. 2016, 5, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroszkiewicz, J.; Chełchowska, M.; Rowicka, G.; Klemarczyk, W.; Strucińska, M.; Gajewska, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Pro-Inflammatory Adipokine Profiles in Children on vegetarian and Omnivorous Diets. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, P.W.; Kriketos, A.D.; Campbell, L.V.; Shen, Y.; Charlesworth, J.A. The metabolism of isoforms of human adiponectin: Studies in human subjects and in experimental animals. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 153, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Izadi, V.; Azadbakht, L. The effect of low calorie diet on adiponectin concentration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Pankow, J.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Couper, D.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Pereira, M.; Duncan, B.B.; Schmidt, M.I. High-molecular-weight adiponectin and the risk of type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 5097–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, M.; Hara, K.; Kamura, Y.; Honoki, H.; Fujisaka, S.; Ishiki, M.; Usui, I.; Yagi, K.; Fukushima, Y.; Takano, A.; et al. Ratio of low molecular weight serum adiponectin to the total adiponectin value is associated with type 2 diabetes through its relation to increasing insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, S.; Que, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Mardinoglu, A. Meta-analysis of adiponectin as a biomarker for the detection of metabolic syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Daniele, A.; Scudiero, O.; Ludovica-Monaco, M.; Roviezzo, F.; D’Agostino, B.; Mazzarella, G.; Bianco, A. Adiponectin in asthma: Implications for phenotyping. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2015, 16, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; RuizLozano, P.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker-Duffen, J.L.; Nakamura, K.; Silver, M.; Kikuchi, R.; Tigges, U.; Yoshida, S.; Denzel, M.S.; Ranscht, B.; Walsh, K. T-cadherin is essential for adiponectin-mediated revascularization. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 24886–24897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalisz, M.; Baranowska, B.; Wolińska-Witort, E.; Mączewski, M.; Mackiewicz, U.; Tułacz, D.; Gora, M.; Martynska, L.; Bik, W. Total and high molecular weight adiponectin levels in the rat model of post-myocardial infarction heart failure. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 673–680. [Google Scholar]
- Jaswal, S.; Saini, V.; Kaur, J.; Gupta, S.; Kaur, H.; Garg, K. Association of Adiponectin with Lung Function Impairment and Disease Severity in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Appl. Basic. Med. Res. 2018, 8, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, M.; Lago, R.; Gomez, R.; Lago, F.; Dieguez, C.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; Gualillo, O. Changes in plasma levels of fat-derived hormones adiponectin, leptin, resistin and visfatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirdar, S.; Serter, M.; Ceylan, E.; Sener, A.G.; Kavak, T.; Karadağ, F. Adiponectin as a biomarker of systemic inflammatory response in smoker patients with stable and exacerbation phases of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2009, 69, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, A.; Shore, S.A. Adiponectin, leptin, and resistin in asthma: Basic mechanisms through population studies. J. Allergy 2013, 2013, e785835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Xue, M. Correlations of severity of asthma in children with body mass index, adiponectin and leptin. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Maarafiya, M.M.; Ashraf Soliman, A.; Noura, B.M.; Younes, N.B.M.; Chandra, P. Serum Leptin and Adiponectin Levels in Obese and Nonobese Asthmatic School Children in relation to Asthma Control. J. Allergy 2013, 2013, e654104. [Google Scholar]
- Yuksel, H.; Sogut, A.; Yilmaz, O.; Onur, E.; Dinc, G. Role of adipokines and hormones of obesity in childhood asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2012, 4, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Chong, L.; Kong, L.; Wen, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, C. Adiponectin alleviates exacerbation of airway inflammation and oxidative stress in obesity-related asthma mice partly through AMPK signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heisler, L.K.; Lam, D.D. An appetite for life: Brain regulation of hunger and satiety. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 37, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Lago, R.; Gomez, R.; Dieguez, C.; Lago, F.; Gomez-Reino, J.; Gualillo, O. Towards a pro-inflammatory and immunomodulatory emerging role of leptin. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G. Intracellular signalling pathways activated by leptin. Biochem. J. 2006, 393, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abella, V.; Scotece, M.; Conde, J.; Pino, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Mera, A.; Lago, F.; Gomez, R.; Gualillo, O. Leptin in the interplay of inflammation, metabolism and immune system disorders. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.R.; Lazar, M.A. Human resistin: Found in translation from mouse to man. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.C.; Kwon, Y.W.; Lee, S.E.; Cho, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Yang, H.M.; et al. Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 is a receptor for human resistin and mediates inflammatory actions of human monocytes. Cell Metab. 2014, 4, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Kwak, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ahima, R.S. Linking resistin, inflammation, and cardiometabolic diseases. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Ford, E.S.; Camargo, C.A. Association between leptin and asthma in adults. Thorax 2006, 61, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, N.; Kirerleri, E.; Ones, U.; Tamay, Z.; Salmayenli, N.; Darendeliler, F. Leptin: Does it have any role in childhood asthma? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodini, A.; Tenero, L.; Sandri, M.; Maffeis, C.; Piazza, M.; Zanoni, L.; Peroni, D.; Boner, A.; Piacentini, G. Serum and exhaled breath condensate leptin levels in asthmatic and obesity children: A pilot study. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 046005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Han, W. Leptin positively regulates MUC5AC production and secretion induced by interleukin-13 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 979–984. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Suzukawa, M.; Arakawa, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Igarashi, S.; Tashimo, H.; Nagai, H.; Tohma, S.; Nagase, T.; Ohta, K. Leptin enhances cytokine/chemokine production by normal lung fibroblasts by binding to leptin receptor. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, G. Expression Levels of Predominant Adipokines and Activations of STAT3, STAT6 in an Experimental Mice Model of Obese Asthma. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 18, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, D.; Scott, H.; MacDonald-Wicks, L.; Gibson, P.G.; Wood, L.G. Resistin is a predictor of asthma risk and resistin: Adiponectin ratio is a negative predictor of lung function in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.L.; Yin, L.J.; Sharma, S.; Kierstein, S.; Wu, H.F.; Eid, G.; Haczku, A.; Corrigan, C.J.; Ying, S. Resistin-like molecule-β (RELM-β) targets airways fibroblasts to effect remodelling in asthma: From mouse to man. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2015, 45, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Kim, Y.D.; Na, H.G.; Bae, C.H.; Song, S.Y.; Choi, Y.S. Resistin upregulates MUC5AC/B mucin gene expression in human airway epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz-Scroggins, M.E.; Yuan, S.; Kerr, S.C.; Dunican, E.M.; Yu, M.; Carrington, S.D.; Fahy, J.V. Abnormalities in MUC5AC and MUC5B protein in airway mucus in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 1296–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frontela-Saseta, C.; González-Bermúdez, C.A.; García-Marcos, L. Diet: A Specific Part of the Western Lifestyle Pack in the Asthma Epidemic. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072063
Frontela-Saseta C, González-Bermúdez CA, García-Marcos L. Diet: A Specific Part of the Western Lifestyle Pack in the Asthma Epidemic. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072063
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrontela-Saseta, Carmen, Carlos A. González-Bermúdez, and Luis García-Marcos. 2020. "Diet: A Specific Part of the Western Lifestyle Pack in the Asthma Epidemic" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072063
APA StyleFrontela-Saseta, C., González-Bermúdez, C. A., & García-Marcos, L. (2020). Diet: A Specific Part of the Western Lifestyle Pack in the Asthma Epidemic. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072063





