Somatotype Components as Useful Predictors of Disordered Eating Attitudes in Young Female Ballet Dance Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Eating Behavior
2.3. Anthropometric Assessment
2.4. Anthropometric Somatotype
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
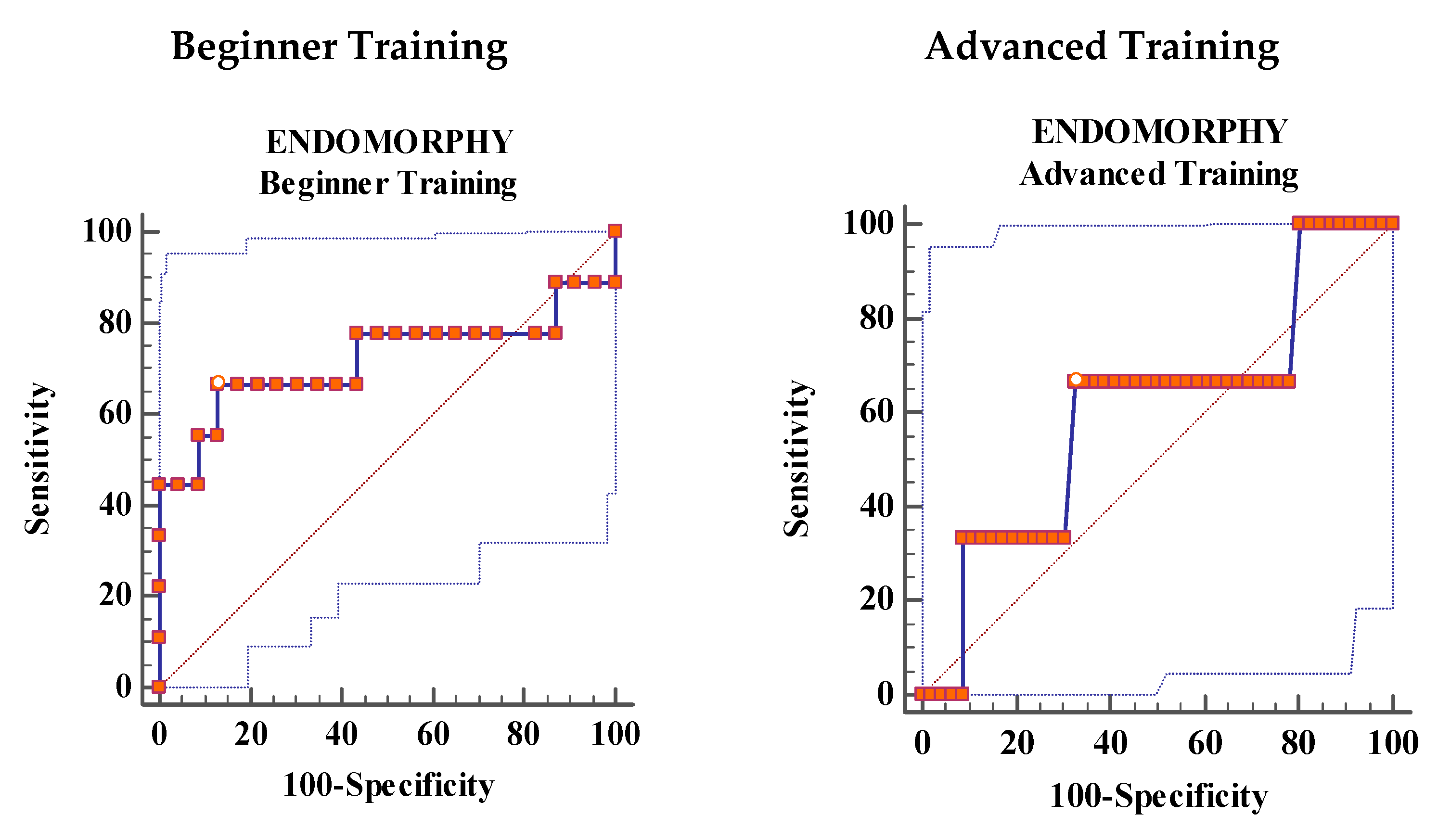
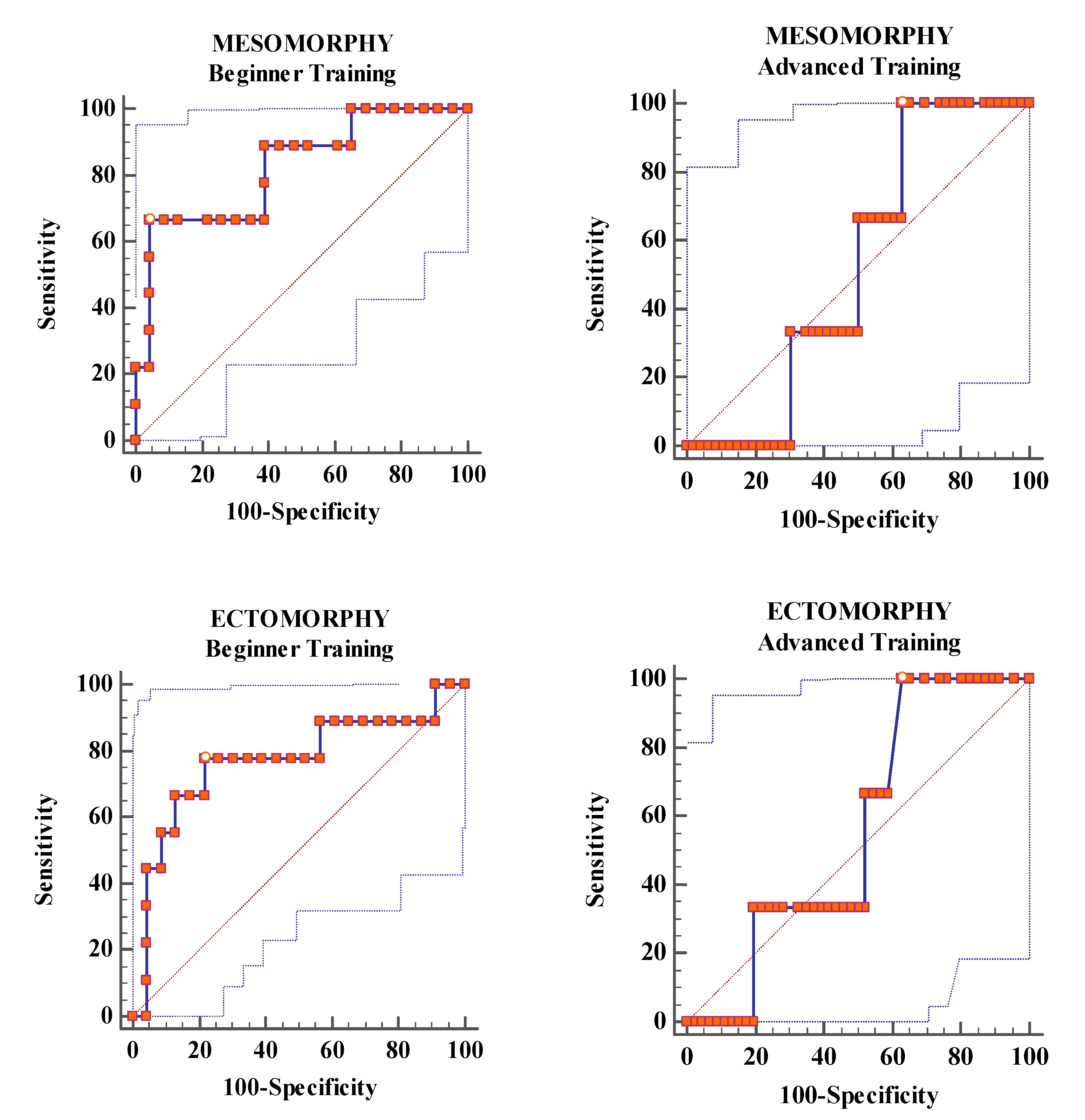
Analysis of ROC Curves
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Gloucester, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780890425541. [Google Scholar]
- Treasure, J.; Duarte, T.A.; Schmidt, U. Eating disorders. Lancet 2020, 395, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, J.; Gomez-Peresmitré, G.; Sentis, J.; Vallés, A.; Casulà, V.; Castro, J.; Pineda, G.; Leon, R.; Platas, S.; Rodriguez, R. Eating disorders and body image in Spanish and Mexican female adolescents. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2006, 41, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, H.; Booij, L. Eating disorders, heredity and environmental activation: Getting epigenetic concepts into practice. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, e1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penniment, K.J.; Egan, S.J. Perfectionism and learning experiences in dance class as risk factors for eating disorders in dancers. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2012, 20, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jáuregui-Lobera, I.; Bolaños-Rios, P.; Valero-Blanco, E.; Ortega-de-la-Torre, A. Eating attitudes, body image and risk for eating disorders in a group of Spanish dancers. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Tylka, T.L. Refinement of the tripartite influence model for men: Dual body image pathways to body change behaviors. Body Image 2011, 8, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uher, R.; Rutter, M. Classification of feeding and eating disorders: Review of evidence and proposals for ICD-11. World Psychiatry 2012, 11, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, E.; Kussman, A.; Nattiv, A. 2016 update on eating disorders in athletes: A comprehensive narrative review with a focus on clinical assessment and management. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, M.; Sundgot-Borgen, J. Higher prevalence of eating disorders among adolescent elite athletes than controls. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Torstveit, M.K. Prevalence of eating disorders in elite athletes is higher than in the general population. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2004, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, J.L. Eating disorders among male athletes. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2008, 7, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, H.; Arcelus, J.; Geach, N.; Meyer, C. Perfectionism and eating psychopathology among dancers: The role of high standards and self-criticism. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2014, 22, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S. Characteristics of eating disorders among young ballet dancers. Psychopathology 1996, 29, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, D.M.; Bohr, Y.; Garfinkel, P.E. The eating attitudes test: Psychometric features and clinical correlates. Psychol. Med. 1982, 12, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcelus, J.; Witcomb, G.L.; Mitchell, A. Prevalence of eating disorders amongst dancers: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2014, 22, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, A.R.; Compte, E.J.; Faya, M.; Villaseñor, A.; Gutierrez, S.; Andrés, P.; Graell, M. Spanish validation of the Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire for Adolescents (EDE-Q-A): Confirmatory factor analyses among a clinical sample. Eat. Disord. 2019, 27, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, T.; Bersabé, R.; Jimenez, M.; Berrocal, C. The eating attitudes test (EAT-26): Reliability and validity in Spanish female samples. Span. J. Psychol. 2010, 13, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez-Fernández, M.A.; Ruiz-Lázaro, P.M.; Labrador, F.J.; Raich, R.M. Validation of the Eating Attitudes Test as a screening instrument for eating disorders in general population. Med. Clin. 2014, 20, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Wall, M.; Larson, N.I.; Eisenberg, M.E.; Loth, K. Dieting and disordered eating behaviors from adolescence to young adulthood: Findings from a 10-year longitudinal study. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübel, C.; Yilmaz, Z.; Schaumberg, K.E.; Breithaupt, L.; Hunjan, A.; Horne, E.; García-González, J.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Bulik, C.M.; Breen, G. Body composition in anorexia nervosa: Meta-analysis and meta-regression of cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 1205–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.; Micali, N.; Misra, M. Eating disorders and bone metabolism in women. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2017, 29, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, B.H.; Carter, J.E.L. A modified somatotype method. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1967, 27, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liiv, H.; Wyon, M.A.; Jürimäe, T.; Saar, M.; Mäestu, J.; Jürimäe, J. Anthropometry, somatotypes, and aerobic power in ballet, contemporary dance, and DanceSport. Med. Probl. Perform. Art. 2013, 28, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, A.J.; Brümmerhoff, A.; Greil, H.; Neumärker, K.J. Shall the anthropometry of physique cast new light on the diagnoses and treatment of eating disorders? Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2003, 12, i54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, S.; Warschburger, P. Weight, shape, and muscularity concerns in male and female adolescents: Predictors of change and influences on eating concern. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2017, 50, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Irala, J.; Cano-Prous, A.; Lahortiga-Ramos, F.; Gual-García, P.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Cervera-Enguix, S. Validation of the Eating Attitudes Test (EAT) as a screening tool in the general population. Med. Clin. 2008, 12, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; Toro, J.; Salamero, M.; Guimerá, E. The eating attitudes test: Validation of the Spanish version. Evaluación Psicológica 1991, 7, 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Marfell-Jones, M.; Olds, L. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Potchefstroom, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle, D.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, S. Applied Statistics for the Behavioural Sciences, 5th ed.; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0618124053. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweig, M.H.; Campbell, G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: A fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.L.; Szabo, M.; Kambanis, P.E.; Murray, S.B.; Thomas, J.J.; Eddy, K.T.; Franko, D.L.; Griffiths, S. Negative psychological correlates of the pursuit of muscularity among women. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 52, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, V.J.; Kwan, M.Y.; Minnich, A.M.; Gordon, K.H. The interaction of sociocultural attitudes and gender on disordered eating. J. Clin. Psychol. 2019, 75, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringham, R.; Klump, K.; Kaye, W.; Stone, D.; Libman, S.; Stowe, S.; Marcus, M. Eating disorder symptomatology among ballet dancers. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2006, 39, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, S.; McLean, N. Eating disorders in athletes: A review of the literature. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2001, 4, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costarelli, V.; Antonopoulou, K.; Mavrovounioti, C. Psychosocial characteristics in relation to disordered eating attitudes in Greek adolescents. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2011, 19, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, L.D.S.; Almeida, S.D.S.; Ferreira, M.E.C. Impacto de variáveis antropométricas sobre a insatisfação corporal e o comportamento alimentar em jovens atletas. J. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2012, 61, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Toro, J.; Guerrero, M.; Sentis, J.; Castro, J.; Puértolas, C. Eating disorders in Ballet dancing students: Problems and risk factors. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2009, 17, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.L.; Fowle, J.L.; Ilyumzhinova, R.; Berona, J.; Mbayiwa, K.; Goldschmidt, A.B.; Bodell, L.P.; Stepp, S.D.; Hipwell, A.E.; Keenan, K.E. The relationship between body mass index, body dissatisfaction, and eating pathology in sexual minority women. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 53, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley-Hash, S.; Banker, J.D.; Walton, M.A.; Ginsburg, Y.; Cunningham, R.M. The prevalence and correlates of eating disorders among emergency department patients aged 14–20 years. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2012, 45, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.M.; Salar, N.V.; Carretero, C.M.; Gimeno, E.C.; Collado, E.R. Eating disorders and diet management in contact sports; EAT-26 questionnaire does not seem appropriate to evaluate eating disorders in sports. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Rouzitalab, T.; Gargari, B.P.; Amirsasan, R.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Naeimi, A.F.; Sanoobar, M. The relationship of disordered eating attitudes with body composition and anthropometric indices in physical education students. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2015, 17, e20727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotti, A.; Fioravanti, M.; Balotta, M.; Tozzi, F.; Cannella, C.; Lazzari, R. Eating behavior of ballet dancers. Eat. Weight Disord. 2002, 71, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, N.; Tanaka, S.; Hirata, N.; Ogino, S.; Ozaki, N. A battery of self-screening instruments and self-reported body frame could not detect eating disorders among college students. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kloub, M.I.; Al-Khawaldeh, O.A.; ALBashtawy, M.; Batiha, A.M.; Al-Haliq, M. Disordered eating in Jordanian adolescents. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2019, 25, e12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, L.D.S.; Cipriani, F.M.; Ferreira, M.E.C. Risk behaviors for eating disorder: Factors associated in adolescent students. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2013, 35, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Beginner Training | Advanced Training | p-Value | Effect Size | Statistical Power | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 32) | (n = 49) | ||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | r | 1-β | ||
| Age (years) | 10.09 | 1.23 | 15.37 | 2.11 | <0.0001 | 0.84 | 0.99 |
| Weight (kg) | 34.93 | 3.63 | 52.28 | 5.79 | <0.0001 | 0.87 | 0.99 |
| Height (m) | 1.40 | 0.07 | 1.59 | 0.08 | <0.0001 | 0.79 | 0.99 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.00 | 1.89 | 20.69 | 1.96 | <0.0001 | 0.57 | 0.99 |
| Endomorphy | 3.85 | 1.23 | 3.19 | 0.64 | 0.003 | 0.32 | 0.81 |
| Mesomorphy | 5.64 | 0.95 | 5.17 | 1.04 | 0.041 | 0.23 | 0.51 |
| Ectomorphy | 2.77 | 1.27 | 2.62 | 1.29 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| Bulimia | 0.94 | 1.50 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.004 | 0.33 | 0.83 |
| Oral control | 3.44 | 4.06 | 3.10 | 3.05 | 0.66 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Dieting | 6.72 | 7.35 | 4.22 | 5.21 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.38 |
| Total score | 11.09 | 11.58 | 7.49 | 8.01 | 0.46 | 0.18 | 0.33 |
| Bulimia | Oral Control | Dieting | Total Score | Age | Weight | Height | BMI | Endo | Meso | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral control | 0.786 ** | |||||||||
| Dieting | 0.667 ** | 0.60 ** | ||||||||
| Total Score | 0.772 ** | 0.821 ** | 0.936 ** | |||||||
| Age | −0.37 * | −0.243 | −0.158 | −0.218 | ||||||
| Weight | −0.132 | −0.212 | −0.093 | −0.17 | 0.54 ** | |||||
| Height | −0.46 ** | −0.48 ** | −0.39 * | −0.45 ** | 0.81 ** | 0.528 ** | ||||
| BMI | 0.193 | 0.197 | 0.204 | 0.184 | −0.169 | 0.537 ** | −0.37 * | |||
| Endo | 0.254 | 0.206 | 0.116 | 0.121 | −0.56 ** | 0.058 | −0.65 ** | 0.63 ** | ||
| Meso | 0.422 * | 0.466 ** | 0.405 * | 0.438 * | −0.166 | 0.32 | −0.43 ** | 0.82 ** | 0.49 ** | |
| Ecto | −0.319 | −0.338 | −0.27 | −0.294 | 0.415 * | -0.291 | 0.62 ** | −0.94 ** | −0.73 ** | −0.8 ** |
| Bulimia | Oral Control | Dieting | Total Score | Age | Weight | Height | BMI | Endo | Meso | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral control | 0.469 ** | |||||||||
| Dieting | 0.489 ** | 0.141 | ||||||||
| Total Score | 0.482 * | 0.828 ** | 0.616 ** | |||||||
| Age | 0.23 | 0.284 * | −0.093 | 0.127 | ||||||
| Weight | 0.237 | 0.35 * | −0.035 | 0.214 | 0.803 ** | |||||
| Height | 0.187 | 0.066 | 0.258 | 0.219 | 0.414 ** | 0.594 ** | ||||
| BMI | 0.103 | 0.294 * | −0.277 | −0.011 | 0.474 ** | 0.51 ** | −0.322 * | |||
| Endo | −0.016 | 0.066 | −0.107 | −0.021 | −0.165 | −0.213 | −0.57 ** | 0.431 ** | ||
| Meso | −0.09 | 0.102 | −0.281 | −0.112 | −0.022 | −0.146 | −0.76 ** | 0.629 ** | 0.544 ** | |
| Ecto | 0.026 | −0.177 | 0.342 * | 0.119 | −0.127 | −0.118 | 0.692 ** | −0.88 ** | −0.59 ** | −0.80 ** |
| Beginner Training | Advanced Training | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endo | Meso | Ecto | Endo | Meso | Ecto | |
| Area under the curve | 0.72 | 0.82 | 0.768 | 0.601 | 0.522 | 0.558 |
| Standard error | 0.135 | 0.089 | 0.111 | 0.212 | 0.114 | 0.139 |
| 95% CI | 0.53 to 0.86 | 0.64 to 0.93 | 0.58 to 0.89 | 0.45 to 0.74 | 0.37 to 0.66 | 0.41 to 0.70 |
| z statistic | 1.631 | 3.61 | 2.41 | 0.477 | 0.191 | 0.418 |
| p-value | 0.1030 | 0.003 | 0.0158 | 0.633 | 0.8483 | 0.6758 |
| Youden’s J index | 0.5362 | 0.6232 | 0.564 | 0.3406 | 0.3696 | 0.3696 |
| Somatotype Component | Training | Cut-Off | Sens | 95% CI | Spec | 95% CI | +LR | 95% CI | −LR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endomorphy | BT | >4.36 | 66.67 | 29.9–92.5 | 86.96 | 66.4–97.2 | 5.11 | 1.6–16.2 | 0.38 | 0.2–1.0 |
| AT | ≤2.88 | 66.67 | 9.4–99.2 | 67.39 | 52.0–80.5 | 2.04 | 0.8–5.0 | 0.49 | 0.10–2.5 | |
| Mesomorphy | BT | >6.34 | 66.67 | 29.9–92.5 | 95.65 | 78.1–99.9 | 15.33 | 2.1–110 | 0.35 | 0.1–0.9 |
| AT | ≤5.72 | 100 | 29.2–100.0 | 36.96 | 23.2–52.5 | 1.59 | 1.3–2.0 | 0 | ||
| Ectomorphy | BT | ≤2.41 | 77.78 | 40.0–97.2 | 78.6 | 56.3–92.5 | 3.58 | 1.5–8.4 | 0.28 | 0.08–1.0 |
| AT | >1.76 | 100 | 29.2–100.0 | 36.96 | 23.2–52.5 | 1.59 | 1.3–2.0 | 0 |
| Overall Model Fit | Hosmer & Lemeshow | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Variable | OR | 95% CI | X2 | p-Value | X2 | p-Value |
| BT | Endo | 2.44 | 1.1608 to 5.1493 | 6.878 | 0.0087 | 7.3902 | 0.5966 |
| Meso | 7.14 | 1.7214 to 29.672 | 12.47 | 0.0004 | 11.0945 | 0.2693 | |
| Ecto | 0.42 | 0.2041 to 0.8972 | 6.22 | 0.0126 | 9.5698 | 0.3864 | |
| AT | Endo | Not retained in the model | |||||
| Meso | Not retained in the model | ||||||
| Ecto | Not retained in the model | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvero-Cruz, J.R.; Parent Mathias, V.; García-Romero, J.C. Somatotype Components as Useful Predictors of Disordered Eating Attitudes in Young Female Ballet Dance Students. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072024
Alvero-Cruz JR, Parent Mathias V, García-Romero JC. Somatotype Components as Useful Predictors of Disordered Eating Attitudes in Young Female Ballet Dance Students. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(7):2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072024
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvero-Cruz, José Ramón, Verónica Parent Mathias, and Jerónimo C. García-Romero. 2020. "Somatotype Components as Useful Predictors of Disordered Eating Attitudes in Young Female Ballet Dance Students" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 7: 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072024
APA StyleAlvero-Cruz, J. R., Parent Mathias, V., & García-Romero, J. C. (2020). Somatotype Components as Useful Predictors of Disordered Eating Attitudes in Young Female Ballet Dance Students. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(7), 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072024






