Low-Volume Nodal Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors and Prognostic Significance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Sentinel Lymph Node Protocol
2.2. Histopathological Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
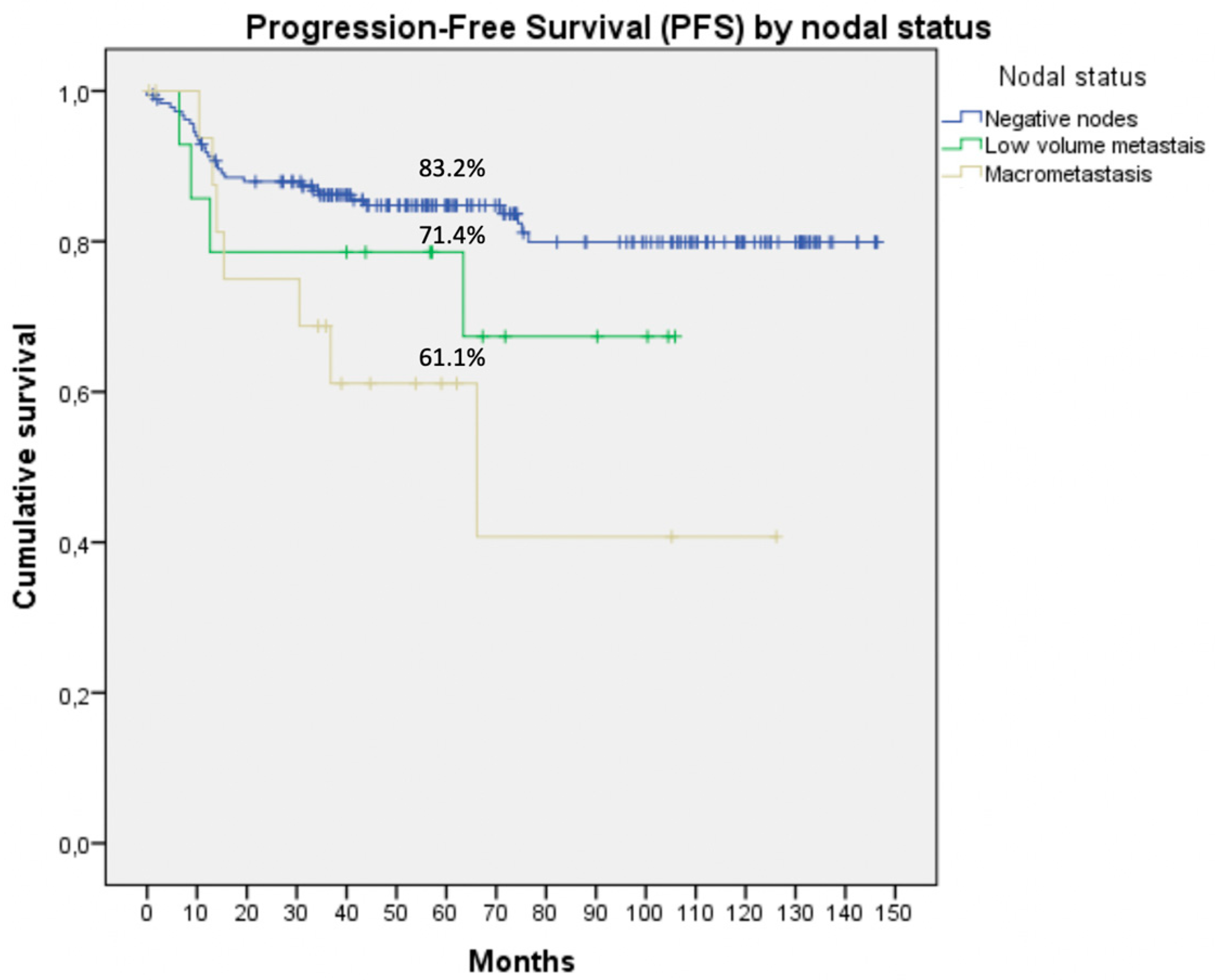
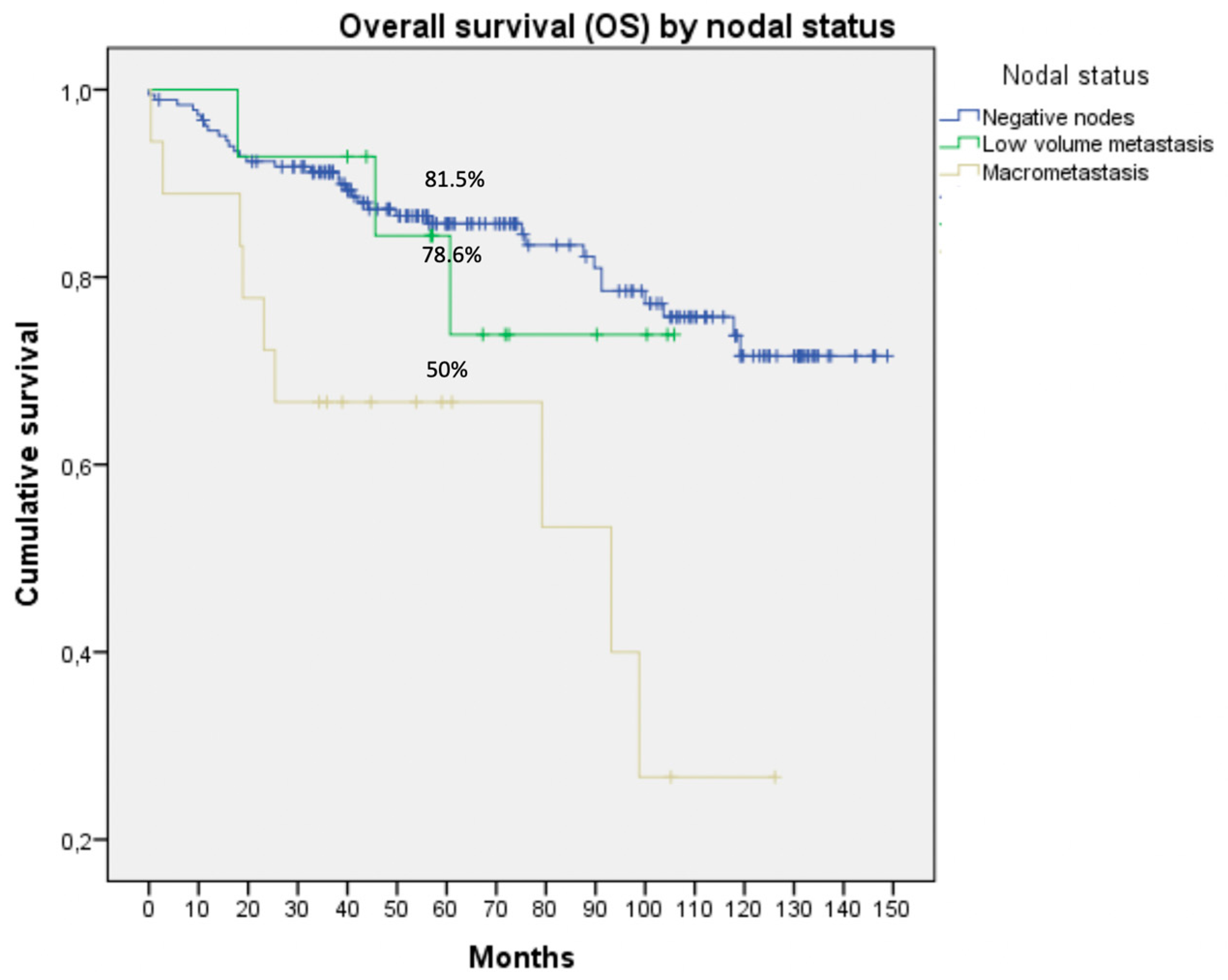
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creasman, W.T.; Morrow, C.P.; Bundy, B.N.; Homesley, H.D.; Graham, J.E.; Heller, P.B. Surgical pathologic spread patterns of endometrial cancer: A gynecologic oncology group study. Cancer 1987, 60, 2035–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, W.M.; Orr, J.; Leitão, M.; Salom, E.; Gehrig, P.; Olawaiye, A.; Brewer, M.; Boruta, D.; Villella, J.; Herzog, T.; et al. Endometrial cancer: A review and current management strategies: Part I. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTEC Study Group; Kitchener, H.; Swart, A.M.C.; Qian, Q.; Amos, C.; Parmar, M.K.B. Efficacy of systematic pelvic lymphadenectomy in endometrial cancer (MRC ASTEC trial): A randomised study. Lancet 2008, 373, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panici, P.B.; Basile, S.; Maneschi, F.; Lissoni, A.A.; Signorelli, M.; Scambia, G.; Angioli, R.; Tateo, S.; Mangili, G.; Katsaros, D.; et al. Systematic Pelvic Lymphadenectomy vs No Lymphadenectomy in Early-Stage Endometrial Carcinoma: Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Comp. Cancer 2020, 16.
- Rossi, E.C.; Kowalski, L.D.; Scalici, J.; Cantrell, L.; Schuler, K.; Hanna, R.K.; Method, M.; Ade, M.; Ivanova, A.; Boggess, J.F. A comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy to lymphadenectomy for endometrial cancer staging (FIRES trial): A multicentre, prospective, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraï, E.; Dubernard, G.; Bats, A.-S.; Heitz, D.; Mathevet, P.; Marret, H.; Querleu, D.; Golfier, F.; Leblanc, E.; Rouzier, R.; et al. Sentinel node biopsy for the management of early stage endometrial cancer: Long-term results of the SENTI-ENDO study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 136, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumovitz, M.; Plante, M.; Lee, P.S.; Sandadi, S.; Lilja, J.F.; Escobar, P. Near infrared fluorescence for detection of sentinel lymph nodes in woman with cervical and uterine cancers (FILM): A randomized, phase 3, multicenter, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, P.T.; Westin, S.N.; Dioun, S.; Sun, C.C.; Euscher, E.; Munsell, M.F.; Fleming, N.D.; Levenback, C.; Frumovitz, M.; Ramirez, P.T.; et al. A prospective validation study of sentinel lymph node mapping for high-risk endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 146, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, R.W.; Gupta, S.; Stavitzski, N.M.; Zhu, X.; Takimoto, E.L.; Gubbi, A.; Bigsby, G.E.; Brudie, L.A.; Kendrick, J.E.; Ahmad, S. Sentinel lymph node mapping with staging lymphadenectomy for patients with endometrial cancer increases the detection of metastasis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 141, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Soslow, R.A.; Park, K.J.; Barber, E.L.; Khoury-Collado, F. Pathologic ultrastaging improves micrometastasis detection in sentinel lymph nodes during endometrial cancer staging. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2013, 23, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delpech, Y.; Cortez, A.; Coutant, C.; Callard, P.; Uzan, S.; Daraï, E.; Barranger, E. The sentinel node concept in endometrial cancer: Histopathologic validation by serial section and immunohistochemistry. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buda, A.; Elisei, F.; Arosio, M.; Dolci, C.; Signorelli, M.; Perego, P.; Giuliani, D.; Recalcati, D.; Cattoretti, G.; Milani, R.; et al. Integration of Hybrid Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography in the Preoperative Assessment of Sentinel Node in Patients With Cervical and Endometrial Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2012, 22, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaman, Y.; Pinkas, L.; Roitman, S.; Ikher, S.; Oustinov, N.; Vaisbuch, E.; Yachnin, A.; Ben-Arie, A. The Added Value of SPECT/CT in Sentinel Lymph Nodes Mapping for Endometrial Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 23, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadia, A.; Imboden, S.; Siegenthaler, F.; Gasparri, M.L.; Mohr, S.; Lanz, S.; Mueller, M.D. Laparoscopic Indocyanine Green Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Endometrial Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, F.L.; Page, D.L.; Fleming, I.D. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 6th ed.; Springer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, N.; Creutzberg, C.L.; Amant, F.; Bosse, T.; González-Martín, A.; Ledermann, J.; Marth, C.; Nout, R.; Querleu, D.; Mirza, M.R.; et al. ESMO–ESGO–ESTRO consensus conference on endometrial cancer: Diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 117, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Body, N.; de Kerdaniel, O.; Lavoué, V.; Leblanc, M.; Henno, S.; Levêque, J. Cancer de lèndomètre au stade précoce: Ganglion sentinelle ou curage pelvien? Gynécologie Obstétrique & Fertilité 2016, 44, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Plante, M.; Stanleigh, J.; Renaud, M.; Sebastianelli, A.; Grégoire, J. Isolated tumor cells (ITC) identified by sentinel lymph node (SLN) mapping in endometrial cancer: Does adjuvant treatment matter? Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 145, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, C.M.S.; Eriksson, A.G.Z.; Ducie, J.A.; Jewell, E.L.; Alektiar, K.M.; Hensley, M.L.; Soslow, R.A.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Leitao, M.M. Low-Volume Lymph Node Metastasis Discovered During Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping for Endometrial Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 23, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatov, A.; Lebius, C.; Ignatov, T.; Ivros, S.; Knueppel, R. Lymph node micrometastasis and outcome of endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 154, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piedimonte, S.; Richer, L.; Souhami, L.; Arseneau, J.; Fu, L.; Gilbert, L.; Alfieri, J.; Jardon, K.; Zeng, X.Z. Clinical significance of isolated tumor cells and micrometastasis in low-grade, stage I endometrial cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 118, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todo, Y.; Kato, H.; Okamoto, K.; Minobe, S.; Yamashiro, K.; Sakuragi, N. Isolated tumor cells and micrometastases in regional lymph nodes in stage I to II endometrial cancer. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, L.K.; Kondo, J.; Carney, M.E.; Tauchi-Nishi, P.; Terada, K.; Shimizu, D. Low-Volume Lymph Node Metastases in Endometrial Carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogani, G.; Mariani, A.; Paolini, B.; Ditto, A.; Raspagliesi, F. Low-volume disease in endometrial cancer: The role of micrometastasis and isolated tumor cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 153, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Hidalgo, N.R.; Ramírez, P.T.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Coreas, N.; Sánchez-Iglesias, J.L.; Cabrera, S. Oncologic impact of micrometastasis or isolated tumor cells in sentinel lymph nodes of patients with endometrial cancer: A meta-analysis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) Median (range) | 65 (32–89) |
| BMI Median (range) | 29 (17–50) |
| Surgical approach | |
| Laparotomy | 27 (10.1%) |
| Laparoscopy | 236 (88.4%) |
| Vaginal | 4 (1.5%) |
| Histology | |
| Endometrioid | 228 (84.1%) |
| Serous carcinoma | 21(7.7%) |
| Clear cell carcinoma | 15(5.5%) |
| Carcinosarcoma | 6 (2.2%) |
| Other | 1 (0.4%) |
| Grade | |
| 1 | 145 (53.7%) |
| 2 | 51 (18.9%) |
| 3 | 74 (27.4%) |
| Lymph-vascular invasion | |
| Negative | 199 (74.3%) |
| Positive | 69 (25.7%) |
| Myometrial invasion | |
| < 50% | 174 (64.2%) |
| ≥ 50% | 97 (35.8%) |
| FIGO Stage | |
| IA | 164 (46.5%) |
| IB | 57 (21%) |
| II | 8 (3%) |
| IIIA | 9 (3.3%) |
| IIIB | 3 (1.1%) |
| IIIC1 | 20 (7.4%) |
| IIIC2 | 8 (3%) |
| IVA | 1 (0.4%) |
| IVB | 1 (0.4%) |
| Lymph node status (n = 230) | |
| Negative | 196 (85.2%) |
| Isolated tumor cells | 6 (2.6%) |
| Micrometastasis | 8 (3.5%) |
| Macrometastasis | 20 (8.7%) |
| Negative Lymph Nodes | Low Volume Metastasis | Macrometastasis | Univariate | Multivariate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N(%) | N(%) | N(%) | p-Value | p-Value | |
| Myometrial invasion | |||||
| <50% | 130 (66.3) | 7 (50) | 3 (15) | p < 0.001 | p = 0.032 |
| ≥50%, cervical stromal invasion | 66 (33.7) | 7 (50) | 17(85) | ||
| Histology | |||||
| Endometrioid | 164 (83.7) | 12 (85.7) | 15 (75) | p = 0.593 | p = 0.593 |
| Non-endometrioid | 32 (16.3) | 2 (14.3) | 5 (25) | ||
| Grade | |||||
| G1 | 104 (53.1) | 6 (42.9) | 5 (26.3) | p = 0.117 | p = 0.990 |
| G2 | 36 (18.4) | 5 (35.7) | 5 (26.3) | p = 0.887 | |
| G3 | 56 (28.6) | 3 (21.4) | 9 (47.4) | p = 0.941 | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | |||||
| No | 152 (78.4) | 6 (42.9) | 6 (31.6) | p < 0.001 | p = 0.054 |
| Yes | 42 (21.6) | 8 (57.1) | 13 (68.4) |
| Node-Negative | LVM | Macrometastasis | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Follow up or VBT | 74.2% (135) | 28.6% (4) | 5.6% (1) | p < 0.001 |
| EBRT ± BT | 13.7% (25) | 28.6% (4) | 11.1% (2) | p < 0.001 |
| CT ± EBRT | 12.1% (22) | 42.9% (6) | 83.3% (15) | p < 0.001 |
| Type LVM | Stage | Histology | Grade | Lymph-Vascular Invasion | Adjuvant Treatment | Recurrence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient 1 | ITC | IB | Endometrioid | 3 | + | CT ± EBRT | None |
| Patient 2 | ITC | IB | Carcinosarcoma | 3 | + | CT ± EBRT | Yes |
| Patient 3 | ITC | IA | Endometrioid | 2 | - | None | Yes |
| Patient 4 | ITC | IA | Endometrioid | 1 | - | EBRT ± BT | None |
| Patient 5 | ITC | IB | Endometrioid | 2 | + | CT ± EBRT | None |
| Patient 6 | ITC | IA | Endometrioid | 1 | - | None | None |
| Patient 7 | MIC | IA | Endometrioid | 1 | + | VBT | None |
| Patient 8 | MIC | IB | Endometrioid | 1 | + | EBRT ± BT | Yes |
| Patient 9 | MIC | IB | Endometrioid | 1 | + | EBRT ± BT | None |
| Patient 10 | MIC | IA | Endometrioid | 1 | + | CT ± EBRT | None |
| Patient 11 | MIC | IB | Endometrioid | 2 | + | EBRT ± BT | Yes |
| Patient 12 | MIC | IA | Endometrioid | 2 | - | None | None |
| Patient 13 | MIC | IA | Endometrioid | 3 | - | CT ± EBRT | None |
| Patient 14 | MIC | IB | Endometrioid | 1 | - | CT ± EBRT | None |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García Pineda, V.; Hernández Gutiérrez, A.; Gracia Segovia, M.; Siegrist Ridruejo, J.; Diestro Tejeda, M.D.; Zapardiel, I. Low-Volume Nodal Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors and Prognostic Significance. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061999
García Pineda V, Hernández Gutiérrez A, Gracia Segovia M, Siegrist Ridruejo J, Diestro Tejeda MD, Zapardiel I. Low-Volume Nodal Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors and Prognostic Significance. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(6):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061999
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía Pineda, Virginia, Alicia Hernández Gutiérrez, Myriam Gracia Segovia, Jaime Siegrist Ridruejo, María Dolores Diestro Tejeda, and Ignacio Zapardiel. 2020. "Low-Volume Nodal Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors and Prognostic Significance" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 6: 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061999
APA StyleGarcía Pineda, V., Hernández Gutiérrez, A., Gracia Segovia, M., Siegrist Ridruejo, J., Diestro Tejeda, M. D., & Zapardiel, I. (2020). Low-Volume Nodal Metastasis in Endometrial Cancer: Risk Factors and Prognostic Significance. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061999






