Estimating the Risk of COVID-19 Death during the Course of the Outbreak in Korea, February–May 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Data Sources
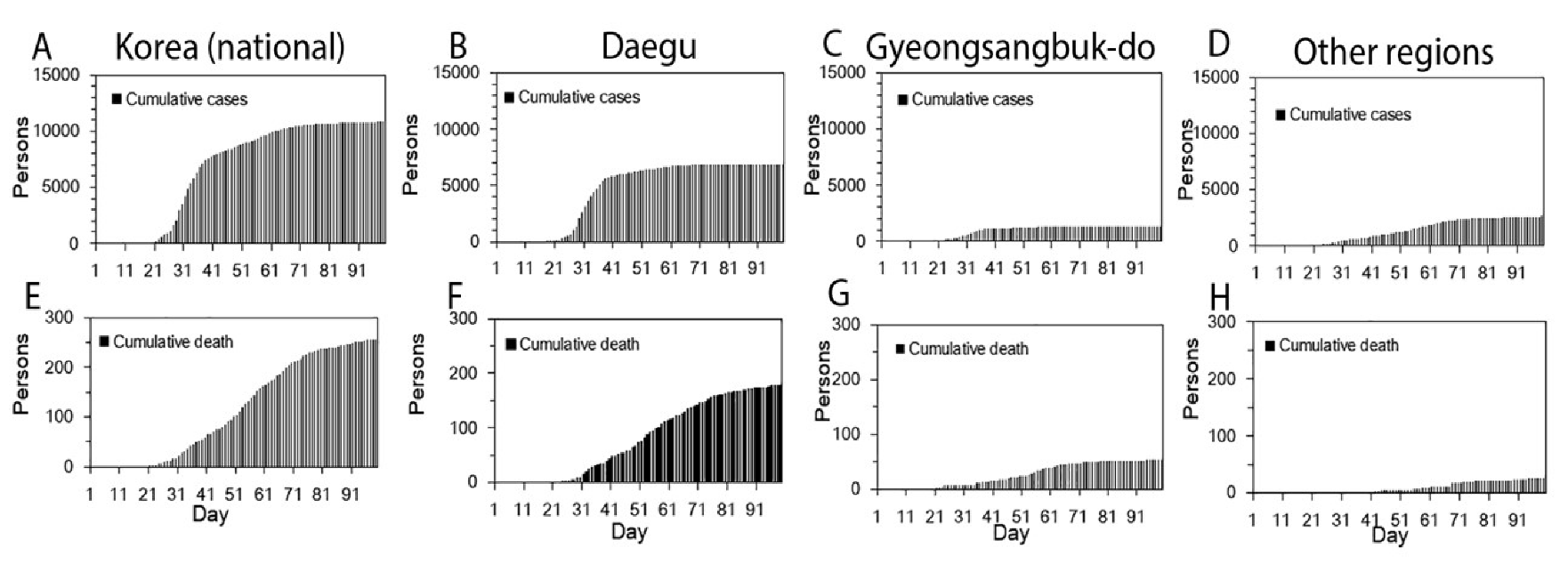
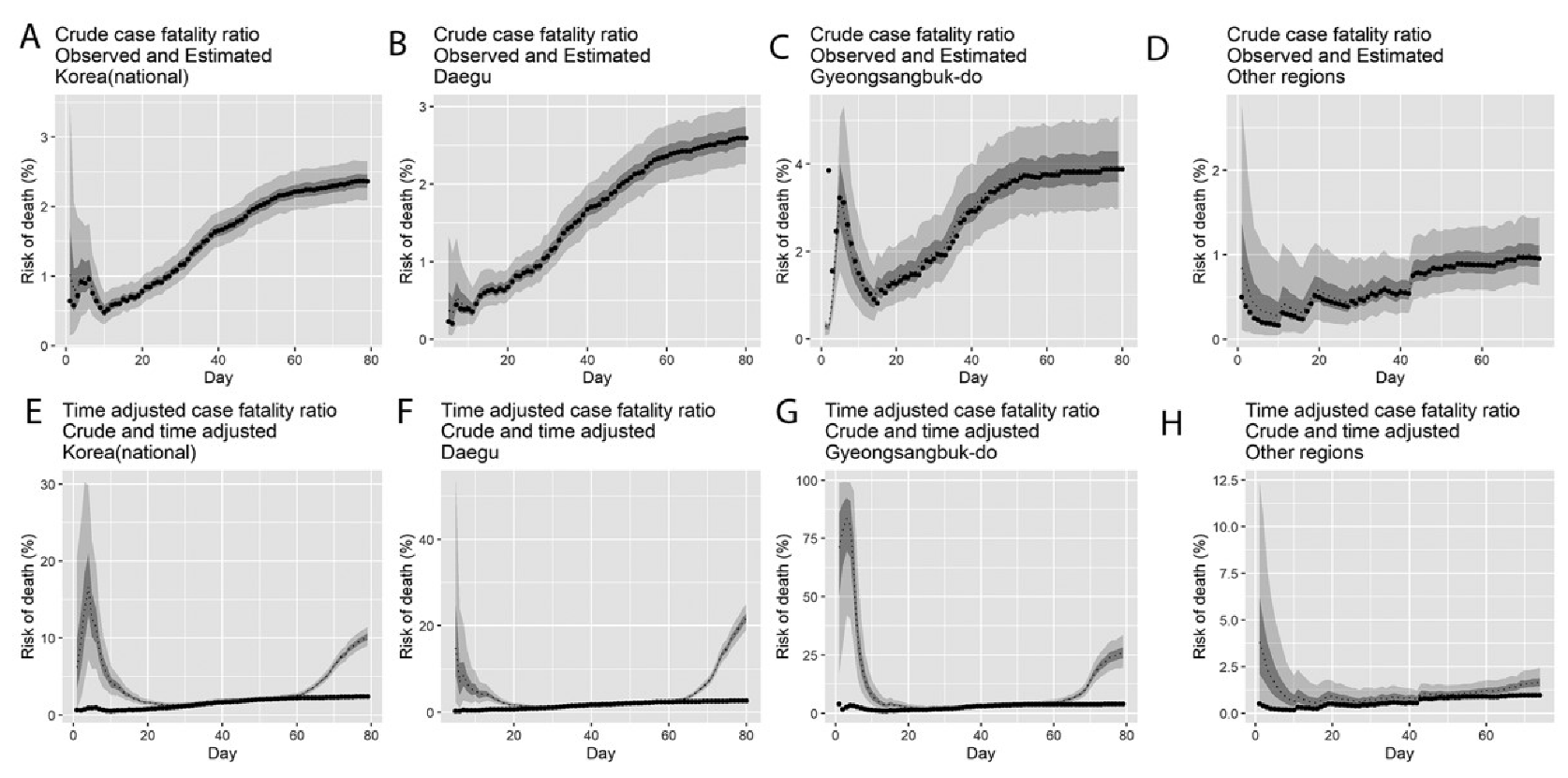
2.2. Case Fatality Ratio
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Situation Reports; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.-H. The fight against the 2019-nCoV outbreak: An arduous march has just begun. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 35, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, E.; Tariq, A.; Choi, W.; Lee, Y.; Gerardo, C. Transmission potential and severity of COVID-19 in South Korea. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KCDC. The Updates of COVID-19 in Republic of Korea; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea, 2020; Available online: https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a30402000000&bid=0030&act=view&list_no=367333&tag=&nPage=1 (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Chinese Preventive Medicine Association. An update on the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19). Chin. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Diao, M.; Yu, W.; Pei, L.; Lin, Z.; Chen, D. Estimation of the reproductive number of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) and the probable outbreak size on the Diamond Princess cruise ship: A data-driven analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.; Bergna, A.; Acciarri, C.; Galli, M.; Zehender, G. Early phylogenetic estimate of the effective reproduction number of SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Liao, J.; Yang, K.; Bai, W.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W. Preliminary prediction of the basic reproduction number of the Wuhan novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV. J. Evid. Based Med. 2020, 92, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.; Lau, E.H.; Wong, J.Y. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 13, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, K.; Kagaya, K.; Chowell, G. Early epidemiological assessment of the transmission potential and virulence of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan City: China, 2019–2020. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.M.; Bridgen, J.R.; Cummings, D.A.; Ho, A.; Jewell, C.P. Novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV: Early estimation of epidemiological parameters and epidemic predictions. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.T.; Ko, J.H.; Shin, H.; Sung, M.; Kim, J.Y. Drive-Through Screening Center for COVID-19: A Safe and Efficient Screening System against Massive Community Outbreak. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, K.; Chowell, G. Estimating Risk for Death from 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease, China, January-February 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y. Letter to the Editor: Case of the Index Patient Who Caused Tertiary Transmission of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korea: The Application of Lopinavir/Ritonavir for the Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonia Monitored by Quantitative RT-PCR. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowell, G.; Mizumoto, K. The COVID-19 pandemic in the USA: What might we expect? Lancet 2020, 395, 1093–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, H.; Klinkenberg, D.; Roberts, M.; Heesterbeek, J.A. Early epidemiological assessment of the virulence of emerging infectious diseases: A case study of an influenza pandemic. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, S.; Lee, H.; Miura, F.; Chan, Y.H.; Jung, S.-M.; Akhmetzhanov, A.R.; Nishiura, H. Dynamics of the pneumonic plague epidemic in Madagascar, August to October 2017. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamerman, D.; Lopes, H.F. Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Stochastic Simulation for Bayesian Inference; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; The Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.D.; et al. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team. The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi Zhonghua Liuxingbingxue Zazhi 2020, 41, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Bushman, M.; Kishore, N.; Niehus, R.; de Salazar, P.M.; Cowling, B.J.; Lipsitch, M.; Leung, G.M. Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Society of Infectious Diseases; Korean Society of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Korean Society of Epidemiology; Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy; Korean Society for Healthcare-associated Infection Control and Prevention; Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Report on the Epidemiological Features of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in the Republic of Korea from January 19 to March 2, 2020. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KCDC. The Updates of COVID-19 in Republic of Korea; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Korea: Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea, 2020; Available online: https://www.cdc.go.kr/board/board.es?mid=a30402000000&bid=0030 (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Lau, E.H.; Hsiung, C.A.; Cowling, B.J.; Chen, C.-H.; Ho, L.-M.; Tsang, T.; Chang, C.-W.; Donnelly, C.A.; Leung, G.M. A comparative epidemiologic analysis of SARS in Hong Kong, Beijing and Taiwan. BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessler, J.; Salje, H.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Ferguson, N.M.; Cauchemez, S.; Rodriquez-Barraquer, I.; Hakeem, R.; Jombart, T.; Aguas, R.; Al-Barrak, A. Estimating the severity and subclinical burden of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.Y.; Wu, P.; Nishiura, H.; Goldstein, E.; Lau, E.H.; Yang, L.; Chuang, S.; Tsang, T.; Peiris, J.M.; Wu, J.T. Infection fatality risk of the pandemic A (H1N1) 2009 virus in Hong Kong. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.O.; Riley, S.; Perera, R.A.; Wei, V.W.; Wu, P.; Wei, L.; Chu, D.K.; Barr, I.G.; Peiris, J.M.; Cowling, B.J. Relative incidence and individual-level severity of seasonal influenza A H3N2 compared with 2009 pandemic H1N1. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cao, P.; Du, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhuang, Z.; Yang, L.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, X.; Wang, X. Early estimation of the case fatality rate of COVID-19 in mainland China: A data-driven analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garske, T.; Legrand, J.; Donnelly, C.A.; Ward, H.; Cauchemez, S.; Fraser, C.; Ferguson, N.M.; Ghani, A.C. Assessing the severity of the novel influenza A/H1N1 pandemic. BMJ 2009, 339, b2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, C.A.; Ghani, A.C.; Leung, G.M.; Hedley, A.J.; Fraser, C.; Riley, S.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Ho, L.-M.; Thach, T.-Q.; Chau, P. Epidemiological determinants of spread of causal agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. Lancet 2003, 361, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Chowell, G.; Abdirizak, F.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Nishiura, H.; Viboud, C. Transmission characteristics of MERS and SARS in the healthcare setting: A comparative study. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 210. [Google Scholar]
- Abdirizak, F.; Lewis, R.; Chowell, G. Evaluating the potential impact of targeted vaccination strategies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) outbreaks in the healthcare setting. Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2019, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothe, C.; Schunk, M.; Sothmann, P.; Bretzel, G.; Froeschl, G.; Wallrauch, C.; Zimmer, T.; Thiel, V.; Janke, C.; Guggemos, W. Transmission of 2019-nCoV infection from an asymptomatic contact in Germany. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Liao, C.-H.; Chang, C.-F.; Chou, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-R. A locally transmitted case of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Taiwan. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y. A Familial Cluster of Infection Associated With the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Possible Person-to-Person Transmission During the Incubation Period. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 382, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizumoto, K.; Kagaya, K.; Zarebski, A.; Chowell, G. Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Yokohama, Japan, 2020. Eurosurveill. Bull. Eur. Mal. Transm. Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Song, C.; Xu, C.; Jin, G.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Ma, H.; Chen, W.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y. Clinical characteristics of 24 asymptomatic infections with COVID-19 screened among close contacts in Nanjing, China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
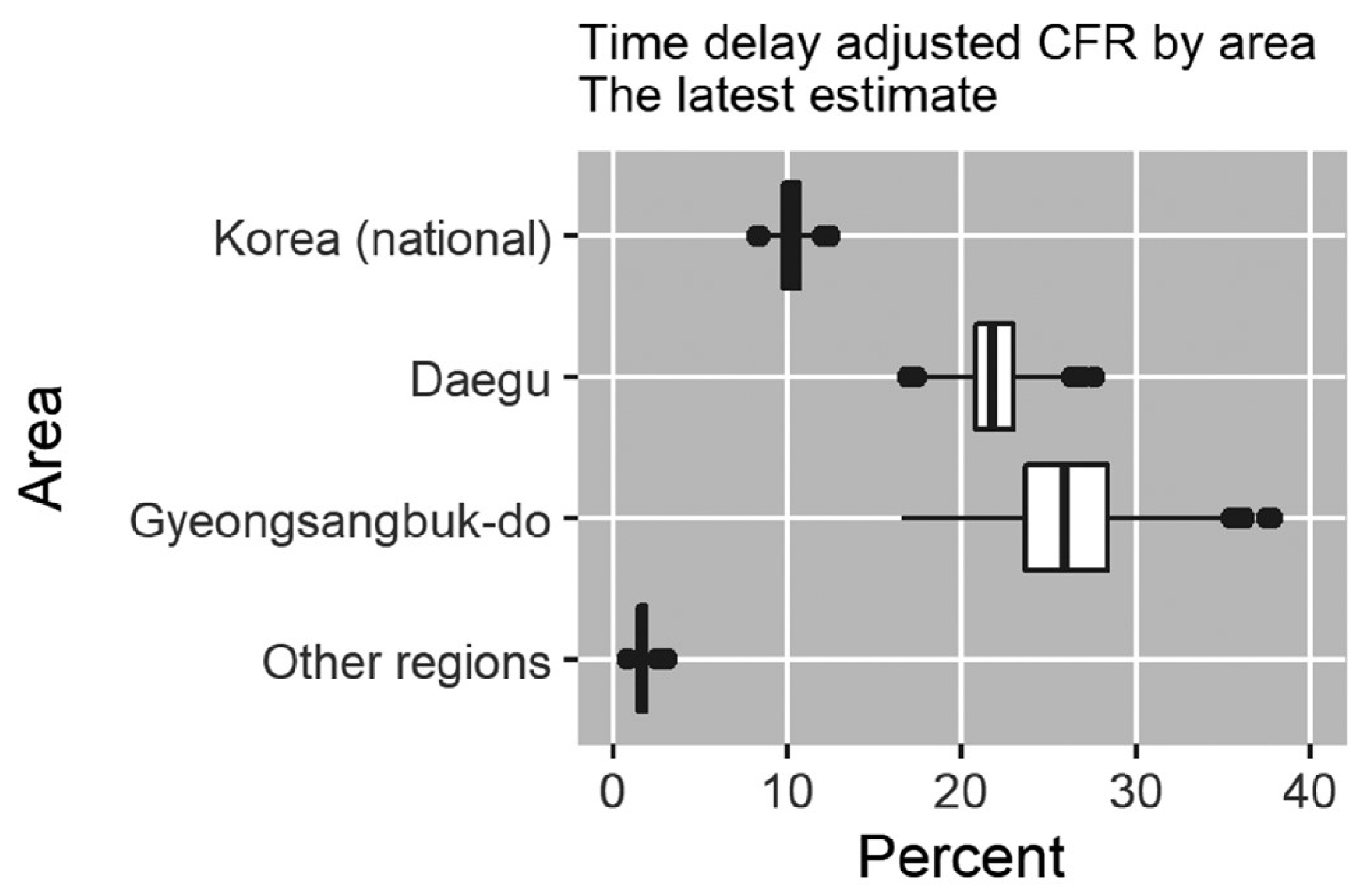
| Area | Latest Estimate | Range of Median Estimates during the Study Period | Crude CFR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Daegu | 20.8% (95% CrI §: 18.1%–24.0%) | 1.2%–20.8% | 2.6% (95% CI ¶: 2.2%–3.0%) 178/6859 |
| Gyeongsangbuk-do | 25.9% (95% CrI: 19.6%–33.6%) | 2.0%–83.6% | 3.9% (95% CI: 2.9%–5.0%) 53/1366 |
| Other regions | 1.7% (95% CrI: 1.1%–2.5%) | 0.6%–3.8% | 1.0% (95% CI: 0.6%–1.4%) 25/2615 |
| Korea (national) | 10.2% (95% CrI: 9.0%–11.5%) | 1.3%–16.6% | 2.4% (95% CI: 2.1%–2.7%) 256/10840 |
| Confirmed Cases # (%) | Deaths # (%) | Fatality Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 10,840 (100.00) | 256 (100.00) | 2.36 | |
| Sex | Male | 4406 (40.65) | 133 (51.95) | 3.02 |
| Female | 6434 (59.35) | 123 (48.05) | 1.91 | |
| Age Group | 0–9 | 141 (1.30) | 0 (0.00) | - |
| 10–19 | 594 (5.48) | 0 (0.00) | - | |
| 20–29 | 2979 (27.48) | 0 (0.00) | - | |
| 30–39 | 1177 (10.86) | 2 (0.78) | 0.17 | |
| 40–49 | 1438 (13.27) | 3 (1.17) | 0.21 | |
| 50–59 | 1958 (18.06) | 15 (5.86) | 0.77 | |
| 60–69 | 1355 (12.50) | 37 (14.45) | 2.73 | |
| 70–79 | 710 (6.55) | 77 (30.08) | 10.85 | |
| 80 and above | 488 (4.50) | 122 (47.66) | 25.00 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shim, E.; Mizumoto, K.; Choi, W.; Chowell, G. Estimating the Risk of COVID-19 Death during the Course of the Outbreak in Korea, February–May 2020. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061641
Shim E, Mizumoto K, Choi W, Chowell G. Estimating the Risk of COVID-19 Death during the Course of the Outbreak in Korea, February–May 2020. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(6):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061641
Chicago/Turabian StyleShim, Eunha, Kenji Mizumoto, Wongyeong Choi, and Gerardo Chowell. 2020. "Estimating the Risk of COVID-19 Death during the Course of the Outbreak in Korea, February–May 2020" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 6: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061641
APA StyleShim, E., Mizumoto, K., Choi, W., & Chowell, G. (2020). Estimating the Risk of COVID-19 Death during the Course of the Outbreak in Korea, February–May 2020. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061641





