Development and Validation of a Risk Score to Predict Low Birthweight Using Characteristics of the Mother: Analysis from BUNMAP Cohort in Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Study Design and Participants
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Quality Assurance Mechanisms
2.6. Data Processing and Analysis
2.6.1. Model Development and Validation
2.6.2. Risk Score Development
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographic, Obstetric, and Clinical Characteristics of Pregnant Women
3.2. A Prediction Model for Low Birthweight
3.3. Risk Classification Using a Simplified Risk Score
4. Discussion
5. Implications for Practice and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Predictor Variable * | Complete Case Analysis | Multiple Imputation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Β | SE | P-Value | β | SE | P-Value | |
| Age (<20) | 1.610 | 0.3770 | <0.001 | 1.593 | 0.3700 | <0.001 |
| Formal education (no) | 0.478 | 0.4469 | 0.2863 | 0.479 | 0.3246 | 0.2841 |
| BMI (<18.5) | 1.533 | 0.3100 | <0.001 | 1.516 | 0.3076 | <0.001 |
| Height (<155cm) | 1.235 | 0.3110 | <0.001 | 1.225 | 0.3038 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (<12.0 mg/dl) | 1.206 | 0.3024 | <0.001 | 1.213 | 0.2998 | <0.001 |
| Gravidity (prim-gravida) | 0.577 | 0.3168 | 0.0600 | 0.606 | 0.3068 | 0.0490 |
| Previous ANC (no) | 0.011 | 0.4644 | 0.9814 | 0.011 | 0.3818 | 0.9801 |
| Comorbidity § (yes) | 1.471 | 0.6221 | 0.0248 | 1.475 | 0.6043 | 0.0246 |
Appendix B
| Cutoff Point * | High Risk n (%) | Sensitivity (95%CI) | Specificity (95%CI) | PPV (95%CI) | NPV (95%CI) | LR+ (95%CI) | LR- (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 152 (40.1) | 0.81 (0.71–0.89) | 0.71 (0.66–0.76) | 0.44 (0.36–0.52) | 0.93 (0.89–0.96) | 2.81 (2.28–3.46) | 0.27 (0.17–0.42) |
| >3.5 | 133 (35.1) | 0.77 (0.67–0.86) | 0.77 (0.71–0.81) | 0.48 (0.39–0.57) | 0.92 (0.88–0.95) | 3.31 (2.61–4.19) | 0.30 (0.20–0.45) |
| >4 | 114 (30.1) | 0.72 (0.61–0.82) | 0.82 (77–86) | 0.53 (43–62) | 0.91 (87–94) | 3.96 (3.01–5.22) | 0.34 (0.24–0.48) |
| >4.5 | 76 (20.1) | 0.53 (0.42–0.64) | 0.89 (0.85–0.92) | 0.58 (0.46–0.69) | 0.87 (0.83–0.91) | 4.90 (3.34–7.21) | 0.53 (0.42–0.66) |
| >5 | 66 (17.4) | 0.49 (0.38–0.61) | 0.92 (0.88–0.94) | 0.62 (0.49–0.74) | 0.87 (0.82–0.90) | 5.85 (3.79–9.02) | 0.55 (0.45–0.69) |
| >5.5 | 42 (11.1) | 0.37 (0.27–0.49) | 0.96 (0.93–0.98) | 0.74 (0.58–0.86) | 0.85 (0.80–0.88) | 10.05 (5.28–19.12) | 0.65 (0.55–0.77) |
References
- WHO. WHO Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Low Birth Weight Policy Brief. Available online: https://www.who.int/nutrition/publications/globaltargets2025_policybrief_lbw/en/ (accessed on 17 May 2019).
- Mahumud, R.A.; Sultana, M.; Sarker, A.R. Distribution and Determinants of Low Birth Weight in Developing Countries. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2017, 50, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wado, Y.D.; Afework, M.F.; Hindin, M.J. Effects of maternal pregnancy intention, depressive symptoms and social support on risk of low birth weight: A prospective study from southwestern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roro, M.; Deressa, W.; Lindtjørn, B. Intrauterine growth patterns in rural Ethiopia compared with WHO and INTERGROWTH-21st growth standards: A community-based longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2020, 14, e0226881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonen, H.K.; Nigatu, B.; Lamers, W.H. Birth weight by gestational age and congenital malformations in Northern Ethiopia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2015, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talie, A.; Taddele, M.; Alemayehu, M. Magnitude of Low Birth Weight and Associated Factors among Newborns Delivered in Dangla Primary Hospital, Amhara Regional State, Northwest Ethiopia, 2017. J. Pregnancy 2019, 2019, 3587239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endalamaw, A.; Engeda, E.H.; Ekubagewargies, D.T.; Belay, G.M.; Tefera, M.A. Low birth weight and its associated factors in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Shastri, S.; Sharma, P. Intrauterine Growth Restriction: Antenatal and Postnatal Aspects. Clin. Med. Insights. Pediatrics 2016, 10, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.C. The Contribution of Low Birth Weight to Infant Mortality and Childhood Morbidity. J. Med. 1985, 312, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, W.J.; Kotecha, S.J.; Kotecha, S. All-Cause Mortality of Low Birthweight Infants in Infancy, Childhood, and Adolescence: Population Study of England and Wales. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, S.; Osrin, D.; Paul, E.; Costello, A. Neonatal mortality of low-birth-weight infants in Bangladesh. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 608–614. [Google Scholar]
- O’Leary, M.; Edmond, K.; Floyd, S.; Newton, S.; Thomas, G.; Thomas, S.L. A cohort study of low birth weight and health outcomes in the first year of life, Ghana. Bull World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiserud, T.; Piaggio, G.; Carroli, G.; Widmer, M.; Carvalho, J.; Jensen, L.N.; Giordano, D.; Cecatti, J.G.; Aleem, H.A.; Talegawkar, S.A.; et al. The World Health Organization fetal growth charts: A multinational longitudinal study of ultrasound biometric measurements and estimated fetal weight. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, D.; Abdollahian, M.; Marion, K. Review of low birth weight prediction models in Indonesia. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Martorell, R.; Ren, A.; Li, Z. Cognition and behavioural development in early childhood: The role of birth weight and postnatal growth. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahian, M.; Ahmad, S.; Huda, S.; Nuryani, S.; Anggraini, D. Investigating the relationship between neonatal mortality rate and mother’s characteristics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Knowledge Engineering (IKE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 16 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorghiou, A.T.; Ohuma, E.; Gravett, M.G.; Hirst, J.; Da Silveira, M.F.; Lambert, A.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A.; Altman, D.G.; Noble, J.; et al. International standards for symphysis-fundal height based on serial measurements from the fetal growth longitudinal study of the INTERGROWTH-21st project: Prospective cohort study in eight countries. BMJ 2016, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B.; Qi, L. Low birthweight and risk of type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Narváez, E.A.; Palmer, J.R.; Gerlovin, H.; Wise, L.A.; Vimalananda, V.G.; Rosenzweig, J.L.; Rosenberg, L. Birth weight and risk of type 2 diabetes in the black women’s health study: Does adult BMI play a mediating role? Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, E.; Wood, P. Birth weight and adult health in historical perspective: Evidence from a New Zealand cohort, 1907–1922. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 107, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agency, C.S. Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey; The DHS Program ICF: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, L.G.; Leland, N.L.; Alexander, G. Effect of maternal age on birth outcomes among young adolescents. Soc. Biol. 1995, 42, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Nasrullah, F.D.; Jaleel, R. Frequency and risk factors of low birth weight in term pregnancy. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Chouhan, R.; Sidhu, K. Maternal Factors for Low Birth Weight Babies. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2009, 65, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwira, A.; Stanley, C.C. Determinants of Low Birth Weight in Malawi: Bayesian Geo-Additive Modelling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achadi, E.; Jones, G. Health Sector Review: Maternal, Neonatal, and Child Health; Ministry of National Development Planning/Bappenas: Jakarta, Republic of Indonesia, 2014.
- Wachamo, T.M.; Yimer, N.B.; Bizuneh, A.D. Risk factors for low birth weight in hospitals of North Wello zone, Ethiopia: A case-control study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, T.B.; Fang, F.; O’Neill, E.; Dirienzo, G. Maternal education, birth weight, and infant mortality in the United States. Demography 2013, 50, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Arya, S.; Chellani, H.; Aggarwal, K.C.; Pandey, R.M. Prediction model for low birth weight and its validation. Indian J. Pediatrics 2014, 81, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejali, M.; Mansourian, M.; Babaei, Z.; Eshrati, B. Prediction of Low Birth Weight Delivery by Maternal Status and Its Validation: Decision Curve Analysis. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.J.A. Regression with Missing X’s: A Review. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1992, 87, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buuren, S.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K. mice: Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 45, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C.; Goel, V.; van Walraven, C. An introduction to multilevel regression models. Can. J. Public Health 2001, 92, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, S. When should epidemiologic regressions use random coefficients? Biometrics 2000, 56, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finazzi, S.; Poole, D.; Luciani, D.; Cogo, P.E.; Bertolini, G. Calibration Belt for Quality-of-Care Assessment Based on Dichotomous Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defazio, A. Classifierplots: Generates a Visualization of Classifier Performance as a Grid of Diagnostic Plots. R Package Version 1.3.3. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=classifierplots (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vickers, A.J.; Elkin, E.B. Decision curve analysis: A novel method for evaluating prediction models. Med. Decis. Mak. 2006, 26, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (TRIPOD): The TRIPOD statement. Br. J. Surg. 2015, 102, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Recommendation On Early Ultrasound in Pregnancy. Available online: https://extranet.who.int/rhl/topics/preconception-pregnancy-childbirth-and-postpartum-care/antenatal-care/who-recommendation-early-ultrasound-pregnancy (accessed on 25 May 2019).
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
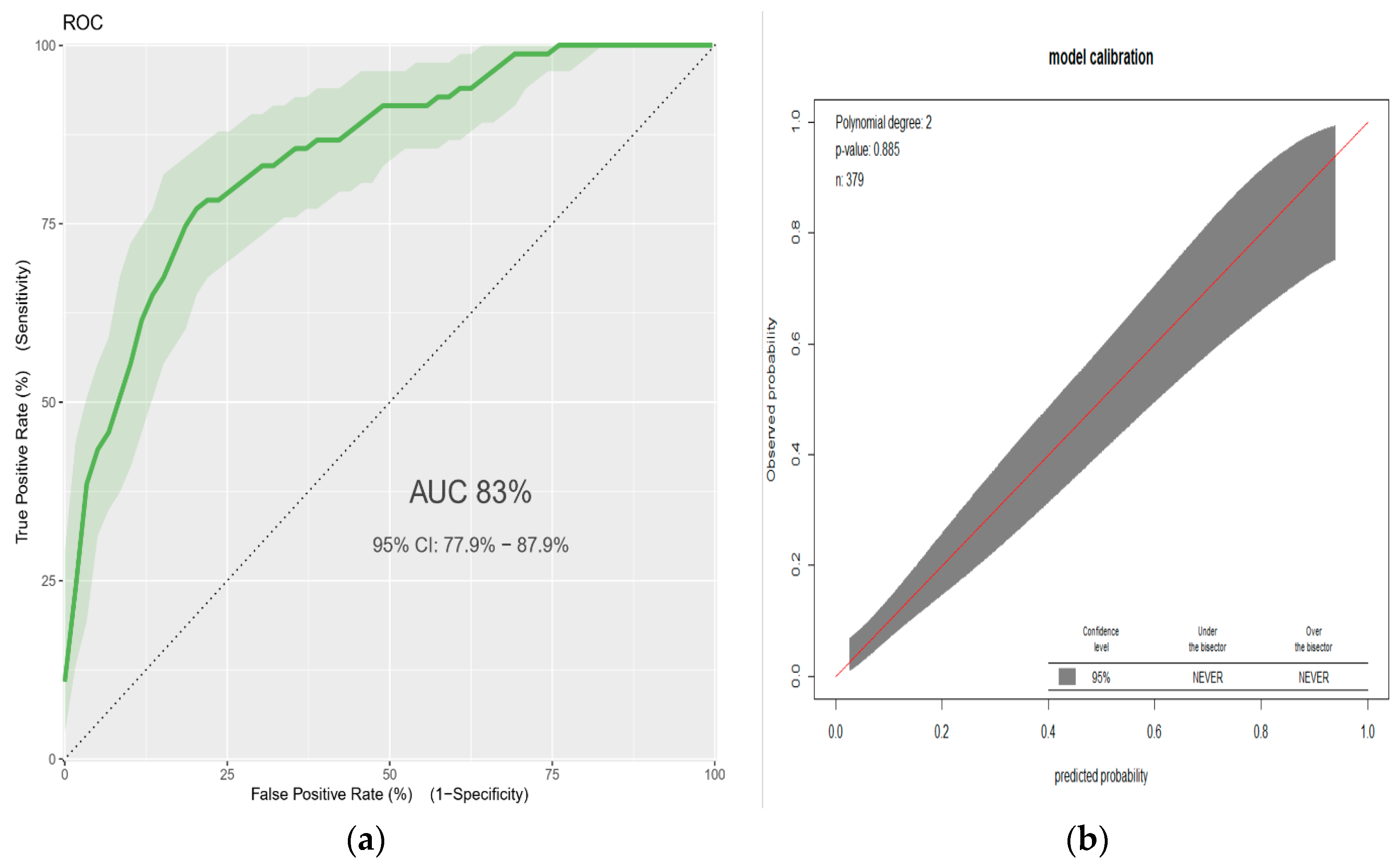
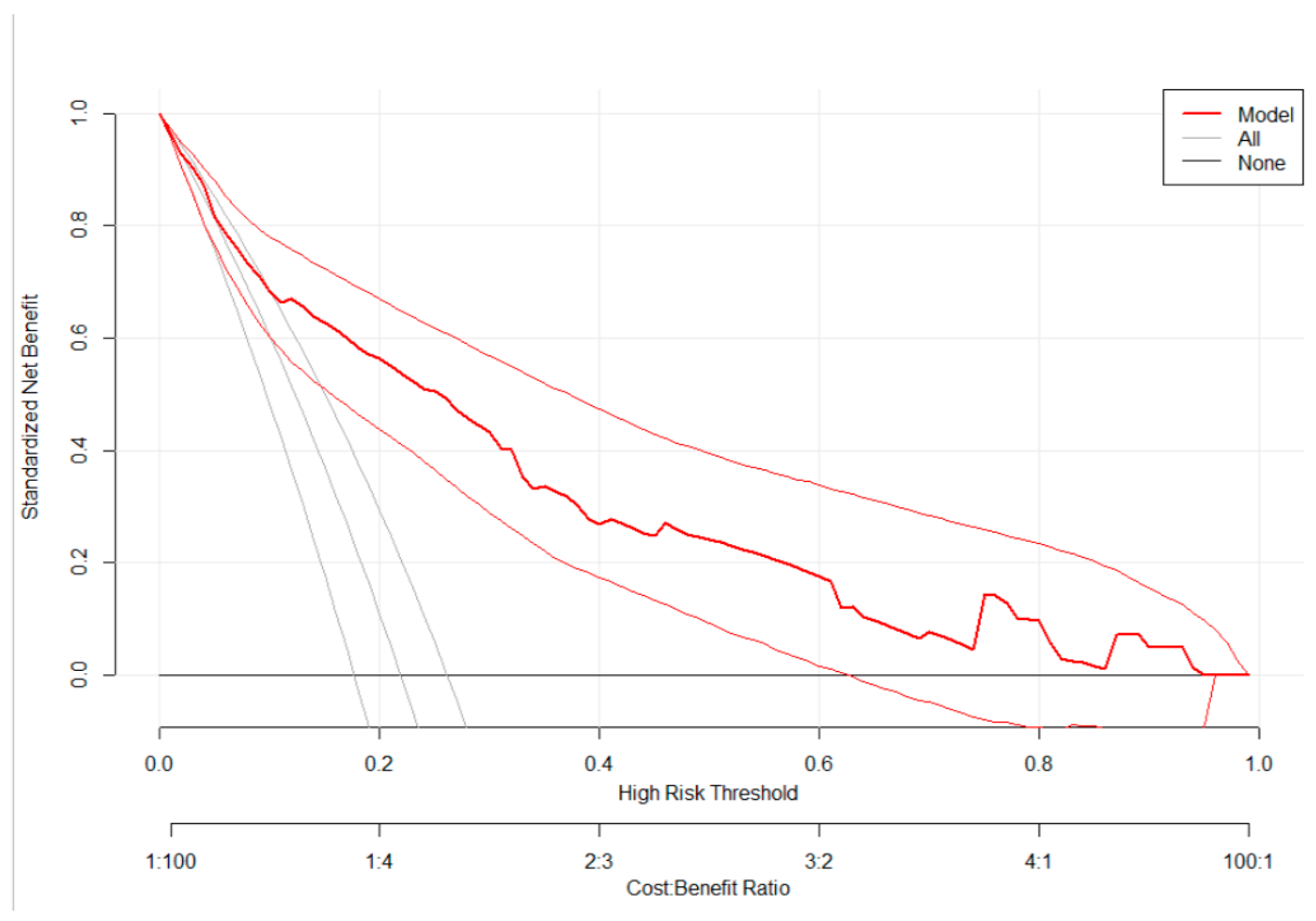
| Characteristics | Missing | Frequency | Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (<20 years) | 0 (0.0) | 51 | (13.5) |
| Marital status (without partner) | 1 (0.1) | 28 | 7.4 |
| Formal education (no) | 0 (0.0) | 221 | 58.3 |
| Gravidity (prim-gravida) | 0 (0.0) | 141 | 37.2 |
| Previous ANC (No) (n = 238) | 0 (0.0) | 69 | 29.0 |
| Intention to pregnancy (un-planned) | 0 (0.0) | 96 | 25.3 |
| Previous Family planning use (yes) | 0 (0.0) | 127 | 33.5 |
| Birth interval (<24 months) (n = 238) | 0 (0.0) | 98 | 41.2 |
| BMI (<18.5) | 7 (1.8) | 104 | 28.0 |
| Height (in cm) (<155) | 6 (1.6) | 156 | 41.8 |
| Hemoglobin (mg/dl) (<11) | 8 (2.1) | 132 | 35.6 |
| Chronic morbidity (yes) | 1 (0.1) | 16 | 4.2 |
| Alcohol (at least once/week) (yes) | 1 (0.1) | 53 | 14.0 |
| Total | 379 | 100 |
| Predictor Variable | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Simplified Risk Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β (95 % CI) | P-Value | β (95 % CI) | P-Value | ||
| Age of the mother (<20) | 1.596 (0.980, 2.222) | <0.01 ¥ | 1.593 (0.856, 2.344) | <0.01 * | 2.5 |
| Marital status (single) | 0.184 (−0.779, 1.033) | 0.69 | NA | - | - |
| Formal education (no) | 0.431 (−0.072, 0.951) | 0.098 ¥ | 0.479 (−0.382, 1.384) | 0.284 | |
| BMI (<18.5) | 1.530 (1.015, 2.053) | <0.01 ¥ | 1.516 (0.915, 2.133) | <0.01 * | 2.5 |
| Height (<155cm) | 1.032 (0.535, 1.543) | <0.01 ¥ | 1.225 (0.637, 1.838) | <0.01 * | 2 |
| Hemoglobin (<11.0 mg/dl) | 1.270 (0.768, 1.783) | <0.01 ¥ | 1.213 (0.626, 1.815) | <0.01 * | 2 |
| Gravidity (prim-gravida) | 0.586 (0.091, 1.080) | 0.02 ¥ | 0.606 (0.001, 1.215) | 0.049 * | 1 |
| Previous ANC (no) | −0.419 (−1.101, 0.288) | 0.235 ¥ | 0.011 (−0.885, 0.949) | 0.98 | - |
| Birth interval (<24month) | −0.014 (−0.691, 0.647) | 0.97 | NA | - | |
| Pregnancy (Unplanned) | 0.079 (−0.491, 0.622) | 0.78 | NA | - | |
| Family planning use (yes) | −0.127 (−0.661, 0.387) | 0.63 | NA | - | |
| Comorbidity § (yes) | 1.627 (0.608, 2.686) | <0.01 ¥ | 1.475 (0.260, 2.744) | 0.02* | 2.5 |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.169 (−0.543, 0.826) | 0.63 | NA | - | |
| Score * (Risk Category) | Prediction Model Based on Maternal Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Women | Incidence of LBW | |
| Low (<4) | 246 (64.9%) | 19 (7.7%) |
| Intermediate (4 to 6) | 91 (24.0%) | 33 (36.3%) |
| High (≥6) | 42 (11.1%) | 31 (73.8%) |
| Total | 379 (100%) | 83 (21.9%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hassen, H.Y.; Gebreyesus, S.H.; Endris, B.S.; Roro, M.A.; Van Geertruyden, J.-P. Development and Validation of a Risk Score to Predict Low Birthweight Using Characteristics of the Mother: Analysis from BUNMAP Cohort in Ethiopia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051587
Hassen HY, Gebreyesus SH, Endris BS, Roro MA, Van Geertruyden J-P. Development and Validation of a Risk Score to Predict Low Birthweight Using Characteristics of the Mother: Analysis from BUNMAP Cohort in Ethiopia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051587
Chicago/Turabian StyleHassen, Hamid Y., Seifu H. Gebreyesus, Bilal S. Endris, Meselech A. Roro, and Jean-Pierre Van Geertruyden. 2020. "Development and Validation of a Risk Score to Predict Low Birthweight Using Characteristics of the Mother: Analysis from BUNMAP Cohort in Ethiopia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051587
APA StyleHassen, H. Y., Gebreyesus, S. H., Endris, B. S., Roro, M. A., & Van Geertruyden, J.-P. (2020). Development and Validation of a Risk Score to Predict Low Birthweight Using Characteristics of the Mother: Analysis from BUNMAP Cohort in Ethiopia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051587





