Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Attention and Memory Performance: An Investigation on Duration-Based Dose-Response Relations and the Impact of Increased Arousal Levels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Data
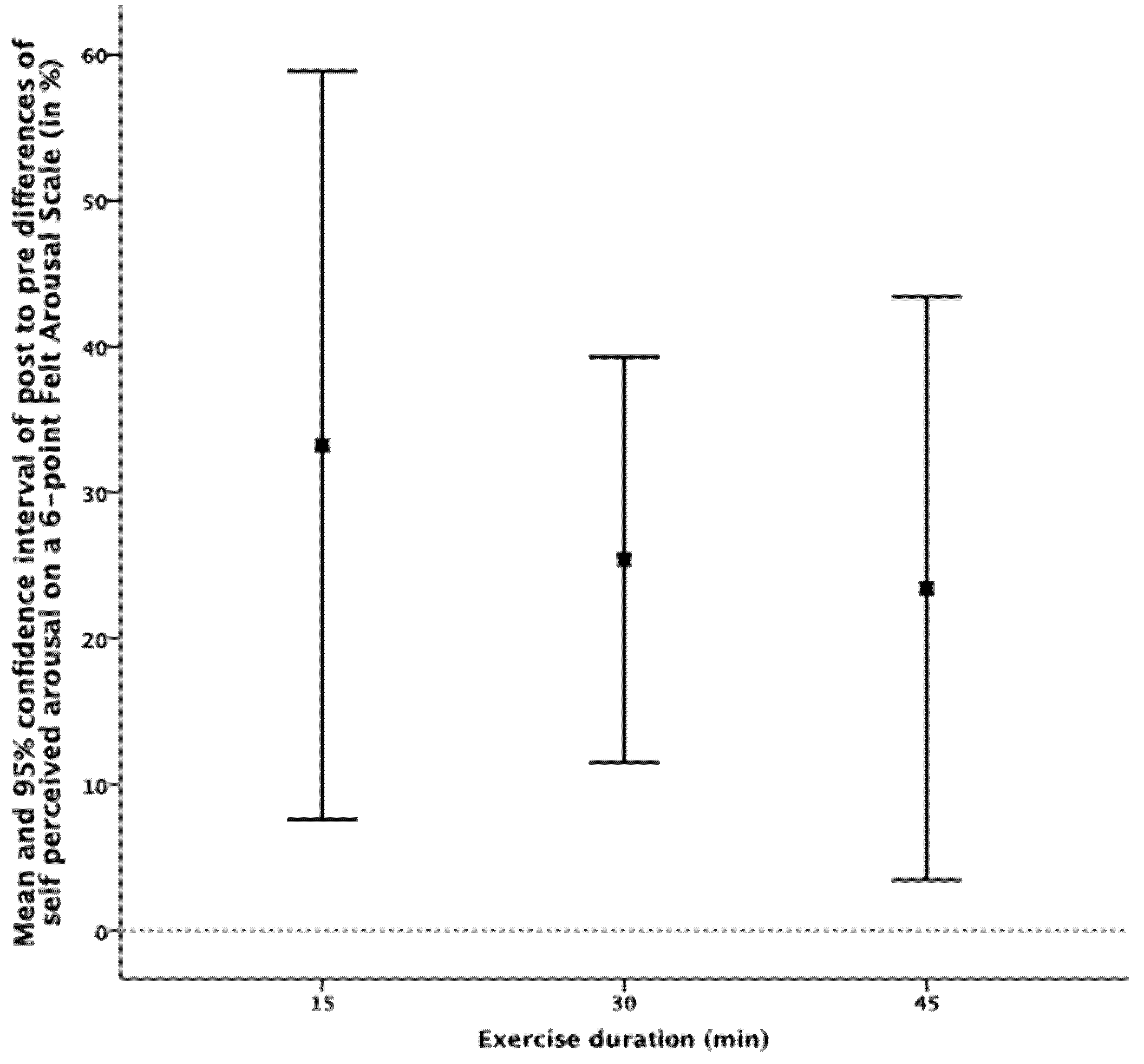
3.2. Subjective and Objective Response to Exercise and Changes in Self-Perceived Arousal
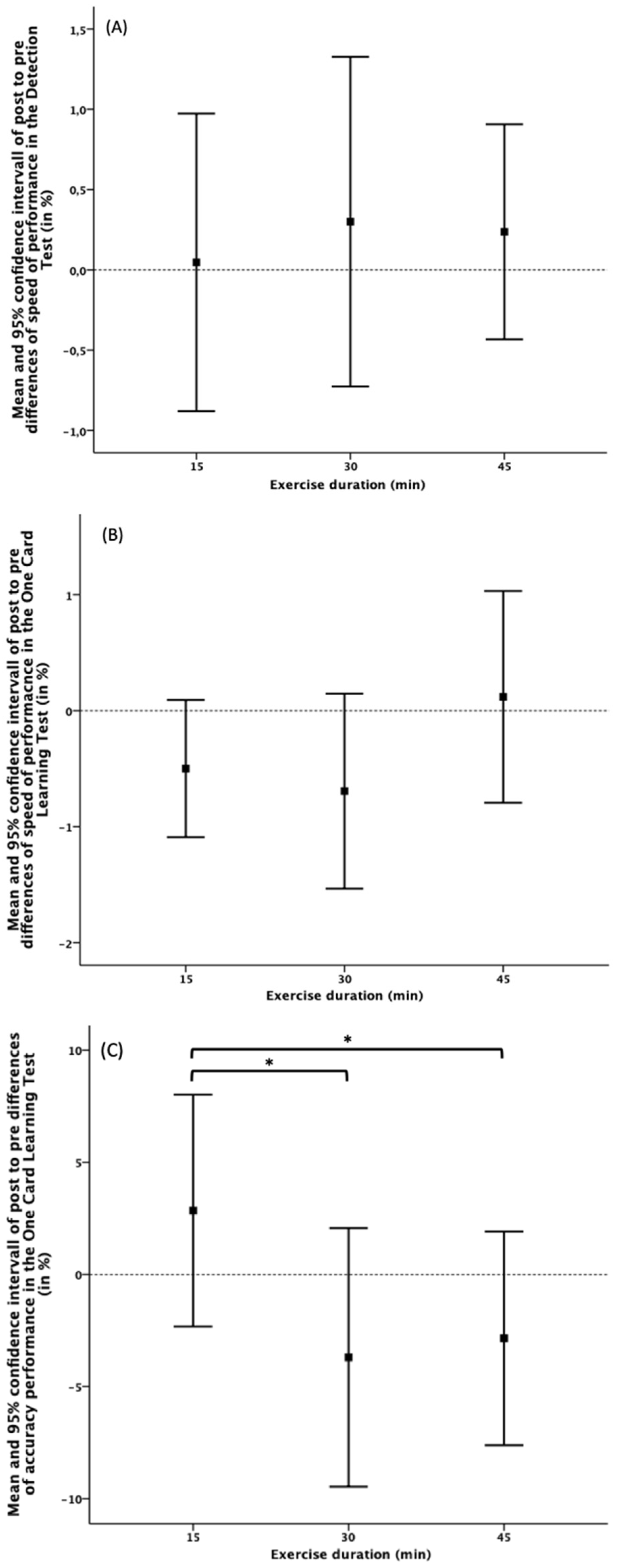
3.3. Changes in Cognitive Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tomporowski, P.D. Effects of Acute Bouts of Exercise on Cognition. Acta Psychol. 2003, 112, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.R.R.; Gualano, B.; Takao, P.P.; Avakian, P.; Fernandes, R.M.; Morine, D.; Takito, M.Y. Effects of Acute Physical Exercise on Executive Functions: A Comparison between Aerobic and Strength Exercise. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2012, 34, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-K.; Alderman, B.L.; Chu, C.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Song, T.-F.; Chen, F.-T. Acute Exercise Has a General Facilitative Effect on Cognitive Function: A Combined ERP Temporal Dynamics and BDNF Study: Acute Exercise, BDNF, ERPs, and Cognition. Psychophysiology 2017, 54, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-K.; Chi, L.; Etnier, J.L.; Wang, C.-C.; Chu, C.-H.; Zhou, C. Effect of Acute Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Performance: Role of Cardiovascular Fitness. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunsky, A.; Abu-Rukun, M.; Tsuk, S.; Dwolatzky, T.; Carasso, R.; Netz, Y. The Effects of a Resistance vs. an Aerobic Single Session on Attention and Executive Functioning in Adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Men, W.-W.; Chang, Y.-K.; Fan, M.-X.; Ji, L.; Wei, G.-X. Acute Aerobic Exercise Increases Cortical Activity during Working Memory: A Functional MRI Study in Female College Students. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontifex, M.B.; Hillman, C.H.; Fernhall, B.; Thompson, K.M.; Valentini, T.A. The Effect of Acute Aerobic and Resistance Exercise on Working Memory. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, K.; Shishido, T.; Nagatomi, R. Executive Function during and after Acute Moderate Aerobic Exercise in Adolescents. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2015, 16, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, T.; Tsai, C.; Etnier, J. Dose–Response Relation Between Exercise Duration And Cognition. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sng, E.; Frith, E.; Loprinzi, P. Temporal Effects Of Acute Walking Exercise On Learning And Memory Function. Am. J. Health Promot. 2018, 32, 1518–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambourne, K.; Audiffren, M.; Tomporowski, P.D. Effects of Acute Exercise on Sensory and Executive Processing Tasks. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, H.; Dan, I.; Tsuzuki, D.; Kato, M.; Okamoto, M.; Kyutoku, Y.; Soya, H. Acute Moderate Exercise Elicits Increased Dorsolateral Prefrontal Activation and Improves Cognitive Performance with Stroop Test. NeuroImage 2010, 50, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, K.; Hyodo, K.; Suwabe, K.; Ochi, G.; Sakairi, Y.; Kato, M.; Dan, I.; Soya, H. Positive Effect of Acute Mild Exercise on Executive Function via Arousal-Related Prefrontal Activations: An FNIRS Study. NeuroImage 2014, 98, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlwend, M.; Olsen, A.; Håberg, A.K.; Palmer, H.S. Exercise Intensity-Dependent Effects on Cognitive Control Function during and after Acute Treadmill Running in Young Healthy Adults. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.K.; Labban, J.D.; Gapin, J.I.; Etnier, J.L. The Effects of Acute Exercise on Cognitive Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Res. 2012, 1453 (Suppl. C), 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, J.; Frith, E.; Sng, E.; Loprinzi, P. Experimental Effects Of Acute Exercise On Episodic Memory Function: Considerations For The Timing Of Exercise. Psychol. Rep. 2018, 122, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, M.; Thomas, R.; Mang, C.; Snow, N.; Ostadan, F.; Boyd, L.; Lundbye-Jensen, J. Time-Dependent Effects Of Cardiovascular Exercise On Memory. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2016, 44, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loprinzi, P.; Blough, J.; Crawford, L.; Ryu, S.; Zou, L.; Li, H. The Temporal Effects of Acute Exercise on Episodic Memory Function: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etnier, J.; Wideman, L.; Labban, J.; Piepmeier, A.; Pendleton, D.; Dvorak, K.; Becofsky, K. The Effects of Acute Exercise on Memory and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2016, 38, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer-Reviewed Abstracts. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02701367.2014.930647 (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Ludyga, S.; Gerber, M.; Brand, S.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Pühse, U. Acute Effects Of Moderate Aerobic Exercise On Specific Aspects Of Executive Function In Different Age And Fitness Groups: A Meta-Analysis. Psychophysiology 2016, 53, 1611–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, D.; Chou, E. The Acute Effect of High-Intensity Exercise on Executive Function: A Meta-Analysis. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 14, 734–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crush, E.; Loprinzi, P. Dose-Response Effects of Exercise Duration and Recovery on Cognitive Functioning. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2017, 124, 1164–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, H.; Suga, T.; Takenaka, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, D.; Hamaoka, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Isaka, T. An Acute Bout of Localized Resistance Exercise Can Rapidly Improve Inhibitory Control. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-K.; Etnier, J.L.; Barella, L.A. Exploring the Relationship between Exercise-Induced Arousal and Cognition Using Fractionated Response Time. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2009, 80, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambourne, K.; Tomporowski, P. The Effect of Exercise-Induced Arousal on Cognitive Task Performance: A Meta-Regression Analysis. Brain Res. 2010, 1341, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMorris, T.; Graydon, J. The effect of incremental exercise on cognitive performance. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 2000, 31, 66–81. [Google Scholar]
- Coles, K.; Tomporowski, P.D. Effects of Acute Exercise on Executive Processing, Short-Term and Long-Term Memory. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giorno, J.M.; Hall, E.E.; O’Leary, K.C.; Bixby, W.R.; Miller, P.C. Cognitive Function during Acute Exercise: A Test of the Transient Hypofrontality Theory. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2010, 32, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamijo, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Sakai, T.; Yahiro, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nishihira, Y. Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2009, 64, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G. Psychophysical Bases of Perceived Exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, L.; Gallagher, M.J.; Robertson, R. Perceived Exertion Laboratory Manual; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, C.J.; Rejeski, W.J. Not What, but How One Feels: The Measurement of Affect during Exercise. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 1989, 11, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svebak, S.; Murgatroyd, S. Metamotivational Dominance: A Multimethod Validation Of Reversal Theory Constructs. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1985, 48, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruff, P.; Thomas, E.; Cysique, L.; Brew, B.; Collie, A.; Snyder, P.; Pietrzak, R.H. Validity of the CogState Brief Battery: Relationship to Standardized Tests and Sensitivity to Cognitive Impairment in Mild Traumatic Brain Injury, Schizophrenia, and AIDS Dementia Complex. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2009, 24, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audiffren, M.; Tomporowski, P.D.; Zagrodnik, J. Acute Aerobic Exercise and Information Processing: Modulation of Executive Control in a Random Number Generation Task. Acta Psychol. 2009, 132, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chu, C.; Chu, I.; Chan, K.; Chang, Y. Executive Function during Acute Exercise: The Role of Exercise Intensity. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2013, 35, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, B.; Balde, J.; Manjunatha, S. The Acute Effects of a Single Bout of Moderate-Intensity Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Functions in Healthy Adult Males. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMorris, T.; Sproule, J.; Turner, A.; Hale, B.J. Acute, Intermediate Intensity Exercise, and Speed and Accuracy in Working Memory Tasks: A Meta-Analytical Comparison of Effects. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 102, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangirana, P.; Sikorskii, A.; Giordani, B.; Nakasujja, N.; Boivin, M.J. Validation of the CogState Battery for Rapid Neurocognitive Assessment in Ugandan School Age Children. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Gao, C. Impaired Visual, Working, and Verbal Memory in First-Episode, Drug-naïve Patients with Major Depressive Disorder in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measure | Overall (n = 16) | Males (n = 8) | Females (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 25.69 ± 3.11 | 25.88 ± 4.09 | 25.5 ± 2.00 |
| Height (cm) | 175.13 ± 9.08 | 182.25 ± 4.17 | 168.00 ± 6.57 |
| Weight (kg) | 70.38 ± 13.67 | 82.49 ± 6.21 | 58.28 ± 5.20 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.76 ± 2.85 | 24.88 ± 2.37 | 20.64 ± 1.22 |
| HRmax (bpm) | 178.69 ± 10.00 | 183.38 ± 10.74 | 174.00 ± 6.99 |
| VO2max (mL/min/kg) | 42.33 ± 6.20 | 43.1 ± 5.92 | 41.50 ± 6.77 |
| Education (years) | 17.06 ± 1.56 | 17.13 ± 2.10 | 17.00 ± 0.89 |
| Fluid intelligence (WMT points) | 13.88 ± 2.28 | 14.38 ± 2.13 | 13.38 ± 2.45 |
| Physical activity (METh/wk) | 4920.75 ± 2490.31 | 4132.88 ± 1721.96 | 5708.63 ± 2984.17 |
| IPAQ SIT (min/day) | 466.88 ± 161.36 | 532.5 ± 182.66 | 401.25 ± 112.18 |
| Session | BL | 15 | 30 | 45 | ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | |||||
| HR | 128.29 ± 10.51 | 139.71 ± 10.26 | 141.32 ± 10.93 | 141.29 ± 10.38 | 0.769 | 0.472 |
| RPE | 12.17 ± 1.13 | 11.79 ± 1.74 | 12.2 ± 1.97 | 12.13 ± 1.74 | 0.991 | 0.383 |
| Feeling | 3.04 ± 1.23 | 3.23 ± 1.62 | 3.13 ± 1.19 | 2.97 ± 1.35 | 0.462 | 0.634 |
| Session | Pre | Post | Absolute Difference | Relative Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DETS | BL | 2.47 ± 0.05 | 2.50 ± 0.05 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 1.02 ± 1.05 |
| 15 | 2.49 ± 0.05 | 2.49 ± 0.04 | 0.00 ± 0.04 | 0.05 ± 1.74 | |
| 30 | 2.49 ± 0.07 | 2.49 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 1.93 | |
| 45 | 2.49 ± 0.07 | 2.50 ± 0.06 | 0.01 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 1.26 | |
| OCLS | BL | 2.98 ± 0.08 | 2.98 ± 0.08 | −0.01 ± 0.04 | −0.26 ± 1.22 |
| 15 | 2.98 ± 0.08 | 2.96 ± 0.09 | −0.01 ± 0.03 | −0.49 ± 1.03 | |
| 30 | 2.98 ± 0.11 | 2.95 ± 0.10 | −0.02 ± 0.04 | −0.76 ± 1.49 | |
| 45 | 2.98 ± 0.08 | 2.99 ± 0.09 | 0.00 ± 0.05 | 0.17 ± 1.61 | |
| OCLA | BL | 1.05 ± 0.07 | 1.08 ± 0.11 | 0.02 ± 0.12 | 2.46 ± 11.11 |
| 15 | 1.10 ± 0.08 | 1.13 ± 0.11 | 0.03 ± 0.11 | 2.85 ± 9.70 | |
| 30 | 1.13 ± 0.07 | 1.09 ± 0.13 | −0.04 ± 0.12 | −3.7 ± 10.82 | |
| 45 | 1.13 ± 0.08 | 1.10 ± 0.10 | −0.04 ± 0.10 | −2.85 ± 8.94 | |
| ARO | BL | 3.75 ± 1.00 | 3.38 ± 1.36 | −0.38 ± 1.31 | −6.88 ± 41.30 |
| 15 | 4.00 ± 1.21 | 4.88 ± 0.62 | 0.88 ± 1.02 | 33.23 ± 48.12 | |
| 30 | 4.19 ± 0.91 | 5.06 ± 0.57 | 0.88 ± 0.89 | 25.42 ± 26.01 | |
| 45 | 4.13 ± 1.02 | 4.81 ± 0.91 | 0.69 ± 1.35 | 23.44 ± 37.45 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hacker, S.; Banzer, W.; Vogt, L.; Engeroff, T. Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Attention and Memory Performance: An Investigation on Duration-Based Dose-Response Relations and the Impact of Increased Arousal Levels. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051380
Hacker S, Banzer W, Vogt L, Engeroff T. Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Attention and Memory Performance: An Investigation on Duration-Based Dose-Response Relations and the Impact of Increased Arousal Levels. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(5):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051380
Chicago/Turabian StyleHacker, Sebastian, Winfried Banzer, Lutz Vogt, and Tobias Engeroff. 2020. "Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Attention and Memory Performance: An Investigation on Duration-Based Dose-Response Relations and the Impact of Increased Arousal Levels" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 5: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051380
APA StyleHacker, S., Banzer, W., Vogt, L., & Engeroff, T. (2020). Acute Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Cognitive Attention and Memory Performance: An Investigation on Duration-Based Dose-Response Relations and the Impact of Increased Arousal Levels. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(5), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051380





