The Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Executive Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Design
2.3. Measures
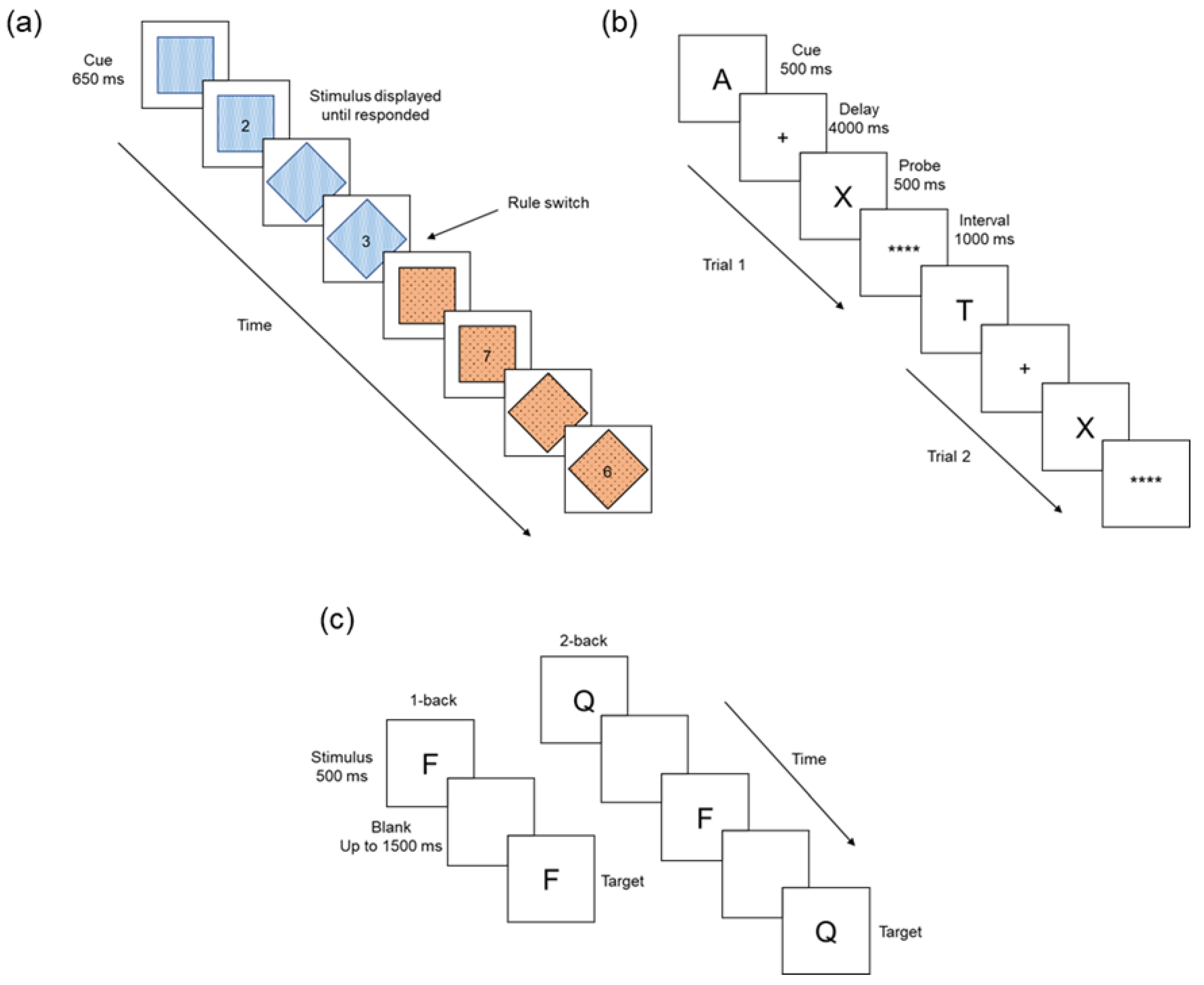
2.3.1. Number-Switching Task
2.3.2. The N-Back Task
2.3.3. The AX Continuous Performance Task
2.3.4. Subjective Measures
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
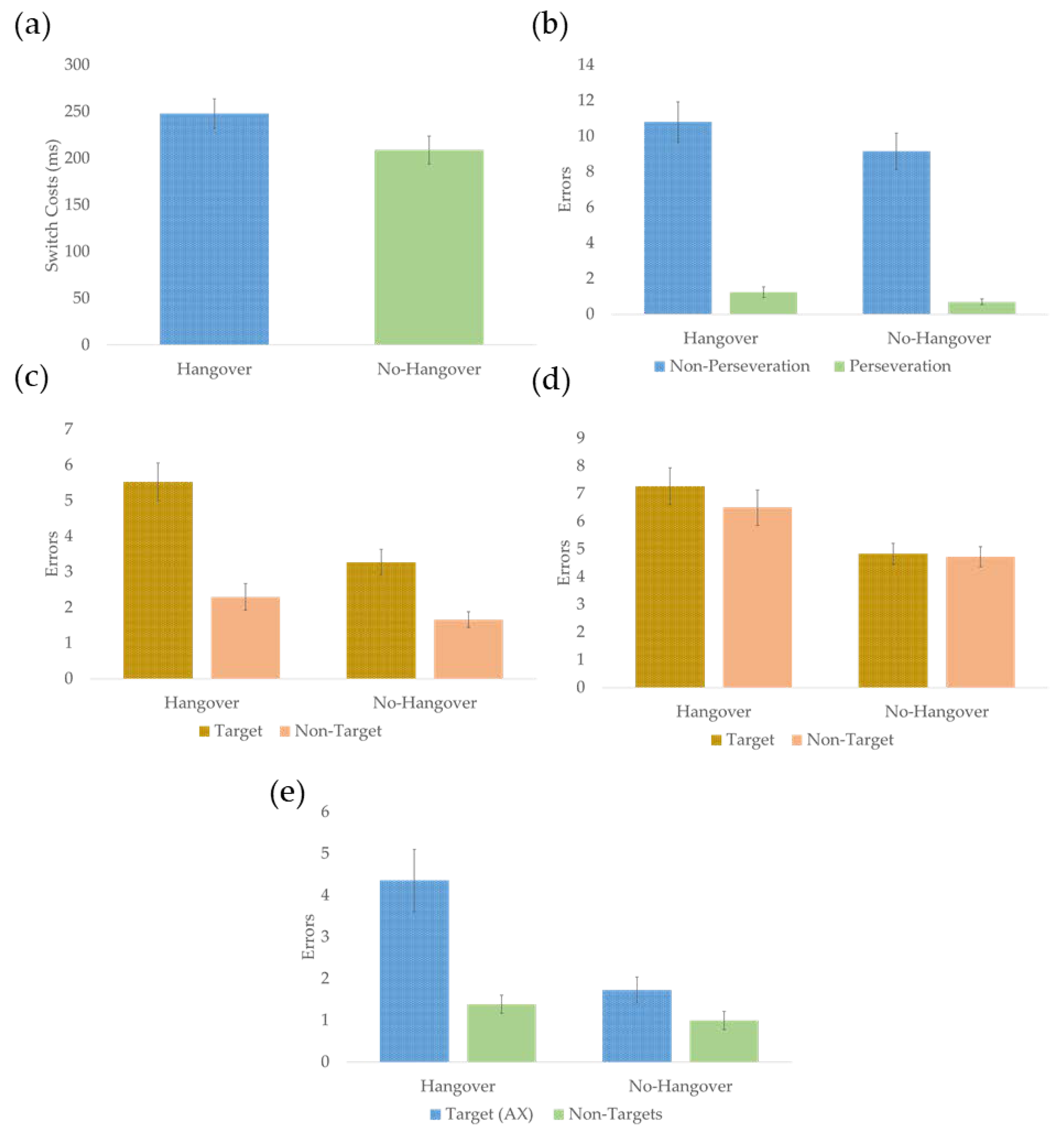
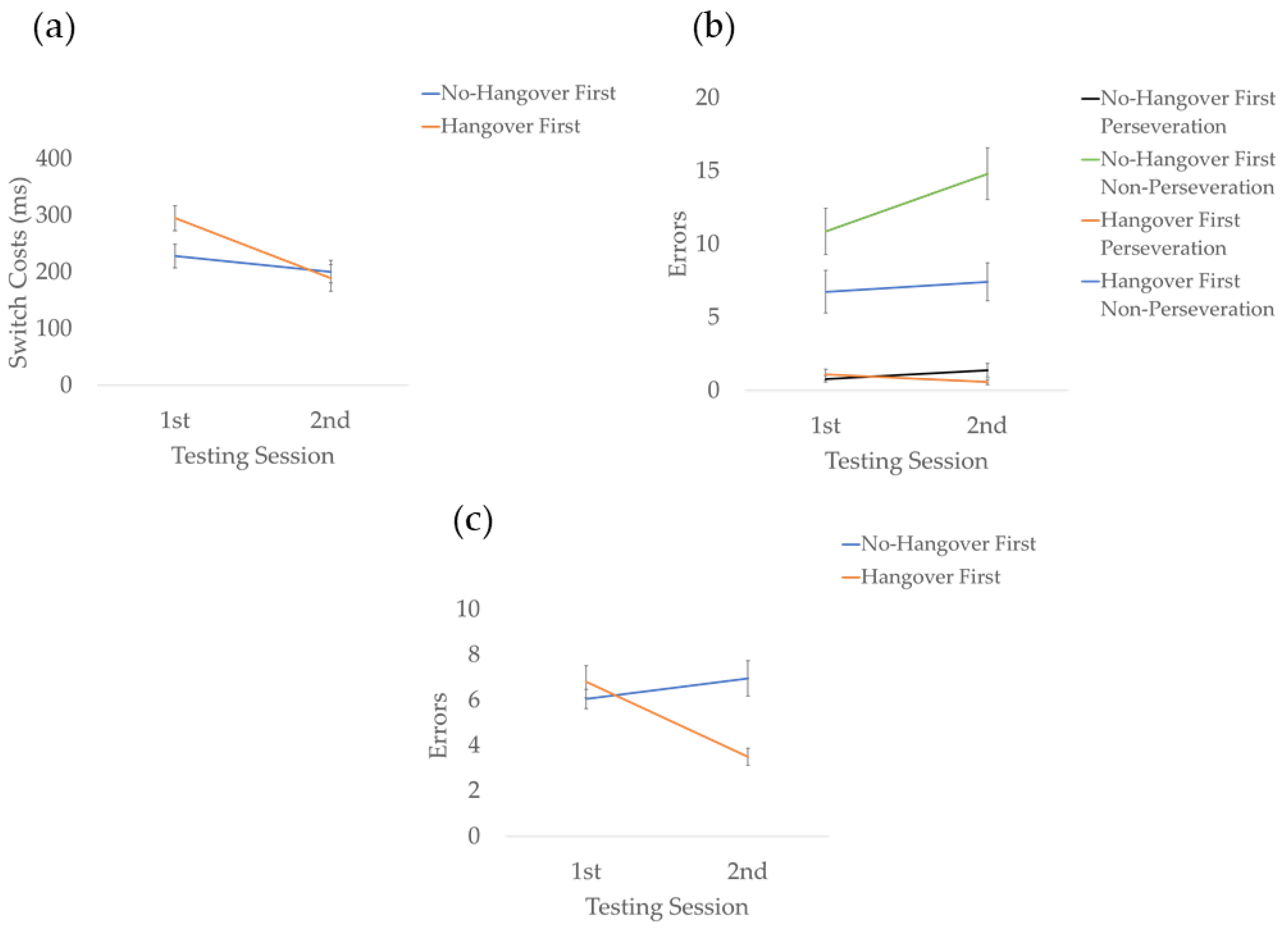
3.2. Effects of Hangover on Switching
3.3. Effects of Hangover on Updating
3.4. Effects of Hangover on Goal Maintenance
3.5. Subjective Measures
3.6. Correlational Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Schrojenstein Lantman, M.; van de Loo, A.; Mackus, M.; Verster, J. Development of a definition for the alcohol hangover: Consumer descriptions and expert consensus. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2017, 9, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, C.; Mackus, M.; Griffin, C.; Munafò, M.R.; Adams, S. A systematic review of the next-day effects of heavy alcohol consumption on cognitive performance. Addiction 2018, 113, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, R.; Kypri, K. Alcohol-related problems experienced by university students in New Zealand. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2004, 28, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devenney, L.E.; Coyle, K.B.; Verster, J.C. Cognitive performance and mood after a normal night of drinking: A naturalistic alcohol hangover study in a non-student sample. Addict. Behav. Rep. 2019, 10, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, A.; Coyle, K.; Penning, R.; Verster, J.C. Next day effects of naturalistic alcohol consumption on tasks of attention. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 27, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, C.; Verster, J.C.; Adams, S. The effects of alcohol hangover on response inhibition and attentional bias towards alcohol-related stimuli. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, X.; Bechara, A.; Dan, B.; Hanak, C.; Verbanck, P. Response inhibition deficit is involved in poor decision making under risk in nonamnesic individuals with alcoholism. Neuropsychology 2007, 21, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeichel, B.J.; Volokhov, R.N.; Demaree, H.A. Working memory capacity and the self-regulation of emotional expression and experience. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2008, 95, 1526–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howse, A.D.; Hassall, C.D.; Williams, C.C.; Hajcak, G.; Krigolson, O.E. Alcohol hangover impacts learning and reward processing within the medial-frontal cortex. Psychophysiology 2018, 2017, e13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, T.; Samuels, A.; Hamilton, C.; McGrath-Brookes, M. Alcohol hangover has detrimental impact upon both executive function and prospective memory. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, T. A state of alcohol hangover impedes everyday prospective memory. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howland, J.; Rohsenow, D.J.; Greece, J.A.; Littlefield, C.A.; Almeida, A.; Heeren, T.; Winter, M.; Bliss, C.A.; Hunt, S.; Hermos, J. The effects of binge drinking on college students’ next-day academic test-taking performance and mood state. Addiction 2010, 105, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, A. Financial Headache: The Cost of Workplace Hangovers and Intoxication to the UK Economy; Institute for Alcohol Studies: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Husain, M. Executive function and behaviour. In Proceedings of the 3rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–27 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, N.P.; Miyake, A. Unity and diversity of executive functions: Individual differences as a window on cognitive structure. Cortex 2017, 86, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lépine, R.; Bernardin, S.; Barrouillet, P. Attention switching and working memory spans. Eur. J. Cogn. Psychol. 2005, 17, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, N.; Bensmann, W.; Beste, C.; Stock, A.-K. Alcohol hangover increases conflict load via faster processing of subliminal information. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, A.; Ayre, B.; Terpstra, C.; Benson, S. Alcohol hangover results in reduced attentional resources. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 188A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, N.; Gussek, P.; Stock, A.-K.; Beste, C. Effects of high-dose ethanol intoxication and hangover on cognitive flexibility. Addict. Biol. 2016, 23, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eysenck, M.W.; Derakshan, N.; Santos, R.; Calvo, M.G. Anxiety and cognitive performance: Attentional control theory. Emotion 2007, 7, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, N.; Dalton, P. Load Theory of Attention and Cognitive Control; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 56–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lavie, N.; Hirst, A.; de Fockert, J.W.; Viding, E. Load theory of selective attention and cognitive control. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2004, 133, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.-K.; Beste, C. Binge drinking and the differential influence of ethanol on cognitive control subprocesses: A novel field of neurotoxicology. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goldstein, R.Z.; Volkow, N.D. Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: Neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, T.; Toivonen, L.; Koskinen, P.; Naveri, H.; Harkonen, M.; Leinonen, H. Effect of ethanol drinking, hangover, and exercise on adrenergic activity and heart rate variability in patients with a history of alcohol-induced atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 1998, 82, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, R.; McKinney, A.; Verster, J.C. Alcohol hangover symptoms and their contribution to the overall hangover severity. Alcohol Alcohol. 2012, 47, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Linden, D.; Frese, M.; Meijman, T.F. Mental fatigue and the control of cognitive processes: Effects on perseveration and planning. Acta Psychol. (Amst) 2003, 113, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verster, J.C.; de Klerk, S.; Bervoets, A.C.; Kruisselbrink, L.D. Editorial: Can hangover immunity be really claimed? Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2014, 6, 253–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholey, A.; Benson, S.; Kaufman, J.; Terpstra, C.; Ayre, E.; Verster, J.C.; Allen, C.; Devilly, G. Effects of alcohol hangover on cognitive performance: Findings from a field/internet mixed methodology study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devenney, L.E.; Coyle, K.B.; Verster, J.C. Memory and attention during an alcohol hangover. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speer, N.K.; Jacoby, L.L.; Braver, T.S. Strategy-dependent changes in memory: Effects on behavior and brain activity. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 3, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonthier, C.; Macnamara, B.N.; Chow, M.; Conway, A.R.A.; Braver, T.S. Inducing proactive control shifts in the AX-CPT. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botto, M.; Basso, D.; Ferrari, M.; Palladino, P. When working memory updating requires updating: Analysis of serial position in a running memory task. Acta Psychol. (Amst) 2014, 148, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.J.; Keogh, E.; Eccleston, C. Headache impairs attentional performance. Pain 2013, 154, 1840–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.J.; Eccleston, C.; Keogh, E. Cognitive load selectively influences the interruptive effect of pain on attention. Pain 2017, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Cancino, D.P.; Azpiroz-Leehan, J.; Jiménez-Angeles, L. The Effects of Sleep Deprivation in Working Memory Using the N-Back Task; IFMBE: Rome, Italy, 2015; Volume 49, pp. 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohsenow, D.J.; Howland, J.; Arnedt, J.T.; Almeida, A.B.; Greece, J.; Minsky, S.; Kempler, C.S.; Sales, S. Intoxication with Bourbon versus Vodka: Effects on hangover sleep and next-day neurocognitive performance in young adults. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verster, J.C. Sleep after an evening of heavy drinking and its impact on daytime sleepiness and alcohol hangover severity. Sleep Biol. Rhythm. 2007, 5 (Suppl. 1), A18. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.T.; Hui, C.M.; Lau, S. A depleted mind feels inefficacious: Ego-depletion reduces self-efficacy to exert further self-control. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2015, 45, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnigan, F.; Schulze, D.; Smallwood, J.; Helander, A. The effects of self-administered alcohol-induced “hangover” in a naturalistic setting on psychomotor and cognitive performance and subjective state. Addiction 2005, 100, 1680–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verster, J.C.; Van De Loo, A.J.; Adams, S.; Stock, A.; Benson, S.; Scholey, A.; Alford, C.; Bruce, G. Advantages and limitations of naturalistic study designs and their implementation in alcohol hangover research. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsell, S.; Sumner, P.; Waters, H. Task-set reconfiguration with predictable and unpredictable task switches. Mem. Cogn. 2003, 31, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attridge, N.; Eccleston, C.; Noonan, D.; Wainwright, E.; Keogh, E. Headache impairs attentional performance: A conceptual replication and extension. J. Pain 2017, 18, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braver, T.S.; Rush, B.K.; Satpute, A.B.; Racine, C.A.; Barch, D.M. Context processing and context maintenance in healthy aging and early stage dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Psychol. Aging 2005, 20, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, J.L.; Barch, D.M.; Racine, C.A.; Braver, T.S. Cognitive control, goal maintenance, and prefrontal function in healthy aging. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 1010–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kypri, K.; Langley, J.; Stephenson, S. Episode-centred analysis of drinking to intoxication in university students. Alcohol Alcohol. 2005, 40, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogewoning, A.; Van de Loo, A.; Mackus, M.; Raasveld, S.J.; De Zeeuw, R.; Bosma, E.; Bouwmeester, N.; Brrokhuis, K.A.; Garssen, J.; Verster, J.C. Characteristics of social drinkers with and without a hangover after heavy alcohol consumption. Subst. Abus. Rehabil. 2016, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zijlstra, F.R.; Van Doorn, L. The Construction of a Scale to Measure Perceived Effort; Department of Philosophy and Social Sciences, Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, C.; Fairchild, G.; Verster, J.; Adams, S. The Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Executive Functions osf.io/n3ydu. Available online: https://osf.io/n3ydu (accessed on 28 January 2019).
- Longman, C.S.; Lavric, A.; Monsell, S. The coupling between spatial attention and other components of task-set: A task-switching investigation. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2016, 69, 2248–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, F.A. Low-Dose Alcohol Effects on Human Behavior and Performance: A Review of Post-1984 Research; Oklahoma Univ Health Sciences Center Oklahoma City: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Loo, A.; Hogewoning, A.; Raasveld, S.J.; De Zeeuw, R.; Bosma, E.R.; Bouwmeester, N.H.; Lukkes, M.; Brookhuis, K.A.; Knipping, K.; Garssen, J.; et al. Saliva cytokine concentrations the day after heavy alcohol consumption in drinkers suffering from a hangover versus those who claim to be hangover resistant. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015, 50 (Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-J.; Kim, W.; Yoon, S.-J.; Choi, B.-M.; Kim, J.-S.; Go, H.J.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jeong, J. Effects of alcohol hangover on cytokine production in healthy subjects. Alcohol 2003, 31, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipple, C.T.; Benson, S.; Scholey, A. A review of the physiological factors associated with alcohol hangover. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2017, 9, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korucuoglu, O.; Sher, K.J.; Wood, P.K.; Saults, J.S.; Altamirano, L.; Miyake, A.; Bartholow, B.D. Acute alcohol effects on set-shifting and its moderation by baseline individual differences: A latent variable analysis. Addiction 2017, 112, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Hangover | No-Hangover | p | Effect Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | |||
| Switching Task | ||||||
| Switch Cost (ms) | 247.83 | 87.09 | 208.95 | 82.27 | 0.078 | d = 0.72 |
| Switch Errors | 6.01 | 2.97 | 4.92 | 2.68 | 0.019 * | d = 1.08 |
| n-back Working Memory Task | ||||||
| 1-back errors | 3.92 | 1.78 | 2.47 | 1.31 | <0.001 * | d = 1.64 |
| 2-back errors | 6.89 | 3.12 | 4.78 | 1.66 | <0.001 * | d = 1.63 |
| AX-CPT Task | ||||||
| Target Errors (AX-type trials) | 4.48 | 4.33 | 1.79 | 163 | <0.001 * | d = 1.52 |
| Non-Target Errors | 1.39 | 1.24 | 1.00 | 1.23 | 0.081 | d = 0.69 |
| Hangover Severity | ||||||
| 1-Item Hangover Severity | 3.83 | 1.84 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 * | d = 2.08 |
| mAHSS | 2.40 | 1.31 | 0.24 | 0.26 | <0.001 * | d = 1.72 |
| Alcohol Consumption | ||||||
| Alcohol Units (night before testing) | 13.28 | 5.13 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 * | d = 5.27 |
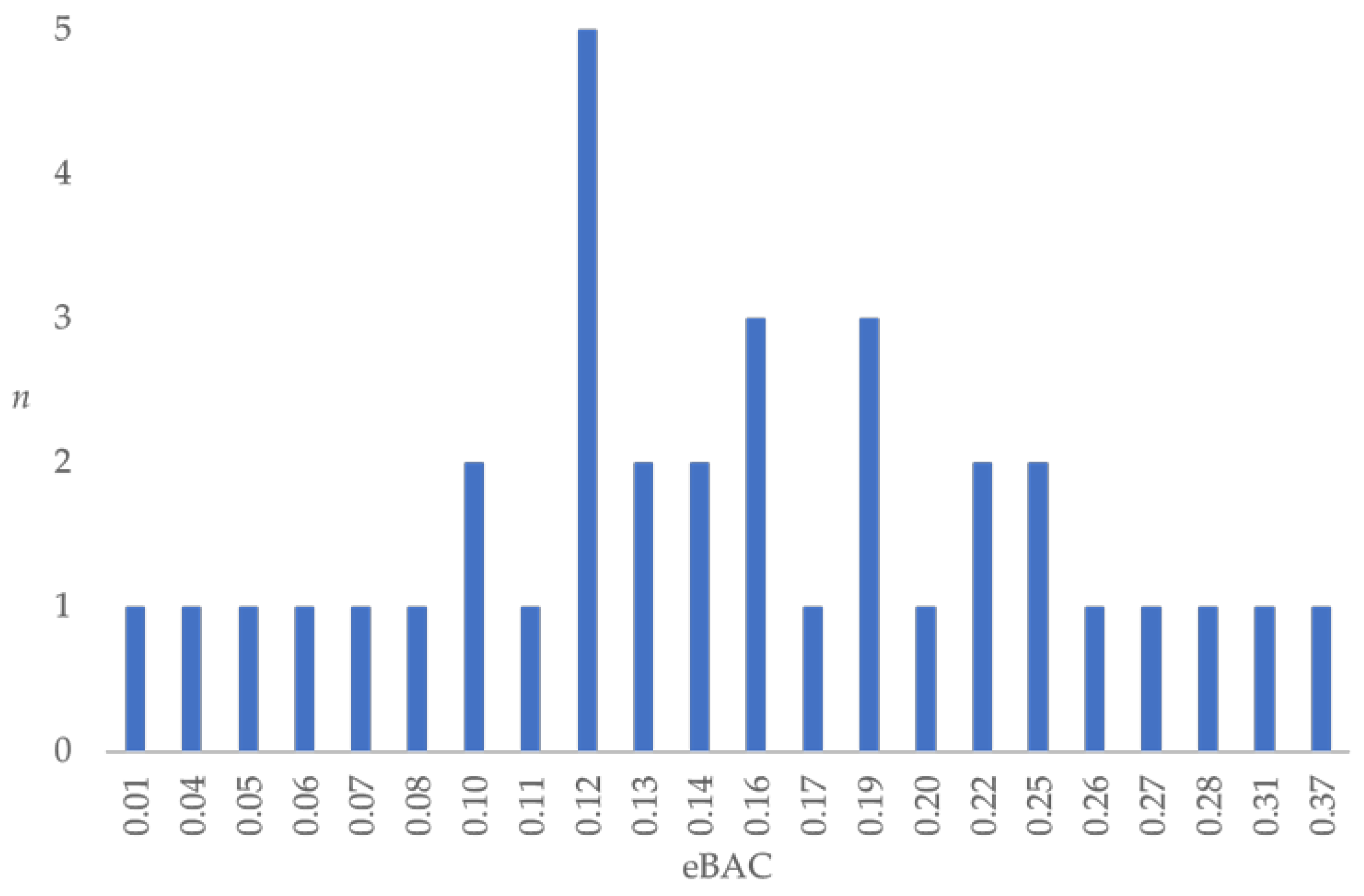
| eBAC | 0.16% | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 * | d = 4.04 |
| Subjective Measures | ||||||
| RSME Switching | 77.27 | 23.7 | 58.72 | 22.78 | 0.001 * | d = 0.72 |
| RSME n-back | 76.41 | 24.22 | 58.79 | 20.81 | 0.001 * | d = 0.65 |
| RSME AX-CPT | 59.69 | 23.70 | 47.41 | 28.67 | 0.008 * | d = 0.55 |
| Self-efficacy Switching | 6.88 | 2.14 | 8.76 | 1.28 | < 0.001 * | d = 1.00 |
| Self-efficacy n-back | 6.31 | 2.18 | 6.74 | 2.5 | 0.384 | d = 0.14 |
| Self-efficacy AX-CPT | 8.53 | 1.38 | 9.06 | 1.41 | 0.051 | d = 0.35 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunn, C.; Fairchild, G.; Verster, J.C.; Adams, S. The Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Executive Functions. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041148
Gunn C, Fairchild G, Verster JC, Adams S. The Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Executive Functions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(4):1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041148
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunn, Craig, Graeme Fairchild, Joris C. Verster, and Sally Adams. 2020. "The Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Executive Functions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 4: 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041148
APA StyleGunn, C., Fairchild, G., Verster, J. C., & Adams, S. (2020). The Effects of Alcohol Hangover on Executive Functions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(4), 1148. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041148







