Dopaminergic Degeneration and Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Who Underwent Shunt Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Imaging
2.2.1. MRI
2.2.2. 99 mTc-TRODAT-1 SPECT
2.3. Surgical Procedures
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Association between Clinical Characteristics and Imaging Biomarkers of 99 mTc-TRODAT-1 SPECT and White Matter Small Vessel Disease
3.2. Adverse Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, R.D.; Fisher, C.M.; Hakim, S.; Ojemann, R.G.; Sweet, W.H. Symptomatic Occult Hydrocephalus with “Normal” Cerebrospinal-Fluid Pressure. A Treatable Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1965, 273, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, J.J.; Kurlan, R.; Schwalb, J.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Gronseth, G.; Gloss, D. Practice guideline: Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Response to shunting and predictors of response: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2015, 85, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, J.P.; Williams, M.A.; Walker, M.L.; Kestle, J.R.W.; Relkin, N.R.; Anderson, A.M.; Gross, P.H.; Browd, S.R. Hydrocephalus Symposium Expert Panel an update on research priorities in hydrocephalus: Overview of the third National Institutes of Health-sponsored symposium “Opportunities for Hydrocephalus Research: Pathways to Better Outcomes”. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisell, M.; Tullberg, M.; Hellström, P.; Edsbagge, M.; Högfeldt, M.; Wikkelsø, C. Shunt surgery in patients with hydrocephalus and white matter changes. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allali, G.; Garibotto, V.; Mainta, I.C.; Nicastro, N.; Assal, F. Dopaminergic imaging separates normal pressure hydrocephalus from its mimics. J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, Y.; Nakayama, T.; Kanno, T.; Yoshikawa, E.; Shinke, T.; Torizuka, T. In vivo presynaptic and postsynaptic striatal dopamine functions in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaraj, D.; Wikkelsø, C.; Rabiei, K.; Marlow, T.; Jensen, C.; Östling, S.; Skoog, I. Mortality and risk of dementia in normal-pressure hydrocephalus: A population study. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrén, K.; Wikkelsø, C.; Tisell, M.; Hellström, P. Natural course of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espay, A.J.; Da Prat, G.A.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Rodriguez-Porcel, F.; Vaughan, J.E.; Rosso, M.; Devoto, J.L.; Duker, A.P.; Masellis, M.; Smith, C.D.; et al. Deconstructing normal pressure hydrocephalus: Ventriculomegaly as early sign of neurodegeneration. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaraj, D.; Agerskov, S.; Rabiei, K.; Marlow, T.; Jensen, C.; Guo, X.; Kern, S.; Wikkelsø, C.; Skoog, I. Vascular factors in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus: A population-based study. Neurology 2016, 86, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazui, H.; Miyajima, M.; Mori, E.; Ishikawa, M. SINPHONI-2 Investigators Lumboperitoneal shunt surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (SINPHONI-2): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Kato, T.; Kazui, H.; Miyake, H.; Miyajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Kuriyama, N.; Tokuda, T.; et al. Guidelines for management of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Second edition. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2012, 52, 775–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virhammar, J.; Laurell, K.; Cesarini, K.G.; Larsson, E.-M. The callosal angle measured on MRI as a predictor of outcome in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, Y.; Kazui, H.; Yoshida, T.; Kito, Y.; Kimura, N.; Tokunaga, H.; Ogino, A.; Miyake, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Takeda, M. Validation of Grading Scale for Evaluating Symptoms of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2007, 25, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, K.; Kanda, T.; Harada, A.; Miyamoto, N.; Kawaguchi, T.; Shimada, K.; Ohkawa, S.; Uemura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Mori, E. Clinical impact of the callosal angle in the diagnosis of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlund, L.O.; Barkhof, F.; Fazekas, F.; Bronge, L.; Augustin, M.; Sjögren, M.; Wallin, A.; Ader, H.; Leys, D.; Pantoni, L.; et al. A new rating scale for age-related white matter changes applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke 2001, 32, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, W.-C.; Lin, S.-Z.; Chiang, M.-F.; Pang, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-Y.; Hsin, Y.-L.; Thajeb, P.; Lee, Y.-J.; Li, H. Early-onset Parkinson’s disease in a Chinese population: 99mTc-TRODAT-1 SPECT, Parkin gene analysis and clinical study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2005, 11, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.S.; Lin, S.Z.; Lin, J.C.; Wey, S.P.; Ting, G.; Liu, R.S. Evaluation of early-stage Parkinson’s disease with 99mTc-TRODAT-1 imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Israelsson, H.; Carlberg, B.; Wikkelsø, C.; Laurell, K.; Kahlon, B.; Leijon, G.; Eklund, A.; Malm, J. Vascular risk factors in INPH: A prospective case-control study (the INPH-CRasH study). Neurology 2017, 88, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Straaten, E.C.W.; Fazekas, F.; Rostrup, E.; Scheltens, P.; Schmidt, R.; Pantoni, L.; Inzitari, D.; Waldemar, G.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Mäntylä, R.; et al. Impact of white matter hyperintensities scoring method on correlations with clinical data: The LADIS study. Stroke 2006, 37, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alperin, N.; Oliu, C.J.; Bagci, A.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kovanlikaya, I.; Adams, D.; Katzen, H.; Ivkovic, M.; Heier, L.; Relkin, N. Low-dose acetazolamide reverses periventricular white matter hyperintensities in iNPH. Neurology 2014, 82, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, P.K.; Sorteberg, W. Changes in intracranial pulse pressure amplitudes after shunt implantation and adjustment of shunt valve opening pressure in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. 2008, 150, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, P.K.; Sorteberg, W. Diagnostic intracranial pressure monitoring and surgical management in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A 6-year review of 214 patients. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, A.J.; Tans, J.T.; Delwel, E.J.; Egeler-Peerdeman, S.M.; Hanlo, P.W.; Wurzer, H.A.; Avezaat, C.J.; de Jong, D.A.; Gooskens, R.H.; Hermans, J. Dutch normal-pressure hydrocephalus study: Prediction of outcome after shunting by resistance to outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 87, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bech, R.A.; Juhler, M.; Waldemar, G.; Klinken, L.; Gjerris, F. Frontal brain and leptomeningeal biopsy specimens correlated with cerebrospinal fluid outflow resistance and B-wave activity in patients suspected of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama, N.; Tokuda, T.; Miyamoto, J.; Takayasu, N.; Kondo, M.; Nakagawa, M. Retrograde jugular flow associated with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, G.A.; Smith, R.L.; Siddique, S.H. Idiopathic hydrocephalus in children and idiopathic intracranial hypertension in adults: Two manifestations of the same pathophysiological process? J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, G.A. Magnetic resonance imaging quantification of compliance and collateral flow in late-onset idiopathic aqueductal stenosis: Venous pathophysiology revisited. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovanes, G.I.; McAllister, J.P.; Lamperti, A.A.; Salotto, A.G.; Truex, R.C. Monoamine alterations during experimental hydrocephalus in neonatal rats. Neurosurgery 1988, 22, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tullberg, M.; Jensen, C.; Ekholm, S.; Wikkelsø, C. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: Vascular white matter changes on MR images must not exclude patients from shunt surgery. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2001, 22, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baroncini, M.; Balédent, O.; Ardi, C.E.; Delannoy, V.D.; Kuchcinski, G.; Duhamel, A.; Ares, G.S.; Lejeune, J.-P.; Hodel, J. Ventriculomegaly in the Elderly: Who Needs a Shunt? A MRI Study on 90 Patients. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2018, 126, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allali, G.; Garibotto, V.; Assal, F. Parkinsonism Differentiates Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus from Its Mimics. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 54, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, T.; Foote, K.D.; Okun, M.S. INPH and Parkinson disease: Differentiation by levodopa response. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bigio, M.R.; Vriend, J.P. Monoamine neurotransmitters and amino acids in the cerebrum and striatum of immature rats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. Brain Res. 1998, 798, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markianos, M.; Lafazanos, S.; Koutsis, G.; Sfagos, C.; Seretis, A. CSF neurotransmitter metabolites and neuropsychiatric symptomatology in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daou, B.; Klinge, P.; Tjoumakaris, S.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Jabbour, P. Revisiting secondary normal pressure hydrocephalus: Does it exist? A review. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerskov, S.; Wallin, M.; Hellström, P.; Ziegelitz, D.; Wikkelsø, C.; Tullberg, M. Absence of Disproportionately Enlarged Subarachnoid Space Hydrocephalus, a Sharp Callosal Angle, or Other Morphologic MRI Markers Should Not Be Used to Exclude Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus from Shunt Surgery. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.M.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Kafka, B.; Caruso, J.P.; Neeley, O.J.; Plitt, A.R.; Aoun, S.G.; Olson, D.; Ruchinskas, R.A.; Cullum, C.M.; et al. Clinical outcomes of normal pressure hydrocephalus in 116 patients: Objective versus subjective assessment. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-G.; Kang, K.; Jung, J.-Y.; Park, S.-P.; Lee, M.-G.; Lee, H.-W. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus, quantitative EEG findings, and the cerebrospinal fluid tap test: A pilot study. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 31, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, M.; Kazui, H.; Mori, E.; Ishikawa, M. One-year outcome in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Comparison of lumboperitoneal shunt to ventriculoperitoneal shunt. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.C.G.; Saad, F.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Pereira, R.M.; de Miranda, F.L.; Tornai, J.B.; Lopes, M.I.R.; Ribas, E.S.C.; Valinetti, E.A.; Teixeira, M.J. Role of endoscopic third ventriculostomy and ventriculoperitoneal shunt in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Preliminary results of a randomized clinical trial. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordan, E.; Palandri, G.; Lanzino, G.; Murad, M.H.; Elder, B.D. Outcomes and complications of different surgical treatments for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, M.; Redaelli, V.; Tringali, G.; Restelli, F.; Romito, L.; Schiavolin, S.; Tagliavini, F.; Broggi, G. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus and Parkinsonism: Preliminary Data on Neurosurgical and Neurological Treatment. World Neurosurg. 2016, 90, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molde, K.; Söderström, L.; Laurell, K. Parkinsonian symptoms in normal pressure hydrocephalus: A population-based study. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hamdeh, S.; Virhammar, J.; Sehlin, D.; Alafuzoff, I.; Cesarini, K.G.; Marklund, N. Brain tissue Aβ42 levels are linked to shunt response in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeraniec, I.J.; Bond, A.E.; Lopes, M.B.; Jane, J.A. Concurrent Alzheimer’s pathology in patients with clinical normal pressure hydrocephalus: Correlation of high-volume lumbar puncture results, cortical brain biopsies, and outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppsson, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Wikkelsø, C. Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Pathophysiology and diagnosis by CSF biomarkers. Neurology 2013, 80, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, M.; Miyajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Ogino, I.; Arai, H. Impact of cerebrospinal fluid shunting for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus on the amyloid cascade. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan-Olive, M.M.; Enger, R.; Hansson, H.-A.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Eide, P.K. Loss of perivascular aquaporin-4 in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Glia 2019, 67, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S.; Binder, D.K.; Bloch, O.; Auguste, K.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Three distinct roles of aquaporin-4 in brain function revealed by knockout mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szu, J.I.; Binder, D.K. The Role of Astrocytic Aquaporin-4 in Synaptic Plasticity and Learning and Memory. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
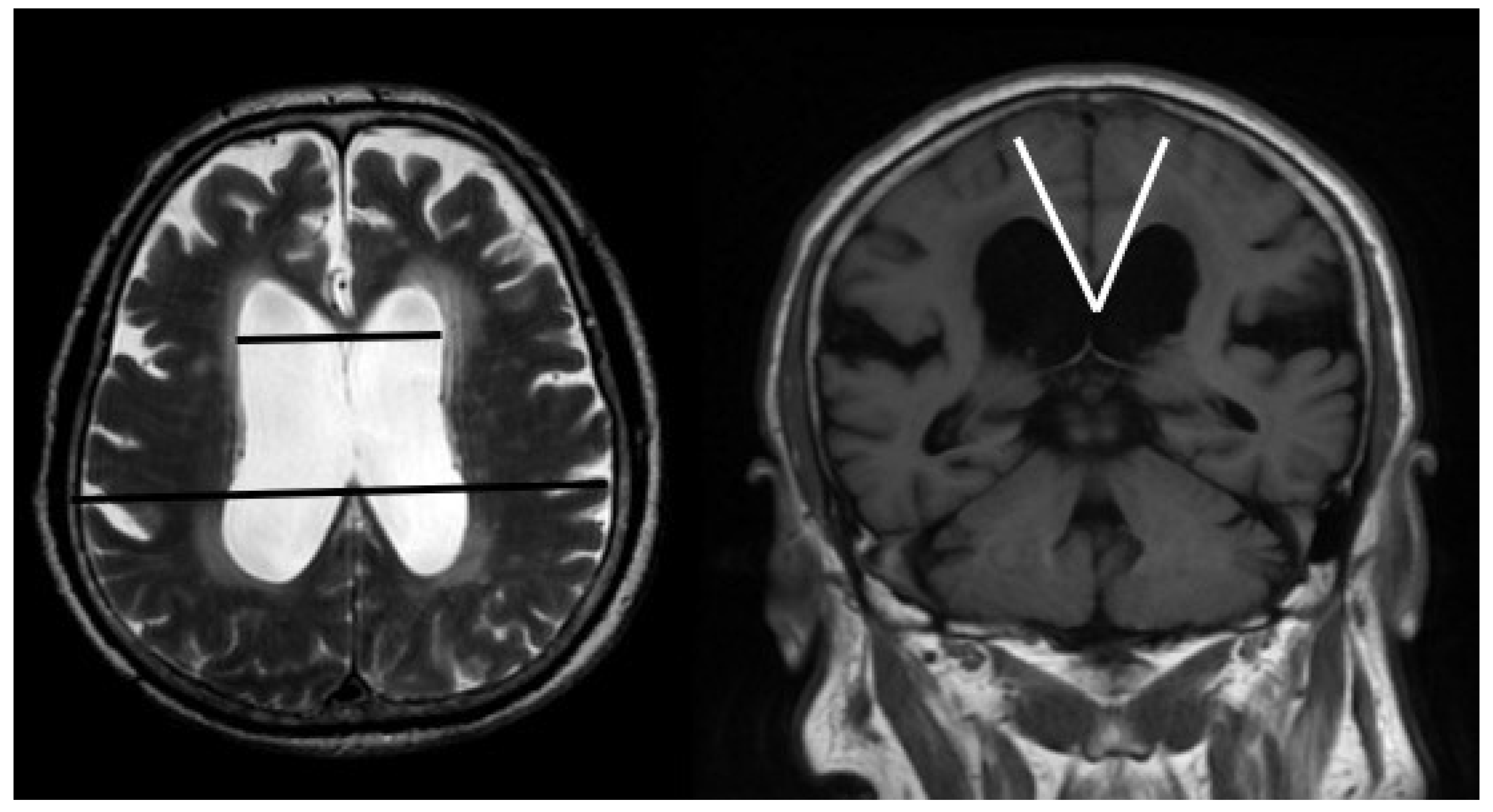
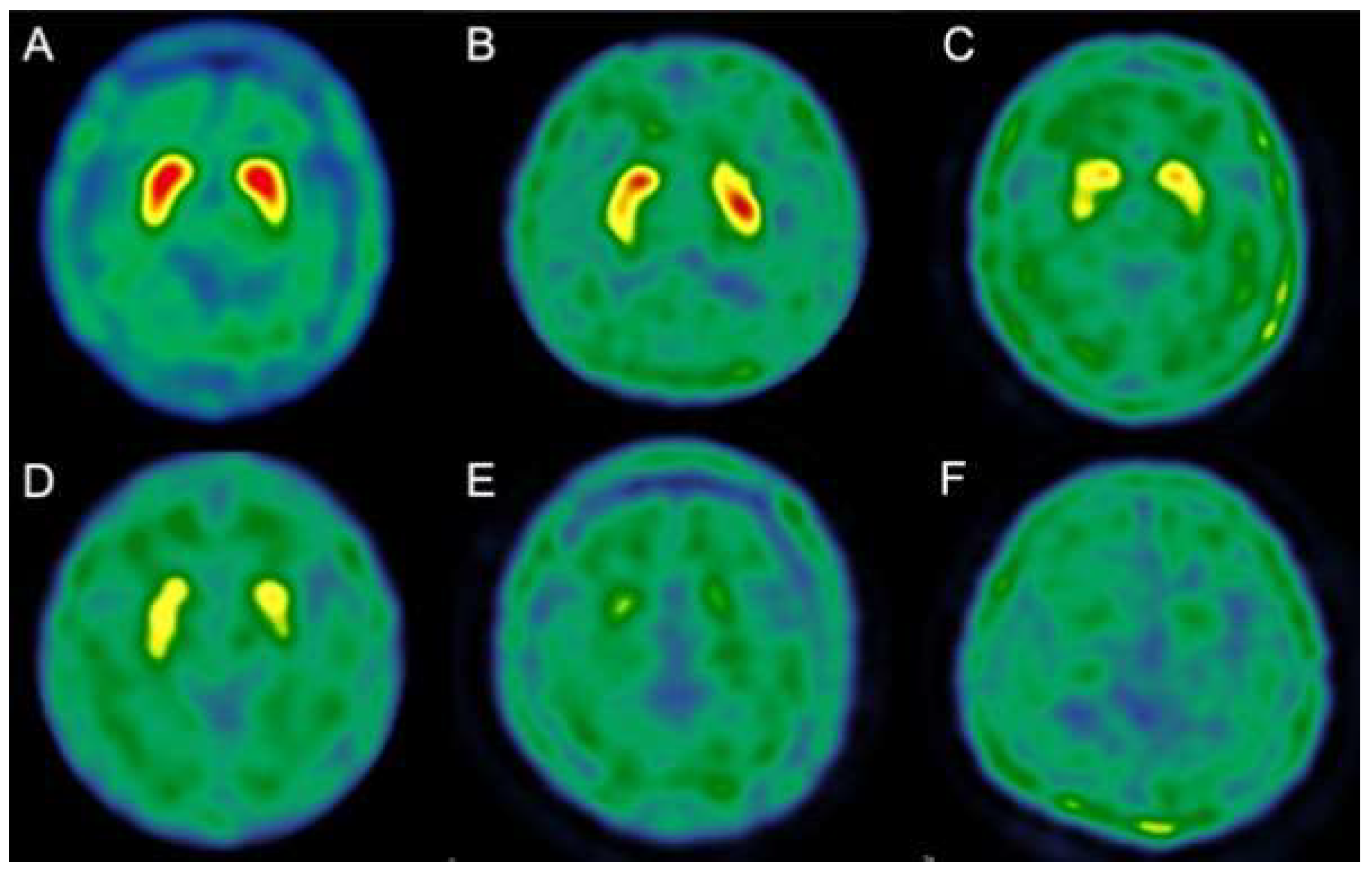
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 75 ± 9.9 |
| Male, Sex | 26 (66.67%) |
| HTN | 23 (58.97%) |
| DM | 9 (23.08%) |
| CAD | 3 (7.69%) |
| CKD | 6 (15.38%) |
| BPH | 10 (38.46%) |
| 99 mTc-TRODAT-1 stages | |
| Average | 2.1 ± 1.2 (0~4) |
| White matter small vessel disease (Fazekas scores) | |
| Periventricular area | 1.6 ± 0.9 (0~3) |
| Putamen | 0.4 ± 0.5 (0~2) |
| Karnofsky Performance Scale | |
| Pre-operative | 56.9 ± 11.8 (30~80) |
| Post-operative | 71 ± 11.9 (50~90) |
| iNPHGS | |
| Pre-operative scores | 7.8 ± 2.6 (5~12) |
| Cognition | 2.3 ± 1 (1~4) |
| Gait | 2.9 ± 0.8 (2~4) |
| Urinary function | 2.5 ± 1.3 (1~4) |
| Post-operative scores | 5.7 ± 2.6 (5~9) |
| Cognition | 2 ± 1 (1~3) |
| Gait | 1.7 ± 0.8 (0~2) |
| Urinary function | 2.0 ± 1.3 (0~3) |
| Intra-cranial pressure (lumbar puncture) | |
| Opening pressure | 11.7 ± 4.6 (4~20) |
| Close pressure | 5.4 ± 3.1 (0~13) |
| Pressure gradient | 6.5 ± 2.9 (3~14) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, T.-W.; Tseng, P.-H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Tseng, G.-F.; Chiu, T.-L.; Lin, S.-Z.; Tsai, S.-T. Dopaminergic Degeneration and Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Who Underwent Shunt Surgery. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041084
Chang T-W, Tseng P-H, Wang Y-C, Tseng G-F, Chiu T-L, Lin S-Z, Tsai S-T. Dopaminergic Degeneration and Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Who Underwent Shunt Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(4):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041084
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Tze-Wei, Pao-Hui Tseng, Yi-Cheng Wang, Guo-Fang Tseng, Tsung-Lang Chiu, Shinn-Zong Lin, and Sheng-Tzung Tsai. 2020. "Dopaminergic Degeneration and Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Who Underwent Shunt Surgery" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 4: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041084
APA StyleChang, T.-W., Tseng, P.-H., Wang, Y.-C., Tseng, G.-F., Chiu, T.-L., Lin, S.-Z., & Tsai, S.-T. (2020). Dopaminergic Degeneration and Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Who Underwent Shunt Surgery. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(4), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9041084





