The Dynamics of Respiratory Microbiota during Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Study Design
2.2. DNA Extraction PCR and Sequencing
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
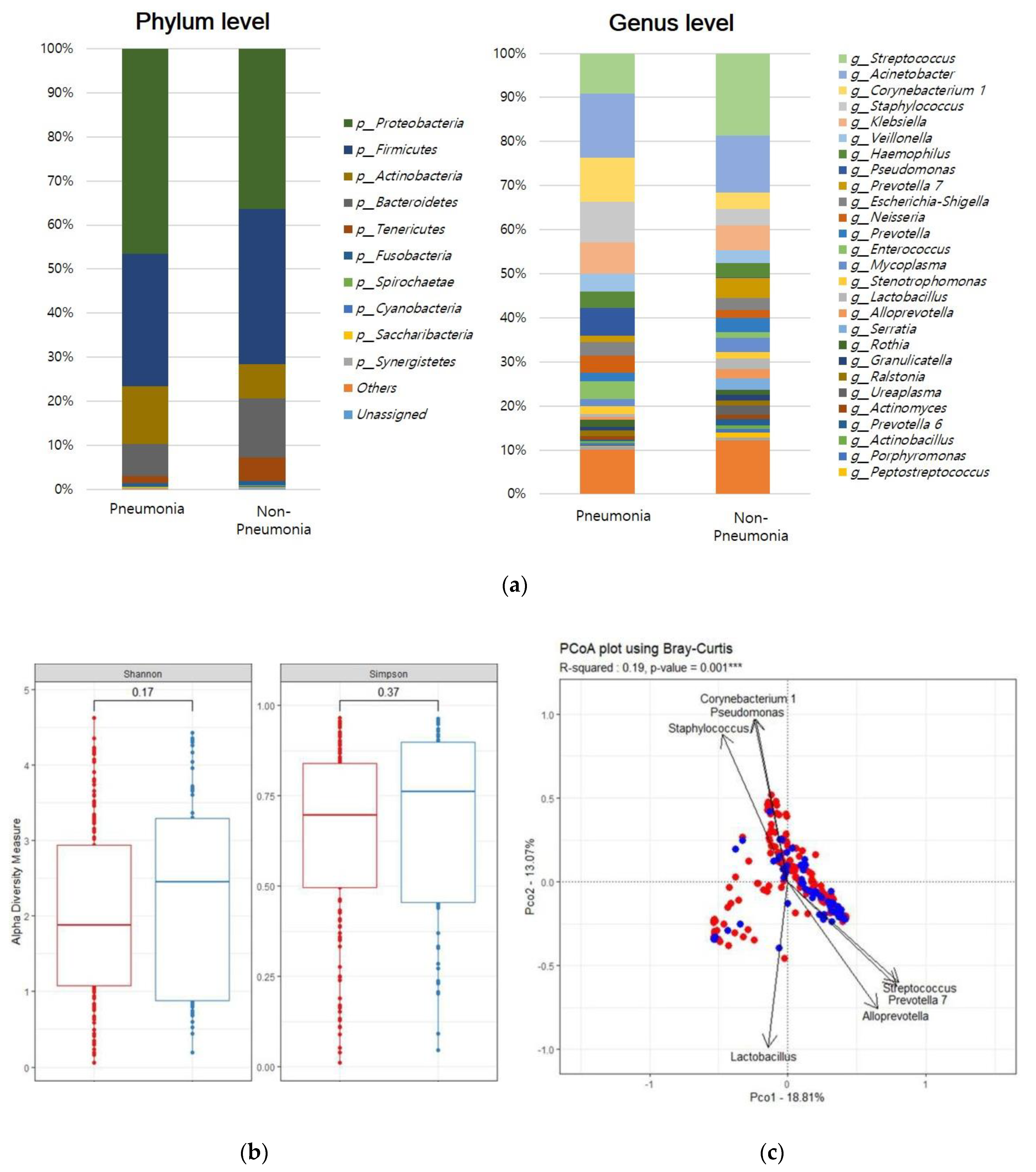
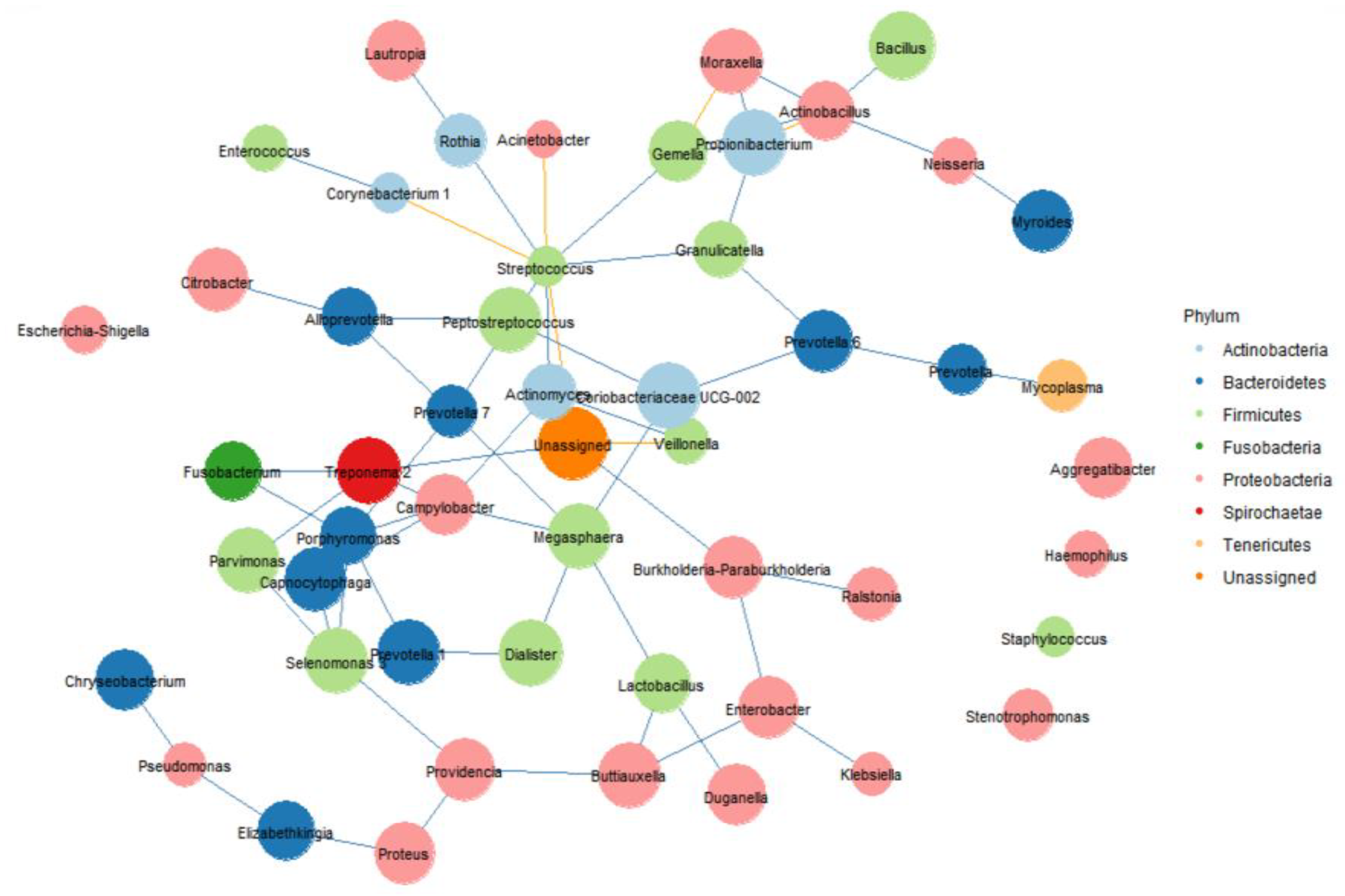
3.2. Day 1 ETA Microbiome Composition in Intubated Patients
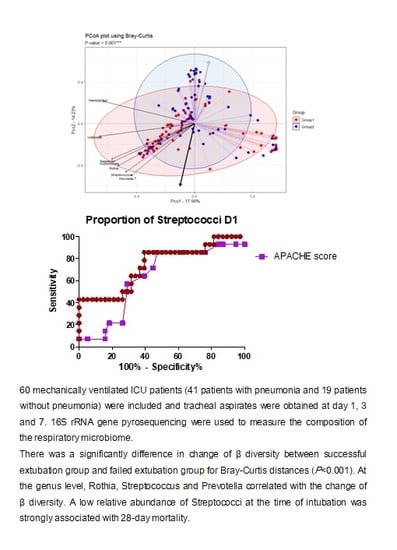
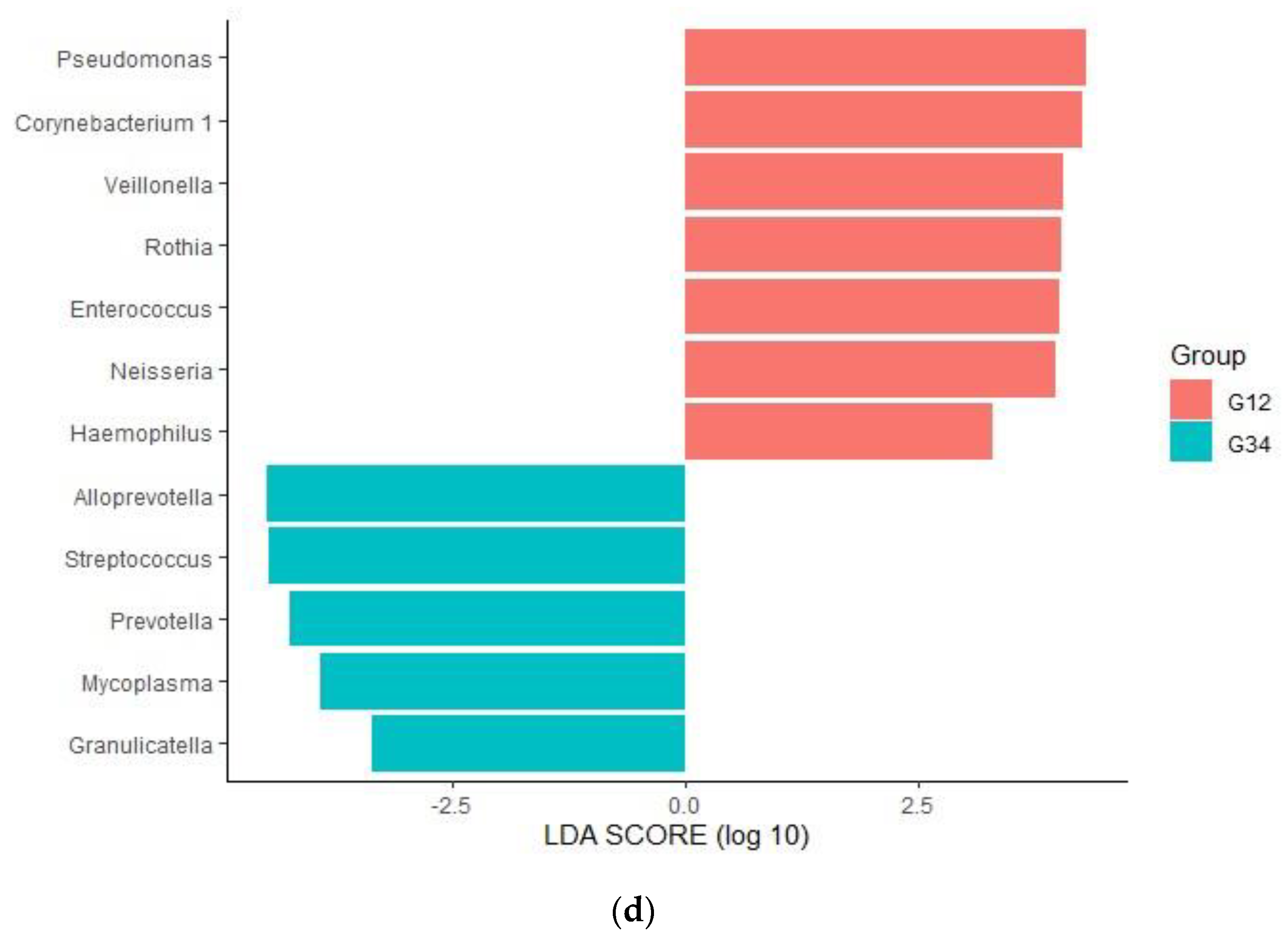
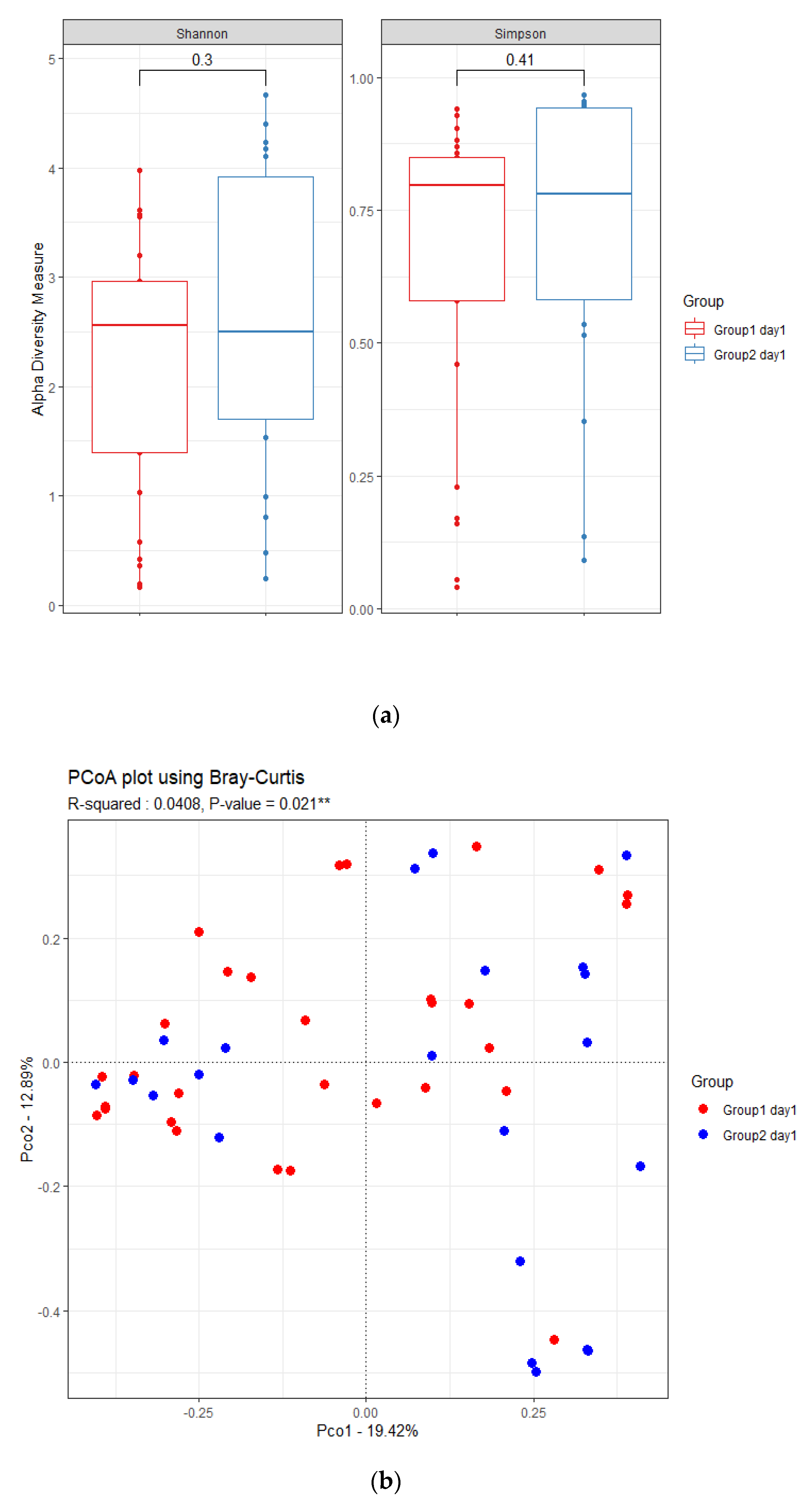
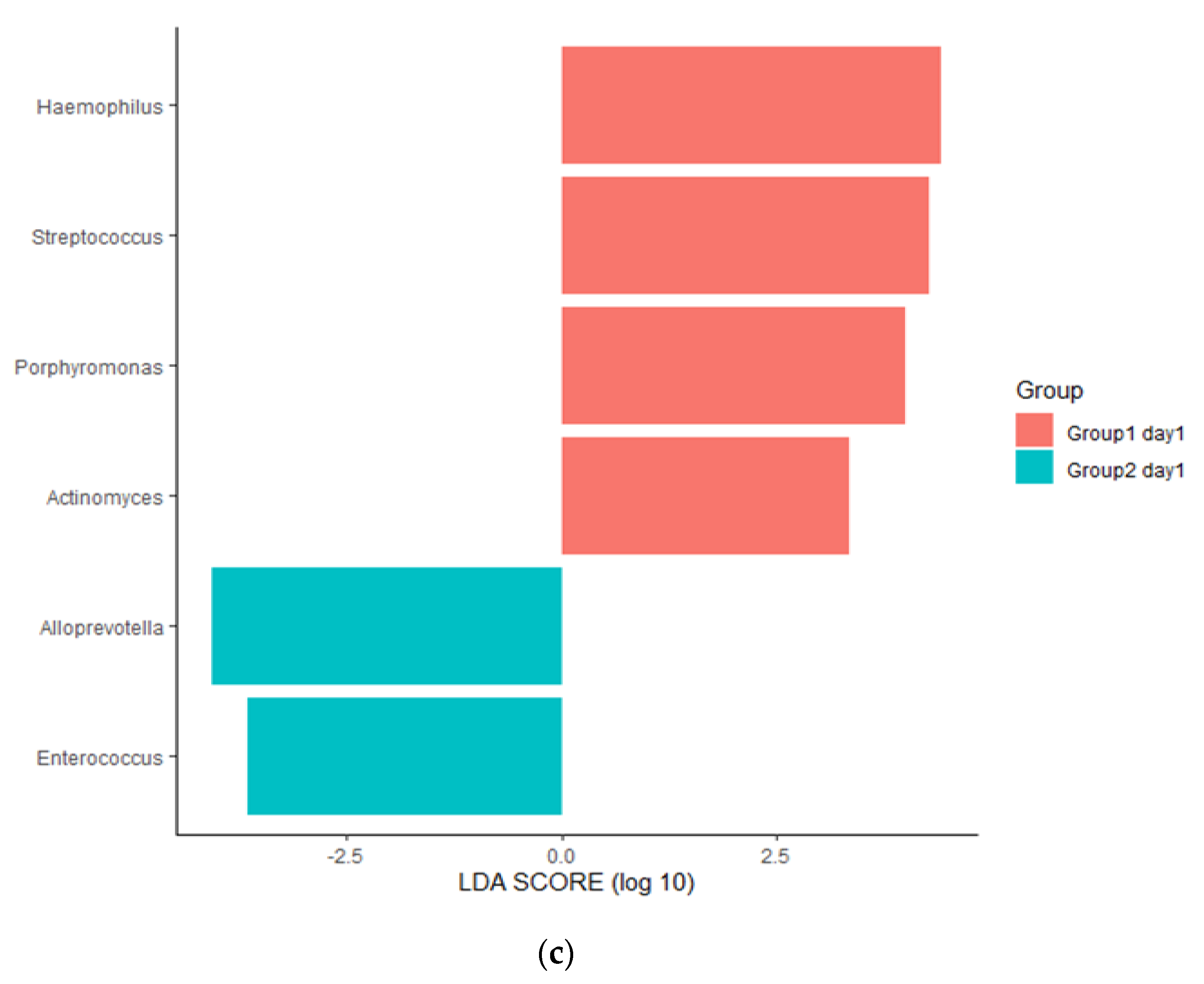
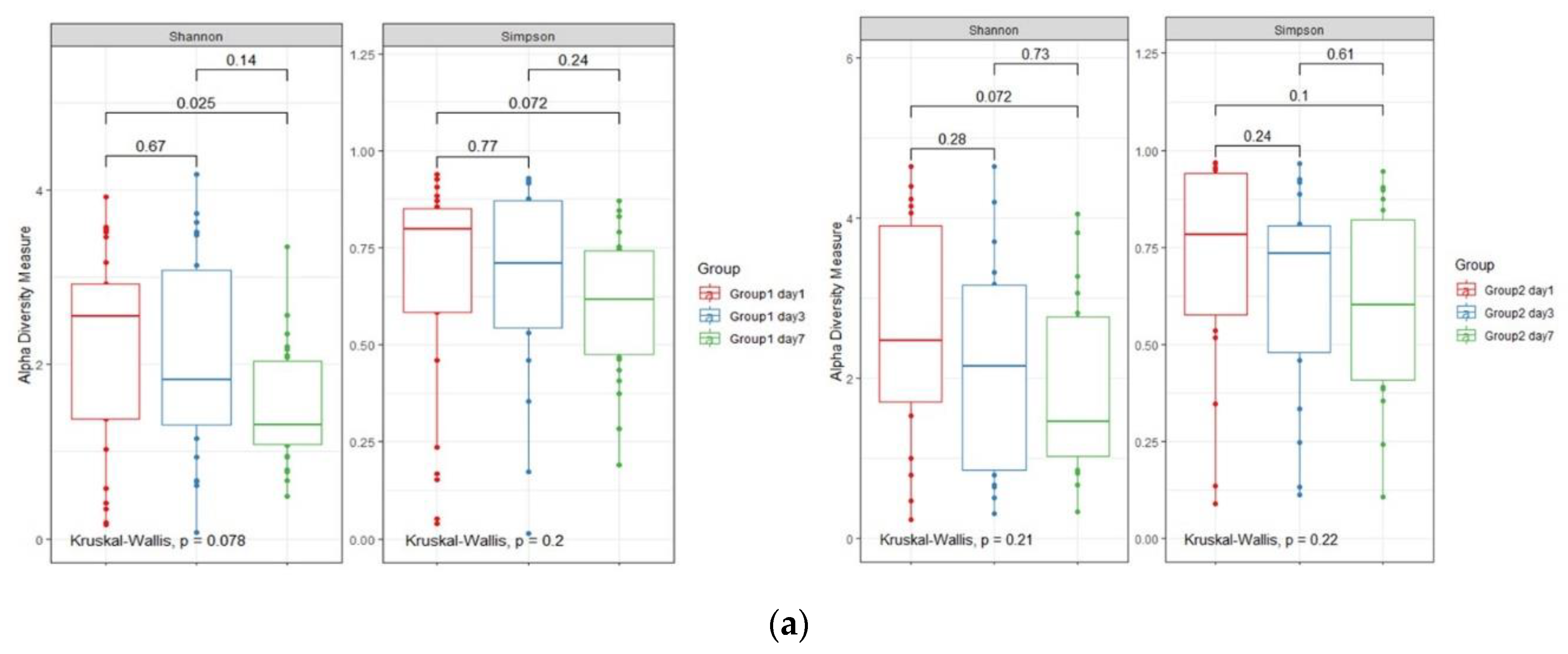
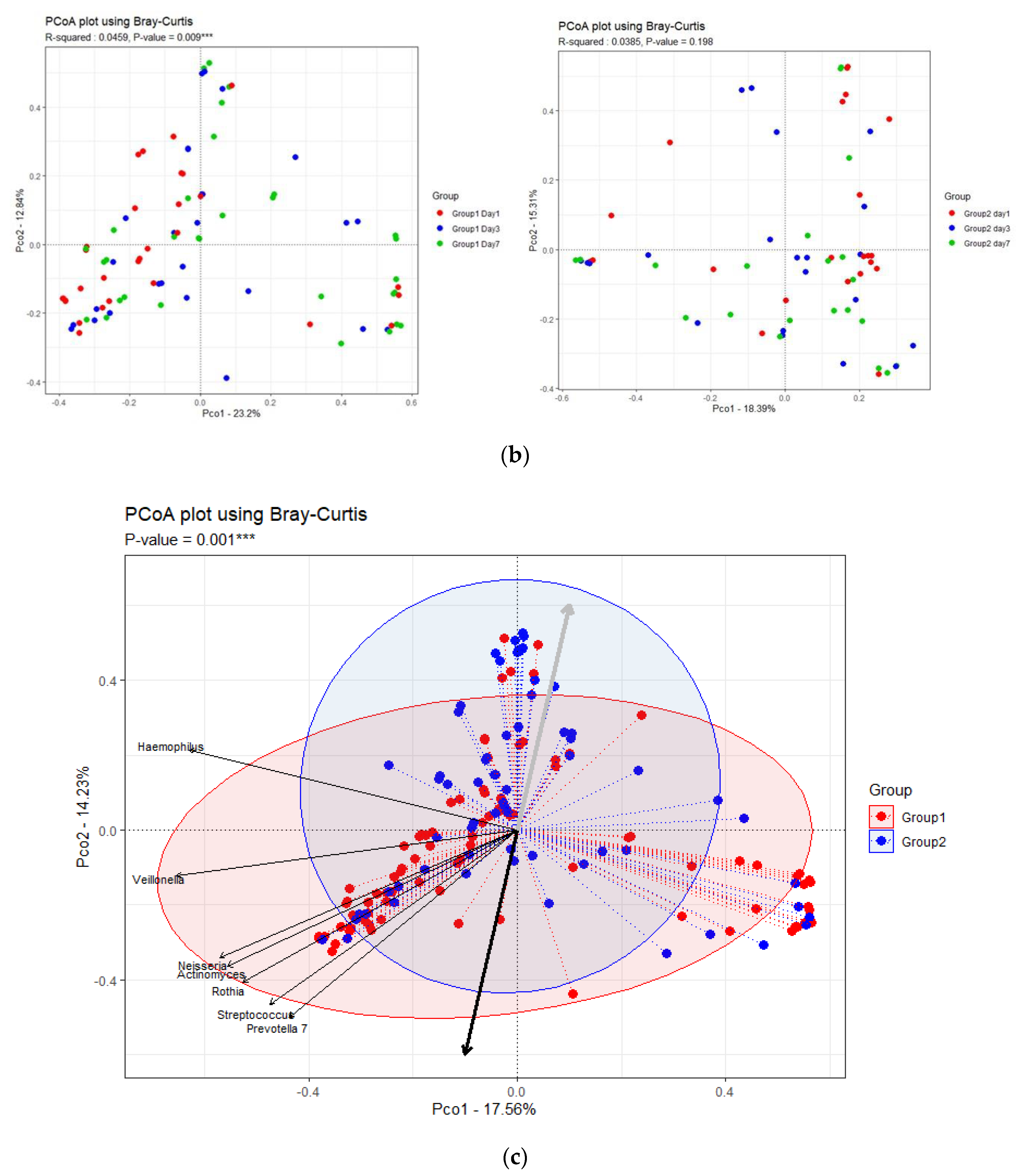
3.3. Changes in Respiratory Microbiota during Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Pneumonia
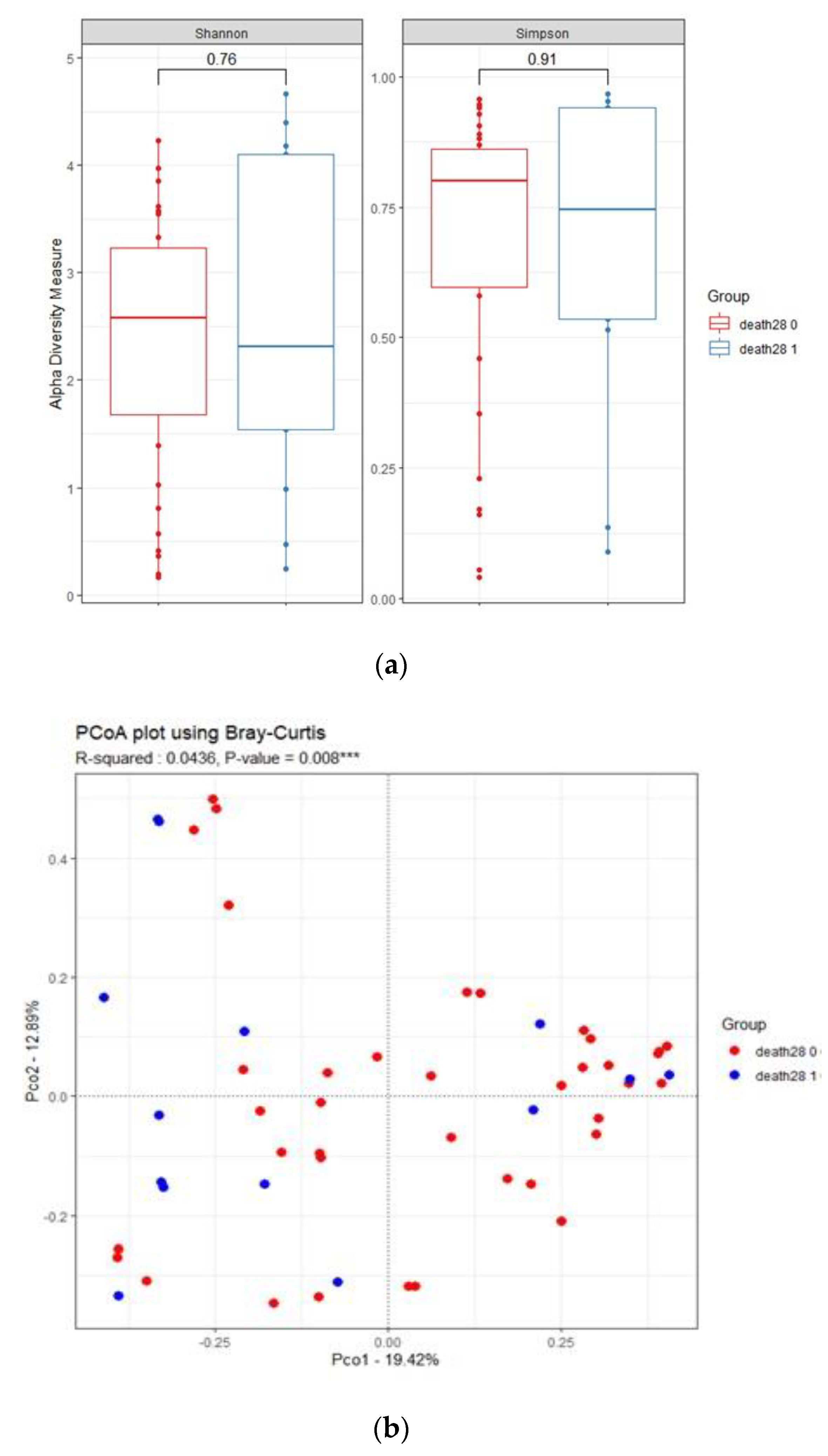
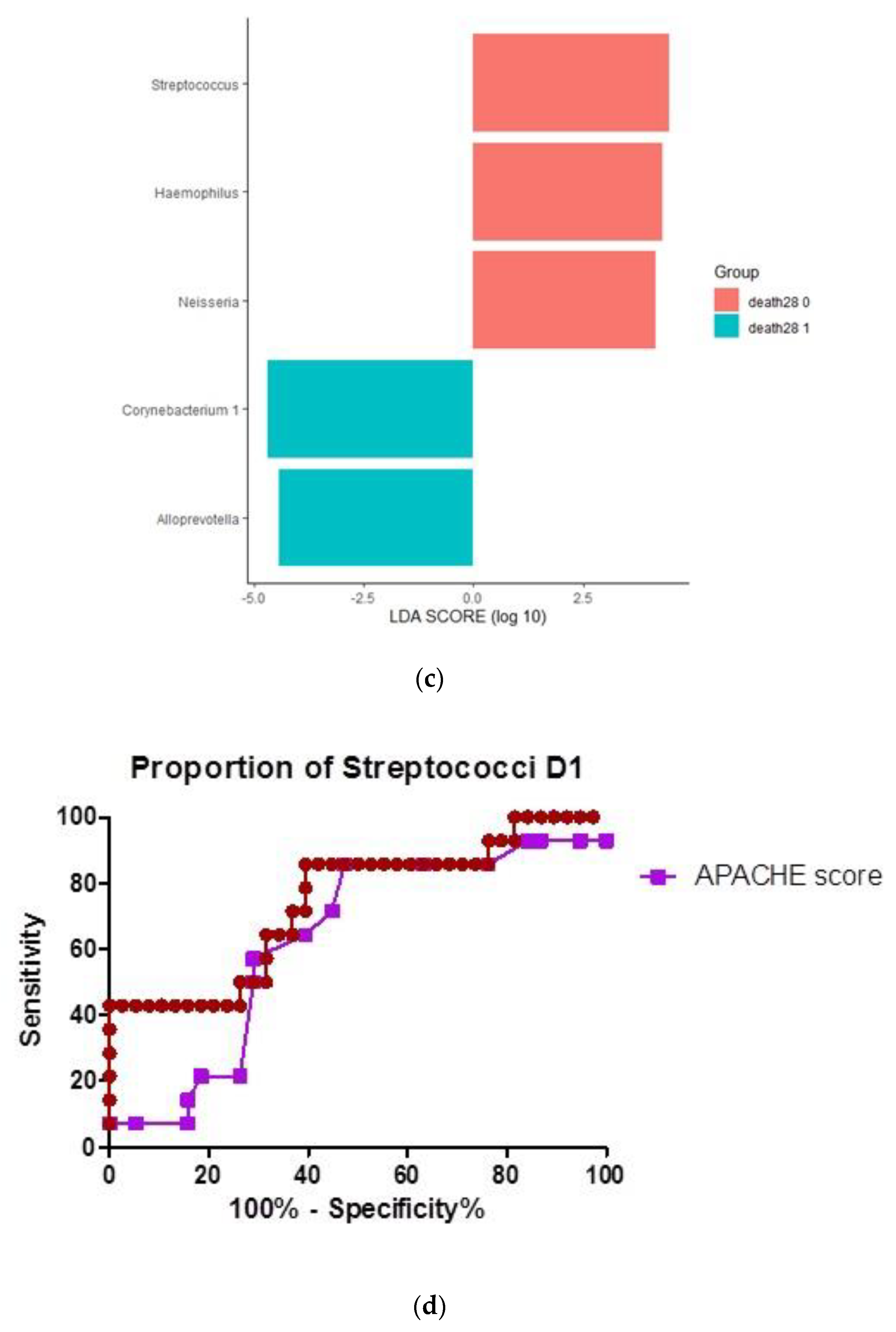
3.4. Influence of 28-Day Mortality on Respiratory Microbiota
4. Discussions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| ETA | Endotracheal aspirates |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic units |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| APACHE II | Acute Physiology Age Chronic Health Evaluation II |
| SOFA | Sequential Organ Failure Assessment |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
References
- Xu, J.; Murphy, S.L.; Kochanek, K.D.; Bastian, B.; Arias, E. Deaths: Final data for 2016. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2018, 67, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Self, W.H.; Wunderink, R.G.; Fakhran, S.; Balk, R.; Bramley, A.M.; Chappell, J.D. Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valley, T.S.; Sjoding, M.W.; Ryan, A.M.; Iwashyna, T.J.; Cooke, C.R. Association of intensive care unit admission with mortality among older patients with pneumonia. JAMA 2015, 314, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, A.C.; Metersky, M.L.; Klompas, M.; Muscedere, J.; Sweeney, D.A.; Palmer, L.B.; El Solh, A.A. Executive Summary: Management of Adults with Hospital-acquired and Ventilator-associated Pneumonia: 2016 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esperatti, M.; Ferrer, M.; Theessen, A.; Liapikou, A.; Valencia, M.; Saucedo, L.M.; Torres, A. Nosocomial pneumonia in the intensive care unit acquired by mechanically ventilated versus nonventilated patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, G.D.; Fitch, A.; Manatakis, D.V.; Rapport, S.F.; Li, K.; Qin, S.; Lee, J.S. Respiratory microbiome profiling for etiologic diagnosis of pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharkina, T.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Matamoros, S.; Povoa, P.; Torres, A.; Kastelijn, J.B.; Sterk, P.J. The dynamics of the pulmonary microbiome during mechanical ventilation in the intensive care unit and the association with occurrence of pneumonia. Thorax 2017, 72, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emonet, S.; Lazarevic, V.; Refondini, C.L.; Gaïa, N.; Leo, S.; Girard, M.; Mostaguir, K. Identification of respiratory microbiota markers in ventilator-associated pneumonia. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarche, D.; Johnstone, J.; Zytaruk, N.; Clarke, F.; Hand, L.; Loukov, D.; McDonald, E. Microbial dysbiosis and mortality during mechanical ventilation: A prospective observational study. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitsios, G.D.; Morowitz, M.J.; Dickson, R.P.; Huffnagle, G.B.; McVerry, B.J.; Morris, A. Dysbiosis in the intensive care unit: Microbiome science coming to the bedside. J. Crit. Care 2017, 38, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, L.N.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Clemente, J.C.; Kulkarni, R.; Wu, B.; Chen, H.; Weiden, M.D. Enrichment of lung microbiome with supraglottic taxa is associated with increased pulmonary inflammation. Microbiome 2013, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The Igraph software package for complex network research. InterJ. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Jalili, M.; Salehzadeh-Yazdi, A.; Asgari, Y.; Arab, S.S.; Yaghmaie, M.; Ghavamzadeh, A.; Alimoghaddam, K. CentiServer: A comprehensive resource, web-based application and R package for centrality analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asshauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.J.; Imai, I.; Bittinger, K.; Laughlin, A.; Fuchs, B.D.; Bushman, F.D.; Collman, R.G. Composition and dynamics of the respiratory tract microbiome in intubated patients. Microbiome 2016, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.; Huijskens, E.G.; Wyllie, A.L.; Biesbroek, G.; Van Den Bergh, M.R.; Veenhoven, R.H.; Sanders, E.A. Dysbiosis of upper respiratory tract microbiota in elderly pneumonia patients. ISME J. 2016, 10, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsios, G.D.; McVerry, B.J. Host-microbiome interactions in the subglottic space. Bacteria ante portas! Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, P.; Barreto, J.N.; Osmon, D.R.; Tosh, P.K. Rothia bacteremia: A 10-year experience at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3184–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, A.S.; Metlay, J.P.; Gent, J.F.; Fennie, K.P.; Kong, Y.; Pettigrew, M.M. Microbial communities of the upper respiratory tract and otitis media in children. MBio 2011, 2, e00245-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbia, S.; Papazian, L.; Saux, P.; Forel, J.M.; Auffray, J.P.; Martin, C.; La Scola, B. Repertoire of intensive care unit pneumonia microbiota. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, L.N.; Clemente, J.C.; Tsay, J.C.J.; Koralov, S.B.; Keller, B.C.; Wu, B.G.; Diaz, P. Enrichment of the lung microbiome with oral taxa is associated with lung inflammation of a Th17 phenotype. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitao Filho, F.S.; Alotaibi, N.M.; Ngan, D.; Tam, S.; Yang, J.; Hollander, Z.; Man, S.P. Sputum microbiome is associated with 1-year mortality after chronic obstructive pulmonary disease hospitalizations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Singh, R.; Miller, B.E.; Tal-Singer, R.; Van Horn, S.; Tomsho, L.; George, L.M. Sputum microbiome temporal variability and dysbiosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations: An analysis of the COPDMAP study. Thorax 2018, 73, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneaux, P.L.; Mallia, P.; Cox, M.J.; Footitt, J.; Willis-Owen, S.A.; Homola, D.; Moffatt, M.F. Outgrowth of the bacterial airway microbiome after rhinovirus exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.M.; Neill, D.R.; Bangert, M.; Gritzfeld, J.F.; Green, N.; Wright, A.K.; Wright, A.D. Controlled human infection and rechallenge with Streptococcus pneumoniae reveals the protective efficacy of carriage in healthy adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.S. Improving pulmonary immunity to bacterial pathogens through Streptococcus pneumoniae colonisation of the nasopharynx. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsi, E.; Carniel, B.; Reiné, J.; Rylance, J.; Zaidi, S.; Soares-Schanoski, A.; Solórzano, C. Nasal pneumococcal density is associated with microaspiration and heightened human alveolar macrophage responsiveness to bacterial pathogens. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberlein, E.; Cohen, J.M.; José, R.; Hyams, C.J.; Callard, R.; Chimalapati, S.; Noursadeghi, M. Importance of bacterial replication and alveolar macrophage-independent clearance mechanisms during early lung infection with Streptococcuspneumoniae. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pneumonia Group | Non-Pneumonia Group | p-Value ‡ | p-Value § | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Successful Extubation | Failed Extubation | ||||
| n = 22 | n = 19 | n = 19 | |||
| Age | 72 (58–75) | 76 (70–85) | 76 (59–81) | 0.738 | 0.063 |
| Male sex † | 16 (72.7%) | 14 (73.7%) | 12 (63.2) | 0.547 | 0.99 |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome † | 2 (9.1%) | 6 (31.6%) | 0 (0%) | 0.047 | 0.115 |
| Charlson comorbidity index * | 2 (0.8–3.3) | 3 (2–5) | 2(1–2) | 0.051 | 0.227 |
| Cause of intubation † | <0.001 | 0.269 | |||
| Cardiac arrest | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (5.3%) | 3 (15.8%) | ||
| Neurological distress | 4 (18.2%) | 1 (5.3%) | 14 (73.7%) | ||
| Postoperative status | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (5.3%) | ||
| Respiratory | 18 (81.8%) | 17 (89.5%) | 1 (5.3%) | ||
| PaO2/FiO2 | 241 (137–325) | 188 (102–292) | 430 (321, 457) | 0.14 | |
| Severity * | |||||
| APACHE score | 17 (15–21.5) | 23 (19–25) | 22 (17–25) | 0.165 | 0.015 |
| SOFA score | 7 (5–8.3) | 8 (7–13) | 6 (4–9) | 0.227 | 0.045 |
| GCS* | 8 (6.8–10) | 9 (5–11) | 6 (5–9) | 0.074 | 0.895 |
| 28-day mortality † | 0 (0%) | 12 (63.2%) | 6 (31.6%) | >0.99 | <0.001 |
| ICU mortality † | 0 (0%) | 17 (89.5%) | 6 (31.6%) | 0.4 | <0.001 |
| MV duration * | 8 (7–14) | 16 (13–25) | 10 (7–14) | 0.238 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/dL) * | 139 (65.8–221.3) | 133 (44–158) | 61 (4.6–132.1) | 0.011 | 0.488 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, S.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, J.P.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, J.Y. The Dynamics of Respiratory Microbiota during Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030638
Woo S, Park S-Y, Kim Y, Jeon JP, Lee JJ, Hong JY. The Dynamics of Respiratory Microbiota during Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Pneumonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(3):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030638
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Seongji, So-Yeong Park, Youngmi Kim, Jin Pyeong Jeon, Jae Jun Lee, and Ji Young Hong. 2020. "The Dynamics of Respiratory Microbiota during Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Pneumonia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 3: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030638
APA StyleWoo, S., Park, S.-Y., Kim, Y., Jeon, J. P., Lee, J. J., & Hong, J. Y. (2020). The Dynamics of Respiratory Microbiota during Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Pneumonia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030638