Kinetic GFR Outperforms CKD-EPI for Slow Graft Function Prediction in the Immediate Postoperative Period Following Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. eGFR Calculations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes
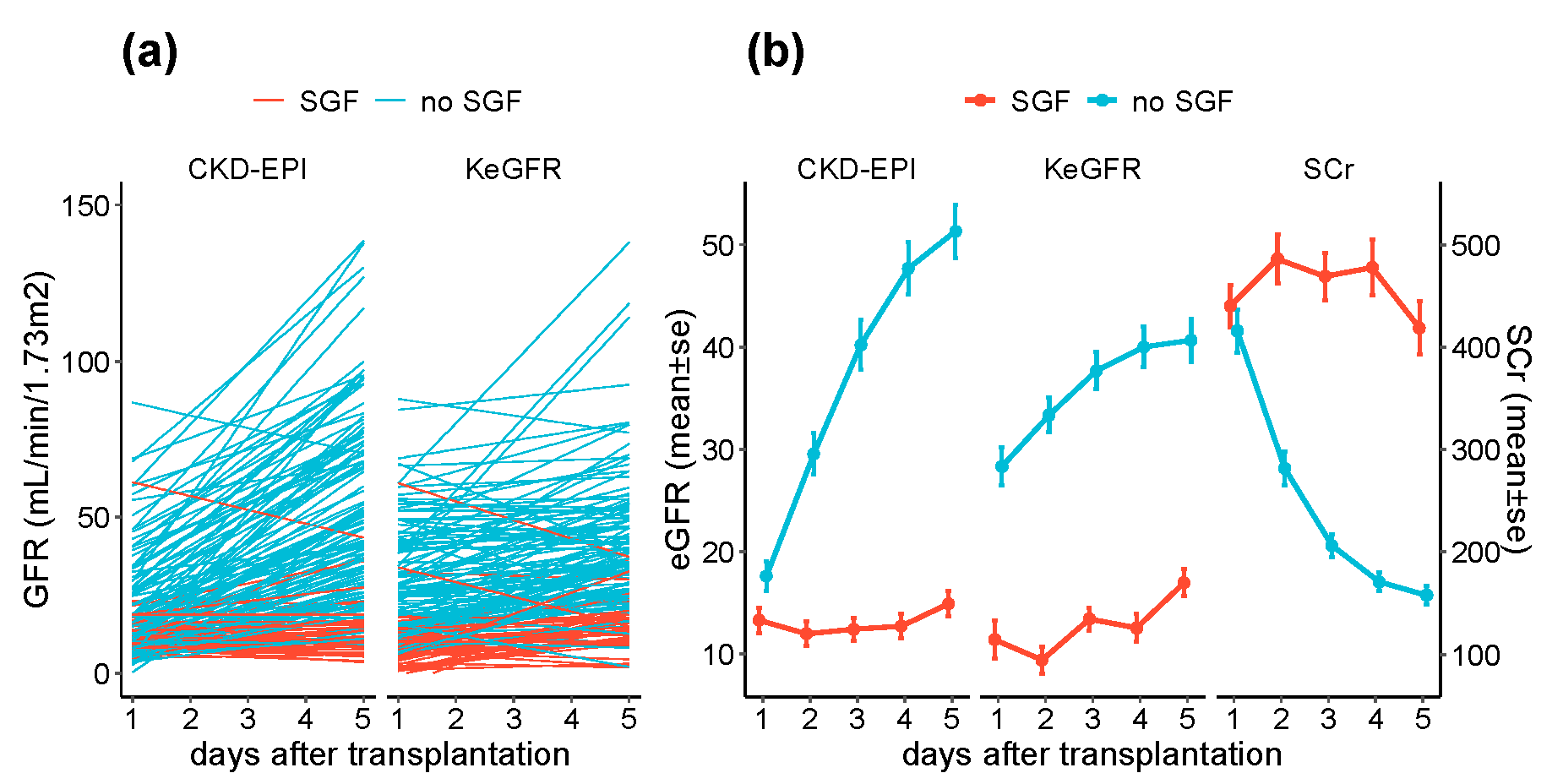
3.2. KeGFR and CKD-EPI in the Immediate Post-Transplantation Period
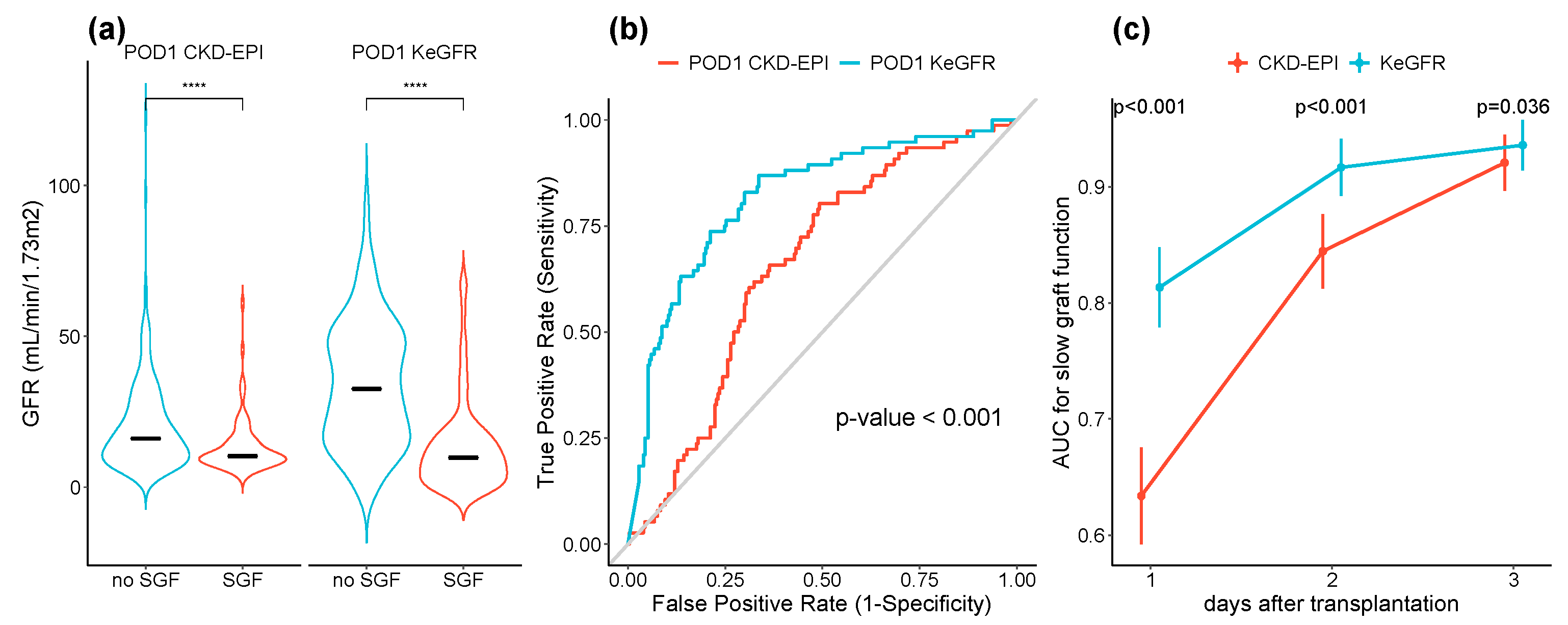
3.3. POD1 KeGFR and CKD-EPI According to SGF Status
3.4. POD1 eGFR, SGF and Renal Function over Follow Up
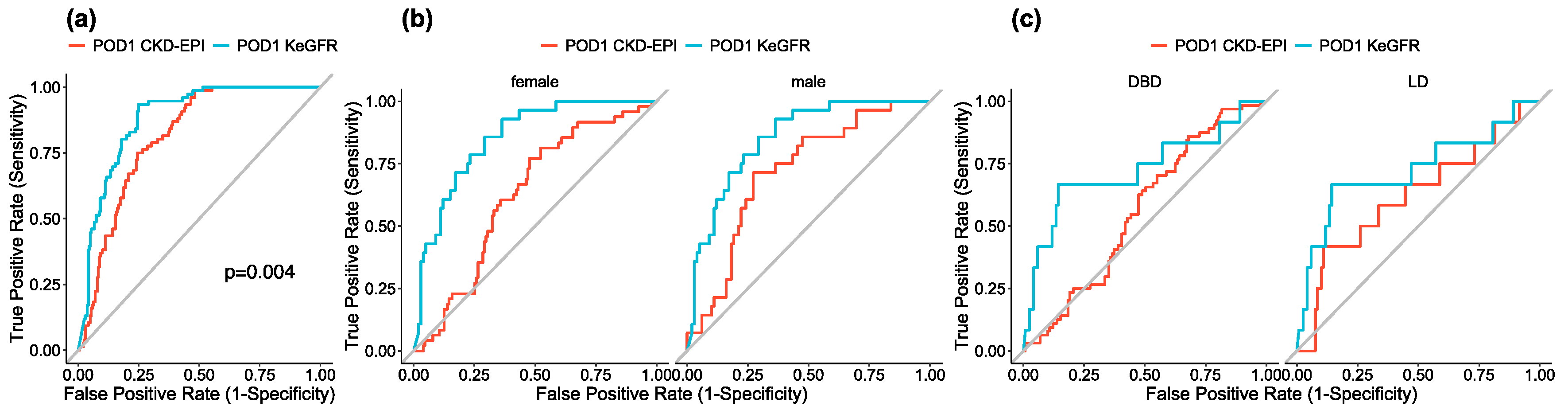
3.5. Sensitivity Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolfe, R.A.; Ashby, V.B.; Milford, E.L.; Ojo, A.O.; Ettenger, R.E.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Held, P.J.; Port, F.K. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, S.G.; Coca, S.G.; Garg, A.X.; Doshi, M.; Poggio, E.; Marcus, R.J.; Parikh, C.R. Marked variation in the definition and diagnosis of delayed graft function: A systematic review. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2995–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, S.G.; Coca, S.G.; Formica, R.N.; Poggio, E.D.; Parikh, C.R. Association between delayed graft function and allograft and patient survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiawala, S.N.; Tinckam, K.J.; Cardella, C.J.; Schiff, J.; Cattran, D.C.; Cole, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Delayed graft function and the risk for death with a functioning graft. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Farney, A.C.; Rogers, J.; Zuckerman, J.; Reeves-Daniel, A.; Hartmann, E.; Iskandar, S.; Adams, P.; Stratta, R.J. Kidney transplantation from donation after cardiac death donors: Lack of impact of delayed graft function on post-transplant outcomes: No impact of DGF in DCD kidneys. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Garonzik Wang, J.M.; Massie, A.B.; Jackson, K.R.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.A.; Brennan, D.C.; Lentine, K.L.; Coresh, J.; Segev, D.L. Early steroid withdrawal in deceased-donor kidney transplant recipients with delayed graft function. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matas, A.J.; Smith, J.M.; Skeans, M.A.; Thompson, B.; Gustafson, S.K.; Stewart, D.E.; Cherikh, W.S.; Wainright, J.L.; Boyle, G.; Snyder, J.J.; et al. OPTN/SRTR 2013 Annual Data Report: Kidney: OPTN/SRTR 2013 Annual Data Report. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, R.R.; Scalea, J.R.; Zens, T.J.; Muth, B.; Kaufman, D.B.; Djamali, A.; Astor, B.C.; Mohamed, M. Predictors and outcomes of delayed graft function after living-donor kidney transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2016, 29, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humar, A.; Johnson, E.M.; Payne, W.D.; Wrenshall, L.; Sutherland, D.E.; Najarian, J.S.; Gillingham, K.J.; Matas, A.J. Effect of initial slow graft function on renal allograft rejection and survival. Clin. Transplant. 1997, 11, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Humar, A.; Ramcharan, T.; Kandaswamy, R.; Gillingham, K.; Payne, W.D.; Matas, A.J. Risk factors for slow graft function after kidney transplants: A multivariate analysis. Clin. Transplant. 2002, 16, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.J.; Tuffaha, A.; Phadnis, M.A.; Mahnken, J.D.; Wetmore, J.B. Association of slow graft function with long-term outcomes in kidney transplant recipients. Ann. Transplant. 2018, 23, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, P.; Vanholder, R. Therapeutic interventions favorably influencing delayed and slow graft function in kidney transplantation: Mission impossible? Transplantation 2008, 85, S31–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pianta, T.J.; Peake, P.W.; Pickering, J.W.; Kelleher, M.; Buckley, N.A.; Endre, Z.H. Clusterin in Kidney Transplantation: Novel biomarkers versus serum creatinine for early prediction of delayed graft function. Transplantation 2015, 99, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, I.E.; Doshi, M.D.; Poggio, E.D.; Parikh, C.R. A comparison of alternative serum biomarkers with creatinine for predicting allograft function after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 2011, 91, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molitoris, B.A.; Reilly, E.S. Quantifying glomerular filtration rates in acute kidney injury: A requirement for translational success. Semin. Nephrol. 2016, 36, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S. Retooling the creatinine clearance equation to estimate kinetic GFR when the plasma creatinine is changing acutely. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, E.D.; Doyle, A. The clinical utility of kinetic glomerular filtration rate. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, sfw108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewitte, A.; Joannès-Boyau, O.; Sidobre, C.; Fleureau, C.; Bats, M.-L.; Derache, P.; Leuillet, S.; Ripoche, J.; Combe, C.; Ouattara, A. Kinetic eGFR and Novel AKI Biomarkers to Predict Renal Recovery. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Kinetic glomerular filtration rate in routine clinical practice-applications and possibilities. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianta, T.J.; Endre, Z.H.; Pickering, J.W.; Buckley, N.A.; Peake, P.W. Kinetic estimation of GFR improves prediction of dialysis and recovery after kidney transplantation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, E.; Varagunam, M.; Yaqoob, M.; Raftery, M.; Thuraisingham, R. Creatinine reduction ratio: A useful marker to identify medium and high-risk renal transplants. Transplantation 2010, 89, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeraati, A.A.; Naghibi, M.; Kianoush, S.; Kianoosh, S.; Ashraf, H. Impact of slow and delayed graft function on kidney graft survival between various subgroups among renal transplant patients. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 2777–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, D.; Vogel, J.; Muller, E.; Barday, Z.; Kahn, D. Slow early graft function: A neglected entity after renal transplantation. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c200–c204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, C.R.; Jani, A.; Mishra, J.; Ma, Q.; Kelly, C.; Barasch, J.; Edelstein, C.L.; Devarajan, P. Urine NGAL and IL-18 are predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Choi, H.M.; Seo, M.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Jun, H.; Jung, C.W.; Park, K.T.; Kim, M.-G.; Jo, S.-K.; et al. Urine liver-type fatty acid-binding protein predicts graft outcome up to 2 years after kidney transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyszko, J.; Bachorzewska-Gajewska, H.; Poniatowski, B.; Malyszko, J.S.; Dobrzycki, S. Urinary and serum biomarkers after cardiac catheterization in diabetic patients with stable angina and without severe chronic kidney disease. Ren. Fail. 2009, 31, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelhammer, T.G.; Maile, M.D.; Heung, M.; Haft, J.W.; Jewell, E.S.; Engoren, M. Kinetic estimated glomerular filtration rate and acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery patients. J. Crit. Care 2016, 31, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Matsuyama, Y.; Ohashi, Y. Estimation of treatment effect adjusting for dependent censoring using the IPCW method: An application to a large primary prevention study for coronary events (MEGA study). Clin. Trials 2007, 4, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Greene, T.; Li, L.; Beck, G.J.; Joffe, M.M.; Froissart, M.; Kusek, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Coresh, J.; et al. Factors other than glomerular filtration rate affect serum cystatin C levels. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No SGF (n = 250) | SGF (n = 76) | Total (n = 326) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (Q1, Q3) | 51.50 (42.00, 62.00) | 58.00 (44.75, 68.00) | 53.00 (43.00, 63.00) | 0.009 |
| Male sex | 151 (60.4%) | 48 (63.2%) | 199 (61.0%) | 0.692 |
| Pre-emptive transplantation | 37 (14.8%) | 4 (5.3%) | 41 (12.6%) | 0.030 |
| ABO incompatible | 21 (7.9%) | 3 (3.8%) | 24 (6.9%) | 0.223 |
| Living donor | 119 (47.6%) | 12 (15.8%) | 131 (40.2%) | <0.001 |
| Donation after cardiac death | 3 (1.2%) | 8 (10.5%) | 11 (3.4%) | <0.001 |
| Donor age, median (Q1, Q3) | 52.00 (43.00, 61.00) | 57.00 (45.50, 68.50) | 53.00 (43.00, 62.50) | 0.017 |
| Dialysis | 2 (0.8%) | 5 (6.6%) | 7 (9.6%) | 0.003 |
| 3 month eGFR, median (Q1, Q3) | 56.12 (47.54, 67.66) | 41.75 (32.04, 62.65) | 54.02 (43.89, 67.32) | <0.001 |
| 6 month eGFR, median (Q1, Q3) | 54.23 (45.47, 68.59) | 46.04 (30.99, 59.97) | 53.22 (42.46, 67.69) | <0.001 |
| 1 year eGFR, median (Q1, Q3) | 56.93 (45.30, 68.57) | 46.92 (37.99, 59.90) | 53.58 (44.35, 67.73) | 0.003 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dash, J.; Verissimo, T.; Faivre, A.; Berchtold, L.; Berney, T.; Pugin, J.; de Seigneux, S.; Legouis, D. Kinetic GFR Outperforms CKD-EPI for Slow Graft Function Prediction in the Immediate Postoperative Period Following Kidney Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124003
Dash J, Verissimo T, Faivre A, Berchtold L, Berney T, Pugin J, de Seigneux S, Legouis D. Kinetic GFR Outperforms CKD-EPI for Slow Graft Function Prediction in the Immediate Postoperative Period Following Kidney Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):4003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124003
Chicago/Turabian StyleDash, Jonathan, Thomas Verissimo, Anna Faivre, Lena Berchtold, Thierry Berney, Jérôme Pugin, Sophie de Seigneux, and David Legouis. 2020. "Kinetic GFR Outperforms CKD-EPI for Slow Graft Function Prediction in the Immediate Postoperative Period Following Kidney Transplantation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 4003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124003
APA StyleDash, J., Verissimo, T., Faivre, A., Berchtold, L., Berney, T., Pugin, J., de Seigneux, S., & Legouis, D. (2020). Kinetic GFR Outperforms CKD-EPI for Slow Graft Function Prediction in the Immediate Postoperative Period Following Kidney Transplantation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 4003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9124003





