Effect of Autologous Serum Eyedrops on Ocular Surface Disease Caused by Preserved Glaucoma Eyedrops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
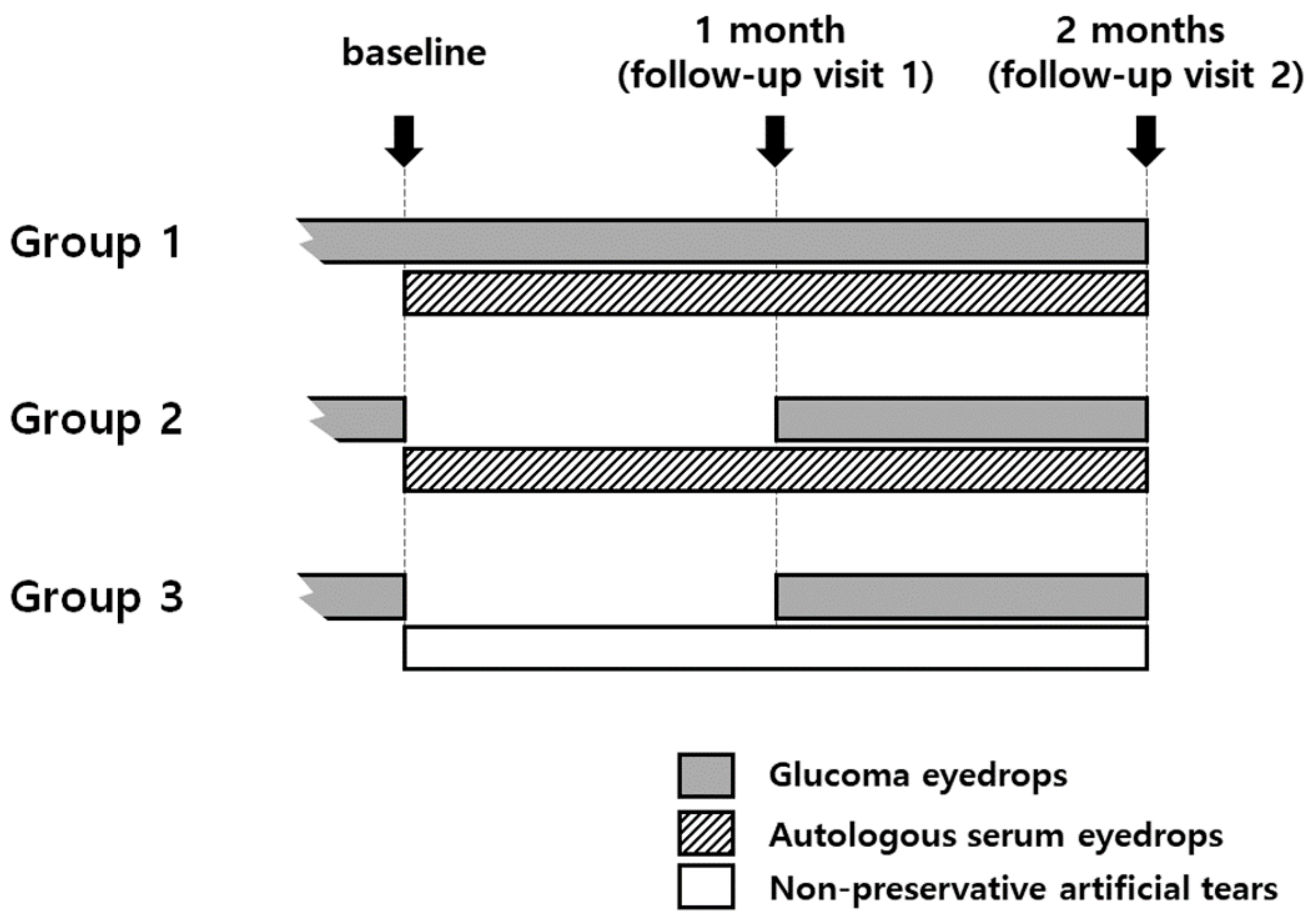
2.1. Patient Groups
2.2. Objective Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petrillo, F.; Pignataro, D.; Lavano, M.A.; Santella, B.; Folliero, V.; Zannella, C.; Astarita, C.; Gagliano, C.; Franci, G.; Avitabile, T.; et al. Current Evidence on the Ocular Surface Microbiota and Related Diseases. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, Z.; Wellik, S.R.; Galor, A. Glaucoma therapy and ocular surface disease: Current literature and recommendations. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 24, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo Bonniard, A.; Yeung, J.Y.; Chan, C.C.; Birt, C.M. Ocular surface toxicity from glaucoma topical medications and associated preservatives such as benzalkonium chloride (BAK). Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bartolomé, F.; Martínez-de-la-Casa, J.M.; Arriola-Villalobos, P.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Polo, V.; García-Feijoó, J. Ocular Surface Disease in Patients under Topical Treatment for Glaucoma. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 27, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiedu, K.; Abu, S.L. The impact of topical intraocular pressure lowering medications on the ocular surface of glaucoma patients: A review. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2019, 31, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makashova, N.V.; Vasilieva, A.E.; Kolosova, O.Y. Effects of artificial tears on ocular surface in glaucomatous patients with long-term instillation of preserved antiglaucoma eye drops. Vestn. Oftalmol. 2018, 134, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberti, G.; Agnifili, L.; Berardo, F.; Riva, I.; Figus, M.; Manni, G.; Quaranta, L.; Oddone, F. Prospective, Randomized, Single Masked, Parallel Study Exploring the Effects of a Preservative-Free Ophthalmic Solution Containing Hyaluronic Acid 0.4% and Taurine 0.5% on the Ocular Surface of Glaucoma Patients Under Multiple Long-Term Topical Hypotensive Therapy. Adv. Ther. 2018, 35, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uusitalo, H.; Egorov, E.; Kaarniranta, K.; Astakhov, Y.; Ropo, A. Benefits of switching from latanoprost to preservative-free tafluprost eye drops: A meta-analysis of two Phase IIIb clinical trials. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisella, P.J.; Pouliquen, P.; Baudouin, C. Prevalence of ocular symptoms and signs with preserved and preservative free glaucoma medication. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzard, G.; Konstantakopoulou, E.; Garway-Heath, D.; Garg, A.; Vickerstaff, V.; Hunter, R.; Ambler, G.; Bunce, C.; Wormald, R.; Nathwani, N.; et al. Selective laser trabeculoplasty versus drops for newly diagnosed ocular hypertension and glaucoma: The LiGHT RCT. Health Technol. Assess. 2019, 23, 1–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, M.; Harissi-Dagher, M.; Germain, M.; Thompson, P.; Robert, M.C. Serum drops for ocular surface disease: National survey of Canadian cornea specialists. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 53, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.K.; Jeoung, J.W.; Oh, J.Y. Effects of topical autologous serum on the ocular surface in patients with toxic corneal epitheliopathy induced by anti-glaucoma drugs. Int. Ophthalmol. 2020, 40, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, A. Autologous Serum and Serum Components. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcher, J.P.; Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Heidenreich, A.M.; Kitagawa, K.; Zhang, S.; Hamann, S.; Larkin, G.; McNamara, N.A.; Greenspan, J.S.; et al. A simplified quantitative method for assessing keratoconjunctivitis sicca from the Sjögren’s Syndrome International Registry. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, R.; Itoh, K.; Inoue, K.; Amano, S. Noncontact infrared meibography to document age-related changes of the meibomian glands in a normal population. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; Benjamin, L.; Snibson, G.R. Meibomian gland disease. Classification and grading of lid changes. Eye 1991, 5, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.C.; Pasinetti, G.M.; Scudeller, L.; Raimondi, M.; Lanteri, S.; Bianchi, P.E. Risk factors to develop ocular surface disease in treated glaucoma or ocular hypertension patients. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 23, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, E.W.; Medeiros, F.A.; Weinreb, R.N. Prevalence of ocular surface disease in glaucoma patients. J. Glaucoma 2008, 17, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, D.W.; Alaghband, P.; Lim, K.S. Preservatives in glaucoma medication. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, S.; Shimizu, K.; Nejima, R.; Kagaya, F.; Aihara, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Shoji, N.; Miyata, K. Conjunctival Bacteria Flora of Glaucoma Patients During Long-Term Administration of Prostaglandin Analog Drops. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 3991–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Actis, A.G.; Rolle, T. Ocular surface alterations and topical antiglaucomatous therapy: A review. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2014, 8, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skalicky, S.E.; Goldberg, I.; McCluskey, P. Ocular surface disease and quality of life in patients with glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 153, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Vadoothker, S.; Munir, W.M.; Saeedi, O. Ocular Surface Disease and Glaucoma Medications: A Clinical Approach. Eye Contact Lens 2019, 45, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannaccare, G.; Versura, P.; Buzzi, M.; Primavera, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Campos, E.C. Blood derived eye drops for the treatment of cornea and ocular surface diseases. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meer, P.F.; Seghatchian, J.; Marks, D.C. Quality standards, safety and efficacy of blood-derived serum eye drops: A review. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2016, 54, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Ko, J.H.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, M.K.; Oh, J.Y. Effects of 20% Human Serum on Corneal Epithelial Toxicity Induced by Benzalkonium Chloride: In vitro and clinical studies. Cornea 2018, 37, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.; Kulkarni, B.; Faraj, L.A.; Abbas, A.; Dua, H.S.; King, A.J. Profiling ocular surface responses to preserved and non-preserved topical glaucoma medications: A 2-year randomized evaluation study. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 48, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, R.; Itoh, K.; Maeda, S.; Maeda, K.; Furuta, A.; Tomidokoro, A.; Aihara, M.; Amano, S. Effects of long-term topical anti-glaucoma medications on meibomian glands. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Shin, Y.U.; Seong, M.; Cho, H.Y.; Kang, M.H. Eyelid Changes Related to Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Early Middle-Aged Patients Using Topical Glaucoma Medications. Cornea 2018, 37, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Total | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 55 | 18 | 22 | 15 |
| Age (Mean ± SD 1, range) | 64.1 ± 10.9, 36 to 81 | 62.6 ± 10.7, 36 to 79 | 67.5 ± 10.3, 45 to 80 | 59.7 ± 11.8, 40 to 81 |
| Male (%) | 17 (30.9%) | 4 (22.2%) | 6 (27.3%) | 7 (46.7%) |
| Diagnosis | ||||
| POAG 2 | 16 (29.1%) | 5 (27.8%) | 7 (31.8%) | 4 (26.7%) |
| NTG 3 | 28 (50.9%) | 8 (44.4%) | 11 (50.0%) | 9 (60%) |
| NVG 4 | 3 (5.5%) | 1 (5.6%) | 2 (9.1%) | 0 |
| Uveitic glaucoma | 8 (14.5%) | 4 (22.2%) | 2 (9.1%) | 2 (13.3%) |
| Medication history | ||||
| monotherapy | 36 (65.5%) | 12 (66.7%) | 15 (68.2%) | 10 (66.7%) |
| combination | 19 (34.5%) | 6 (33.3%) | 7 (31.8%) | 5 (33.3%) |
| Medication duration | ||||
| <1 year | 11 (20.0%) | 3 (16.7%) | 5 (22.7%) | 9 (60.0%) |
| ≥1 year | 44 (80.0%) | 15 (83.3%) | 17 (77.3%) | 6 (40.0%) |
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD 4 | p-Value 5 | Mean ± SD | p-Value 5 | Mean ± SD | p-Value 5 | |||||||
| Initial | 1 m | 2 m | Initial | 1 m | 2 m | Initial | 1 m | 2 m | ||||
| Schirmer I | 4.2 ± 2.4 | 4.7 ± 3.3 | 5.7 ± 5.2 | 0.9815 | 3.7 ± 1.5 | 4.5 ± 3.0 | 5.4 ± 2.7 | 0.0702 | 4.7 ± 3.9 | 5.5 ± 3.0 | 5.5 ± 2.2 | 0.2510 |
| TBUT 1 | 3.2 ± 1.6 | 3.9 ± 1.9 | 5.6 ± 2.0 * | 0.0020 | 3.4 ± 2.0 | 3.6 ± 1.7 | 4.1 ± 1.7 * | 0.0195 | 2.8 ± 2.3 | 4.2 ± 2.7 | 3.1 ± 2.1 | 0.2744 |
| OSS 2 | 5.7 ± 2.5 | 4.2 ± 2.4 | 1.9 ± 1.3 * | <0.0001 | 5.5 ± 2.9 | 2.9 ± 1.2 * | 1.6 ± 1.3 * | <0.0001 | 5.1 ± 2.3 | 3.1 ± 1.8 | 4.5 ± 1.9 | 0.0480 |
| Meiboscore | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 1.000 | 1.5 ± 1.0 | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 0.9774 | 1.3 ± 1.2 | 1. 5 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 0.8909 |
| Meibum quality | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 0.6 ± 0.7 | 0.1098 | 1.3 ± 1.2 | 1.0 ± 0.8 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 0.4023 | 1.1 ± 1.2 | 0.8 ± 0.9 | 1.1 ± 1.2 | 0.7812 |
| OSDI 3 | 51.9 ± 24.8 | 43.5 ± 19.6 | 30.0 ± 16.4 * | 0.0037 | 52.2 ± 22.5 | 35.3 ± 17.5 * | 28.9 ± 12.7 * | 0.0004 | 45.1 ± 16.4 | 35.8 ± 14.8 | 41.1 ± 16.6 | 0.0736 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
So, H.-R.; Park, H.Y.L.; Chung, S.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Byun, Y.-S. Effect of Autologous Serum Eyedrops on Ocular Surface Disease Caused by Preserved Glaucoma Eyedrops. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123904
So H-R, Park HYL, Chung S-H, Kim H-S, Byun Y-S. Effect of Autologous Serum Eyedrops on Ocular Surface Disease Caused by Preserved Glaucoma Eyedrops. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(12):3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123904
Chicago/Turabian StyleSo, Ha-Rim, Hae Young Lopilly Park, So-Hyang Chung, Hyun-Seung Kim, and Yong-Soo Byun. 2020. "Effect of Autologous Serum Eyedrops on Ocular Surface Disease Caused by Preserved Glaucoma Eyedrops" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 12: 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123904
APA StyleSo, H.-R., Park, H. Y. L., Chung, S.-H., Kim, H.-S., & Byun, Y.-S. (2020). Effect of Autologous Serum Eyedrops on Ocular Surface Disease Caused by Preserved Glaucoma Eyedrops. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(12), 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9123904





