Winter Exercise and Speleotherapy for Allergy and Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
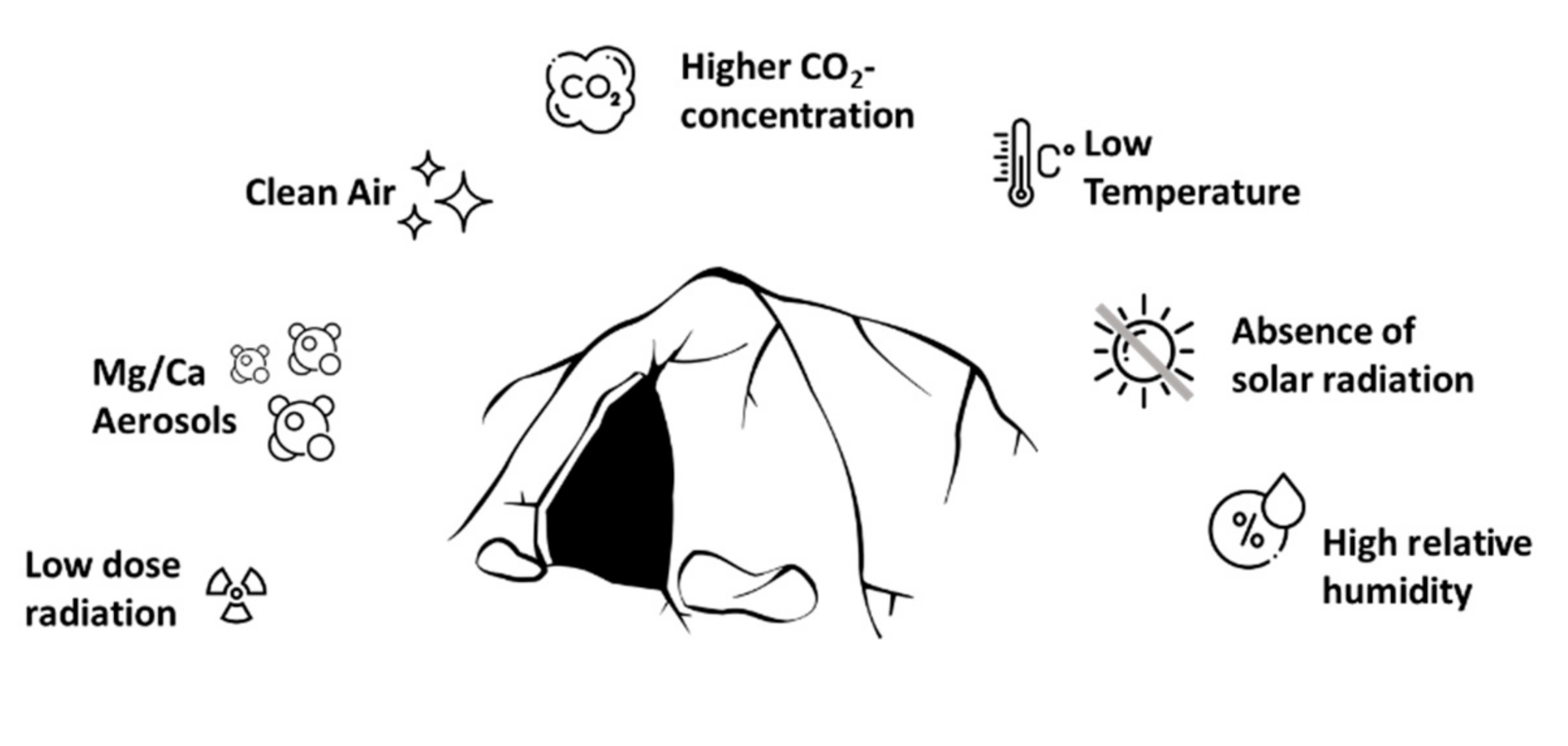
1.1. High Relative Humidity
1.2. Cave Aerosols
1.3. Slow Air Motion and Air Pollution
1.4. Radiation and Ionization
1.5. Absence of Solar Radiation and Ozone
2. Materials and Methods
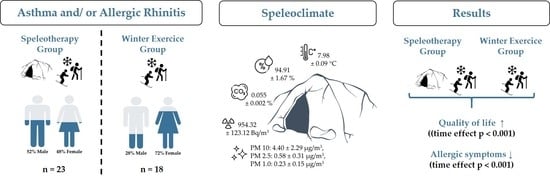
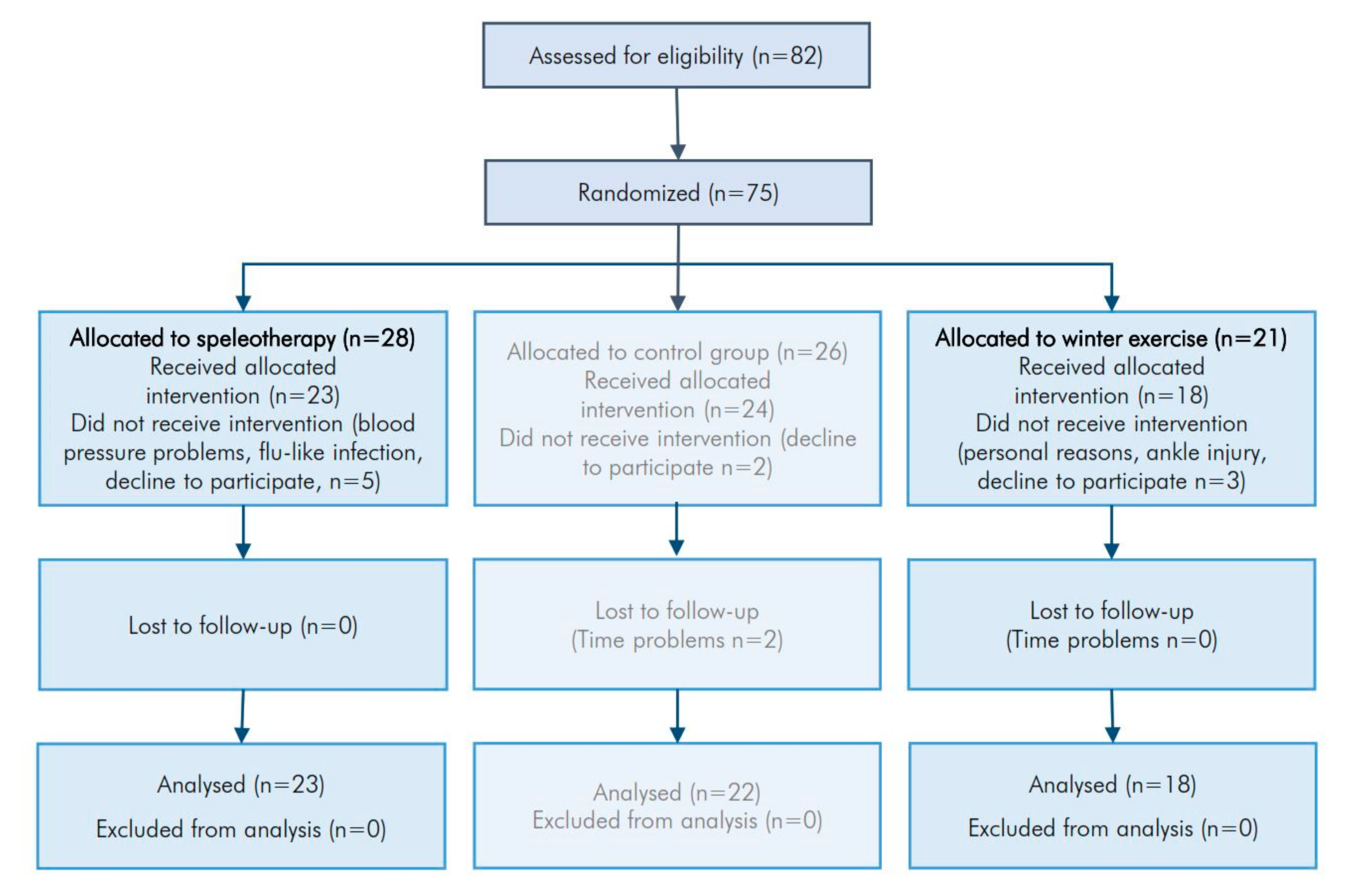
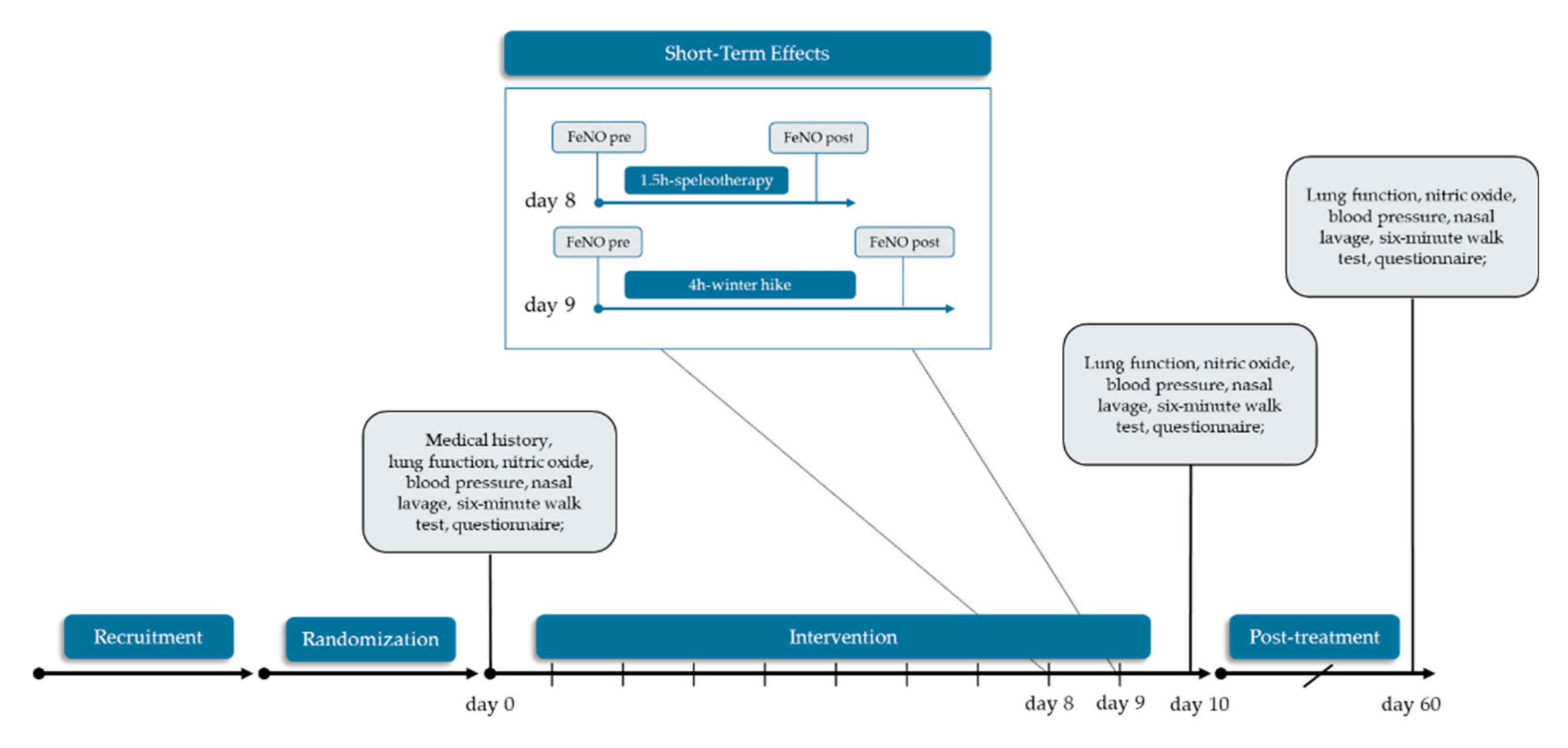
2.1. Study Design and Settings
2.2. Participants
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Data Collection and Outcomes
2.4.1. Physical Characterization of the Speleotherapy Location
2.4.2. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Nasal Nitric Oxide
2.4.3. Spirometry and Six-Minute Walk Test
2.4.4. Nasal Lavage and Saccharin Test
2.5. Statistcial Analysis
2.6. Randomization and Sample Size
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Environmental Parameters
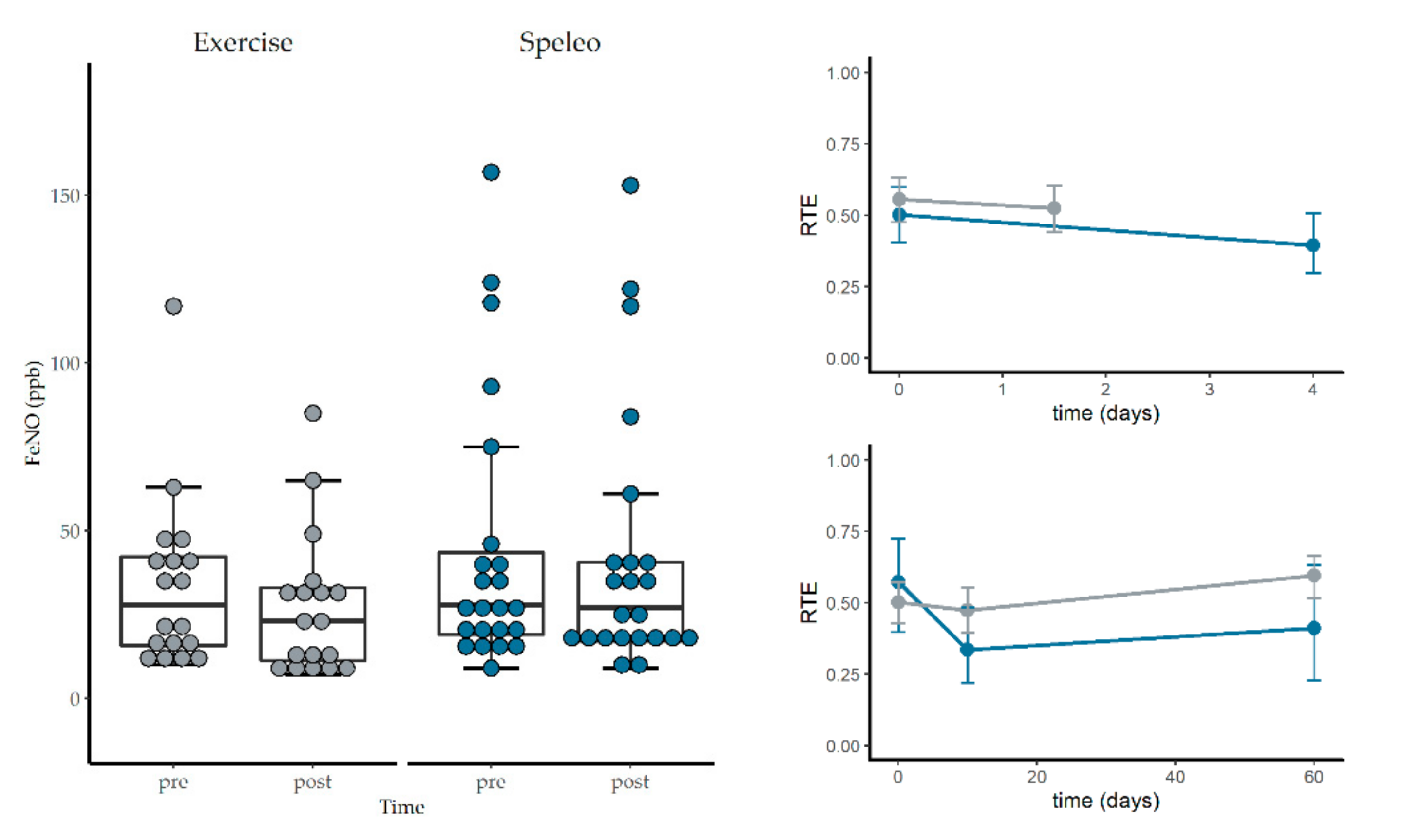
3.3. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide, Nasal Nitric Oxide and Spirometry
3.4. Short-Term Effects of Winter Hiking and Speleotherapy
3.5. RhinAsthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (German Adapted Version)
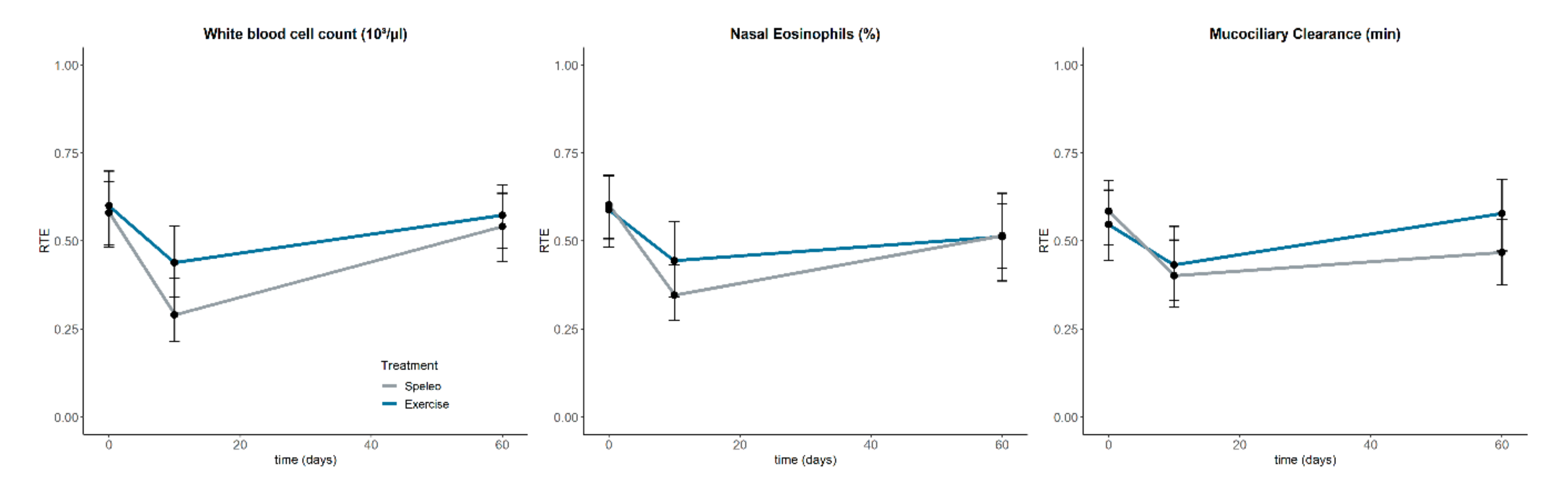
3.6. Nasal Eosinophilic Count and Muco-ciliary Clearance Time
3.7. Differential Blood Count
3.8. Six-Minute Walk Test
3.9. Visual Analogue Scale
3.10. Sample Size Simulation
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATS/ETS | American thoracic society/European respiratory society |
| FeNO | Fractional exhaled nitric oxide |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| FEV1/FVC | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s of forced vital capacity |
| FVC | Forced expiratory volume |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| MEF25–75% | Mid-expiratory flow at 25–75% of the FVC |
| nparLD | Nonparametric longitudinal data analysis |
| PEF | Peak expiratory flow |
| PVE | Peak minute ventilation |
| RAST | Radio-allergo-sorbent-test |
| RBC | Red blood cell count |
| RTE | Relative treatment effect |
| VAS | Visual analogue scale |
| WBC | White blood cell count |
| 222Rn | Radon radioisotope |
| 40K | Potassium radioisotope |
| 6MWT | Six-minute walk test |
References
- World Health Organization. Asthma. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma (accessed on 18 February 2020).
- Bousquet, J.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Khaltaev, N. Aria Workshop Group; World Health Organization Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, S147–S334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousquet, J.; Khaltaev, N.; Cruz, A.A.; Denburg, J.; Fokkens, W.J.; Togias, A.; Zuberbier, T.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Canonica, G.W.; van Weel, C.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy 2008, 63 (Suppl. 86), 8–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavina-Bianchi, P.; Aun, M.V.; Takejima, P.; Kalil, J.; Agondi, R.C. United airway disease: Current perspectives. J. Asthma Allergy 2016, 9, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morjaria, J.B.; Caruso, M.; Emma, R.; Russo, C.; Polosa, R. Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis as a Strategy for Preventing Asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, M.L. Asthma pharmacotherapy. Otolaryngol. Clin. North Am. 2014, 47, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, P.A.; Diener, S.N.; Kofmehl, R.; Spengler, C.M. Effects of Exercise Training on Airway Hyperreactivity in Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Khafagy, A.; Blanc, P.D.; Brimkulov, N.; Steinmaus, C. High-altitude alpine therapy and lung function in asthma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. ERJ Open Res. 2016, 2, 00097–02015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prossegger, J.; Huber, D.; Grafetstätter, C.; Pichler, C.; Braunschmid, H.; Weisböck-Erdheim, R.; Hartl, A. Winter Exercise Reduces Allergic Airway Inflammation: A Randomized Controlled Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmel, H. Beiträge zu Speläotherapie und Höhlenklima, I. Akten des 9. internationalen Symposium für Speläotherapie, Bad Bleiberg (Kärnten), September 1987. Höhle Wiss. Beih. Zur Z. 1992, 1, 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Dredge, J.; Fairchild, I.J.; Harrison, R.M.; Fernandez-Cortes, A.; Sanchez-Moral, S.; Jurado, V.; Gunn, J.; Smith, A.; Spötl, C.; Mattey, D.; et al. Cave aerosols: Distribution and contribution to speleothem geochemistry. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2013, 63, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, J.U.; Baldini, L.M.; McDermott, F.; Clipson, N. Carbon dioxide sources, sinks, and spatial variability in shallow temperate zone caves: Evidence from Ballynamintra Cave, Ireland. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2006, 68, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, A.; Krämer, E.; Steinbrugger, B.; Fabian, J.; Eber, E.; Sandri, B. Therapeutic effects of radon inhalation and hyperthermia in the curative Gastein galleries on children with bronchial asthma [Der therapeutische Einfluss von Radon–Inhalation und Hyperthermie im Gasteiner Heilstollen auf das Asthma bronchiale im Kindesalter]. Höhle 1994, 48, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Lemko, O.I.; Lemko, I.S. Speleotherapy, halotherapy, haloaerosoltherapy: Definitions, mechanisms of influence, perspectives of usage (part І). ACTMA TA AЛEРГIЯ 2017, 3, 50–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bengesser, R.; Pavuza, R. Zum Stand der Speläotherapie in Österreich. Höhle 2004, 55, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kluterthöhle & Freizeit Verwaltungs- und Betriebs-GmbH & Co. KG Geschichtliches. Available online: https://www.kluterthoehle.de/hoehlenwelt/geschichtliches (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Deutscher Heilstollenverband Gesundheit aus dem Schoß der Erde. Available online: https://www.deutscher-heilstollenverband.de/ (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Heilklimastollen Friedrich Frei atmen. Besonderes Klima mit Heilender Wirkung. Available online: https://www.heilklimastollen.at (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Terzer, C.; Rainer, R. Landesmuseum Bergbau Ich Atme. Available online: https://www.bergbaumuseum.it/de/prettau/klimastollen/ich-atme-979.html (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Kalab, Z. Sanatorium Edel Practical information about the stay at the speleotherapy 2016. Available online: https://www.speleoterapie.cz/speleoterapie/o-speleoterapii/ (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Beamon, S.; Falkenbach, A.; Fainburg, G.; Linde, K. Speleotherapy for asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2001, CD001741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielory, L. Complementary and Alternative Medicine in the Treatment of Allergic and Asthmatic Disease. In Allergy and Asthma; Mahmoudi, M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 531–552. ISBN 978-3-319-30833-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ricny, D.; Sandri, B.; Trimmel, H. Beiträge zu Speläotherapie und Höhlenklima, II. Akten des 10. internationalen Symposium für Speläotherapie, Bad Bleiberg (Kärnten), Oktober 1992. Höhle Wiss. Beih. Zur Z. 1994, 48, 1–299. [Google Scholar]
- Lunghi, E.; Manenti, R.; Ficetola, G.F. Cave features, seasonality and subterranean distribution of non-obligate cave dwellers. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randell, S.H.; Boucher, R.C. Effective Mucus Clearance Is Essential for Respiratory Health. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alföldy, B.; Török, S.; Balásházy, I.; Hofmann, W.; Winkler-Heil, R. EPMA and XRF characterization of therapeutic cave aerosol particles and their deposition in the respiratory system. X-Ray Spectrom. 2002, 31, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, S.; Pegah, A.; Davood, F.; Said, A.; Babak, M.; Mani, M.; Mahdi, R.; Peyman, H. The effect of nebulized magnesium sulfate in the treatment of moderate to severe asthma attacks: A randomized clinical trial. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.L.; Ford, W.R.; Kidd, E.J.; Broadley, K.J.; Powell, C. Effects of nebulised magnesium sulphate on inflammation and function of the guinea-pig airway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 801, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sompornrattanaphan, M.; Thongngarm, T.; Ratanawatkul, P.; Wongsa, C.; Swigris, J.J. The contribution of particulate matter to respiratory allergy. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kertész, Z.S.; Balásházy, I.; Borbély-Kiss, I.; Hofmann, W.; Hunyadi, I.; Salma, I.; Winkler-Heil, R. Composition, size distribution and lung deposition distribution of aerosols collected in the atmosphere of a speleotherapeutic cave situated below Budapest, Hungary. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2002, 189, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faimon, J.; Troppová, D.; Baldík, V.; Novotný, R. Air circulation and its impact on microclimatic variables in the Císařská Cave (Moravian Karst, Czech Republic). Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 599–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, A. An analytical study of air circulation in caves. Int. J. Speleol. 1968, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlai, J.; Hakl, J.; Kávási, N.; Szeiler, G.; Szabó, P.; Kovács, T. Annual average radon concentration in the show caves of Hungary. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 287, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, A. Radon in Caves. Int. J. Speleol. 2005, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiot-Guilhe, C.; Seidel, J.-L.; Jourde, H.; Hébrard, O.; Bailly-Comte, V. Seasonal variations of CO 2 and 222 Rn in a Mediterranean sinkhole-spring (Causse d’Aumelas, SE France). Int. J. Speleol. 2007, 36, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doss, M. Shifting the Paradigm in Radiation Safety. Dose-Response 2012, 10, 562–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckey, T.D. Radiation Hormesis: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Dose-Response 2006, 4, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korzhe, V. Changing of the abiotic parameters of karst cave Belojacha in pannonian suburb (Slovenia). Geol. Maced. 2017, 31, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gaus, W.; Weber, H. Efficacy and Safety of Speleotherapy in Children with Asthma Bronchiale. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Kurortmed. 2010, 20, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C. Speleotherapy - scientific relevance in the last five years (2013 – 2017)—A systematic review. Balneo Res. J. 2017, 8, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuers, M.; Chapron, A.; Guihard, H.; Bouchez, T.; Darmon, D. Impact of non-drug therapies on asthma control: A systematic review of the literature. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 25, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maierean, A.; Ciumarnean, L.; Alexescu, T.G.; Domokos, B.; Rajnoveanu, R.; Arghir, O.; Todea, D.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Dogaru, G.; Bordea, R.I. Complementary therapeutic approaches in asthma. Balneo Res. J. 2019, 10, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, R.A.; Sorkness, C.A.; Kosinski, M.; Schatz, M.; Li, J.T.; Marcus, P.; Murray, J.J.; Pendergraft, T.B. Development of the asthma control test: A survey for assessing asthma control. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mösges, R.; Schmalz, P.; Köberlein, J.; Kaciran, M.; Baiardini, I. The RHINASTHMA-Quality of Life Scale German Adapted Version: Validation of a new disease specific quality of life scale for patients suffering from allergic rhinitis and bronchial hyperreactivity. HNO 2007, 55, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATS. Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetta, A.; Zanini, A.; Pisi, G.; Aiello, M.; Tzani, P.; Neri, M.; Olivieri, D. Reference values for the 6-min walk test in healthy subjects 20–50 years old. Respir. Med. 2006, 100, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, I.; Camner, P.; Jensen, P.L.; Philipson, K.; Proctor, D.F. A comparison of nasal and tracheobronchial clearance. Arch. Environ. Health 1974, 29, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Gel, Y.R.; Brunner, E.; Konietschke, F. nparLD: An R software package for the nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, D. Consolidated data analysis and presentation using an open-source add-in for the Microsoft Excel® spreadsheet software. Med. Writ. 2014, 23, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunneborg, C.E. Bootstrap Applications for the Behavioral Sciences. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1987, 47, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; Schulz, E. Abschlußbericht über das Forschungs- und Entwicklungsvorhaben “Klimatische und lufthygienische Qualitätsstandards für Speläotherapieeinrichtungen”; Deutscher Wetterdienst, Geschäftsfeld Medizin-Metereologie: Freiburg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dweik, R.A.; Boggs, P.B.; Erzurum, S.C.; Irvin, C.G.; Leigh, M.W.; Lundberg, J.O.; Olin, A.-C.; Plummer, A.L.; Taylor, D.R. An Official ATS Clinical Practice Guideline: Interpretation of Exhaled Nitric Oxide Levels (FeNO) for Clinical Applications. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.A.; Latham, J.R.; Callister, R.; Pretto, J.J.; Baines, K.; Saltos, N.; Upham, J.W.; Wood, L.G. Acute exercise is associated with reduced exhaled nitric oxide in physically inactive adults with asthma. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015, 114, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.; Collins, P.B.; Khosravi, M.; Lin, R.-L.; Lee, L.-Y. Bronchoconstriction Triggered by Breathing Hot Humid Air in Patients with Asthma: Role of Cholinergic Reflex. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 185, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, G.; Iravani, J.; Melville, G.N.; Richter, H.-G. Influence of Temperature and Decreased Water Content of Inspired Air on the Ciliated Bronchial Epithelium A Physiological and Electron Microscopical Study. Acta Otolaryngol. (Stockh.) 1977, 84, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, H. Radonbelastung in Österreich. Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft; Bundesministerium für Land- und Forstwirtschaft, Umwelt und Wasserwirtschaft: Vienna, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garber, C.E.; Blissmer, B.; Deschenes, M.R.; Franklin, B.A.; Lamonte, M.J.; Lee, I.-M.; Nieman, D.C.; Swain, D.P.; American College of Sports Medicine American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: Guidance for prescribing exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, F.A.R.; Almeida, F.M.; Cukier, A.; Stelmach, R.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Martins, M.A.; Carvalho, C.R.F. Effects of aerobic training on airway inflammation in asthmatic patients. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, M.; Moonie, S. Physical activity participation among adult Nevadans with self-reported asthma. J. Asthma Off. J. Assoc. Care Asthma 2011, 48, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystad, W.; Harris, J.; Borgen, J.S. Asthma and wheezing among Norwegian elite athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.D.; Daviskas, E. The mechanism of exercise-induced asthma is…. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Environment Agency. Air quality in Europe—2018. EEA Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranabetter, A.; Gཫl, M.; Herzog, M. Messbericht Feinstaub im Winter 2013/2014. Winter Exercise and Speleotherapy for Allergy and Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial 2014, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]

| Baseline Variables | Exercise Group (n = 18) | Speleotherapy Group (n = 23) | Baseline Tests | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Median ± IQR | Mean ± SD | Median ± IQR | |||
| Gender | male n = 5 | female n = 13 | male n = 12 | female n = 11 | 0.21 | χ2 Test |
| Residence+ | rural n = 5 | urban n = 13 | rural n = 6 | urban n = 17 | 0.67 | χ2 Test |
| RAST/PRICK | 2 or + n = 8 | >3 or > ++ n = 10 | 2 or + n = 7 | >3 or > ++ n = 16 | 0.52 | χ2 Test |
| Age (years) | 40.61 ± 12.12 | 45.0 ± 22.25 | 32.78 ± 9.90 | 29.00 ± 14.00 | 0.03 * | T-Test |
| Height (m) | 172.61 ± 6.66 | 172.0 ± 7.50 | 174.35 ± 9.10 | 175.00 ± 12.50 | 0.48 | T-Test |
| Weight (kg) | 69.83 ± 9.83 | 69.0 ± 10.00 | 68.39 ± 16.24 | 70.00 ± 15.00 | 0.73 | T-Test |
| Pulse (bpm) | 70.99 ± 12.57 | 70.38 ± 23.00 | 72.91 ± 13.30 | 70.00 ± 19.50 | 0.64 | T-Test |
| BP-Systole (mmHg) | 125.28 ± 14.46 | 123.5 ± 14.50 | 121.48 ± 11.29 | 124.00 ± 9.50 | 0.48 | U-Test |
| BP-Diastole (mmHg) | 76.44 ± 9.97 | 78.0 ± 15.00 | 74.74 ± 10.46 | 75.00 ± 15.50 | 0.60 | T-Test |
| ACT (score) | 21.39 ± 3.57 | 22.5 ± 4.50 | 22.17 ± 3.04 | 23.00 ± 3.50 | 0.54 | U-Test |
| FeNO (ppb) | 40.78 ± 23.03 | 38.0 ± 39.00 | 36.91 ± 28.26 | 28.00 ± 23.00 | 0.69 | T-Test |
| FEV1 (%) | 96.28 ± 20.98 | 98.5 ± 21.25 | 101.39 ± 17.78 | 104.00 ± 14.00 | 0.38 | U-Test |
| FVC (%) | 108.17 ± 17.66 | 108.0 ± 12.75 | 107.22 ± 14.48 | 107.00 ± 12.50 | 0.78 | U-Test |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 93.39 ± 11.81 | 95.0 ± 17.00 | 97.43 ± 9.26 | 99.00 ± 9.50 | 0.20 | U-Test |
| 6MWT-Distance (%) | 104.35 ± 8.17 | 105.99 ± 10.97 | 112.01 ± 13.36 | 111.74 ± 21.38 | 0.03 * | T-Test |
| Timepoint | Exercise Group (n = 18) | Speleotherapy Group (n = 23) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Type | Distance (km) | Altitude (m) | Type | Distance (km) | Altitude (m) |
| day 1 | winter hiking | 9.9 km | 557 m | winter hiking | 10.0 km | 400 m |
| day 2 | alpine skiing | 42.8 km | - | alpine skiing | 23.2 km | - |
| day 3 | winter hiking | 15.3 km | 448 m | cross-country skiing | 5.4 km | 60 m |
| day 5 | alpine skiing | 38.7 km | - | winter hiking | 8.1 km | 335 m |
| day 6 | winter hiking | 5.9 km | 258 m | winter hiking | 2.5 km | 100 m |
| day 7 | alpine skiing | 55.8 km | - | winter hiking | 8.2 km | 217 m |
| day 8 | alpine skiing | 31.0 km | - | alpine skiing | 34 km | - |
| day 9 | winter hiking | 13.4 km | 381 m | winter hiking | 7.0 km | 248 m |
| day 1–10 | average hiking | 11.1 km | 411 m | average hiking | 6.9 km | 226.7 m |
| day 1–10 | average skiing | 42.1 km | - | average skiing | 28.6 km | - |
| Parameter | F1-LD-F1 Model | Relative Treatment Effects (RTE) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p-Value | Time | Speleotheapy | Winter Exercise | ||||||
| FeNO | Speleo | 0.52 | Exercise | 0.44 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.65 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.54 | Sp. × T0 | 0.50 | Ex. × T0 | 0.57 | |
| Time | 4.06 (1.37, ∞) | 0.093 | n.s | T1 | 0.40 | Sp. × T1 | 0.47 | Ex. × T1 | 0.34 | |
| Treat × Time | 3.93 (1.37, ∞) | 0.103 | n.s | T2 | 0.50 | Sp. × T2 | 0.60 | Ex. × T2 | 0.41 | |
| Nasal NO | Speleo | 0.51 | Exercise | 0.47 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.21 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.52 | Sp. × T0 | 0.49 | Ex. × T0 | 0.55 | |
| Time | 0.33 (1.83, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T1 | 0.46 | Sp. × T1 | 0.50 | Ex. × T1 | 0.42 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.76 (1.83, ∞) | 0.733 | n.s | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.54 | Ex. × T2 | 0.44 | |
| Nasal eosinophils (%) | Speleo | 0.49 | Exercise | 0.52 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.13 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.60 | Sp. × T0 | 0.60 | Ex. × T0 | 0.59 | |
| Time | 11.76 (1.73, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.40 | Sp. × T1 | 0.35 | Ex. × T1 | 0.44 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.10 (1.73, ∞) | 0.654 | n.s | T2 | 0.51 | Sp. × T2 | 0.52 | Ex. × T2 | 0.51 | |
| Mucociliary clearance (min) | Speleo | 0.48 | Exercise | 0.52 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.23 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.57 | Sp. × T0 | 0.59 | Ex. × T0 | 0.55 | |
| Time | 6.78 (1.84, ∞) | 0.006 | ** | T1 | 0.42 | Sp. × T1 | 0.40 | Ex. × T1 | 0.43 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.58 (1.84, ∞) | 0.470 | n.s | T2 | 0.52 | Sp. × T2 | 0.47 | Ex. × T2 | 0.58 | |
| FVC (%) | Speleo | 0.48 | Exercise | 0.53 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.28 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.48 | Sp. × T0 | 0.47 | Ex. × T0 | 0.50 | |
| Time | 0.23 (1.90, ∞) | 0.220 | n.s | T1 | 0.50 | Sp. × T1 | 0.48 | Ex. × T1 | 0.52 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.33 (1.90, ∞) | 0.705 | n.s | T2 | 0.52 | Sp. × T2 | 0.49 | Ex. × T2 | 0.56 | |
| FEV1 (%) | Speleo | 0.53 | Exercise | 0.46 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.60 (1.00, ∞) | 0.689 | n.s | T0 | 0.49 | Sp. × T0 | 0.53 | Ex. × T0 | 0.45 | |
| Time | 1.04 (1.91, ∞) | 0.416 | n.s | T1 | 0.51 | Sp. × T1 | 0.54 | Ex. × T1 | 0.48 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.51 (1.91, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.52 | Ex. × T2 | 0.46 | |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | Speleo | 0.54 | Exercise | 0.44 | ||||||
| Treat | 1.24 (1.00, ∞) | 0.585 | n.s | T0 | 0.50 | Sp. × T0 | 0.56 | Ex. × T0 | 0.44 | |
| Time | 6.72 (1.76, ∞) | 0.008 | ** | T1 | 0.52 | Sp. × T1 | 0.55 | Ex. × T1 | 0.48 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.81 (1.76, ∞) | 0.504 | n.s | T2 | 0.46 | Sp. × T2 | 0.52 | Ex. × T2 | 0.41 | |
| PEF (%) | Speleo | 0.53 | Exercise | 0.46 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.58 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.47 | Sp. × T0 | 0.47 | Ex. × T0 | 0.46 | |
| Time | 2.08 (1.95, ∞) | 0.253 | n.s | T1 | 0.50 | Sp. × T1 | 0.55 | Ex. × T1 | 0.44 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.77 (1.95, ∞) | 0.326 | n.s | T2 | 0.53 | Sp. × T2 | 0.57 | Ex. × T2 | 0.48 | |
| MEF25–75% (%) | Speleo | 0.55 | Exercise | 0.43 | ||||||
| Treat | 1.93 (1.00, ∞) | 0.501 | n.s | T0 | 0.49 | Sp. × T0 | 0.56 | Ex. × T0 | 0.42 | |
| Time | 3.64 (1.92, ∞) | 0.112 | n.s | T1 | 0.51 | Sp. × T1 | 0.56 | Ex. × T1 | 0.47 | |
| Treat × Time | 2.28 (1.92, ∞) | 0.314 | n.s | T2 | 0.48 | Sp. × T2 | 0.55 | Ex. × T2 | 0.41 | |
| WBC (103/µL) | Speleo | 0.47 | Exercise | 0.54 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.94 (1.00, ∞) | 0.791 | n.s | T0 | 0.59 | Sp. × T0 | 0.58 | Ex. × T0 | 0.60 | |
| Time | 16.01 (1.89, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.36 | Sp. × T1 | 0.29 | Ex. × T1 | 0.44 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.35 (1.89, ∞) | 0.518 | n.s | T2 | 0.56 | Sp. × T2 | 0.54 | Ex. × T2 | 0.57 | |
| RBC (106/µL) | Speleo | 0.54 | Exercise | 0.45 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.99 (1.00, ∞) | 0.642 | n.s | T0 | 0.51 | Sp. × T0 | 0.54 | Ex. × T0 | 0.47 | |
| Time | 0.22 (1.86, ∞) | 0.783 | n.s | T1 | 0.49 | Sp. × T1 | 0.54 | Ex. × T1 | 0.45 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.06 (1.86, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.53 | Ex. × T2 | 0.44 | |
| Neutrophil granulocytes (%) | Speleo | 0.51 | Exercise | 0.49 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.08 (1.00, ∞) | 0.837 | n.s | T0 | 0.54 | Sp. × T0 | 0.55 | Ex. × T0 | 0.54 | |
| Time | 2.47 (1.77, ∞) | 0.184 | n.s | T1 | 0.45 | Sp. × T1 | 0.43 | Ex. × T1 | 0.47 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.12 (1.77, ∞) | 0.321 | n.s | T2 | 0.50 | Sp. × T2 | 0.54 | Ex. × T2 | 0.46 | |
| Eosinophil granulocytes (%) | Speleo | 0.47 | Exercise | 0.54 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.61 (1.00, ∞) | 0.872 | n.s | T0 | 0.48 | Sp. × T0 | 0.40 | Ex. × T0 | 0.56 | |
| Time | 2.25 (2.00, ∞) | 0.214 | n.s | T1 | 0.55 | Sp. × T1 | 0.56 | Ex. × T1 | 0.54 | |
| Treat × Time | 3.38 (2.00, ∞) | 0.070 | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.46 | Ex. × T2 | 0.51 | ||
| Parameter | F1-LD-F1 Model | Relative Treatment Effects (RTE) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p-Value | Time | Speleotheapy | Winter Exercise | ||||||
| 6MWT Distance (%) | Speleo | 0.60 | Exercise | 0.37 | ||||||
| Treat | 9.59 (1.00, ∞) | 0.010 | * | T0 | 0.43 | Sp. × T0 | 0.53 | Ex. × T0 | 0.34 | |
| Time | 5.04 (1.95, ∞) | 0.019 | * | T1 | 0.53 | Sp. × T1 | 0.68 | Ex. × T1 | 0.39 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.50 (1.95, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.59 | Ex. × T2 | 0.39 | |
| Peak respiratory | Speleo | 0.50 | Exercise | 0.50 | ||||||
| frequency (L/min) | Treat | 0.00 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.50 | Sp. × T0 | 0.46 | Ex. × T0 | 0.54 |
| Time | 0.06 (1.83, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T1 | 0.50 | Sp. × T1 | 0.52 | Ex. × T1 | 0.49 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.42 (1.83, ∞) | 0.449 | n.s | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.51 | Ex. × T2 | 0.47 | |
| Peak minute | Speleo | 0.60 | Exercise | 0.38 | ||||||
| ventilation (L/min) | Treat | 8.51 (1.00, ∞) | 0.018 | * | T0 | 0.44 | Sp. × T0 | 0.53 | Ex. × T0 | 0.35 |
| Time | 5.81 (1.80, ∞) | 0.018 | * | T1 | 0.55 | Sp. × T1 | 0.70 | Ex. × T1 | 0.40 | |
| Treat × Time | 2.21 (1.80, ∞) | 0.579 | n.s | T2 | 0.47 | Sp. × T2 | 0.56 | Ex. × T2 | 0.38 | |
| BORG Dyspnea | Speleo | 0.48 | Exercise | 0.52 | ||||||
| pre (score) | Treat | 0.35 (1.00, ∞) | 0.725 | n.s | T0 | 0.54 | Sp. × T0 | 0.51 | Ex. × T0 | 0.57 |
| Time | 2.42 (1.66, ∞) | 0.198 | n.s | T1 | 0.45 | Sp. × T1 | 0.42 | Ex. × T1 | 0.48 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.28 (1.66, ∞) | 0.841 | n.s | T2 | 0.52 | Sp. × T2 | 0.51 | Ex. × T2 | 0.52 | |
| BORG Dyspnea post | Speleo | 0.55 | Exercise | 0.44 | ||||||
| (score) | Treat | 1.84 (1.00, ∞) | 0.876 | n.s | T0 | 0.54 | Sp. × T0 | 0.56 | Ex. × T0 | 0.52 |
| Time | 2.66 (1.80, ∞) | 0.229 | n.s | T1 | 0.46 | Sp. × T1 | 0.50 | Ex. × T1 | 0.43 | |
| Treat × Time | 2.70 (1.80, ∞) | 0.376 | n.s | T2 | 0.48 | Sp. × T2 | 0.58 | Ex. × T2 | 0.38 | |
| BORG Fatigue pre | Speleo | 0.52 | Exercise | 0.48 | ||||||
| (score) | Treat | 0.31 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.60 | Sp. × T0 | 0.62 | Ex. × T0 | 0.57 |
| Time | 10.60 (1.89, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.41 | Sp. × T1 | 0.40 | Ex. × T1 | 0.43 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.16 (1.89, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.49 | Sp. × T2 | 0.53 | Ex. × T2 | 0.44 | |
| BORG Fatigue post | Speleo | 0.54 | Exercise | 0.45 | ||||||
| (score) | Treat | 1.46 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.56 | Sp. × T0 | 0.61 | Ex. × T0 | 0.51 |
| Time | 6.81 (1.94, ∞) | 0.006 | ** | T1 | 0.49 | Sp. × T1 | 0.53 | Ex. × T1 | 0.45 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.08 (1.94, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.44 | Sp. x T2 | 0.49 | Ex. × T2 | 0.39 | |
| Parameter | F1-LD-F1 Model | Relative Treatment Effects (RTE) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p Value | Time | Speleotheapy | Winter Exercise | ||||||
| RhinAsthma Total score (score) | Speleo | 0.53 | Exercise | 0.46 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.64 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.59 | Sp. × T0 | 0.64 | Ex. × T0 | 0.55 | |
| Time | 12.52 (1.86, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.45 | Sp. × T1 | 0.44 | Ex. × T1 | 0.45 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.68 (1.86, ∞) | 0.566 | n.s | T2 | 0.45 | Sp. × T2 | 0.50 | Ex. × T2 | 0.40 | |
| RhinAshtma Limitation in daily life (score) | Speleo | 0.54 | Exercise | 0.45 | ||||||
| Treat | 1.25 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.58 | Sp. × T0 | 0.66 | Ex. × T0 | 0.51 | |
| Time | 12.07 (1.90 ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.47 | Sp. × T1 | 0.50 | Ex. × T1 | 0.43 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.08 (1.90, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.43 | Sp. × T2 | 0.46 | Ex. × T2 | 0.40 | |
| RhinAsthma Respiratory problems (score) | Speleo | 0.50 | Exercise | 0.50 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.00 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.61 | Sp. × T0 | 0.63 | Ex. × T0 | 0.58 | |
| Time | 10.99 (1.94, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.44 | Sp. × T1 | 0.41 | Ex. × T1 | 0.46 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.96 (1.94, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.46 | Sp. × T2 | 0.45 | Ex. × T2 | 0.47 | |
| RhinAsthma Rhino-conjunctivitis score (score) | Speleo | 0.52 | Exercise | 0.48 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.32 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.58 | Sp. × T0 | 0.58 | Ex. × T0 | 0.57 | |
| Time | 9.36 (1.94, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.39 | Sp. × T1 | 0.37 | Ex. × T1 | 0.41 | |
| Treat × Time | 2.23 (1.94, ∞) | 0.328 | n.s | T2 | 0.53 | Sp. × T2 | 0.60 | Ex. × T2 | 0.45 | |
| RhinAsthma Treatment and med. problems (score) | Speleo | 0.51 | Exercise | 0.48 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.18 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.59 | Sp. × T0 | 0.61 | Ex. × T0 | 0.56 | |
| Time | 11.57 (1.88, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.49 | Sp. × T1 | 0.51 | Ex. × T1 | 0.47 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.21 (1.88, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.42 | Sp. × T2 | 0.42 | Ex. × T2 | 0.41 | |
| RhinAsthma Impairment in sensory percept. (score) | Speleo | 0.51 | Exercise | 0.48 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.12 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s. | T0 | 0.55 | Sp. × T0 | 0.58 | Ex. × T0 | 0.51 | |
| Time | 3.30 (1.88, ∞) | 0.199 | n.s. | T1 | 0.49 | Sp. × T1 | 0.47 | Ex. × T1 | 0.50 | |
| Treat × Time | 1.12 (1.88, ∞) | 0.648 | n.s. | T2 | 0.46 | Sp. × T2 | 0.49 | Ex. × T2 | 0.43 | |
| Speleo | 0.50 | Exercise | 0.50 | |||||||
| VAS Allergy (score) | Treat | 0.01 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.40 | Sp. × T0 | 0.45 | Ex. × T0 | 0.36 |
| Time | 13.41 (1.98, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.62 | Sp. × T1 | 0.61 | Ex. × T1 | 0.62 | |
| Treat × Time | 2.68 (1.98, ∞) | 0.138 | n.s | T2 | 0.48 | Sp. × T2 | 0.43 | Ex. × T2 | 0.53 | |
| Treat × T2 | 5.17 (1.00, ∞) | 0.069 | ||||||||
| VAS Health Status (score) | Speleo | 0.52 | Exercise | 0.48 | ||||||
| Treat | 0.33 (1.00, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T0 | 0.37 | Sp. × T0 | 0.40 | Ex. × T0 | 0.33 | |
| Time | 16.01 (1.56, ∞) | <0.001 | *** | T1 | 0.60 | Sp. × T1 | 0.62 | Ex. × T1 | 0.57 | |
| Treat × Time | 0.30 (1.56, ∞) | 1.000 | n.s | T2 | 0.53 | Sp. × T2 | 0.53 | Ex. × T2 | 0.53 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freidl, J.; Huber, D.; Braunschmid, H.; Romodow, C.; Pichler, C.; Weisböck-Erdheim, R.; Mayr, M.; Hartl, A. Winter Exercise and Speleotherapy for Allergy and Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103311
Freidl J, Huber D, Braunschmid H, Romodow C, Pichler C, Weisböck-Erdheim R, Mayr M, Hartl A. Winter Exercise and Speleotherapy for Allergy and Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103311
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreidl, Johanna, Daniela Huber, Herbert Braunschmid, Carina Romodow, Christina Pichler, Renate Weisböck-Erdheim, Michaela Mayr, and Arnulf Hartl. 2020. "Winter Exercise and Speleotherapy for Allergy and Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103311
APA StyleFreidl, J., Huber, D., Braunschmid, H., Romodow, C., Pichler, C., Weisböck-Erdheim, R., Mayr, M., & Hartl, A. (2020). Winter Exercise and Speleotherapy for Allergy and Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103311