Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D
Abstract
:1. Introduction
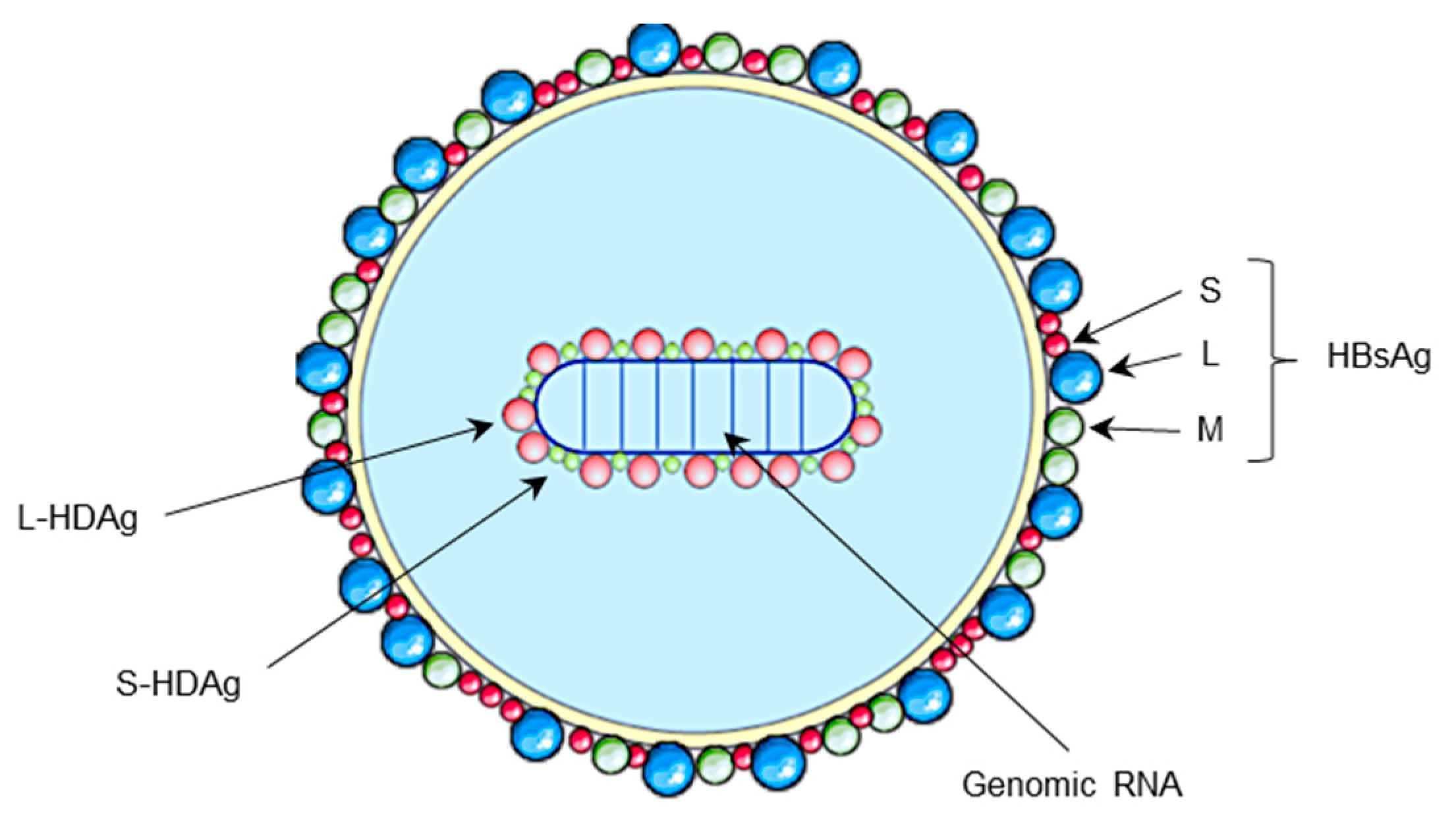
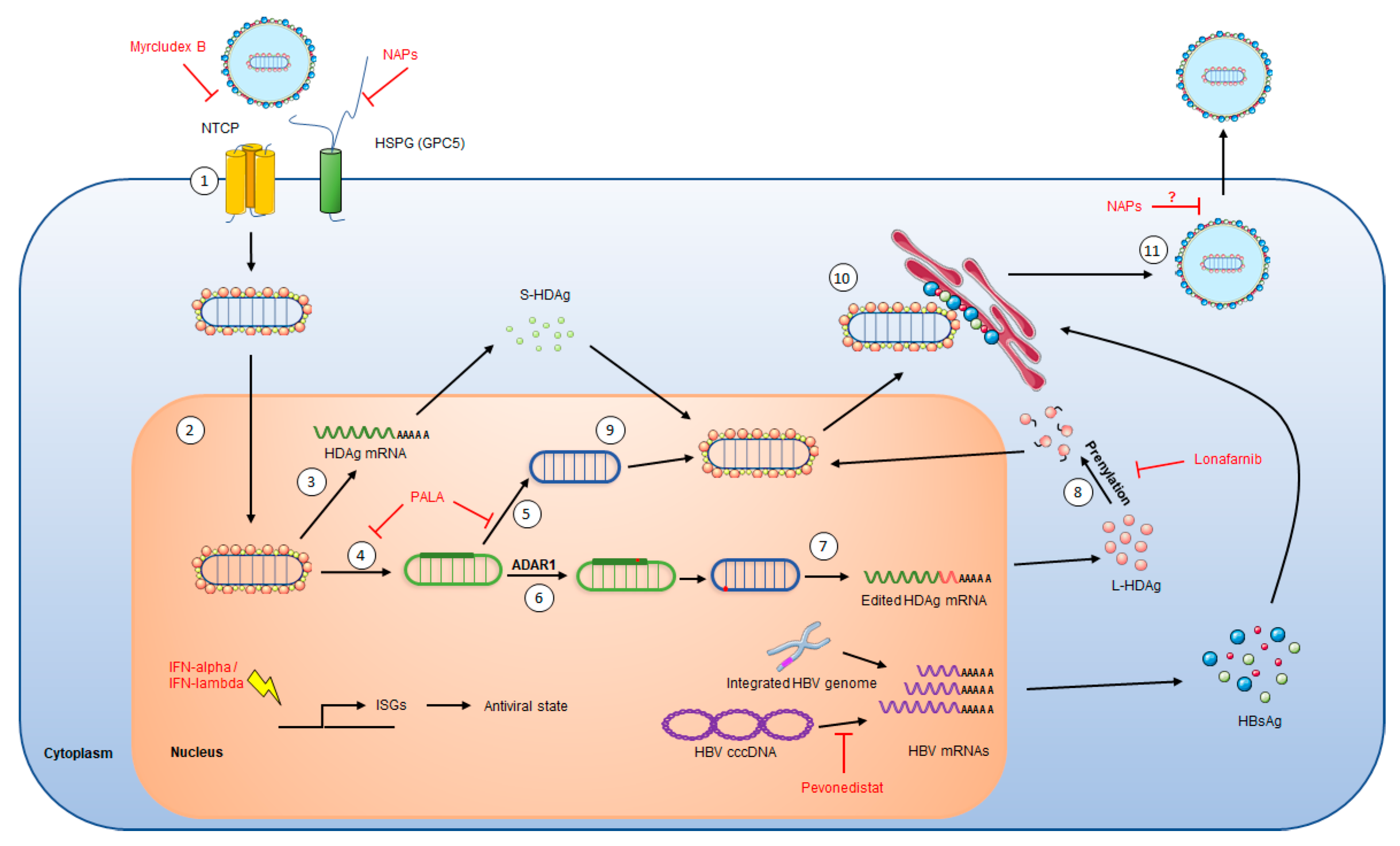
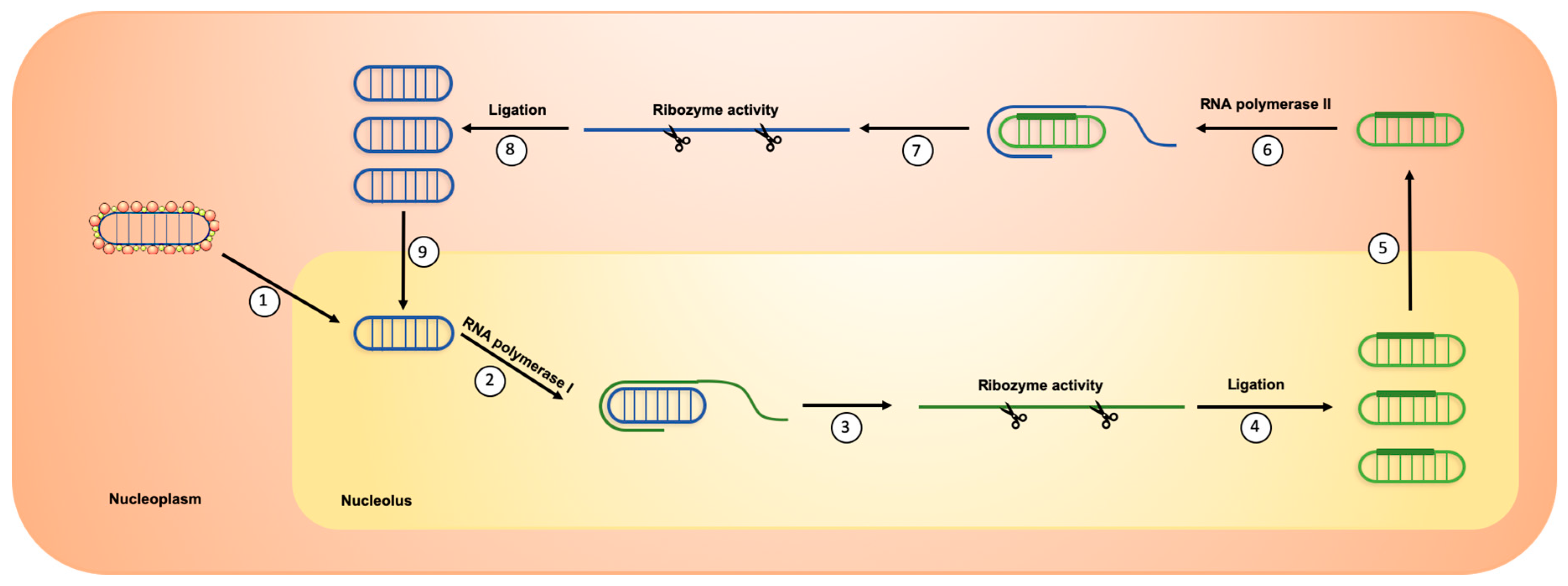
2. HDV Life Cycle
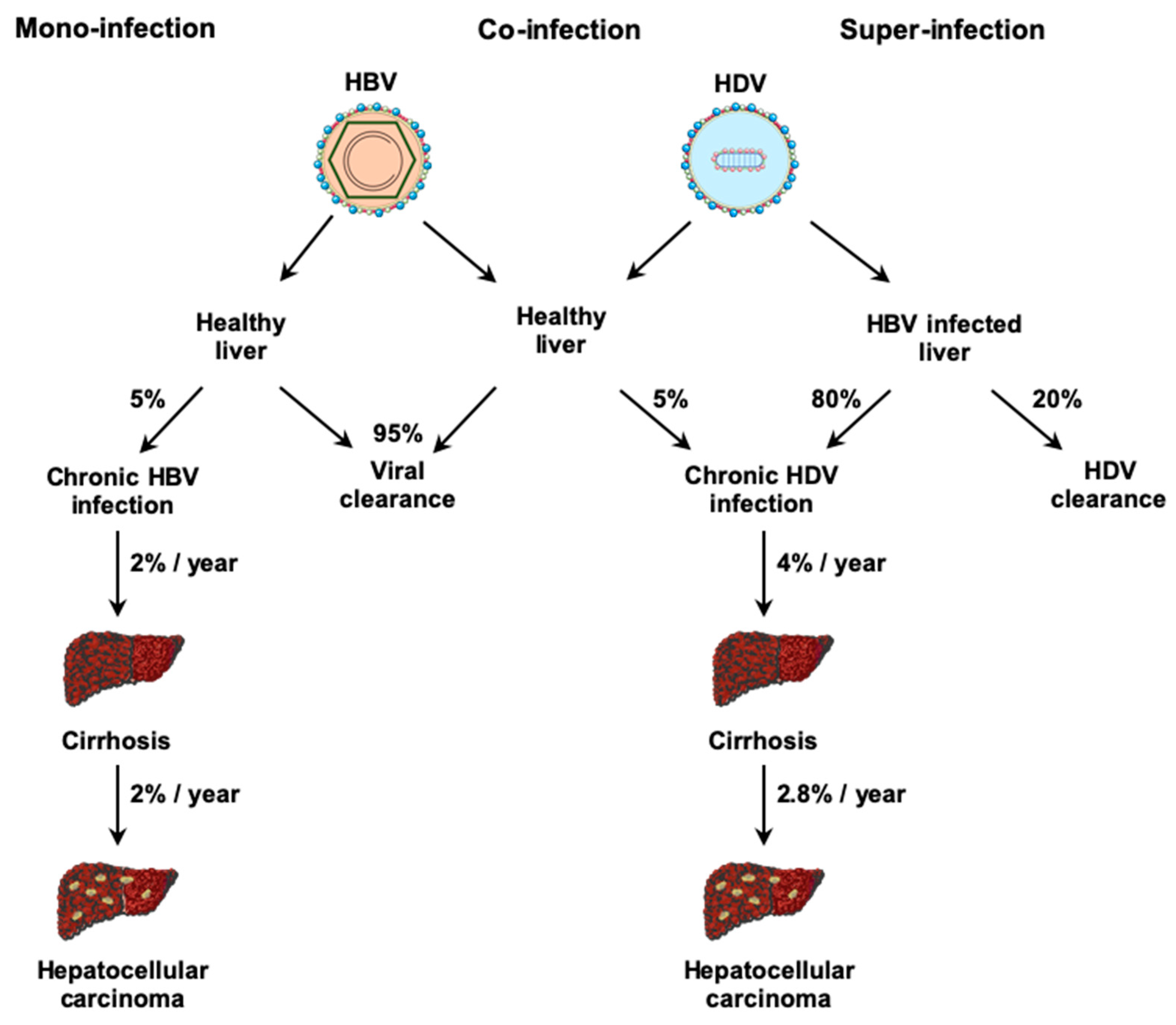
3. Physiopathology
4. Therapeutics: Past and Future
4.1. Current Treatment: Pegylated Interferon Alpha
4.2. New Therapeutic Agents in Clinical Trials
4.2.1. Interferon-Lambda, a Better Tolerated Immunomodulator
4.2.2. Myrcludex B, an Entry Inhibitor
4.2.3. Lonafarnib, a Morphogenesis Inhibitor
4.2.4. Nucleic Acid Polymers, Inhibitor of HBsAg Secretion
4.3. In Vitro Studies
4.3.1. PALA, Inhibitor of HDV Replication
4.3.2. Pevonedistat, Inhibitor of HBV Transcription
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sureau, C.; Negro, F. The hepatitis delta virus: Replication and pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzetto, M.; Canese, M.G.; Aricò, S.; Crivelli, O.; Trepo, C.; Bonino, F.; Verme, G. Immunofluorescence detection of new antigen-antibody system (delta/anti-delta) associated to hepatitis B virus in liver and in serum of HBsAg carriers. Gut 1977, 18, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzetto, M.; Hoyer, B.; Canese, M.G.; Shih, J.W.; Purcell, R.H.; Gerin, J.L. delta Agent: Association of delta antigen with hepatitis B surface antigen and RNA in serum of delta-infected chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 6124–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sureau, C.; Guerra, B.; Lanford, R.E. Role of the large hepatitis B virus envelope protein in infectivity of the hepatitis delta virion. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fattovich, G.; Giustina, G.; Schalm, S.W.; Hadziyannis, S.; Sanchez-Tapias, J.; Almasio, P.; Christensen, E.; Krogsgaard, K.; Degos, F.; de Moura, M.C.; et al. Occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma and decompensation in western European patients with cirrhosis type B. The EUROHEP Study Group on Hepatitis B Virus and Cirrhosis. Hepatology 1995, 21, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fattovich, G.; Giustina, G.; Christensen, E.; Pantalena, M.; Zagni, I.; Realdi, G.; Schalm, S.W. Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on morbidity and mortality in compensated cirrhosis type B. The European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (Eurohep). Gut 2000, 46, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.Y.; Shen, D.T.; Ji, D.Z.; Han, P.C.; Zhang, W.M.; Ma, J.F.; Chen, W.S.; Goyal, H.; Pan, S.; Xu, H.G. Prevalence and burden of hepatitis D virus infection in the global population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2018, 68, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ou, X.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Liu, J.; Pan, Q. Estimating the global prevalence, disease progression and clinical outcome of hepatitis delta virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gal, F.; Dziri, S.; Gerber, A.; Alloui, C.; Ben Abdesselam, Z.; Roulot, D.; Brichler, S.; Gordien, E. Performance Characteristics of a New Consensus Commercial Kit for Hepatitis D Virus RNA Viral Load Quantification. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocco, C.; Bonavolta, R.; Vallefuoco, L.; Braschi, U.; Sorrentino, R.; Terracciano, D.; Portella, G. Comparison of anti-hepatitis D virus (HDV) ETI-AB-DELTAK-2 assay and the novel LIAISON® XL MUREX anti-HDV assay in the diagnosis of HDV infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 114873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niro, G.A.; Ciancio, A.; Gaeta, G.B.; Smedile, A.; Marrone, A.; Olivero, A.; Stanzione, M.; David, E.; Brancaccio, G.; Fontana, R.; et al. Pegylated interferon alpha-2b as monotherapy or in combination with ribavirin in chronic hepatitis delta. Hepatology 2006, 44, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelnau, C.; Le Gal, F.; Ripault, M.P.; Gordien, E.; Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Boyer, N.; Pham, B.N.; Maylin, S.; Bedossa, P.; Dény, P.; et al. Efficacy of peginterferon alpha-2b in chronic hepatitis delta: Relevance of quantitative RT-PCR for follow-up. Hepatology 2006, 44, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenci, P.; Formann, E.; Romeo, R. Successful treatment of chronic hepatitis D with a short course of peginterferon alfa-2a. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1626–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, A.; Dijkema, R.; Arnberg, A.C.; van der Meide, P.H.; Schellekens, H. The hepatitis delta (delta) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature 1986, 323, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.J.; Kalpana, G.; Goldberg, J.; Mason, W.; Werner, B.; Gerin, J.; Taylor, J. Structure and replication of the genome of the hepatitis delta virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8774–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.S.; Choo, Q.L.; Weiner, A.J.; Ou, J.H.; Najarian, R.C.; Thayer, R.M.; Mullenbach, G.T.; Denniston, K.J.; Gerin, J.L.; Houghton, M. Structure, sequence and expression of the hepatitis delta (delta) viral genome. Nature 1986, 323, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonino, F.; Heermann, K.H.; Rizzetto, M.; Gerlich, W.H. Hepatitis delta virus: Protein composition of delta antigen and its hepatitis B virus-derived envelope. J. Virol. 1986, 58, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, N.; Cunha, C.; Menne, S.; Gudima, S.O. Envelope proteins derived from naturally integrated hepatitis B virus DNA support assembly and release of infectious hepatitis delta virus particles. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5742–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botelho-Souza, L.F.; Vasconcelos, M.P.A.; de Oliveira dos Santos, A.; Salcedo, J.M.V.; Vieira, D.S. Hepatitis delta: Virological and clinical aspects. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farci, P.; Chessa, L.; Balestrieri, C.; Serra, G.; Lai, M.E. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D. J. Viral Hepat. 2007, 14, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Mehrle, S.; Nkongolo, S.; Kaufman, C.; Fälth, M.; Stindt, J.; Königer, C.; Nassal, M.; Kubitz, R.; et al. Hepatitis B and D viruses exploit sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide for species-specific entry into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Colpitts, C.C.; Sureau, C.; Baumert, T.F. Hepatitis B virus receptors and molecular drug targets. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Colpitts, C.C.; Bach, C.; Heydmann, L.; Weiss, A.; Renaud, M.; Durand, S.C.; Habersetzer, F.; Durantel, D.; Abou-Jaoudé, G.; et al. A targeted functional RNA interference screen uncovers glypican 5 as an entry factor for hepatitis B and D viruses. Hepatology 2016, 63, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas Longarela, O.; Schmidt, T.T.; Schöneweis, K.; Romeo, R.; Wedemeyer, H.; Urban, S.; Schulze, A. Proteoglycans Act as Cellular Hepatitis Delta Virus Attachment Receptors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sureau, C.; Salisse, J. A conformational heparan sulfate binding site essential to infectivity overlaps with the conserved hepatitis B virus A-determinant. Hepatology 2013, 57, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.P.; Yeh, C.T.; Ou, J.H.; Lai, M.M. Characterization of nuclear targeting signal of hepatitis delta antigen: Nuclear transport as a protein complex. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, C.; Freitas, N.; Cunha, C. Characterization of the nuclear localization signal of the hepatitis delta virus antigen. Virology 2008, 370, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modahl, L.E.; Macnaughton, T.B.; Zhu, N.; Johnson, D.L.; Lai, M.M.C. RNA-Dependent Replication and Transcription of Hepatitis Delta Virus RNA Involve Distinct Cellular RNA Polymerases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6030–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheu, G.T. Initiation of hepatitis delta virus (HDV) replication: HDV RNA encoding the large delta antigen cannot replicate. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Nie, X.; Chang, H.E.; Han, Z.; Taylor, J. Transcription of Hepatitis Delta Virus RNA by RNA Polymerase II. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macnaughton, T.B.; Shi, S.T.; Modahl, L.E.; Lai, M.M.C. Rolling circle replication of hepatitis delta virus RNA is carried out by two different cellular RNA polymerases. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3920–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.J.; Macnaughton, T.; Gao, L.; Lai, M.M.C. RNA-templated replication of hepatitis delta virus: Genomic and antigenomic RNAs associate with different nuclear bodies. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6478–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, P.J. Nucleolar targeting of hepatitis delta antigen abolishes its ability to initiate viral antigenomic RNA replication. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verrier, E.R.; Weiss, A.; Bach, C.; Heydmann, L.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Kopp, A.; El Saghire, H.; Crouchet, E.; Pessaux, P.; Garcia, T.; et al. Combined small molecule and loss-of-function screen uncovers estrogen receptor alpha and CAD as host factors for HDV infection and antiviral targets. Gut 2020, 69, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayan, G.C.; Casey, J.L. Increased RNA Editing and Inhibition of Hepatitis Delta Virus Replication by High-Level Expression of ADAR1 and ADAR2. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3819–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartwig, D.; Schütte, C.; Warnecke, J.; Dorn, I.; Hennig, H.; Kirchner, H.; Schlenke, P. The large form of ADAR 1 is responsible for enhanced hepatitis delta virus RNA editing in interferon-alpha-stimulated host cells. J. Viral Hepat. 2006, 13, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.S.; Watson, J.A.; Havel, C.M.; White, J.M. Identification of a prenylation site in delta virus large antigen. Science 1992, 256, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, J.C.; Casey, P.J. The hepatitis delta virus large antigen is farnesylated both in vitro and in animal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 4569–4572. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.B.; Lai, M.M. Isoprenylation masks a conformational epitope and enhances trans-dominant inhibitory function of the large hepatitis delta antigen. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 2958–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.C.; Lee, C.P.; Liu, H.K.; Chang, M.F.; Lai, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, C. Cellular Nuclear Export Factors TAP and Aly Are Required for HDAg-L-mediated Assembly of Hepatitis Delta Virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26226–26238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Chang, S.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, M.F. A novel chromosome region maintenance 1-independent nuclear export signal of the large form of hepatitis delta antigen that is required for the viral assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8142–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.B.; Lai, M.M. Isoprenylation mediates direct protein-protein interactions between hepatitis large delta antigen and hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 7659–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Negro, F. Hepatitis D virus coinfection and superinfection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a021550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fattovich, G.; Boscaro, S.; Noventa, F.; Pornaro, E.; Stenico, D.; Alberti, A.; Ruol, A.; Realdi, G. Influence of hepatitis delta virus infection on progression to cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis type B. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saracco, G.; Macagno, S.; Rosina, F.; Rizzetto, M. Serologic markers with fulminant hepatitis in persons positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. A worldwide epidemiologic and clinical survey. Ann. Intern. Med. 1988, 108, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedile, A.; Verme, G.; Cargnel, A.; Dentico, P.; Opolon, P.; Vergani, D.; Farci, P.; Caredda, F.; Caporaso, N.; Trepo, C.; et al. Influence of delta infection on severity of hepatitis B. Lancet 1982, 320, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, S.; Chin, K.P.; Redeker, A.G.; Peters, R.L. Fulminant B viral hepatitis: Role of delta agent. Gastroenterology 1984, 86, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Farci, P.; Niro, G.A. Clinical features of hepatitis D. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonino, F.; Negro, F.; Baldi, M.; Brunetto, M.R.; Chiaberge, E.; Capalbo, M.; Maran, E.; Lavarini, C.; Rocca, N.; Rocca, G. The natural history of chronic delta hepatitis. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1987, 234, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Romeo, R.; Del Ninno, E.; Rumi, M.; Russo, A.; Sangiovanni, A.; de Franchis, R.; Ronchi, G.; Colombo, M. A 28-Year Study of the Course of Hepatitis Δ Infection: A Risk Factor for Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.C.; Chen, P.J.; Kuo, M.Y.; Lee, S.D.; Chen, D.S.; Ting, L.P. Production of hepatitis delta virus and suppression of helper hepatitis B virus in a human hepatoma cell line. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaper, M.; Rodriguez-Frias, F.; Jardi, R.; Tabernero, D.; Homs, M.; Ruiz, G.; Quer, J.; Esteban, R.; Buti, M. Quantitative longitudinal evaluations of hepatitis delta virus RNA and hepatitis B virus DNA shows a dynamic, complex replicative profile in chronic hepatitis B and D. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, J.L.; Crespo, J.; de la Cruz, F.; Casafont, F.; Lopez-Arias, M.J.; Martín-Ramos, L.; Pons-Romero, F. Correlation between hepatitis B viremia and the clinical and histological activity of chronic delta hepatitis. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1994, 183, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Yim, S.A.; Heydmann, L.; El Saghire, H.; Bach, C.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Mailly, L.; Durand, S.C.; Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Evasion from Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase Sensing in Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, B.Y.; Gaska, J.M.; Lipkowitz, G.; Bram, Y.; Parekh, A.; Parsons, L.; Leach, R.; Jindal, R.; Cho, C.H.; Shrirao, A.; et al. Analysis of Host Responses to Hepatitis B and Delta Viral Infections in a Micro-scalable Hepatic Co-culture System. Hepatology 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Filzmayer, C.; Ni, Y.; Sültmann, H.; Mutz, P.; Hiet, M.S.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Hepatitis D virus replication is sensed by MDA5 and induces IFN-β/λ responses in hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giersch, K.; Allweiss, L.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Bierwolf, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Pollok, J.M.; Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Lütgehetmann, M. Hepatitis Delta co-infection in humanized mice leads to pronounced induction of innate immune responses in comparison to HBV mono-infection. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.; Brichler, S.; Radjef, N.; Lebon, P.; Goffard, A.; Hober, D.; Fagard, R.; Kremsdorf, D.; Dény, P.; Gordien, E. Hepatitis delta virus proteins repress hepatitis B virus enhancers and activate the alpha/beta interferon-inducible MxA gene. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatsralt-Od, B.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Endo, K.; Inoue, J.; Okamoto, H. High prevalence of dual or triple infection of hepatitis B, C, and delta viruses among patients with chronic liver disease in Mongolia. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 77, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardi, R.; Rodriguez, F.; Buti, M.; Costa, X.; Cotrina, M.; Galimany, R.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J. Role of hepatitis B, C, and D viruses in dual and triple infection: Influence of viral genotypes and hepatitis B precore and basal core promoter mutations on viral replicative interference. Hepatology 2001, 34, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Vargas, J.; Amirache, F.; Boson, B.; Mialon, C.; Freitas, N.; Sureau, C.; Fusil, F.; Cosset, F.L. Enveloped viruses distinct from HBV induce dissemination of hepatitis D virus in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lempp, F.A.; Ni, Y.; Urban, S. Hepatitis delta virus: Insights into a peculiar pathogen and novel treatment options. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Yurdaydìn, C.; Dalekos, G.N.; Erhardt, A.; Çakaloğlu, Y.; Değertekin, H.; Gürel, S.; Zeuzem, S.; Zachou, K.; Bozkaya, H.; et al. Peginterferon plus Adefovir versus Either Drug Alone for Hepatitis Delta. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yurdaydin, C. New treatment option for delta virus: Is a cure in sight? J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchmann, B.; Döhner, K.; Schirdewahn, T.; Sodeik, B.; Manns, M.P.; Wedemeyer, H.; Ciesek, S.; von Hahn, T. A screening assay for the identification of host cell requirements and antiviral targets for hepatitis D virus infection. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollard, S.M.; Kanmogne, G.D. Maraviroc: A review of its use in HIV infection and beyond. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5447–5468. [Google Scholar]
- Awady, M.K.E.; Dawood, R.M. Resistance to Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents in Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infections. In Update on Hepatitis C; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.; Magri, A.; Bonsall, D.; Ip, C.L.C.; Trebes, A.; Brown, A.; Piazza, P.; Bowden, R.; Nguyen, D.; Ansari, M.A.; et al. Resistance analysis of genotype 3 hepatitis C virus indicates subtypes inherently resistant to nonstructural protein 5A inhibitors. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syedbasha, M.; Egli, A. Interferon Lambda: Modulating Immunity in Infectious Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Etzion, O.; Hamid, S.S.; Lurie, Y.; Gane, E.; Bader, N.; Yardeni, D.; Nevo-Shor, A.; Channa, S.; Mawani, M.; Parkash, O.; et al. PS-052-End of study results from LIMT HDV study: 36% durable virologic response at 24 weeks post-treatment with pegylated interferon lambda monotherapy in patients with chronic hepatitis delta virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripon, P.; Rumin, S.; Urban, S.; Seyec, J.L.; Glaise, D.; Cannie, I.; Guyomard, C.; Lucas, J.; Trepo, C.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. Infection of a human hepatoma cell line by hepatitis B virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15655–15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Mier, W.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; von Weizsäcker, F.; Haberkorn, U.; Fischer, L.; Pollok, J.M.; Erbes, B.; et al. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in vivo by entry inhibitors derived from the large envelope protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lütgehetmann, M.; Mancke, L.V.; Volz, T.; Helbig, M.; Allweiss, L.; Bornscheuer, T.; Pollok, J.M.; Lohse, A.W.; Petersen, J.; Urban, S.; et al. Humanized chimeric uPA mouse model for the study of hepatitis B and D virus interactions and preclinical drug evaluation. Hepatology 2012, 55, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: First results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Bogomolov, P.; Blank, A.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri-Petersen, M.; Bremer, B.; Voronkova, N.; Schöneweis, K.; Pathil, A.; Burhenne, J.; et al. Final results of a multicenter, open-label phase 2b clinical trial to assess safety and efficacy of Myrcludex B in combination with Tenofovir in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Schöneweis, K.; Bogomolov, P.O.; Voronkova, N.; Chulanov, V.; Stepanova, T.; Bremer, B.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; Burhenne, J.; et al. GS-13-Final results of a multicenter, open-label phase 2 clinical trial (MYR203) to assess safety and efficacy of myrcludex B in cwith PEG-interferon Alpha 2a in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e81–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loglio, A.; Ferenci, P.; Uceda Renteria, S.C.; Tham, C.Y.L.; van Bömmel, F.; Borghi, M.; Holzmann, H.; Perbellini, R.; Trombetta, E.; Giovanelli, S.; et al. Excellent safety and effectiveness of high-dose myrcludex-B monotherapy administered for 48 weeks in HDV-related compensated cirrhosis: A case report of 3 patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSM. ATU de Cohorte en Cours—ANSM: Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé. Available online: https://www.ansm.sante.fr/Activites/Autorisations-temporaires-d-utilisation-ATU/ATU-de-cohorte-en-cours/(offset)/4 (accessed on 17 December 2019).
- Berndt, N.; Hamilton, A.D.; Sebti, S.M. Targeting protein prenylation for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karakaya, F.; Çalişkan, A.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Bozdayi, A.M.; Koh, C.; Heller, T.; et al. Optimizing lonafarnib treatment for the management of chronic delta hepatitis: The LOWR HDV-1 study. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Idilman, R.; Keskin, O.; Kalkan, C.; Karakaya, M.F.; Caliskan, A.; Yurdcu, E.; Karatayli, S.C.; Bozdayi, M.; Koh, C.; et al. A phase 2 dose-optimization study of lonafarnib with ritonavir for the treatment of chronic delta hepatitis—End of treatment results from the LOWR HDV-2 study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, S33–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Surana, P.; Han, T.; Fryzek, N.; Kapuria, D.; Etzion, O.; Takyar, V.; Rotman, Y.; Canales, R.; Dahari, H.; et al. A phase 2 study exploring once daily dosing of ritonavir boosted lonafarnib for the treatment of chronic delta hepatitis—End of study results from the LOWR HDV-3 study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, S101–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Port, K.; Deterding, K.; Wranke, A.; Kirschner, J.; Bruno, B.; Martins, B.; Glenn, J.S.; Kornberg, M.; Manns, M.P. A phase 2 dose-escalation study of lonafarnib plus ritonavir in patients with chronic hepatitis D: Final results from the Lonafarnib with ritonavir in HDV-4 (LOWR HDV-4) study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.; Da, B.L.; Surana, P.; Huang, A.; Kapuria, D.; Rotman, Y.; Vittal, A.; Gilman, C.; Ben-Yakov, G.; Lai, C.; et al. A phase 2 study of lonafarnib, ritonavir and peginterferon lambda for 24 weeks: Interim end-of-treatment results from the LIFT HDV study. Hepatology 2019, 70, S101–S102. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, T.; Hu, Z.; Kato, T.; Dreux, M.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Imamura, M.; Hiraga, N.; Juteau, J.M.; Cosset, F.L.; Chayama, K.; et al. Amphipathic DNA polymers inhibit hepatitis C virus infection by blocking viral entry. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernstein, D.I.; Goyette, N.; Cardin, R.; Kern, E.R.; Boivin, G.; Ireland, J.; Juteau, J.M.; Vaillant, A. Amphipathic DNA polymers exhibit antiherpetic activity in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beilstein, F.; Blanchet, M.; Vaillant, A.; Sureau, C. Nucleic Acid Polymers Are Active against Hepatitis Delta Virus Infection In Vitro. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaillant, A. Nucleic acid polymers: Broad spectrum antiviral activity, antiviral mechanisms and optimization for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Mahtab, M.; Bazinet, M.; Vaillant, A. Safety and Efficacy of Nucleic Acid Polymers in Monotherapy and Combined with Immunotherapy in Treatment-Naive Bangladeshi Patients with HBeAg+Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazinet, M.; Pântea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Albrecht, J.; Schmid, P.; Le Gal, F.; Gordien, E.; Krawczyk, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of REP 2139 and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis D virus co-infection (REP 301 and REP 301-LTF): A non-randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Krawczyk, A.; Dittmer, U.; Vaillant, A. Ongoing analysis of functional control/cure of HBV and HDV infection following REP 2139-CA and pegylated interferon alpha-2a therapy in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection: 3-year follow-up results from the REP 301-LTF study. Hepatology 2019, 70, 440. [Google Scholar]
- Vaillant, A. REP 2139: Antiviral Mechanisms and Applications in Achieving Functional Control of HBV and HDV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, A.C.; Bauer, T.M.; Aggarwal, C.; Lee, C.B.; Harvey, R.D.; Cohen, R.B.; Sedarati, F.; Nip, T.K.; Faessel, H.; Dash, A.B.; et al. Phase Ib study of pevonedistat, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, in combination with docetaxel, carboplatin and paclitaxel, or gemcitabine, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Yamagami, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Seimiya, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, E.; Ishibashi, R.; Funato, K.; et al. Pevonedistat, a Neuronal Precursor Cell-Expressed Developmentally Down-Regulated Protein 8–Activating Enzyme Inhibitor, Is a Potent Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löffler, M.; Fairbanks, L.D.; Zameitat, E.; Marinaki, A.M.; Simmonds, H.A. Pyrimidine pathways in health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadler, S.; Gleissner, B.; Hilgenfeld, R.U.; Thiel, E.; Haynes, H.; Kaleya, R.; Rozenblit, A.; Kreuser, E.D. Phase II trial of N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate (PALA), 5-fluorouracil and recombinant interferon-alpha-2b in patients with advanced gastric carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, B.; Yurdaydın, C.; Kabaçam, G.; Ratsch, B.A.; Zachou, K.; Bremer, B.; Dalekos, G.N.; Erhardt, A.; Tabak, F.; Yalcin, K.; et al. Late HDV RNA relapse after peginterferon alpha-based therapy of chronic hepatitis delta. Hepatology 2014, 60, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enchev, R.I.; Schulman, B.A.; Peter, M. Protein neddylation: Beyond cullin-RING ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decorsière, A.; Mueller, H.; van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Nio, K.; Reszka-Blanco, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Su, L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes Degradation of SMC5/6 to Enhance HBV Replication. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Cellular Target/Step of HDV Life Cycle | Current Clinical Trial Step | Posology | EOT | FU (24w) | Drawbacks | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MyrB + PEG-IFNA | NTCP/Entry inhibitor | Phase III | Phase II CT: | LLOQ: 15/30 (50%) | LLOQ: 12/30 (40%) | 3 relapses at FU (24 weeks); SSE: 5 | [78] |
| 2 or 5 mg MyrB daily + 180 µg IFNA weekly (48 weeks) | |||||||
| LNF + RTV + LMB | Farnesylation/Assembly inhibitor | Phase III | Phase II CT: | >2log decrease: 18/19 (95%) | ND | ALT flares at EOT | [86] |
| 50 mg LNF + 100 mg RTV twice a day | LLOQ: 10/19 (53%) | ||||||
| 180 mcg LMB weekly | |||||||
| REP2139 | ?/HBsAg secretion inhibitor | Phase II | 500 mg weekly (15 weeks), 250 mg + 180 µg IFNA (15 weeks), 180 µg IFNA (33 weeks) | >2log decrease: 9/11 (82%) | >2log decrease: 9/11 (82%) | SSE in 4/11 patients (33%) | [92,93] |
| LLOQ: 9/11 (82%) | LLOQ: 7/11 (63%) | ||||||
| PALA | CAD/HDV replication | Preclinical study | 100 µM in cultured PHH without toxicity | ND | ND | Safety in an animal model not assessed yet | [35] |
| Pevonedistat | NAE1/HBV transcription | Preclinical study | 1 µM in cultured PHH without toxicity | ND | ND | Mild to strong SE observed in phase Ib CT | [95,96] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turon-Lagot, V.; Saviano, A.; Schuster, C.; Baumert, T.F.; Verrier, E.R. Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010222
Turon-Lagot V, Saviano A, Schuster C, Baumert TF, Verrier ER. Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010222
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuron-Lagot, Vincent, Antonio Saviano, Catherine Schuster, Thomas F. Baumert, and Eloi R. Verrier. 2020. "Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010222
APA StyleTuron-Lagot, V., Saviano, A., Schuster, C., Baumert, T. F., & Verrier, E. R. (2020). Targeting the Host for New Therapeutic Perspectives in Hepatitis D. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010222





