Usefulness of the Inferior Articular Process’s Cross-Sectional Area as a Morphological Parameter for Predicting Central Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patients
2.2. Imaging Parameters
2.3. Image Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.X.; Jing, X.W.; Cui, P.; He, X.; Hao, D.J.; Li, S.J. Effectiveness of dynamic fixation Coflex treatment for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, N.; Tani, T.; Kiyasu, K.; Kumon, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Takemasa, R.; Tadokoro, N.; Nishida, K.; Ikeuchi, M. Unilateral repetitive tibial nerve stimulation improves neurogenic claudication and bilateral F-wave conduction in central lumbar spinal stenosis. J. Orthop. Sci. 2018, 23, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.U.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Karm, M.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoo, J.I.; Chon, S.W.; Suh, J.H. The Role of the Ligamentum Flavum Area as a Morphological Parameter of Lumbar Central Spinal Stenosis. Pain Physician 2017, 20, E419–E424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.F.; Fekete, T.F.; Pacifico, D.; O’Riordan, D.; Nauer, S.; von Buren, M.; Schizas, C. Dural sac cross-sectional area and morphological grade show significant associations with patient-rated outcome of surgery for lumbar central spinal stenosis. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 2552–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessberg, P.; Frennered, K. Central lumbar spinal stenosis: Natural history of non-surgical patients. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orita, S.; Yamashita, M.; Eguchi, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Inoue, G.; Miyagi, M.; Watanabe, T.; Ozawa, T.; Kamoda, H.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Pregabalin for Refractory Radicular Leg Pain due to Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Preliminary Prospective Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2016, 2016, 5079675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmundsson, F.G.; Jonsson, B.; Stromqvist, B. Determinants of patient satisfaction after surgery for central spinal stenosis without concomitant spondylolisthesis: A register study of 5100 patients. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, J.; Hamoud, K.; Masharawi, Y.M.; May, H.; Hay, O.; Medlej, B.; Peled, N.; Hershkovitz, I. Ligamentum flavum thickness in normal and stenotic lumbar spines. Spine Phila Pa 1976 2010, 35, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.U.; Kong, Y.G.; Lee, J.; Cheong, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.K.; Park, J.Y.; Suh, J.H. Clinical symptoms of lumbar spinal stenosis associated with morphological parameters on magnetic resonance images. Eur. Spine J. 2015, 24, 2236–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.H.; Choi, S.I.; Cho, H.R.; Kang, K.N.; Rhyu, C.J.; Chae, E.Y.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.U. Optimal Cut-Off Value of the Superior Articular Process Area as a Morphological Parameter to Predict Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 7914836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogikubo, O.; Forsberg, L.; Hansson, T. The relationship between the cross-sectional area of the cauda equina and the preoperative symptoms in central lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine Phila Pa 1976 2007, 32, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchikanti, L.; Kaye, A.D.; Manchikanti, K.; Boswell, M.; Pampati, V.; Hirsch, J. Efficacy of epidural injections in the treatment of lumbar central spinal stenosis: A systematic review. Anesth Pain Med. 2015, 5, e23139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchikanti, L.; Falco, F.J.; Pampati, V.; Hirsch, J.A. Lumbar interlaminar epidural injections are superior to caudal epidural injections in managing lumbar central spinal stenosis. Pain Phys. 2014, 17, E691–E702. [Google Scholar]
- Manchikanti, L.; Helm, S., 2nd; Pampati, V.; Racz, G.B. Cost Utility Analysis of Percutaneous Adhesiolysis in Managing Pain of Post-lumbar Surgery Syndrome and Lumbar Central Spinal Stenosis. Pain Pract. 2015, 15, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L.; Cash, K.A.; McManus, C.D.; Pampati, V. Assessment of effectiveness of percutaneous adhesiolysis in managing chronic low back pain secondary to lumbar central spinal canal stenosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Yeom, J.S.; Kang, H.S. Diagnostic advancement of axial loaded lumbar spine MRI in patients with clinically suspected central spinal canal stenosis. Spine Phila Pa 1976 2013, 38, E1342–E1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korse, N.S.; Kruit, M.C.; Peul, W.C.; Vleggeert-Lankamp, C.L.A. Lumbar spinal canal MRI diameter is smaller in herniated disc cauda equina syndrome patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiiwa, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Notani, N.; Ishihara, T.; Kawano, M.; Tsumura, H. Analysis of the Relationship between Ligamentum Flavum Thickening and Lumbar Segmental Instability, Disc Degeneration, and Facet Joint Osteoarthritis in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Asian Spine J. 2016, 10, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lu, T.; Li, H. Single-Session Combined Anterior-Posterior Approach for Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis with Obvious Displaced Lower Cervical Spine Fractures and Dislocations. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9205834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X. Age-related changes in the orientation of lumbar facet joints. Spine Phila Pa 1976 2009, 34, E596–E598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.M.; Hwang, S.W.; Safain, M.G.; Riesenburger, R.I. Iatrogenic Spinal Cord Injury during Removal of the Inferior Articular Process in the Presence of Ossification of the Ligamentum Flavum. Case Rep. Surg. 2016, 2016, 2318759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Das, S.; Suri, R.; Kapur, V. An asymmetrical inferior articular process of a lumbar vertebra. Folia Morphol. Warsz 2006, 65, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barz, C.; Melloh, M.; Staub, L.P.; Lord, S.J.; Merk, H.R.; Barz, T. Reversibility of nerve root sedimentation sign in lumbar spinal stenosis patients after decompression surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, Y.; Ito, S.; Hida, T.; Ito, K.; Harada, A.; Watanabe, K. Clinical outcome of lumbar spinal stenosis based on new classification according to hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. J. Orthop. Sci. 2017, 22, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, R.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Rong, L. The nerve root sedimentation sign for differential diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: A retrospective, consecutive cohort study. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, D.; Gautam, S.; Agarwal, A.; Khuba, S.; Kumar, S. Unexplained episode of sensory-motor deficit following lumbar epidural analgesia. Korean J. Pain 2019, 32, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, P.B.; Choe, G.Y.; Moon, J.Y.; Nahm, F.S.; Kim, Y.C. Therapeutic effect of epidurally administered lipo-prostaglandin e1 agonist in a rat spinal stenosis model. Korean J. Pain 2014, 27, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kwon, J.Y.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.H. Sudden hemodynamic collapse after making prone position on the Jackson spine table for spinal surgery. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L.; Pampati, V.; Kaye, A.D.; Hirsch, J.A. Therapeutic lumbar facet joint nerve blocks in the treatment of chronic low back pain: Cost utility analysis based on a randomized controlled trial. Korean J. Pain 2018, 31, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanie, M.S.; Ghobadifar, M.A. Risks and Pitfalls of Epidural Injections during Management of Lumbar Disc Herniation: Few Comments. Korean J. Pain 2015, 28, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.M.; Park, H.S.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, J. The effects of a forceful transforaminal epidural steroid injection on radicular pain: A preliminary study. Korean J. Pain 2014, 27, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Jung, S.W.; Lee, S.Y. Does spinal stenosis correlate with MRI findings and pain, psychologic factor and quality of life? Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2015, 68, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Han, C.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, E.M.; Choi, Y.R.; Chung, M.H. Motor Weakness after Caudal Epidural Injection Using the Air-acceptance Test. Korean J. Pain 2013, 26, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.J.; Park, H.S.; Park, M.K. The effect of needle tip position on the analgesic efficacy of pulsed radiofrequency treatment in patients with chronic lumbar radicular pain: A retrospective observational study. Korean J. Pain 2019, 32, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.K. Lumbar foraminal neuropathy: An update on non-surgical management. Korean J. Pain 2019, 32, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, E.; Kang, Y.; Ahn, J.M.; Kang, H.S. Systemic effects of fluoroscopically guided epidural steroid injection with dexamethasone. Korean J. Pain 2019, 32, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Koh, W.U.; Park, S.J.; Choi, W.J.; Suh, J.H.; Leem, J.G.; Park, P.H.; Shin, J.W. Clinical experiences of transforaminal balloon decompression for patients with spinal stenosis. Korean J. Pain 2012, 25, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
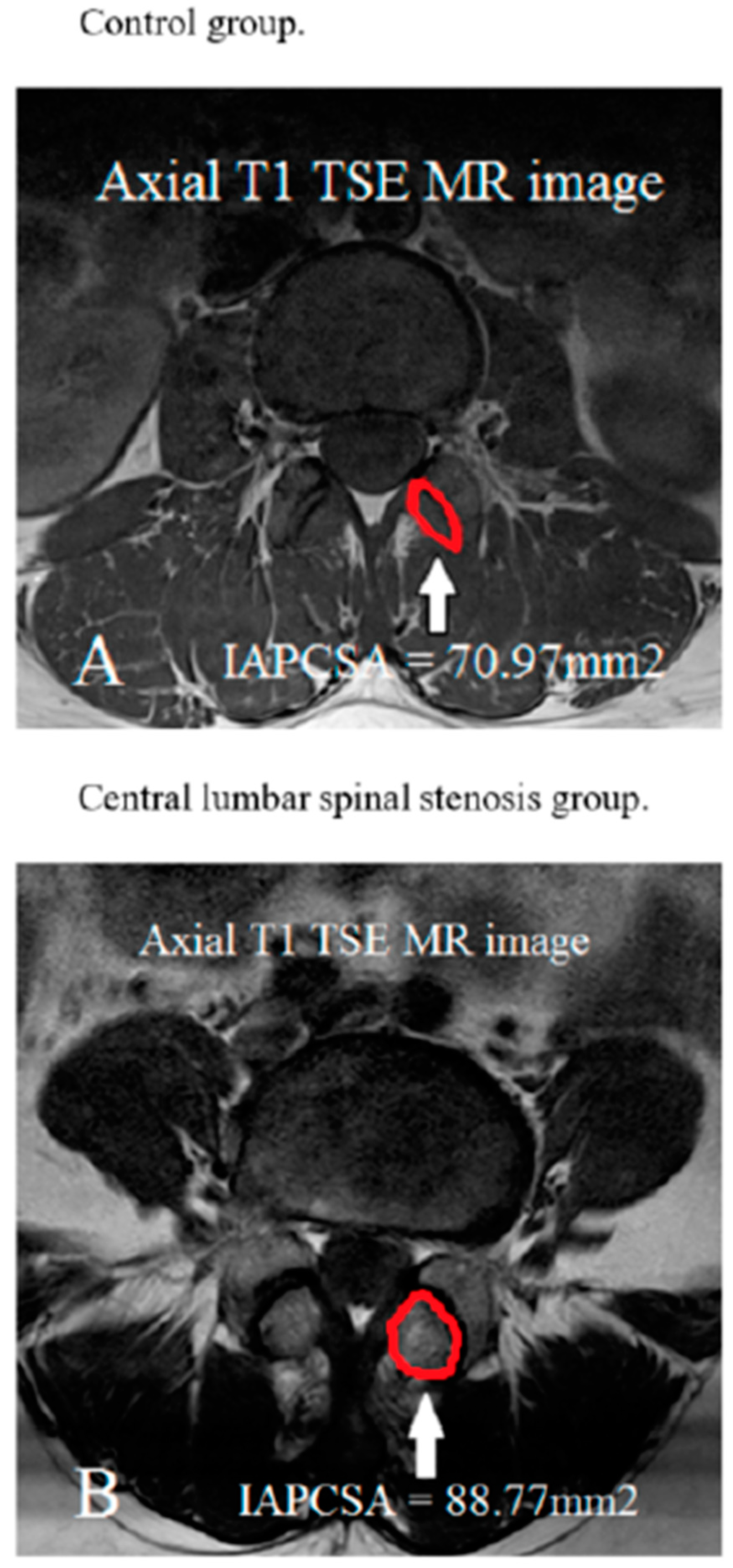
| Variable | Control Group n = 102 | CLSS Group n = 116 | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male/female) | 22/80 | 38/78 | NS |
| Age (yrs) IAPCSA (mm2) | 62.25 ± 8.51 70.97 ± 13.02 | 63.14 ± 8.41 88.77 ± 18.52 | NS p < 0.001 |
| Age Distribution (Years) | Total (N) |
|---|---|
| 50–59 | 69.40 ± 12.31 mm2 (46) |
| 60–69 | 70.28 ± 13.39 mm2 (36) |
| 70–82 | 75.81 ± 13.43 mm2 (20) p value = 0.172 |
| Age Distribution (Years) | Total (N) |
|---|---|
| 50–59 | 91.38 ± 21.36 mm2 (44) |
| 60–69 | 85.93 ± 17.09 mm2 (44) |
| 70–83 | 89.14 ± 15.65 mm2 (28) p value = 0.386 |
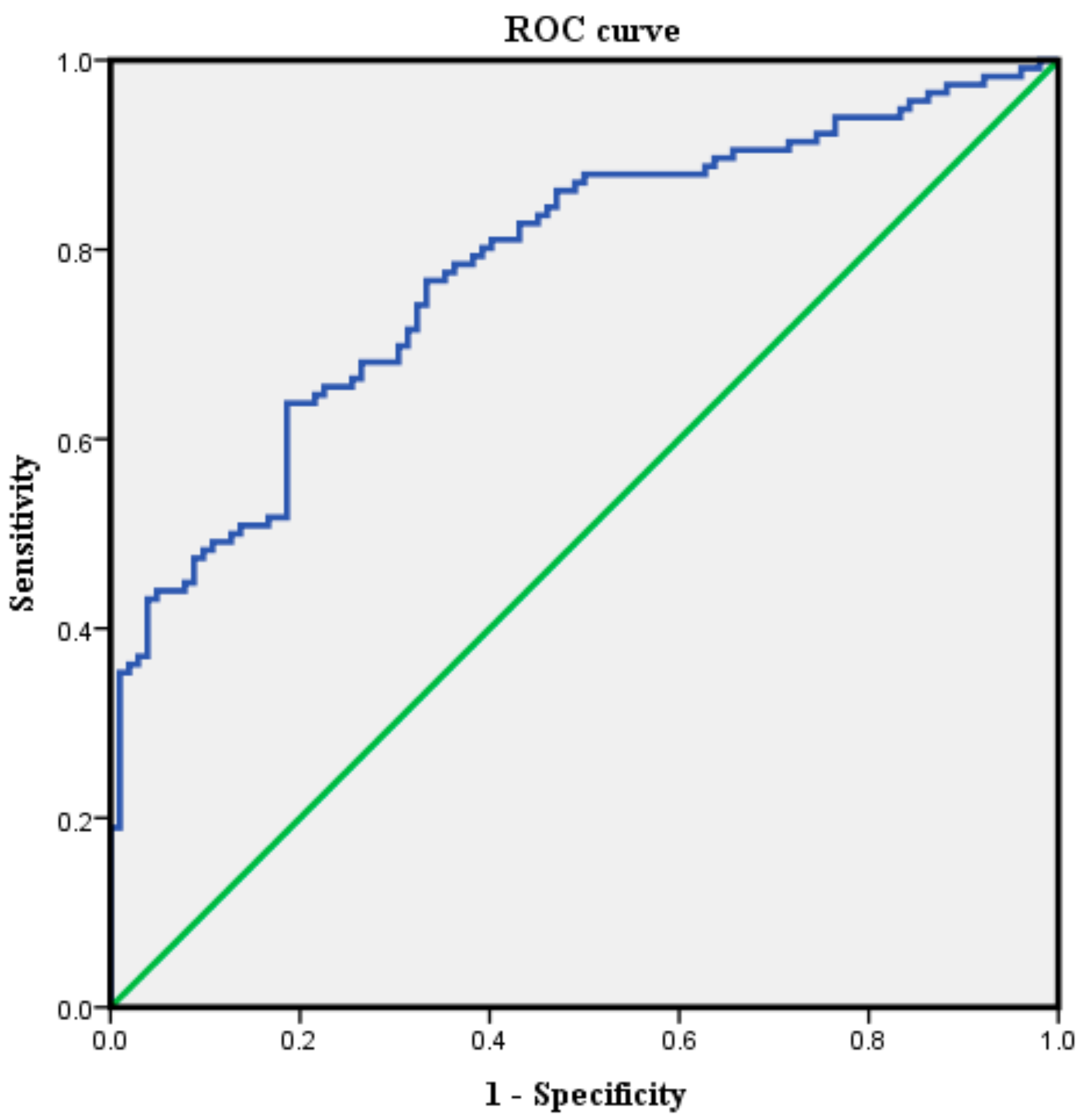
| IAPCSA (mm2) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 45.02 | 100 | 2.0 |
| 60.74 | 94.0 | 20.6 |
| 70.98 | 82.8 | 55.9 |
| 75.88 a | 71.6 | 68.6 |
| 84.88 | 55.2 | 81.4 |
| 98.11 | 35.3 | 98.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Lim, T.; Lim, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.U. Usefulness of the Inferior Articular Process’s Cross-Sectional Area as a Morphological Parameter for Predicting Central Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010214
Lee S, Lim T, Lim Y-S, Kim YU. Usefulness of the Inferior Articular Process’s Cross-Sectional Area as a Morphological Parameter for Predicting Central Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(1):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010214
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sooho, Taeha Lim, Young-Seob Lim, and Young Uk Kim. 2020. "Usefulness of the Inferior Articular Process’s Cross-Sectional Area as a Morphological Parameter for Predicting Central Lumbar Spinal Stenosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 1: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010214
APA StyleLee, S., Lim, T., Lim, Y.-S., & Kim, Y. U. (2020). Usefulness of the Inferior Articular Process’s Cross-Sectional Area as a Morphological Parameter for Predicting Central Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(1), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010214




