Association between Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Vascular Complications in Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Source and Ethics Statement
2.3. Outcome Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
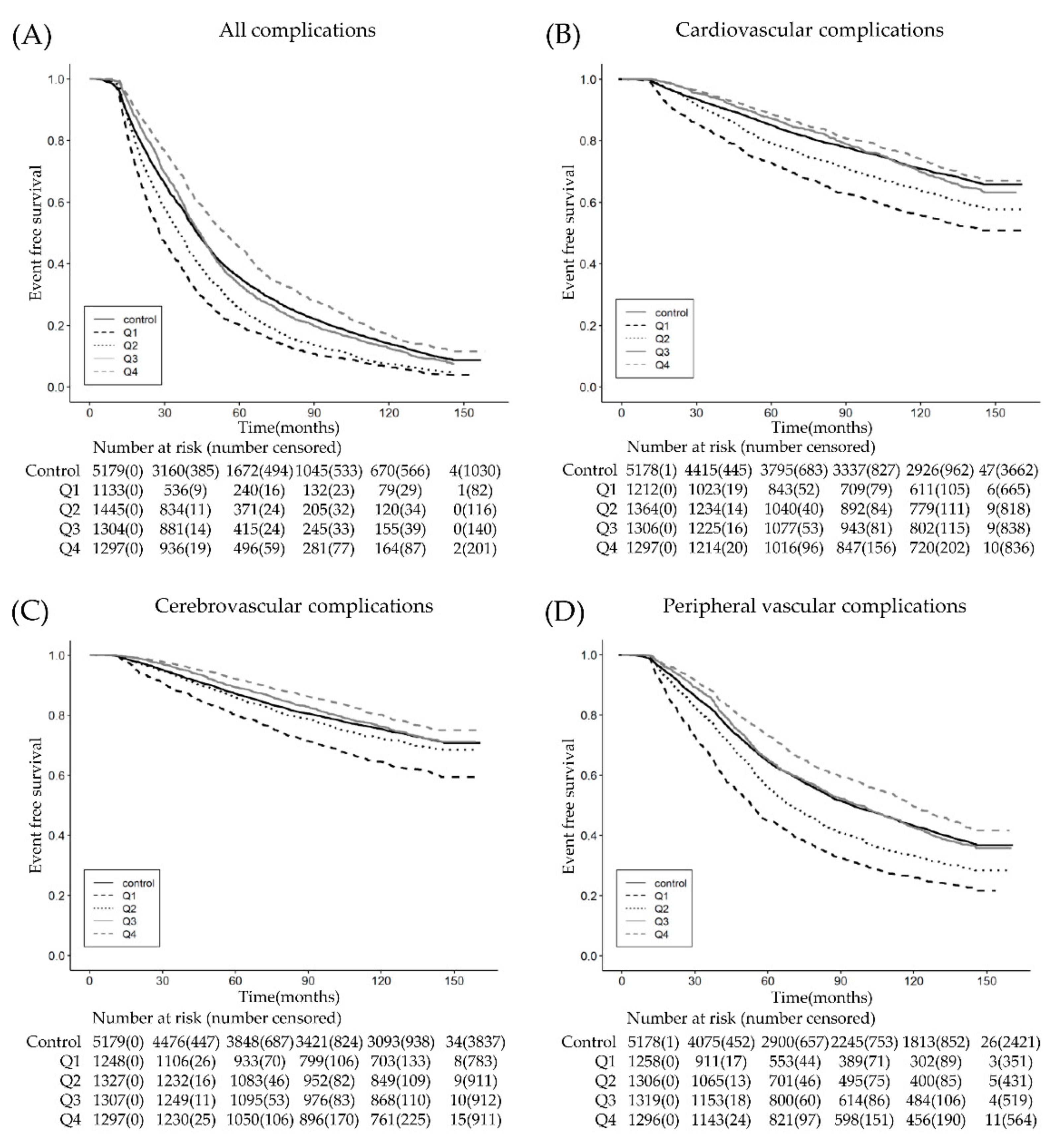
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gibbons, G.W.; Shaw, P.M. Diabetic vascular disease: Characteristics of vascular disease unique to the diabetic patient. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 25, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahagi, K.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Lutter, C.; Mori, H.; Romero, M.E.; Finn, A.V.; Virmani, R. Pathology of human coronary and carotid artery atherosclerosis and vascular calcification in diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, T.; Bornfeldt, K.E. Diabetic vascular disease and the potential role of macrophage glucose metabolism. Ann. Med. 2012, 44, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Kushiyama, A.; Yoneda, M.; Nakatsu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ono, H.; Kanna, M.; Sakoda, H.; Ono, H.; et al. Macrophage foam cell formation is augmented in serum from patients with diabetic angiopathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.; Ren, Y.; Shi, K.; Jiang, H. Inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor reduces diabetic nephropathy in type II diabetes mice. Inflammation 2014, 37, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; Stampfer, M.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar]
- Koye, D.N.; Magliano, D.J.; Nelson, R.G.; Pavkov, M.E. The global epidemiology of diabetes and kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, M.J.; Walters, J.; Walters, E.H. Adverse effects of beta-agonists: Are they clinically relevant? Am. J. Respir. Med. 2003, 2, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Yu, M.R.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, B.W.; Wu, I.H.; Matsumoto, M.; King, G.L. Beta 2-adrenergic receptor agonists are novel regulators of macrophage activation in diabetic renal and cardiovascular complications. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S. Thirty years of national health insurance in South Korea: Lessons for achieving universal health care coverage. Health Policy Plan. 2009, 24, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.Y.; Noh, J.; Jhee, J.H.; Chang, T.I.; Kang, E.W.; Kee, Y.K.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Yun, H.R.; Jung, S.Y.; et al. Warfarin use in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing hemodialysis: A nationwide population-based study. Stroke 2017, 48, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraka, A.M.; Darwish, I.E.; Ghoneim, M.T.; Korayem, H.K. beta2-Adrenoceptor agonists as potential therapeutic drugs in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Eur. J. Pharm. 2015, 746, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Givvimani, S.; Metreveli, N.; Tyagi, S.C. Attenuation of beta2-adrenergic receptors and homocysteine metabolic enzymes cause diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Juliet, P.A.; Miyazaki-Akita, A.; Funami, J.; Matsui-Hirai, H.; Fukatsu, A.; Iguchi, A. beta1 antagonist and beta2 agonist, celiprolol, restores the impaired endothelial dependent and independent responses and decreased TNFalpha in rat with type II diabetes. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzola, M.; Calzetta, L.; Bettoncelli, G.; Cricelli, C.; Romeo, F.; Matera, M.G.; Rogliani, P. Cardiovascular disease in asthma and COPD: A population-based retrospective cross-sectional study. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.F.; Van Eeden, S.; Sin, D.D. Vascular risk in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Role of inflammation and other mediators. Can. J. Cardiol. 2012, 28, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Chalmers, J.D.; Choudhury, G.; Akram, A.R.; Hill, A.T. Vascular complications are associated with poor outcome in community-acquired pneumonia. QJM 2011, 104, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren-Gash, C.; Smeeth, L.; Hayward, A.C. Influenza as a trigger for acute myocardial infarction or death from cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, T.C.; Thompson, M.; Meade, T.W. Recent respiratory infection and risk of cardiovascular disease: Case-control study through a general practice database. Eur. Heart J. 2008, 29, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.K.; Colville, D.; Canty, P.; Hutchinson, A.; Wong, A.; Luong, V.; Wong, T.Y.; McDonald, C.; Savige, J. Hypertensive/microvascular disease and COPD: A case control study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oncel, C.; Baser, S.; Cam, M.; Akdag, B.; Taspinar, B.; Evyapan, F. Peripheral neuropathy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD 2010, 7, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Boo, S.; Yoo, M.; Lee, J.; Kang, N.R. Impact of chronic kidney disease among Korean adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2017, 49, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownrigg, J.R.; de Lusignan, S.; McGovern, A.; Hughes, C.; Thompson, M.M.; Ray, K.K.; Hinchliffe, R.J. Peripheral neuropathy and the risk of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Heart 2014, 100, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Molarius, A.; Forsen, T.; Rastenyte, D.; Sarti, C.; Reunanen, A. Incidence of cardiovascular disease in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic subjects with and without diabetic nephropathy in Finland. Diabetologia 1998, 41, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hecke, M.V.; Dekker, J.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Polak, B.C.; Fuller, J.H.; Sjolie, A.K.; Kofinis, A.; Rottiers, R.; Porta, M.; Chaturvedi, N.; et al. Diabetic retinopathy is associated with mortality and cardiovascular disease incidence: The EURODIAB prospective complications study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordin, D.; Harjutsalo, V.; Tinsley, L.; Fickweiler, W.; Sun, J.K.; Forsblom, C.; Amenta, P.S.; Pober, D.; D’Eon, S.; Khatri, M.; et al. Differential association of microvascular attributions with cardiovascular disease in patients with long duration of Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovshin, J.A.; Bjornstad, P.; Lovblom, L.E.; Bai, J.-W.; Lytvyn, Y.; Boulet, G.; Farooqi, M.A.; Santiago, S.; Orszag, A.; Scarr, D.; et al. Atherosclerosis and Microvascular Complications: Results From the Canadian Study of Longevity in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljunid, S.M.; Srithamrongsawat, S.; Chen, W.; Bae, S.J.; Pwu, R.F.; Ikeda, S.; Xu, L. Health-care data collecting, sharing, and using in Thailand, China mainland, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Malaysia. Value Health 2012, 15, S132–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | β2AR Agonist Group (n = 5179) | Non-β2AR Agonist Group | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Matching (n = 30,066) | After Matching (n = 5179) | ||||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | Before | After | ||
| Sex | Male | 2577 | 49.8 | 21,320 | 70.9 | 2724 | 52.6 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| Female | 2602 | 50.2 | 8746 | 29.1 | 2455 | 47.4 | |||
| Age (years) | 20~39 | 491 | 9.5 | 5057 | 16.8 | 596 | 11.5 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 40~59 | 2287 | 44.2 | 17,630 | 58.6 | 2375 | 45.9 | |||
| ≥60 | 2401 | 46.4 | 7379 | 24.5 | 2208 | 42.6 | |||
| Hypertension | No | 2870 | 55.4 | 20,371 | 67.8 | 2882 | 55.6 | <0.001 | 0.812 |
| Yes | 2309 | 44.6 | 9695 | 32.2 | 2297 | 44.4 | |||
| Hyperlipidemia | No | 4381 | 84.6 | 26,261 | 87.3 | 4274 | 82.5 | <0001 | 0.005 |
| Yes | 798 | 15.4 | 3805 | 12.7 | 905 | 17.5 | |||
| COPD | No | 3381 | 65.3 | 28,405 | 94.5 | 3518 | 67.9 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| Yes | 1798 | 34.7 | 1661 | 5.5 | 1661 | 32.1 | |||
| Asthma | No | 2772 | 53.5 | 28,946 | 96.3 | 4059 | 78.4 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 2407 | 46.5 | 1120 | 3.7 | 1120 | 21.6 | |||
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |||||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| All complications * | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <8 | 1.52 | 1.42 | 1.63 | <0.001 | 1.56 | 1.46 | 1.67 | <0.001 | ||
| <17 | 1.29 | 1.21 | 1.37 | <0.001 | 1.30 | 1.22 | 1.38 | <0.001 | ||
| <42 | 1.06 | 1.00 | 1.13 | 0.069 | 1.01 | 0.95 | 1.08 | 0.740 | ||
| 42≤ | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.021 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.86 | <0.001 | ||
| Cardiovascular complications † | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <11 | 1.65 | 1.50 | 1.82 | <0.001 | 1.72 | 1.56 | 1.90 | <0.001 | ||
| <25 | 1.34 | 1.21 | 1.48 | <0.001 | 1.32 | 1.19 | 1.45 | <0.001 | ||
| <67 | 1.11 | 1.00 | 1.24 | 0.046 | 1.04 | 0.93 | 1.15 | 0.5 | ||
| 67≤ | 1.16 | 1.05 | 1.29 | 0.005 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 1.01 | 0.068 | ||
| Cerebrovascular complications ‡ | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <12 | 1.46 | 1.31 | 1.62 | <0.001 | 1.55 | 1.39 | 1.73 | <0.001 | ||
| <26 | 1.12 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 0.045 | 1.11 | 0.99 | 1.24 | 0.066 | ||
| <68 | 1.04 | 0.93 | 1.17 | 0.483 | 0.96 | 0.85 | 1.07 | 0.440 | ||
| 68≤ | 1.07 | 0.95 | 1.20 | 0.281 | 0.79 | 0.69 | 0.89 | <0.001 | ||
| Peripheral vascular complications § | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <10 | 1.64 | 1.52 | 1.77 | <0.001 | 1.68 | 1.56 | 1.82 | <0.001 | ||
| <21 | 1.29 | 1.20 | 1.40 | <0.001 | 1.29 | 1.20 | 1.40 | <0.001 | ||
| <55 | 1.05 | 0.97 | 1.14 | 0.217 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 1.07 | 0.823 | ||
| 55≤ | 0.96 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 0.381 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.89 | <0.001 | ||
| Renal complications ¥ | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <12 | 1.54 | 1.38 | 1.73 | <0.001 | 1.54 | 1.37 | 1.72 | <0.001 | ||
| <27 | 1.03 | 0.92 | 1.16 | 0.601 | 1.01 | 0.90 | 1.14 | 0.869 | ||
| <72 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 1.00 | 0.041 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.96 | 0.009 | ||
| 72≤ | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.92 | 0.002 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.86 | <0.001 | ||
| Peripheral nerve complications ¶ | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <11 | 1.60 | 1.47 | 1.73 | <0.001 | 1.64 | 1.51 | 1.79 | <0.001 | ||
| <23 | 1.20 | 1.10 | 1.31 | <0.001 | 1.21 | 1.11 | 1.33 | <0.001 | ||
| <62 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 1.04 | 0.222 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 1.02 | 0.126 | ||
| 62≤ | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.90 | <0.001 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.83 | <0.001 | ||
| Ophthalmic complications # | Period (days) | control | reference | reference | ||||||
| <11 | 1.68 | 1.55 | 1.83 | <0.001 | 1.70 | 1.57 | 1.85 | <0.001 | ||
| <24 | 1.29 | 1.19 | 1.41 | <0.001 | 1.29 | 1.18 | 1.40 | <0.001 | ||
| <62 | 1.09 | 1.00 | 1.19 | 0.061 | 1.07 | 0.98 | 1.17 | 0.135 | ||
| 62≤ | 0.90 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.027 | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.97 | 0.008 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.; Oh, S.H.; Park, S.; Jung, K.-Y.; Kim, H.; Kwon, S.H.; Jeon, J.S.; Han, D.C.; Noh, H. Association between Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Vascular Complications in Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081145
Lee HJ, Lee H, Oh SH, Park S, Jung K-Y, Kim H, Kwon SH, Jeon JS, Han DC, Noh H. Association between Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Vascular Complications in Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(8):1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081145
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hee Jeong, Haekyung Lee, Song Hee Oh, Suyeon Park, Kwang-Young Jung, Hyoungnae Kim, Soon Hyo Kwon, Jin Seok Jeon, Dong Cheol Han, and Hyunjin Noh. 2019. "Association between Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Vascular Complications in Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 8: 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081145
APA StyleLee, H. J., Lee, H., Oh, S. H., Park, S., Jung, K.-Y., Kim, H., Kwon, S. H., Jeon, J. S., Han, D. C., & Noh, H. (2019). Association between Beta2-Adrenergic Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Vascular Complications in Diabetic Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(8), 1145. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8081145





