Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Infectious Diseases
1.2. Inflammatory Diseases
2. Radiolabelled White Blood Cell Scintigraphy for the Diagnosis of Osteomyelitis (OM) and Therapy Follow-Up
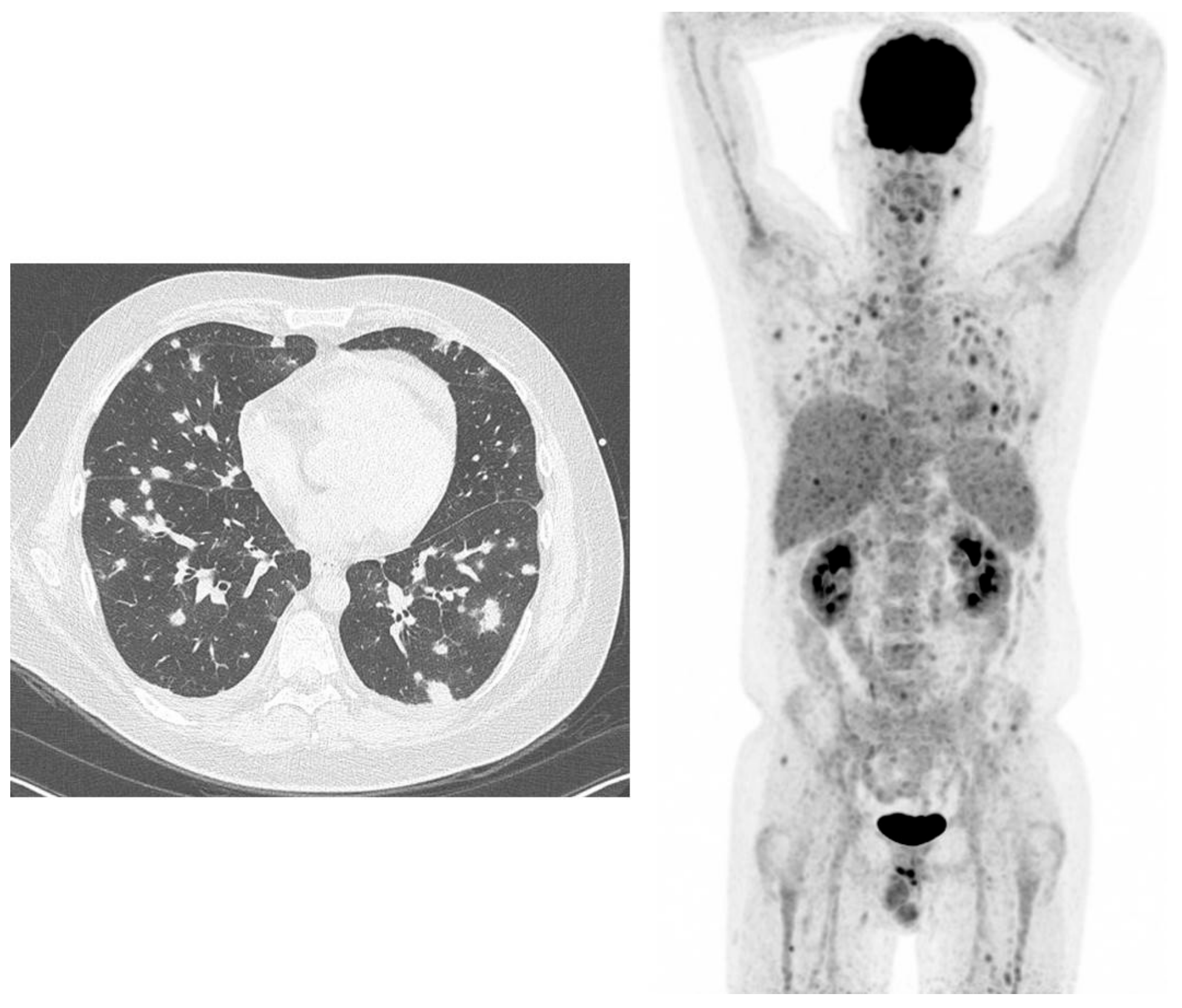
3. (18F)-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography ((18F)-FDG-PET/CT) for Imaging and Monitoring Therapy of Fungal Infections
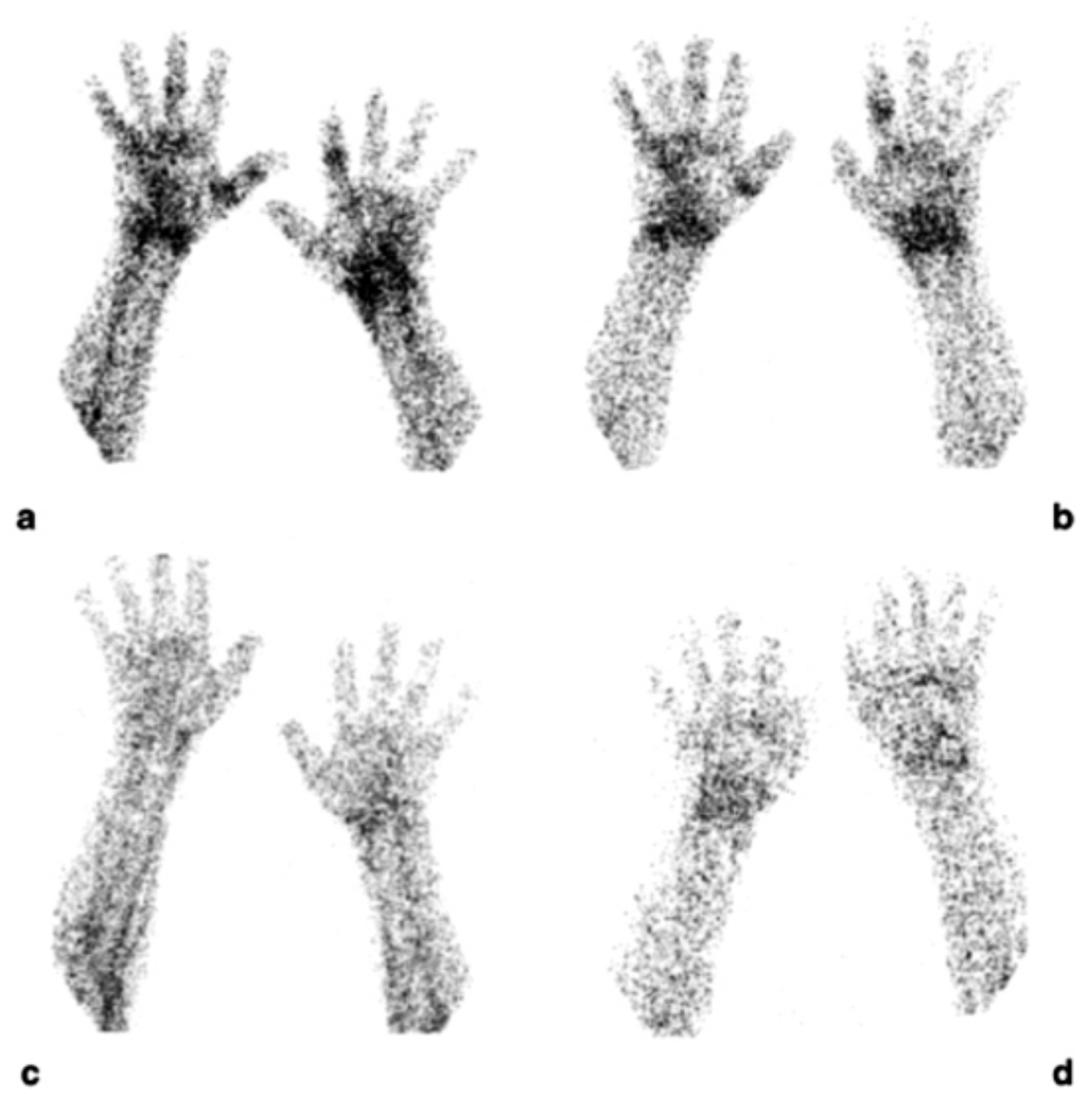
4. Radiolabelled Somatostatin Analogues in Rheumatoid Arthritis
5. Radiolabelled Anti-CD20 and Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor (Anti-TNFα) Monoclonal Antibodies in Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.1. (99mTc)-Infliximab Scintigraphy
5.2. 99mTc Radiolabelled Adalimumab Scintigraphy
5.3. 99mTc-Rituximab Scintigraphy
5.4. 99mTc Radiolabelled Certolizumab Pegol Scintigraphy
6. 18F-FDG-PET/CT to Image Large Vessel Vasculitis
6.1. Diagnosis, Extent and Impact of (18F)-FDG-PET/CT on the Management of Large Vessel Vasculitis (LVV)
6.2. Role of (18F)-FDG-PET/CT in Monitoring the Treatment Response in LVV
7. Imaging Immunological Network in Cancer
7.1. Programmed Cell Death Protein (PD-1) Imaging
7.2. Programmed Cell Death Protein Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Imaging
7.3. CTLA-4 Imaging
7.4. CD25 as Target for Imaging Tumour-Infiltrating Lymphocytes
7.5. Evaluation or Response to Immunotherapy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Signore, A.; Anzola, K.L.; Auletta, S.; Varani, M.; Petitti, A.; Pacilio, M.; Galli, F.; Lauri, C. Current status of molecular imaging in inflammatory disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaudemans, A.W.; Prandini, N.; Di Girolamo, M.; Argento, G.; Lauri, C.; Lazzeri, E.; Muto, M.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Signore, A. Hybrid imaging of musculoskeletal infections. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chianelli, M.; Boerman, O.C.; Malviya, G.; Galli, F.; Oyen, W.J.; Signore, A. Receptor binding ligands to image infection. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3316–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, J.; Oeser, C.; Amthauer, H. Clinical role of anti-granulocyte MoAb versus radiolabeled white blood cells. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 54, 599–616. [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe, C.; Dupont, A.C.; Maia, S.; Venel, Y.; Erra, B.; Santiago-Ribeiro, M.J.; Arlicot, N. Estimation of the added value of 99mTc-HMPAO labelled white blood cells scintigraphy for the diagnosis of infectious foci. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaudemans, A.W.; de Vries, E.F.; Galli, F.; Dierckx, R.A.; Slart, R.H.; Signore, A. The use of (18)F-FDG-PET/CT for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of inflammatory and infectious diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 623036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auletta, S.; Galli, F.; Lauri, C.; Martinelli, D.; Santino, I.; Signore, A. Imaging bacteria with radiolabelled quinolones, cephalosporins and siderophores for imaging infection: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2016, 4, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.G.; Mather, S.J. Pathogen identification by nuclear imaging—almost there? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 1173–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buursma, A.R.; Rutgers, V.; Hospers, G.A.; Mulder, N.H.; Vaalburg, W.; de Vries, E.F. 18F-FEAU as a radiotracer for herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene expression: In-vitro comparison with other PET tracers. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2006, 27, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gialleonardo, V.; Signore, A.; Glaudemans, A.W.; Dierckx, R.A.; de Vries, E.F. N-(4-18F-fluorobenzoyl)interleukin-2 for PET of human-activated T lymphocytes. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandria, C.; di Gialleonardo, V.; Chianelli, M.; Mather, S.J.; de Vries, E.F.; Scopinaro, F.; Dierck, R.A.; Signore, A. Synthesis and optimization of the labelling procedure of 99mTc-HYNIC-interleukin-2 for in vivo imaging of activated T lymphocytes. Mol. Imaging. Biol. 2010, 12, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianelli, M.; Parisella, M.G.; Visalli, N.; Mather, S.J.; D’Alessandria, C.; Pozzilli, P.; Signore, A. IMDIAB study group. Pancreatic scintigraphy with 99mTc-interleukin-2 at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes and after 1 year of nicotinamide therapy. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2008, 24, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annovazzi, A.; Biancone, L.; Caviglia, R.; Chianelli, M.; Capriotti, G.; Mather, S.J.; Caprilli, R.; Pallone, F.; Scopinaro, F.; Signore, A. 99mTc-interleukin-2 and (99m)Tc-HMPAO granulocyte scintigraphy in patients with inactive Crohn’s disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A.; Chianelli, M.; Ronga, G.; Pozzilli, P.; Beverley, P.C. In vivo labelling of activated T lymphocytes by i.v. injection of 123I-IL2 for detection of insulitis in type 1 diabetes. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1990, 355, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhagen, P.M.; Markusse, H.M.; Lamberts, S.W.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; Reubi, J.C.; Krenning, E.P. Somatostatin receptor imaging. The presence of somatostatin receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, S.C.; Emery, P. Biological therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: Where are we now? Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 73, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Ceccarelli, F.; Priori, R.; Iagnocco, A.; Signore, A.; Valesini, G. Intra-articular infliximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis with monoarthritis resistant to local glucocorticoids. Clinical efficacy extended to patients on systemic anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1787–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malviya, G.; Anzola, K.L.; Podestà, E.; Laganà, B.; Del Mastro, C.; Dierckx, R.A.; Scopinaro, F.; Signore, A. (99m)Tc-labeled rituximab for imaging B lymphocyte infiltration in inflammatory autoimmune disease patients. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iodice, V.; Laganà, B.; Lauri, C.; Capriotti, G.; Germano, V.; D’Amelio, R.; Picchianti Diamanti, A. Imaging B lymphocytes in autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 58, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malviya, G.; Signore, A.; Laganà, B.; Dierckx, R.A. Radiolabelled peptides and monoclonal antibodies for therapy decision making in inflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiemann, A.H.; Hofmann, G.O. Principles of the therapy of bone infections in adult extremities: Are there any new developments? Strateg. Trauma Limb. Reconstr. 2009, 4, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutte, P.; Lazzeri, E.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Cassar-Pullicino, V.; Trampuz, A.; Petrosillo, N.; Signore, A. Diagnostic flowcharts in osteomyelitis, spondylodiscitis and prosthetic joint infection. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 58, 2–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lew, D.P.; Waldvogel, F.A. Osteomyelitis. Lancet 2004, 364, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestro, C.J. Radionuclide imaging of osteomyelitis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2015, 45, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A.; Lauri, C.; Galli, F. Radiolabelled probes targeting infection and inflammation for personalized medicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 2338–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, P.A.; Glaudemans, A.W.; Veltman, N.C.; Sollini, M.; Pacilio, M.; Galli, F.; Dierckx, R.A.; Signore, A. Image acquisition and interpretation criteria for 99mTc-HMPAO-labelled white blood cell scintigraphy: Results of a multicentre study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaudemans, A.W.; de Vries, E.F.; Vermeulen, L.E.; Slart, R.H.; Dierckx, R.A.; Signore, A. A large retrospective single-centre study to define the best image acquisition protocols and interpretation criteria for white blood cell scintigraphy with 99mTc-HMPAO-labelled leucocytes in musculoskeletal infections. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, M.; de Vries, E.F.; Jamar, F.; Israel, O.; Signore, A. Guidelines for the labelling of leucocytes with (111)In-oxine. Inflammation/Infection Taskgroup of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, E.F.; Roca, M.; Jamar, F.; Israel, O.; Signore, A. Guidelines for the labelling of leucocytes with (99m)Tc-HMPAO. Inflammation/Infection Taskgroup of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A.; Jamar, F.; Israel, O.; Buscombe, J.; Martin-Comin, J.; Lazzeri, E. Clinical indications, image acquisition and data interpretation for white blood cells and anti-granulocyte monoclonal antibody scintigraphy: An EANM procedural guideline. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1816–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Glaudemans, A.W. The molecular imaging approach to image infections and inflammation by nuclear medicine techniques. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2011, 25, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signore, A. Techniques, image acquisition and interpretation criteria. In Diagnostic Imaging of Infections and Inflammatory Diseases: A Multidisciplinary Approach; Signore, A., Quintero, A.M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Glaudemans, A.W.; Galli, F.; Pacilio, M.; Signore, A. Leukocyte and bacteria imaging in prosthetic joint infection. Eur. Cell Mater. 2013, 25, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palestro, C.; Swyer, A.; Kim, C.; Goldsmith, S. Infected knee prosthesis: Diagnosis with In-111 leukocyte, Tc-99m sulfur colloid, and Tc-99m MDP imaging. Radiology 1991, 179, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandini, N.; Lazzeri, E.; Rossi, B.; Erba, P.; Parisella, M.G.; Signore, A. Nuclear medicine imaging of bone infections. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2006, 27, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauri, C.; Tamminga, M.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Juárez Orozco, L.E.; Erba, P.A.; Jutte, P.C.; Lipsky, B.A.; IJzerman, M.J.; Signore, A.; Slart, R.H.J.A. Detection of Osteomyelitis in the Diabetic Foot by Imaging Techniques: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Comparing MRI, White Blood Cell Scintigraphy, and FDG-PET. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirce, R.; Carril, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Mendiguchía, C.; Serrano, J.; Rabasa, J.M.; Bernal, J.M. Assessment of the diagnostic capacity of planar scintigraphy and SPECT with 99mTc-HMPAO-labelled leukocytes in superficial and deep sternal infections after median sternotomy. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2002, 23, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palestro, C.J.; Love, C.; Tronco, G.G.; Tomas, M.B.; Rini, J.N. Combined Labeled Leukocyte and Technetium 99m Sulfur Colloid Bone Marrow Imaging for Diagnosing Musculoskeletal Infection. Radiographics 2006, 26, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verberne, S.J.; Sonnega, R.J.A.; Temmerman, O.P.P.; Raijmakers, P.G. What is the Accuracy of Nuclear Imaging in the Assessment of Periprosthetic Knee Infection? A Meta-analysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammen, L.; Palestro, C.J.; Holinka, J.; Windhager, R.; Sinzinger, H. A retrospective analysis of the accuracy of radioactively labeled autologous leukocytes in patients with infected prosthetic joints. Nucl. Med. Rev. 2017, 20, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberatore, M.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Rubello, D. White blood cell scan in the follow-up of infectious diseases: Is the withdrawal of antibiotic therapy necessary? Nucl. Med. Commun. 2007, 28, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrah, O.A.; Sathekge, M.M.; Dierckx, R.A.; Glaudemans, A.W. Imaging fungal infections in children. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2016, 4, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrah, O.A.; Klein, H.C.; Span, L.F.R.; de Vries, E.F.J.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Sathekge, M.M.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M. The role of PET in monitoring therapy in fungal infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.P.; Thursky, K.A.; Worth, L.J.; Drummond, E.; Hogg, A.; Hicks, R.J.; Slavin, M.A. FDG PET/CT imaging in detecting and guiding management of invasive fungal infections: A retrospective comparison to conventional CT imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy-Freschini, B.; Treglia, G.; Argemi, X.; Bund, C.; Kessler, R.; Herbrecht, R.; Imperiale, A. 18F-FDG PET/CT for invasive fungal infection in immunocompromised patients. QJM Int. J. Med. 2018, 111, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrah, O.A.; Span, L.F.R.; Klein, H.C.; de Jong, P.A.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Kwee, T.C.; Sathekge, M.M.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M. Role of FDG PET/CT in monitoring treatment response in patients with invasive fungal infections. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van del Laken, C.J.; Huisman, M.H.; Voskuyl, A.E. Nuclear imaging of rheumatic diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 26, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunder, A.; Strau, H.; Gay, S.; Funk, J.; Müller-Ladner, U. Molecular imaging: Novel tools in visualizing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Weissleder, R.; Mahmood, U. Molecular imaging. Radiology 2001, 219, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Markusse, H.M.; Krenning, E.P.; Vanhagen, M.; Laissue, J.A. Vascular somatostatin receptors in synovium from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 271, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, G.L.; Cuccurullo, V.; Mansi, L. The non-tumour uptake of 111In-octreotide creates new clinical indications in benign diseases, but also in oncology. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 54, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Virgolini, I.; Pangerl, T.; Bischof, C.; Smith-Jones, P.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Somatostatine receptor subtype expression in human tissues: A prediction for diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 27, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeba, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Takeno, M.; Asai, T.; Tsuboi, S.; Hoshino, T.; Sakane, T. Modulation of synovial cell function by somatostatine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzola, L.K.; Galli, F.; Dierckx, R. Spect radiopharmaceuticals for imaging chronic inflammatory diseases in the last decade. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 59, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roivainen, A.; Jalkanen, S.; Nanni, C. Gallium-labelled peptides for imaging of inflammation. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, S68–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzola, L.K.; Chianelli, M.; Galli, F.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Martin Martin, L.; Todino, V.; Migliore, A.; Signore, A. Somatostatine receptor scintigraphy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and secondary Sjögren´s síndrome treated with Infliximab: A pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging Res. 2016, 6, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Roivainen, A.; Parkkola, R.; Yli-Kerttula, T.; Lehikoinen, P.; Viljanen, T.; Mottonen, T.; Nuutila, P.; Minn, H. Use of positron emission tomography with methyl-11C-choline and 2-18F-fluoro-2- deoxy-D-glucose in comparison with magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of inflammatory proliferation of synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, C.; Ribbens, C.; André, B.; Marcelis, S.; Kaye, O.; Mathy, L.; Kaiser, M.J.; Hustinx, R.; Foidart, J.; Malaise, M.G. Assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis with (18)F-FDG PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 956–964. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosini, V.; Campana, D.; Bodei, L.; Nanni, C.; Castellucci, P.; Allegri, V.; Montini, G.C.; Tomassetti, P.; Paganelli, G.; Fanti, S. 68Ga-DOTANOC PET/CT clinical impact in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pettinato, C.; Sarnelli, A.; Di Donna, M.; Civollani, S.; Nanni, C.; Montini, G.; Di Pierro, D.; Ferrari, M.; Marengo, M.; Bergamini, C. 68Ga-DOTANOC: Biodistribution and dosimetry in patients affected by neuroendocrine tumors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, V.; Zompatori, M.; De Luca, F.; Antonia, D.; Allegri, V.; Nanni, C.; Malvi, D.; Tonveronachi, E.; Fasano, L.; Fabbri, M.; et al. 68Ga-DOTANOC PET/CT allows somatostatin receptor imaging in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Preliminary results. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1950–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianelli, M.; D’Alessandria, C.; Conti, F.; Priori, R.; Valesini, G.; Annovazzi, A.; Signore, A. New radiopharmaceuticals for imaging rheumatoid arthritis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2006, 50, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Barrera, P.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Boerman, O.C.; van Riel, P.L.C.M. Scintigraphic detection of tumor necrosis factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandria, C.; Malviya, G.; Viscido, A.; Aratari, A.; Maccioni, F.; Amato, A.; Scopinaro, F.; Caprilli, R.; Signore, A. Use of a 99m-Technetium labelled anti-TNFa monoclonal antibody in Crohn’s Disease: In vitro and in vivo studies. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 51, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, F.; Ceccarelli, F.; Massaro, L.; Cipriano, E.; Di Franco, M.; Alessandri, C.; Spinelli, F.R.; Scrivo, R. Biological therapies in rheumatic diseases. Clin. Ter. 2013, 164, e413–e428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sedger, L.M.; McDermott, M.F. TNF and TNF-receptors: From mediators of cell death and inflammation to therapeutic giants—Past, present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valesini, G.; Iannuccelli, C.; Marocchi, E.; Pascoli, L.; Scalzi, V.; Di Franco, M. Biological and clinical effects of anti-TNFalpha treatment. Autoimmun. Rev. 2007, 7, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Priori, R.; Chimenti, M.S.; Coari, G.; Annovazzi, A.; Valesini, G.; Signore, A. Successful treatment with intraarticular infliximab for resistant knee monarthritis in a patient with spondylarthropathy: A role for scintigraphy with 99mTc-infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, F.; Malviya, G.; Ceccarelli, F.; Priori, R.; Iagnocco, A.; Valesini, G.; Signore, A. Role of scintigraphy with 99mTc-infliximab in predicting the response of intraarticular infliximab treatment in patients with refractory monoarthritis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roimicher, L.; Lopes, F.P.; de Souza, S.A.; Mendes, L.F.; Domingues, R.C.; da Fonseca, L.M.; Gutfilen, B. (99m)Tc-anti-TNF-α scintigraphy in RA: A comparison pilot study with MRI and clinical examination. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malviya, G.; D’Alessandria, C.; Lanzolla, T.; Lenza, A.; Conti, F.; Valesini, G.; Scopinaro, F.; Dierckx, R.; Signore, A. 99mTechnetium labelled anti-TNF-α antibodies for the therapy decision-making and follow-up of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 52(2) (Suppl 1(2)), 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, L.; Huitema, A.D.; van Rijswijk, M.H.; Dinant, H.J.; Baars, J.W.; Beijnen, J.H.; Vogel, W.V. CD20 antigen imaging with 124I-rituximab PET/CT in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum. Antibodies 2011, 20, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, B.; Carron, P.; D’Asseler, Y.; Bacher, K.; Van den Bosch, F.; Elewaut, D.; Verbruggen, G.; Beyaert, R.; Dumolyn, C.; De Vos, F. 99mTc-labelled S-HYNIC certolizumab pegol in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis patients: A biodistribution and dosimetry study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging Res. 2016, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carron, P.; Lambert, B.; Van Praet, L.; De Vos, F.; Varkas, G.; Jans, L.; Elewaut, D.; Van den Bosch, F. Scintigraphic detection of TNF-driven inflammation by radiolabelled certolizumab pegol in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis. RMD Open 2016, 2, e000265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiyanathan, A.; Patel, C.N.; Scarsbrook, A.F.; Chowdhury, F.U. FDG PET/CT in infection and inflammation-current and emerging clinical applications. Clin. Radiol. 2015, 70, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slart, R.H. FDG-PET/CT(A) imaging in large vessel vasculitis and polymyalgia rheumatica: Joint procedural recommendation of the EANM, SNMMI, and the PET Interest Group (PIG), and endorsed by the ASNC. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1250–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, J.; Sahlmann, C.O.; Gürocak, O.; Liersch, T.; Meller, B. FDG-PET in Patients with FUO: The importance of diagnosis large vessels vasculitis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 53, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Espígol-Frigolé, G.; Prieto-González, S.; Alba, M.A.; Tavera-Bahillo, I.; García-Martínez, A.; Gilabert, R.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Cid, M.C. Advances in the diagnosis of large vessel vasculitis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 41, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versari, A.; Pipitone, N.; Casali, M.; Jamar, F.; Pazzola, G. Use of imaging techniques in Large Vessel Vasculitis and related conditions. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Soussan, M.; Nicolas, P.; Schramm, C.; Katsahian, S.; Pop, G.; Fain, O.; Mekinian, A. Management of large vessel vasculitis with FDG-PET: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, L.; Kanji, T.; Malette, J.; Pagnoux, C. Imaging modalities for the diagnosis and disease activity assessment of Takayasu’s arteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimm. Rev. 2018, 17, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotthardt, M.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Boerman, O.C.; Oyen, W.J.G. Imaging of Inflammation by PET, Conventional Scintigraphy, and Other Imaging Techniques. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppo, C.; Massollo, M.; Paparo, F.; Camellino, D.; Piccardo, A.; Naseri, M.S.Z.; Villavecchia, G.; Rollandi, G.A.; Cimmino, M.A. Giant cell arteritis: A systematic review of the qualitative and semiquantitative methods to assess vasculitis with 18F-fluoro-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 574248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-González, S.; Espígol-Frigolé, G.; García-Martínez, A.; Alba, M.A.; Tavera-Bahillo, I.; Hernández-Rodríguez, J.; Renú, A.; Gilabert, R.; Lomeña, F.; Cid, M.C. The Epanding Role of Imaging in Systemic Vasculitis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, J.; Strutz, F.; Siefker, U.; Scheel, A.; Sahlmann, C.O.; Lehmann, K.; Conrad, M.; Vosshenrich, R. Early diagnosis and follow-up of aortitis with [(18)F]FDG PET and MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blockmans, D.; de Ceuninck, L.; Vanderschueren, S.; Knockaert, D.; Mortelmans, L.; Bobbaers, H. Repetitive 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in giant cell arteritis: A prospective study of 35 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 55, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, A.; Pazzola, G.; Boiardi, L.; Casali, M.; Muratore, F.; Pipitone, N.; Catanoso, M.; Aldigeri, R.; Cimino, L.; Versari, A.; et al. Distribution patterns of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose in large vessels of Takayasu’s and giant cell arteritis using positron emission tomography. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, S99–S106. [Google Scholar]
- Muratore, F.; Crescentini, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Pazzola, G.; Casali, M.; Boiardi, L.; Pipitone, N.; Croci, S.; Galli, E.; Aldigeri, R.; et al. Aortic dilatation in patients with large vessel vasculitis: A longitudinal case control study using PET/CT. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, S.C.; Krumm, P.; Henes, J.; Nikolaou, K.; la Fougère, C.; Pfannenberg, C.; Schwenzer, N. Imaging giant cell arteritis and Aortitis in contrast enhanced 18F-FDG PET/ CT: Which imaging score correlates best with laboratory inflammation markers? Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 99, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Buchtala, S.; Achajew, N.; Haerle, P.; Ehrenstein, B.; Lighvani, H.; Fleck, M.; Marienhagen, J. 18F-FDG PET as a diagnostic procedure in large vessel vasculitis-a controlled, blinded re-examination of routine PET scans. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besson, F.L.; de Boysson, H.; Parienti, J.; Bouvard, G.; Bienvenu, B.; Agostini, D. Towards an optimal semiquantitative approach in giant cell arteritis: An 18F-FDG PET/CT case-control study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 41, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Briel, M.; Daikeler, T.; Walker, U.A.; Rasch, H.; Berg, S.; Ng, Q.K.; Raatz, H.; Jayne, D.; Kötter, I.; et al. The impact of 18F-FDG PET on the management of patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspieler, I.; Thürmel, K.; Pyka, T.; Eiber, M.; Wolfram, S.; Moog, P.; Reeps, C.; Essler, M. Imaging large vessel vasculitis with fully integrated PET/MRI: A pilot study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertagna, F.; Bosio, G.; Caobelli, F.; Motta, F.; Biasiotto, G.; Giubbini, R. Role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for therapy evaluation of patients with large-vessel vasculitis. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2010, 28, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boysson, H.; Aide, N.; Liozon, E.; Lambert, M.; Parienti, J.J.; Monteil, J.; Huglo, D.; Bienvenu, B.; Manrique, A.; Aouba, A. Repetitive 18F-FDG-PET/CT in patients with large-vessel giant-cell arteritis and controlled disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 46, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martìnez-Rodrìguez, I.; Jiménez-Alonso, M.; Quirce, R.; Jiménez-Bonilla, J.; Martìnez-Amador, N.; De Arcocha-Torres, M.; Loricera, J.; Blanco, R.; González-Gay, M.Á.; Banzo, I. 18F-FDG PET/CT in the follow-up of large-vessel vasculitis: A study of 37 consecutive patients. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Direskeneli, H. Clinical assessment in Takayasu’s arteritis: Major challenges and controversies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 103, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Karunanithi, S.; Sharma, P.; Bal, C.; Kumar, R. (18)F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosis and treatment response evaluation in large vessel vasculitis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 586–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, G.; Yamashita, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Miyata, Y.; Morooka, M.; Minamimoto, R.; Kubota, K.; Kaneko, H.; Kano, T.; Mimori, A. Large vessel vasculitis in elderly patients: Early diagnosis and steroid-response evaluation with FDG-PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henes, J.C.; Mueller, M.; Pfannenberg, C.; Kanz, L.; Koetter, I. Cyclophosphamide for large vessel vasculitis: Assessment of response by PET/CT. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, S43–S48. [Google Scholar]
- Salvarani, C.; Magnani, L.; Catanoso, M.; Pipitone, N.; Versari, A.; Dardani, L.; Pulsatelli, L.; Meliconi, R.; Boiardi, L. Tocilizumab: A novel therapy for patients with large-vessel vasculitis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenter, V.; Sommer, N.N.; Kooijman, H.; Maurus, S.; Treitl, M.; Czihal, M.; Dechant, C.; Unterrainer, M.; Albert, N.L.; Treitl, K.M. Clinical value of [18F]FDG-PET/CT and 3D-black-blood 3T-MRI for the diagnosis of large vessel vasculitis and single-organ vasculitis of the aorta. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounni, N.E.; Noel, A. Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couzin-Frankel, J. Breakthrough of the year 2013. Cancer immunotherapy. Science 2013, 342, 1432–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guldbrandsen, K.F.; Hendel, H.W.; Langer, S.W.; Fischer, B.M. Nuclear Molecular Imaging Strategies in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Diagnostic 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, L.; de Jong, M.; del Vecchio, S.; Cai, W. The new era of cancer immunotherapy: What can molecular imaging do the help? Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa, C.; Mousa, S.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Current treatment and future advances. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazandjian, D.; Suzman, D.L.; Blumenthal, G.; Mushti, S.; He, K.; Libeg, M.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Nivolumab for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy. Oncologist 2016, 21, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Garon, E.B.; Patnaik, A.; Gandhi, L.; Leighl, N.B.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Goldman, J.W.; Eder, J.P.; Johnson, E.; Blumenschein, G.R.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of MK-3475 as initial therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Annovazzi, A.; Barone, R.; Bonanno, E.; D’Alessandria, C.; Chianelli, M.; Mather, S.J.; Bottoni, U.; Panetta, C.; Innocenzi, D.; et al. 99mTc-interleukin-2 scintigraphy as a potential tool for evaluating tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in melanoma lesions: A validation study. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Loose, D.; Signore, A.; Staelens, L.; Bulcke, K.V.; Vermeersch, H.; Dierckx, R.A.; Bonanno, E.; Van de Wiele, C. (123)I-Interleukin-2 uptake in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, V.; Staelens, L.; Signore, A.; Van Belle, S.; Dierckx, R.A.; Van De Wiele, C. Iodine-123-interleukin-2 scintigraphy in metastatic hypernephroma: A pilot study. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 51, 352–356. [Google Scholar]
- Zeelen, C.; Paus, C.; Draper, D.; Heskamp, S.; Signore, A.; Galli, F.; Griessinger, C.M.; Aarntzen, E.H. In vivo imaging of tumor-infiltrating immune cells: Implications for cancer immunotherapy. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62, 56–77. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, A.; Mayer, A.T.; Xu, L.; Reeves, R.E.; Gano, J.; Gambhir, S.S. Novel Radiotracer for ImmunoPET Imaging of PD-1 Checkpoint Expression on Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettich, M.; Braun, F.; Bartholoma, M.D.; Schirmbeck, R.; Niedermann, G. High-Resolution PET Imaging with Therapeutic Antibody-based PD-1/PD-L1 Checkpoint Tracers. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Mayer, A.T.; Reeves, R.E.; Nagamine, C.M.; Gambhir, S.S. Development of Novel ImmunoPET Tracers to Image Human PD-1 Checkpoint Expression on Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in a Humanized Mouse Model. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, C.G.; Jiang, D.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Rekoske, B.T.; Ellison, P.A.; Hernandez, R.; Barnhart, T.E.; McNeel, D.G.; Huang, P.; Cai, W. 89Zr-labeled nivolumab for imaging of T-cell infiltration in a humanized murine model of lung cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, E.L.; Kim, J.; Donnelly, D.J.; Smith, R.A.; Cohen, D.; Lafont, V.; Morin, P.E.; Huang, R.Y.; Chow, P.L.; Hayes, W.; et al. Radiosynthesis and preclinical PET evaluation of 89Zr-nivolumab (BMS-936558) in healthy non-human primates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5407–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, C.G.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Hernandez, R.; Rekoske, B.T.; Graves, S.A.; Sun, H.; Liu, G.; McNeel, D.G.; Barnhart, T.E.; Cai, W. Preclinical Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution Studies of 89Zr-Labeled Pembrolizumab. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Patel, C.B.; Habte, F.; Gambhir, S.S. Dosimetry Prediction for Clinical Translation of 64Cu-Pembrolizumab ImmunoPET Targeting Human PD-1 Expression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lesniak, W.G.; Gabrielson, M.; Lisok, A.; Wharram, B.; Sysa-Shah, P.; Azad, B.B.; Pomper, M.G.; Nimmagadda, S. A humanized antibody for imaging immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1 expression in tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10215–10227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, W.G.; Chatterjee, S.; Gabrielson, M.; Lisok, A.; Wharram, B.; Pomper, M.G.; Nimmagadda, S. PD-L1 Detection in Tumors Using [(64)Cu]Atezolizumab with PET. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, F.; van der Veen, E.; Jorritsma, A.; Lub-de Hooge, M.; Boellaard, R.; Oosting, S.; Schroder, C.; Hiltermann, J.; van der Wekken, A.; Groen, H.; et al. First-in-human PET imaging with the PD-L1 antibody 89Zr-atezolizumab. Cancer Res. 2017, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lesniak, W.G.; Nimmagadda, S. Noninvasive Imaging of Immune Checkpoint Ligand PD-L1 in Tumors and Metastases for Guiding Immunotherapy. Mol. Imaging 2017, 16, 1536012117718459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedrow, J.R.; Josefsson, A.; Park, S.; Ranka, S.; Roy, S.; Sgouros, G. Imaging of Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1: Impact of Protein Concentration on Distribution of Anti-PD-L1 SPECT Agents in an Immunocompetent Murine Model of Melanoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, M.; Clump, D.A.; Srivastava, R.M.; Sun, L.; Zeng, D.; Diaz-Perez, J.A.; Anderson, C.J.; Edwards, W.B.; Ferris, R.L. Preclinical immunoPET/CT imaging using Zr-89-labeled anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody for assessing radiation-induced PD-L1 upregulation in head and neck cancer and melanoma. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1329071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heskamp, S.; Hobo, W.; Molkenboer-Kuenen, J.D.; Olive, D.; Oyen, W.J.; Dolstra, H.; Boerman, O.C. Noninvasive Imaging of Tumor PD-L1 Expression Using Radiolabeled Anti-PD-L1 Antibodies. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2928–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, F.; van der Veen, E.L.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; Jorritsma-Smit, A.; Boellaard, R.; Kok, I.C.; Oosting, S.F.; Schröder, C.P.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; van der Wekken, A.J.; et al. 89Zr-atezolizumab imaging as a non-invasive approach to assess clinical response to PD-L1 blockade in cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.T.; Natarajan, A.; Gordon, S.R.; Maute, R.L.; McCracken, M.N.; Ring, A.M.; Weissman, I.L.; Gambhir, S.S. Practical Immuno-PET Radiotracer Design Considerations for Human Immune Checkpoint Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gonzàlez Trotter, D.E.; Meng, X.; McQuade, P.; Rubins, D.; Klimas, M.; Zeng, Z.; Connolly, B.M.; Miller, P.J.; O’Malley, S.S.; Lin, S.A.; et al. In Vivo Imaging of the Programmed Death Ligand 1 by 18F PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1852–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truillet, C.; Oh, H.L.J.; Yeo, S.P.; Lee, C.; Huynh, L.T.; Wei, J.; Parker, M.F.L.; Blakely, C.; Sevillano, N.; Wang, Y.; et al. Imaging PD-L1 Expression with ImmunoPET. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashikawa, K.; Yagi, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kamino, S.; Ueda, M.; Hiromura, M.; Enomoto, S. 64Cu-DOTA-anti-CTLA-4 mAb enabled PET visualization of CTLA-4 on the T-cell infiltrating tumor tissues. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidian, M.; Ingram, J.R.; Dougan, M.; Dongre, A.; Whang, K.A.; LeGall, C.; Cragnolini, J.J.; Bierie, B.; Gostissa, M.; Gorman, J.; et al. Predicting the response to CTLA-4 blockade by longitudinal noninvasive monitoring of CD8 T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2243–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, R.J.; Mayer, P.C.; Garlick, R. Retention of biological activity following radioiodination of human interleukin 2: Comparison with biosynthetically labeled growth factor in receptor binding assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1985, 81, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennuso, R.; Spigelman, M.K.; Vallabhajosula, S.; Moore, F.; Zappulla, R.A.; Nieves, J.; Strauchen, J.A.; Paciucci, P.A.; Malis, L.I.; Goldsmith, S.J.; et al. Systemic biodistribution of radioiodinated interleukin-2 in the rat. J. Biol. Response Mod. 1989, 8, 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Koths, K.; Halenbech, R. Pharmacokinetic studies on 35S-labeled recombinant interleukin-2 in mice. In Cellular and Molecular Biology of Lymphokines; Sorg, C., Schimpl, A., Eds.; Academic Press Inc: Orlando, FL, USA, 1985; pp. 779–783. [Google Scholar]
- Signore, A.; Beverley, P.C.; Parman, A.; Negri, M.; Pozzilli, P. Labelling of interleukin-2 (IL-2) with 123-iodine with retention of its capacity to bind to activated lymphocytes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. 1987, 89, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Parman, A.; Pozzilli, P.; Andreani, D.; Beverley, P.C. Detection of activated lymphocytes in endocrine pancreas of BB/W rats by injection of 123I-interleukin-2: An early sign of type 1 diabetes. Lancet 1987, 2, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Chianelli, M.; Ferretti, E.; Toscano, A.; Britton, K.E.; Andreani, D.; Gale, E.A.; Pozzilli, P. New approach for in vivo detection of insulitis in type I diabetes: Activated lymphocyte targeting with 123I-labelled interleukin 2. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1994, 131, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandsson, O.; Stigbrand, T.; Riklundåhlström, K.; Eary, J.; Greenbaum, C. Accumulation of (125)iodine labeled interleukin-2 in the pancreas of NOD mice. J. Autoimmun. 2001, 17, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbs, I.C.; Pratt, J.R.; Dallman, M.J.; Sacks, S.H. Analysis of activated T cell infiltrates in rat renal allografts by gamma camera imaging after injection of 123iodine-interleukin 2. Transpl. Immunol. 1993, 1, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Chianelli, M.; Annovazzi, A.; Rossi, M.; Maiuri, L.; Greco, M.; Ronga, G.; Britton, K.E.; Picarelli, A. Imaging active lymphocytic infiltration in coeliac disease with iodine-123-interleukin-2 and the response to diet. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2000, 27, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signore, A.; Chianelli, M.; Annovazzi, A.; Bonanno, E.; Spagnoli, L.G.; Pozzilli, P.; Pallone, F.; Biancone, L. 123I-interleukin-2 scintigraphy for in vivo assessment of intestinal mononuclear cell infiltration in Crohn’s disease. J. Nucl. Med. 2000, 41, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Signore, A.; Picarelli, A.; Annovazzi, A.; Britton, K.E.; Grossman, A.B.; Bonanno, E.; Maras, B.; Barra, D.; Pozzilli, P. 123I-Interleukin-2: Biochemical characterization and in vivo use for imaging autoimmune diseases. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2003, 24, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianelli, M.; Signore, A.; Fritzberg, A.R.; Mather, S.J. The development of technetium-99m-labelled interleukin-2: A new radiopharmaceutical for the in vivo detection of mononuclear cell infiltrates in immune-mediated diseases. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1997, 24, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianelli, M.; Mather, S.J.; Grossman, A.; Sobnak, R.; Fritzberg, A.; Britton, K.E.; Signore, A. 99mTc-interleukin-2 scintigraphy in normal subjects and in patients with autoimmune thyroid diseases: A feasibility study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annovazzi, A.; Bonanno, E.; Arca, M.; D’Alessandria, C.; Marcoccia, A.; Spagnoli, L.G.; Violi, F.; Scopinaro, F.; De Toma, G.; Signore, A. 99mTc-interleukin-2 scintigraphy for the in vivo imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2006, 33, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Stompór, T.; Kalembkiewicz, M.; Krzanowski, M.; Mikolajczak, R.; Sowa-Staszczak, A.; Tabor-Ciepiela, B.; Karczmarczyk, U.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Sulowicz, W. Identification of inflamed atherosclerotic plaque using 123 I-labeled interleukin-2 scintigraphy in high-risk peritoneal dialysis patients: A pilot study. Perit. Dial. Int. 2009, 29, 568–574. [Google Scholar]
- Di Gialleonardo, V.; Signore, A.; Willemsen, A.T.; Sijbesma, J.W.; Dierckx, R.A.; de Vries, E.F. Pharmacokinetic modelling of N-(4-[(18)F]fluorobenzoyl)interleukin-2 binding to activated lymphocytes in an xenograft model of inflammation. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartimath, S.V.; Draghiciu, O.; van de Wall, S.; Manuelli, V.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Nijman, H.W.; Daemen, T.; de Vries, E.F.J. Noninvasive monitoring of cancer therapy induced activated T cells using [18F]FB-IL-2 PET imaging. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1248014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartimath, S.V.; Manuelli, V.; Zijlma, R.; Signore, A.; Nayak, T.K.; Freimoser-Grundschober, A.; Klein, C.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; de Vries, E.F.J. Pharmacokinetic properties of radiolabeled mutant Interleukin-2v: A PET imaging study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7162–7174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Markovic SNGalli, F.; Suman, V.J.; Nevala, W.K.; Paulsen, A.M.; Hung, J.C.; Gansen, D.N.; Erickson, L.A.; Marchetti, P.; Wiseman, G.A.; Signore, A. Non-invasive visualization of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with metastatic melanoma undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A pilot study. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 30268–30278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Terroir, M.; Caramella, C. Advances in oncological treatment: Limitations of RECIST 1.1 criteria. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, A.A. Tremelimumab: A review of development date in solid tumors. Immunotherapy 2013, 5, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoos, A.; Parmiani, G.; Hege, K.; Sznol, M.; Loibner, H.; Eggermont, A.; Urba, W.; Blumenstein, B.; Sacks, N.; Keilholz, U.; et al. Cancer Vaccine Clinical Trial Working Group. A clinical development paradigm for cancer vaccines and related biologics. J. Immunother. 2007, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Perrone, A.; Ford, R.; Schwartz, L.H.; Mandrekar, S.; Lin, N.U.; Litière, S.; Dancey, J.; Chen, A.; et al. RECIST working group. iRECIST: Guidelines for response criteria for use in trials testing immunotherapeutics. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e143–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bier, G.; Hoffmann, V.; Kloth, C.; Othman, A.E.; Eigentler, T.; Garbe, C.; La Fougère, C.; Pfannenberg, C.; Nikolaou, K.; Klumpp, B. CT imaging of bone and bone marrow infiltration in malignant melanoma—Challenges and limitations for clinical staging in comparison to 18FDG-PET/CT. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.Y.; Menzies, A.M.; Saunders, C.A.; Liniker, E.; Ramanujam, S.; Guminski, A.; Kefford, R.F.; Long, G.V.; Carlino, M.S. Residual FDG-PET metabolic activity in metastatic melanoma patients with prolonged response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Radiopharmaceutical | Indication | |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious diseases | 99mTc/(111In)-WBC | Infection |
| 99mTc-besilesomab (Scintimun) | Infection | |
| 18F-FDG | Infection, inflammation, oncology | |
| 99mTc-ciprofloxacin (Infecton®) | Bacterial infection | |
| 99mTc-ubiquicidin | Bacterial infection | |
| 99mTc-fluconazole | Fungal infection | |
| 18F-FEAU | Herpes Simplex Virus | |
| Inflammatory diseases | 99mTc/123I/18F-IL2 | Inflammatory bowel disease, Sjögren Syndrome, type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis, inflammatory plaque, rheumatoid arthritis |
| 111In/68Ga-somatostatin analogues | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| 99mTc/111In/123I-anti-TNFα MoAb (infliximab, adalimumab, golimumab, certolizumab pegol, etanercept) | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| 99mTc/111In/89Zr-rituximab® | Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| Tumour environment | 99mTc/111In/89Zr-bevacizumab | Breast cancer, renal cell carcinoma |
| 99mTc/123I/18F-IL2 | Melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck, renal cell carcinoma | |
| 111In/89Zr/64Cu-PD1/PDL-1 MoAb (pembrolizumab, nivolumab, atezolizumab) | Metastatic lung cancer, bladder cancer, urothelial carcinoma, melanoma | |
| 18F/89Zr/64Cu-CTLA-4 MoAbs (ipilimumab, tremelimumab) | Melanoma, colon cancer |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Signore, A.; Lauri, C.; Auletta, S.; Anzola, K.; Galli, F.; Casali, M.; Versari, A.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M. Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050681
Signore A, Lauri C, Auletta S, Anzola K, Galli F, Casali M, Versari A, Glaudemans AWJM. Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(5):681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050681
Chicago/Turabian StyleSignore, Alberto, Chiara Lauri, Sveva Auletta, Kelly Anzola, Filippo Galli, Massimiliano Casali, Annibale Versari, and Andor W.J.M. Glaudemans. 2019. "Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 5: 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050681
APA StyleSignore, A., Lauri, C., Auletta, S., Anzola, K., Galli, F., Casali, M., Versari, A., & Glaudemans, A. W. J. M. (2019). Immuno-Imaging to Predict Treatment Response in Infection, Inflammation and Oncology. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), 681. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050681







