Association between Sarcopenia and Depression in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Patients
2.2. Questionnaire Survey
2.3. Measurement of GS and SMI and Our Study
2.4. Statistical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Patient Baseline Characteristics
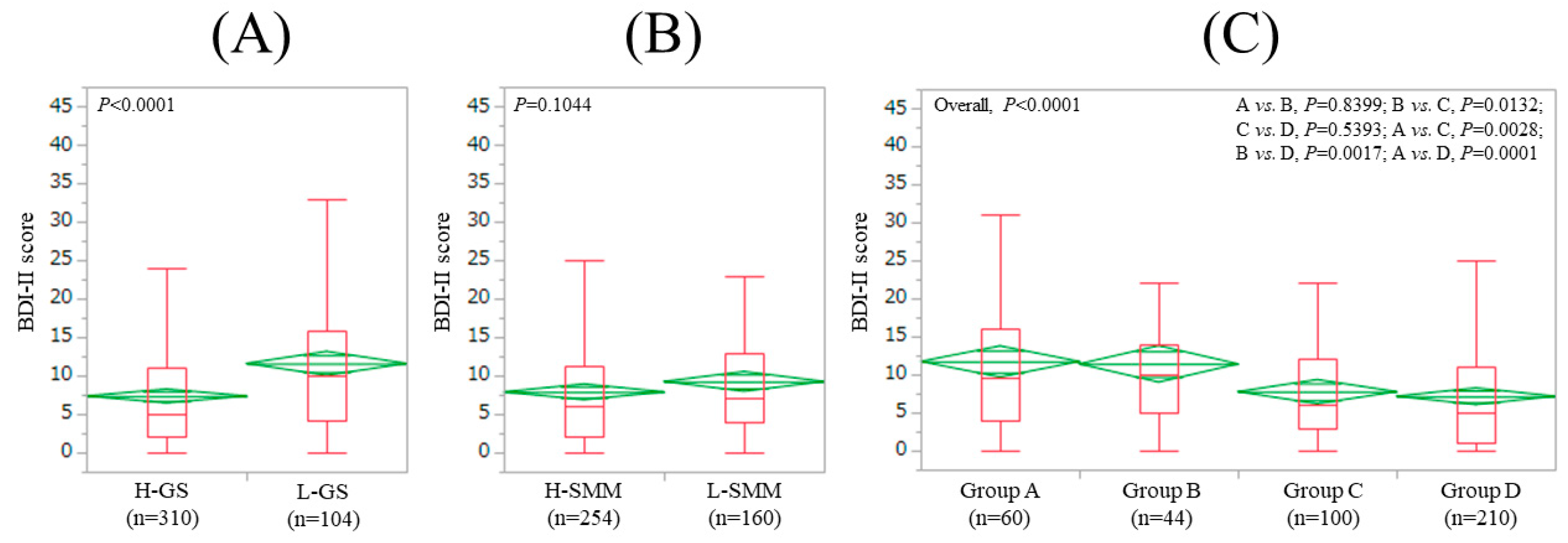
3.2. Impact of GS and SMM on BDI-II Score for All Cases (n = 414)
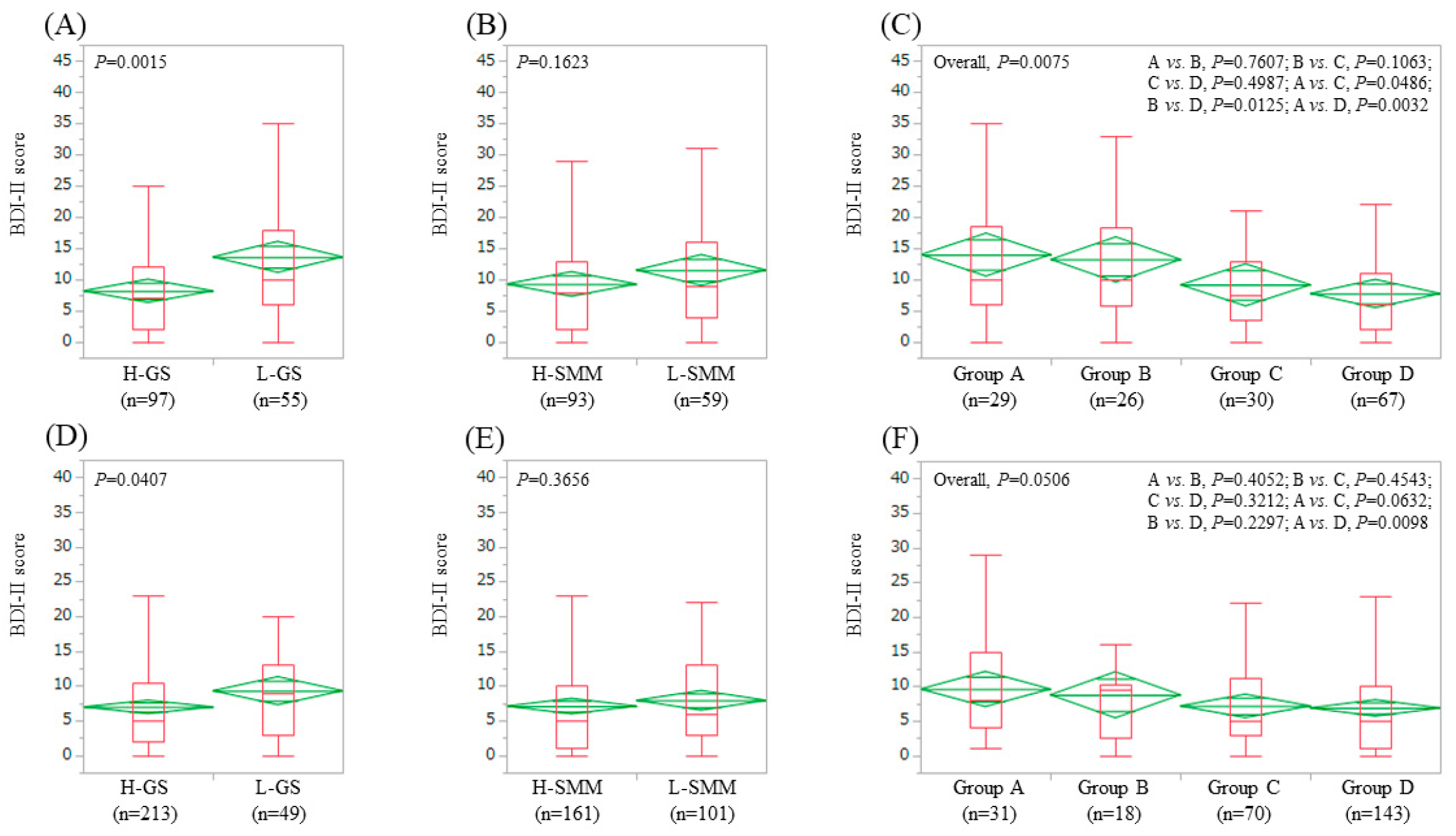
3.3. Impact of GS and SMM on BDI-II Score for LC Patients (n = 152) and Non-LC Patients (n = 262)
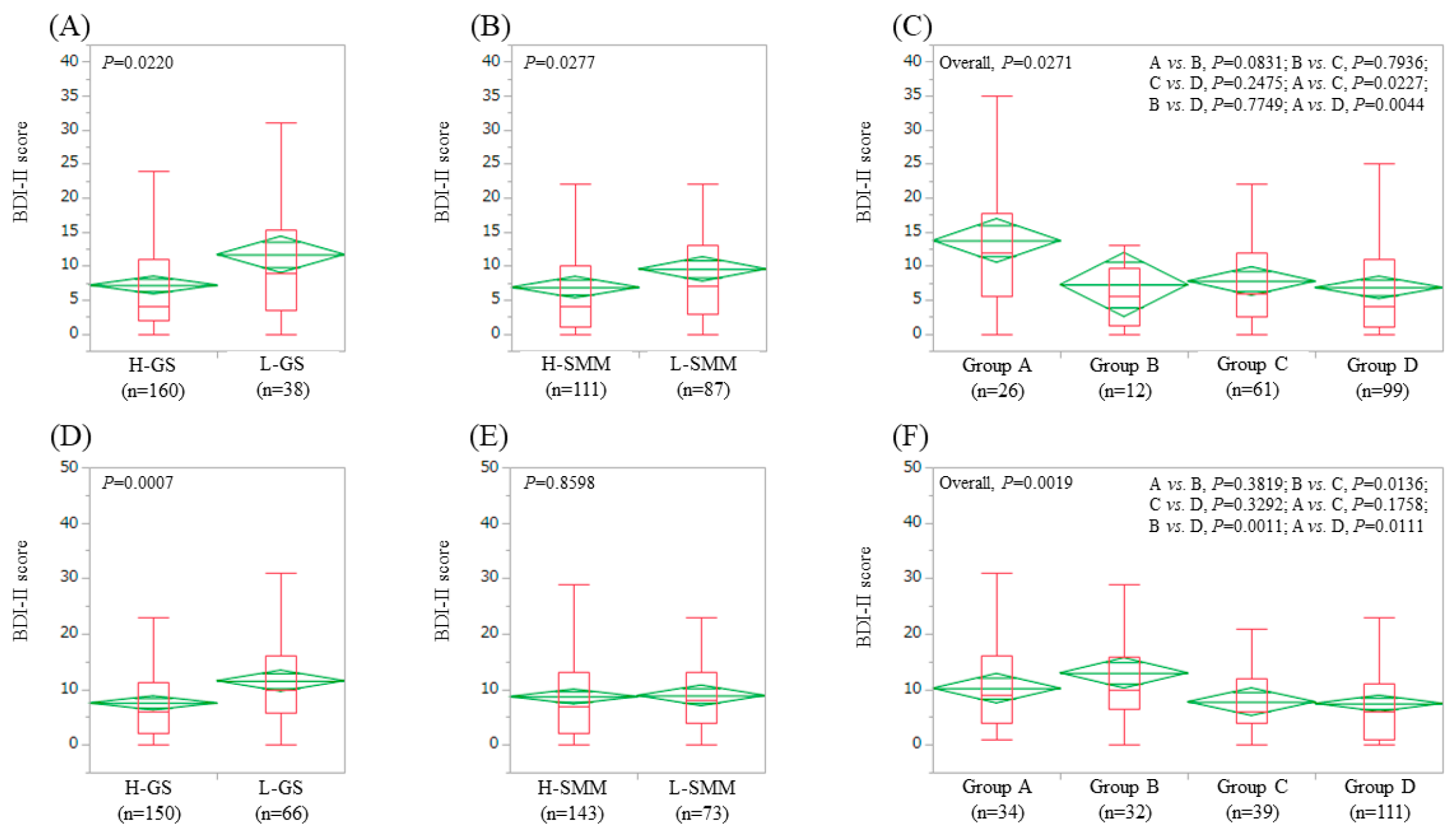
3.4. Impact of GS and SMM on BDI-II Score for Male Patients (n = 198) and Female Patients (n = 216)
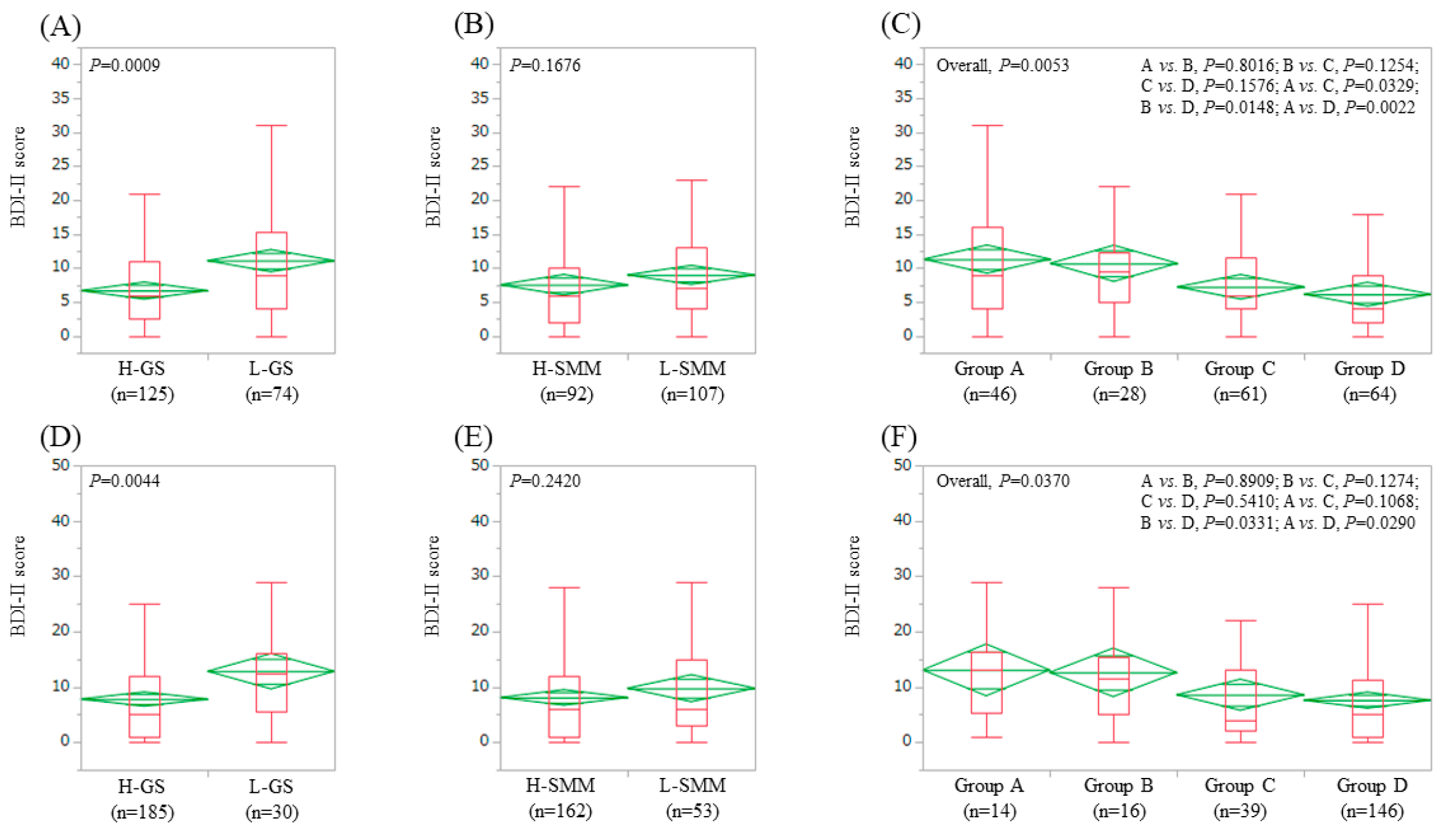
3.5. Impact of GS and SMM on BDI-II Score for Patients Aged ≥65 Years (n = 199) and Patients Aged <65 Years (n = 215)
3.6. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Factors Associated with BDI-II Score ≥11
3.7. Correlation between BDI-II Score and GS and SMI in Male and Female
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Buganza-Torio, E.; Mitchell, N.; Abraldes, J.G.; Thomas, L.; Ma, M.; Bailey, R.J.; Tandon, P. Depression in cirrhosis—A prospective evaluation of the prevalence, predictors and development of a screening nomogram. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 49, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.K.; Hepgul, N.; Higginson, I.J.; Gao, W. Symptom prevalence and quality of life of patients with end-stage liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Palliat. Med. 2018, 33, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeoh, S.W.; Holmes, A.C.N.; Saling, M.M.; Everall, I.P.; Nicoll, A.J. Depression, fatigue and neurocognitive deficits in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Nevola, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Romano, C.; Giordano, M. Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Depression. Clin. Liver Dis. 2017, 21, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y. Depression and Chronic Liver Diseases: Are There Shared Underlying Mechanisms? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Leighton, J.; Lee, W.L.; Jones, D.E. Symptoms of PBC—Pathophysiology and management. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 34–35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirks, M.; Haag, K.; Pflugrad, H.; Tryc, A.B.; Schuppner, R.; Wedemeyer, H.; Potthoff, A.; Tillmann, H.L.; Sandorski, K.; Worthmann, H.; et al. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in hepatitis C patients resemble those of patients with autoimmune liver disease but are different from those in hepatitis B patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 26, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, C.; Wahl, I.; Weiler-Normann, C.; Voigt, K.; Wiegard, C.; Glaubke, C.; Brähler, E.; Löwe, B.; Lohse, A.W.; Rose, M. Health-related quality of life, depression, and anxiety in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, L.E.; Nevola, R.; Lus, G.; Restivo, L.; Guerrera, B.; Romano, C.; Zampino, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Sellitto, A.; Giordano, M.; et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection and neurological and psychiatric disorders: An overview. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Henry, L. The impact of the new antiviral regimens on patient reported outcomes and health economics of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, S186–S196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Glischinski, M.; von Brachel, R.; Hirschfeld, G. How depressed is “depressed”? A systematic review and diagnostic meta-analysis of optimal cut points for the Beck Depression Inventory revised (BDI-II). Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Hoshi, A.; Suzuki, M.; Mitobe, Y.; Yamada, E.; Abeywickrama, H.M.; Seki, N.; Koyama, C.; Aoki, H.; et al. Relationship Between Sarcopenia and Both Physical Activity and Lifestyle in Patients With Chronic Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2018, 10, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Abe, K.; Fujita, M.; Okai, K.; Takahashi, A.; Ohira, H. Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan Society of Hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease (1st edition): Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano-Loza, A.J. Clinical relevance of sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8061–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; Schneider, S.M.; Zúñiga, C.; Arai, H.; Boirie, Y.; Chen, L.K.; Fielding, R.A.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; et al. Prevalence of and interventions for sarcopenia in ageing adults: A systematic review. Report of the International Sarcopenia Initiative (EWGSOP and IWGS). Age Ageing 2014, 43, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M.; Gow, P.J.; Grossmann, M.; Angus, P.W. Review article: Sarcopenia in cirrhosis-aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.K.; Liu, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Hsu, P.S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus Report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Ishii, A.; Iwata, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishii, N.; Yuri, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Elevated serum myostatin level is associated with worse survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, K.; Otten, L. Financial impact of sarcopenia or low muscle mass—A short review. Clin. Nutr. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, N.; Kaido, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Okumura, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Shirai, H.; Yao, S.; Yagi, S.; Uemoto, S. Impact of sarcopenic obesity on outcomes in patients undergoing living donor liver transplantation. Clin. Nutr. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bandt, J.P.; Jegatheesan, P.; Tennoune-El-Hafaia, N. Muscle Loss in Chronic Liver Diseases: The Example of Nonalcoholic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Chen, J.D.; Wu, W.T.; Huang, K.C.; Hsu, C.T.; Han, D.S. Association between Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass and Mortality and Tumor Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Liver Cancer 2018, 7, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.J.; Liu, H.; Garcia, J.M. Sex Differences in Muscle Wasting. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1043, 153–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.Z.; No, M.H.; Heo, J.W.; Park, D.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kwak, H.B. Role of exercise in age-related sarcopenia. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2018, 14, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budui, S.L.; Rossi, A.P.; Zamboni, M. The pathogenetic bases of sarcopenia. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2015, 12, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Szlejf, C.; Suemoto, C.K.; Brunoni, A.R.; Viana, M.C.; Moreno, A.B.; Matos, S.M.A.; Lotufo, P.A.; Benseñor, I.M. Depression is Associated With Sarcopenia Due to Low Muscle Strength: Results From the ELSA-Brasil Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.M.; Titus, A.J.; Bruce, M.L.; Orzechowski, N.M.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Bartels, S.J.; Batsis, J.A. Depression and Handgrip Strength Among U.S. Adults Aged 60 Years and Older from NHANES 2011–2014. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hai, S.; Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Dong, B. Association between depressive symptoms and sarcopenia in older Chinese community-dwelling individuals. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.K.; Dong, H.K.; Yong, S.P. Body Composition, Sarcopenia, and Suicidal Ideation in Elderly Koreans: Hallym Aging Study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 604–610. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.V.; Hsu, T.H.; Wu, W.T.; Huang, K.C.; Han, D.S. Is sarcopenia associated with depression? A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Age Ageing 2017, 46, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.K.; Hsu, L.W.; Huang, K.T.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, T.L.; Li, W.F.; Goto, S.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, C.C. Assessment of relevant factors with respect to psychosocial properties in potential living donor candidates before liver transplantation. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, C.L.; Butt, Z.; Ladner, D.P.; Skaro, A.I.; Abecassis, M.M. A review of quality of life instruments used in liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, S.; Oda, N.; Ochiai, T.; Alev, L. Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Phase II(IQR)Trial of Duloxetine Monotherapy in Japanese Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016, 41, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunami, K.; Nishida, N.; Kaneko, N.; Ikeo, K.; Toyo-Oka, L.; Takeuchi, H.; Matsuura, K.; Tamori, A.; Nomura, H.; Yoshiji, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies ZNF354C Variants Associated with Depression from Interferon-Based Therapy for Chronic Hepatitis C. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kawase, K.; Kondo, K.; Saito, T.; Shimasaki, A.; Takahashi, A.; Kamatani, Y.; Kawabe, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Ikeda, M.; Kubo, M.; et al. Risk factors and clinical characteristics of the depressive state induced by pegylated interferon therapy in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: A prospective study. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2016, 70, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Han, P.; Fu, L.; Jia, L.; Yu, H.; Yu, X.; Hou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; et al. Twelve-Month Incidence of Depressive Symptoms in Suburb-Dwelling Chinese Older Adults: Role of Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 20, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallgren, M.; Herring, M.P.; Owen, N.; Dunstan, D.; Ekblom, Ö.; Helgadottir, B.; Nakitanda, O.A.; Forsell, Y. Exercise, physical activity, and sedentary behavior in the treatment of depression: Broadening the scientific perspectives and clinical opportunities. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.S.; Eun, C.R.; Seo, J.A.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; Park, M.H.; et al. Depression is associated with sarcopenia, not central obesity, in elderly korean men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2011, 59, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumori, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takegami, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Onishi, Y.; Sekiguchi, M.; Otani, K.; Konno, S.; Kikuchi, S.; Fukuhara, S. Association between hand-grip strength and depressive symptoms: Locomotive syndrome and health outcomes in Aizu Cohort Study (LOHAS). Age Ageing 2015, 44, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yu, B.; Meng, G.; Liu, F.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Shen, S.; Han, P.; et al. Both muscle mass and muscle strength are inversely associated with depressive symptoms in an elderly Chinese population. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 32, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life in Chronic Liver Diseases: A Strong Impact of Hand Grip Strength. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, N. Depression and diabetes. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horne, R.; Foster, J.A. Metabolic and Microbiota Measures as Peripheral Biomarkers in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Lange, S.M.M. Metabolic syndrome in psychiatric patients: Overview, mechanisms, and implications. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, S.; Chang, C.; Tanaka, T.; Kuroda, A.; Tsuji, T.; Akishita, M.; Iijima, K. The Association between Sarcopenic Obesity and Depressive Symptoms in Older Japanese Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Busetto, L.; Cesaretti, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Deutsch, L.; Iannelli, A. Nutritional issues in patients with obesity and cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3330–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, C.; Piccoli, G.B.; Barsotti, M.; Tassi, S.; Giannese, D.; Morganti, R.; Cupisti, A. Prevalence and Correlates of Sarcopenia among Elderly CKD Outpatients on Tertiary Care. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, C.; Brismar, T.B.; Majeed, A.; Wahlin, S. Assessment of muscle mass depletion in chronic liver disease: Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry compared with computed tomography. Nutrition 2019, 61, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Modality | Cut-off Value |
|---|---|
| Bioimpedance analysis | Male: 7.0 kg/m² |
| Female: 5.7 kg/m² | |
| Grip strength | Male: 26 kg |
| Female: 18 kg |
| Variables | All Cases (n = 414) | Group A (n = 60) | Group B (n = 44) | Group C (n = 100) | Group D (n = 210) | Overall p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 61.5 ± 12.7 (52, 71) | 68.3 ± 12.2 (65, 75) | 65.9 ± 10.7 (63, 73) | 64.6 ± 12.2 (60, 72) | 57.1 ± 11.8 (48, 66) | <0.0001 |
| Gender, male/female | 198/216 | 26/34 | 12/32 | 61/39 | 99/111 | 0.0019 |
| HBV/HCV/HBV and HCV/NBNC (Etiology) | 61/257/8/88 | 5/41/2/12 | 7/27/0/10 | 15/67/3/15 | 34/122/3/51 | 0.4858 |
| Presence of LC, yes/no | 152/262 | 29/31 | 26/18 | 30/70 | 67/143 | 0.0007 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.3 ± 3.8 (20.6, 25.5) | 21.2 ± 2.2 (19.8, 22.7) | 25.8 ± 3.8 (22.9, 28.8) | 20.8 ± 2.5 (19.0, 22.1) | 24.6 ± 3.8 (21.9, 26.7) | <0.0001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.98 ± 0.60 (0.6, 1.1) | 0.9 ± 0.4 (0.6, 1.0) | 1.3 ± 0.9 (0.6, 1.7) | 0.9 ± 0.4 (0.7, 1.0) | 1.0 ± 0.6 (0.6, 1.1) | 0.1482 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.1 ± 0.5 (3.9, 4.5) | 3.9 ± 0.6 (3.5, 4.4) | 3.9 ± 0.6 (3.5, 4.2) | 4.3 ± 0.4 (4.1, 4.6) | 4.2 ± 0.5 (4.0, 4.5) | <0.0001 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 86.4 ± 15.9 (79.3, 96.5) | 85.4 ± 16.6 (77.7, 94.4) | 77.3 ± 16.5 (62.6, 89.5) | 86.9 ± 16.2 (82.0, 96.3) | 88.4 ± 14.9 (80.2, 98.6) | 0.0004 |
| Platelet count (×104/mm3) | 17.0 ± 7.1 (11.7, 21.2) | 16.6 ± 7.4 (10.4, 21.2) | 13.3 ± 6.7 (7.4, 17.9) | 16.7 ± 6.0 (12.1, 20.1) | 18.0 ± 7.4 (12.6, 22.5) | 0.0013 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 181.1 ± 41.7 (150, 207.5) | 177.4 ± 53.2 (143, 209) | 161.8 ± 38.2 (135, 186) | 184.1 ± 38.5 (157, 206) | 184.7 ± 39.3 (154, 212) | 0.0085 |
| AST (IU/L) | 36.9 ± 26.5 (21, 42) | 41.4 ± 31.1 (21, 49) | 41.4 ± 27.0 (22, 48) | 35.0 ± 23.4 (22, 37) | 35.5 ± 26.3 (21, 40) | 0.2554 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 36.1 ± 35.7 (16, 44) | 37.3 ± 43.9 (15, 42) | 37.7 ± 37.1 (16, 43) | 33.3 ± 28.4 (16, 40) | 36.7 ± 36.1 (16, 44) | 0.8485 |
| ALP (IU/L) | 284.1 ± 274.2 (195, 300) | 377.4 ± 640.4 (206, 343) | 281.2 ± 110.9 (215, 314) | 253.1 ± 93.6 (195, 279) | 272.2 ± 141.8 (192, 298) | 0.2601 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 47.3 ± 58.7 (17, 49) | 48.4 ± 69.6 (16, 47) | 54.6 ± 56.2 (21, 58) | 44.4 ± 54.5 (17, 46) | 46.8 ± 58.1 (17, 49) | 0.8193 |
| eGFR mL/min/1.73 m2) | 83.6 ± 21.4 (72.0, 95.5) | 78.6 ± 24.1 (65.8, 90.5) | 82.4 ± 25.5 (71, 93) | 81.4 ± 19.7 (71, 90) | 86.3 ± 20.1 (74, 99) | 0.0495 |
| HbA1c (NGSP) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (5.4, 6.0) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (5.3, 6.0) | 5.8 ± 0.9 (5.2, 6.4) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (5.5, 6.0) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (5.4, 6.0) | 0.9614 |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 140.1 ± 2.4 (139, 142) | 139.6 ± 3.2 (138, 142) | 139.9 ± 2.8 (139, 142) | 140.4 ± 2.3 (140, 142) | 140.1 ± 2.2 (139, 141) | 0.1840 |
| BDI-II score | 8.4 ± 8.3 (2, 13) | 11.7 ± 9.6 (4, 16) | 11.4 ± 9.9 (5, 14) | 7.8 ± 7.0 (3, 12) | 7.2 ± 7.7 (1, 11) | <0.0001 |
| Variables | BDI-II Score ≥11 (n = 130) | BDI-II Score <11 (n = 284) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60.3 ± 13.5 (50.75, 70.25) | 62.0 ± 12.3 (54, 71) | 0.2064 |
| Gender, male/female | 61/69 | 137/157 | 0.8326 |
| HBV/HCV/HBV and HCV/NBNC | 17/86/2/25 | 44/171/6/63 | 0.7106 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.2 ± 3.9 (20.3, 25.025) | 23.3 ± 3.8 (20.625, 25.6) | 0.6580 |
| Presence of LC, yes/no | 59/71 | 93/191 | 0.0157 |
| Group, A/B/C/D | 28/16/30/56 | 32/28/70/154 | 0.0259 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.95 ± 0.55 (0.6, 1.1) | 0.99 ± 0.62 (0.6, 1.0) | 0.5333 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.05 ± 0.54 (3.8, 4.4) | 4.15 ± 0.52 (3.9, 4.5) | 0.0445 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 85.9 ± 15.8 (77.65, 96.375) | 86.6 ± 16.0 (79.625, 97.1) | 0.6875 |
| Platelet count (×104/mm3) | 16.4 ± 7.0 (10.975, 20.625) | 17.2 ± 7.2 (11.95, 21.8) | 0.2924 |
| AST (IU/L) | 39.5 ± 26.6 (21, 48) | 35.7 ± 26.4 (21, 39.75) | 0.1703 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 39.2 ± 40.5 (16, 47.25) | 34.6 ± 33.2 (16, 42) | 0.2200 |
| ALP (IU/L) | 278.7 ± 140.0 (200, 305.5) | 286.5 ± 317.6 (193.25, 299.75) | 0.7936 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 52.1 ± 69.4 (21, 50) | 45.0 ± 52.9 (17, 49) | 0.2630 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 176.6 ± 39.6 (145, 204.25) | 183.1 ± 42.6 (151.75, 211) | 0.1492 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 84.8 ± 20.8 (73, 96) | 83.0 ± 21.6 (71, 95) | 0.4335 |
| Serum sodium (mmol/L) | 140.0 ± 2.9 (139, 142) | 140.1 ± 2.2 (139, 142) | 0.6158 |
| HbA1c (NGSP) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (5.3, 6.0) | 5.8 ± 0.8 (5.4, 6.075) | 0.8769 |
| Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Presence of LC | |||
| Yes | 0.658 | 0.394–1.099 | 0.1101 |
| No | 1.000 | Reference | |
| Serum albumin (per 1.0 g/dL) | 1.027 | 0.641–1.646 | 0.910 |
| Group | |||
| A (L-GS and L-SMM) | 0.438 | 0.239–0.801 | 0.0074 |
| B (L-GS and H-SMM) | 0.705 | 0.349–1.423 | 0.3289 |
| C (H-GS and L-SMM) | 0.813 | 0.477–1.385 | 0.4460 |
| D (H-GS and H-SMM) | 1.000 | Reference | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Kishino, K.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; et al. Association between Sarcopenia and Depression in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050634
Nishikawa H, Enomoto H, Yoh K, Iwata Y, Sakai Y, Kishino K, Ikeda N, Takashima T, Aizawa N, Takata R, et al. Association between Sarcopenia and Depression in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(5):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050634
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Hiroki, Hirayuki Enomoto, Kazunori Yoh, Yoshinori Iwata, Yoshiyuki Sakai, Kyohei Kishino, Naoto Ikeda, Tomoyuki Takashima, Nobuhiro Aizawa, Ryo Takata, and et al. 2019. "Association between Sarcopenia and Depression in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 5: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050634
APA StyleNishikawa, H., Enomoto, H., Yoh, K., Iwata, Y., Sakai, Y., Kishino, K., Ikeda, N., Takashima, T., Aizawa, N., Takata, R., Hasegawa, K., Ishii, N., Yuri, Y., Nishimura, T., Iijima, H., & Nishiguchi, S. (2019). Association between Sarcopenia and Depression in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050634




