Long-Term Nasal Growth after Primary Rhinoplasty for Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity: A Three-Dimensional Photogrammetric Study with Comparative Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Primary Cleft Rhinoplasty
2.2. Intermediate Cleft Rhinoplasty
2.3. D Photogrammetric Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Intragroup Comparative Analyses
3.2. Intergroup Comparative Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulliken, J.B.; Wu, J.K.; Padwa, B.L. Repair of bilateral cleft lip: Review, revisions, and reflections. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2003, 14, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.X.; Arneja, J.S. Evidence-Based Medicine: The bilateral cleft lip repair. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 152e–165e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allori, A.C.; Marcus, J.R. Modern tenets for repair of bilateral cleft lip. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, T.D.; Upton, J. Lengthening of the short columella associated with bilateral cleft lip. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1978, 1, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, D.R., Jr. Closure of bilateral cleft lip and elongation of columella by two operations in infancy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1971, 47, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edgerton, M.T.; Marsh, J.L. Results of surgical lengthening of the short nose in the bilateral cleft lip patient. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1978, 61, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordhoff, M.S. Reconstruction of vermilion in unilateral and bilateral cleft lips. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1984, 73, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McComb, H. Primary repair of the bilateral cleft lip nose: A 15-year review and a new treatment plan. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1990, 86, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, J.A.; Mohan, N. A preliminary report on one stage open tip rhinoplasty at the time of lip repair in bilateral cleft lip and palate: The alor setar experience. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1993, 46, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, H. Primary repair of the bilateral cleft lip nose: A 4-year review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 94, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, J.B. Bilateral complete cleft lip and nasal deformity: An anthropometric analysis of staged to synchronous repair. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1995, 96, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulliken, J.B. Primary repair of bilateral cleft lip and nasal deformity. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 108, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutting, C.; Grayson, B.; Brecht, L.; Santiago, P.; Wood, R.; Kwon, S. Presurgical columellar elongation and primary retrograde nasal reconstruction in one-stage bilateral cleft lip and nose repair. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 101, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Ogata, H.; Sakuma, H. Long-term outcome of simultaneous repair of bilateral cleft lip and nose (a 15 year experience). Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2003, 56, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Garfinkle, J.S.; Warren, S.M.; Brecht, L.E.; Cutting, C.B.; Grayson, B.H. Nasoalveolar molding improves appearance of children with bilateral cleft lip-cleft palate. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Salyer, K.E.; Genecov, E.R. Primary bilateral one-stage cleft lip/nose repair: 40-year Dallas experience: Part I. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2009, 20, 1913–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aufricht, G. Paper Presented at: 1955 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Maxillo-Facial Surgeons; American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Viale-González, M.; Ortiz-Monasterio, F. Observations on growth of the columella and prolabium in the bilateral cleft lip. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1970, 46, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, K.; Vargervik, K. Nasal growth in complete bilateral cleft lip and palate. J. Craniofac. Surg. 1996, 7, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.P.; Greene, A.K.; Mulliken, J.B. Current surgical management of bilateral cleft lip in North America. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.C.; Park, J.M. Mulliken method of bilateral cleft lip repair: Anthropometric evaluation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, H.K. Primary repair of the bilateral cleft lip nose: A long-term follow-up. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, M.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, K.C. Long-term results in the bilateral cleft lip repair by Mulliken’s method. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2009, 20, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfinkle, J.S.; King, T.W.; Grayson, B.H.; Brecht, L.E.; Cutting, C.B. A 12-year anthropometric evaluation of the nose in bilateral cleft lip-cleft palate patients following nasoalveolar molding and cutting bilateral cleft lip and nose reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, W.S.; Oh, T.S.; Choi, J.W.; Koh, K.S. Effect of preoperative nasal retainer on nasal growth in patients with bilateral incomplete cleft lip: A 3-year follow-up study. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2017, 44, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottgers, S.A.; Lim, S.Y.; Hall, A.M.; Zurakowski, D.; Mulliken, J.B. Longitudinal photogrammetric analysis of the columellar-labial angle following primary repair of bilateral cleft lip and nasal deformity. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.C.; Mulliken, J.B. Direct anthropometry of repaired bilateral complete cleft lip: A long-term assessment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 326e–332e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavri, S.; Zhu, V.Z.; Steinbacher, D.M. Postoperative edema resolution following rhinoplasty: A three-dimensional morphometric assessment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 973e–979e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.A.; Ahmad, R.; Asi, S.M.; Ismail, N.H.; Rahman, Z.A. Three-dimensional quantitative evaluation of facial morphology in adults with unilateral cleft lip and palate, and patients without clefts. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 52, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzler, P.; Geiger, E.J.; Chang, C.C.; Sirisoontorn, I.; Steinbacher, D.M. Assessment of three-dimensional nasolabial response to Le Fort I advancement. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2014, 67, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, T.K.; Caughlin, B.P.; Munaretto, N.; Toriumi, D.M. Three-dimensional evaluation of unilateral cleft rhinoplasty results. Facial Plast. Surg. 2013, 29, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, E.; Morrison, C.S.; Stuhaug, E.; Shapiro, L.G.; Tse, R.W. Novel computer vision analysis of nasal shape in children with unilateral cleft lip. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, B.; Maal, T.J.; Plooij, J.M.; Ingels, K.J.; Borstlap, W.A.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Spauwen, P.H.; Bergé, S.J. 3D Stereophotogrammetric assessment of pre- and postoperative volumetric changes in the cleft lip and palate nose. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, P.H.; Hughes-Lawson, C.A. Stereophotogrammetric study of growth and development of the nose. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1989, 96, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C.; Poggio, C.E.; Schmitz, J.H. Three-dimensional study of growth and development of the nose. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 1997, 34, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C.; Poggio, C.E.; Schmitz, J.H. Facial volume changes during normal human growth and development. Anat Rec. 1998, 250, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, V.F.; Sforza, C.; Poggio, C.E.; Schmitz, J.H. Soft-tissue facial morphometry from 6 years to adulthood: A three-dimensional growth study using a new modeling. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 103, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforza, C.; Grandi, G.; De Menezes, M.; Tartaglia, G.M.; Ferrario, V.F. Age- and sex-related changes in the normal human external nose. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 204, 205.e1–205.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordhoff, M.S. Bilateral cleft lip reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 78, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.J.; Wong, F.H.; Mardini, S.; Chen, Y.R.; Noordhoff, M.S. Assessment of bilateral cleft lip nose deformity: A comparison of results as judged by cleft surgeons and laypersons. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 110, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, E.J.; Subramanian, M.; Chen, P.K. Progressive changes of columella length and nasal growth after nasoalveolar molding in bilateral cleft patients: A 3-year follow-up study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 119, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.S.; Liao, Y.F.; Wallace, C.G.; Chan, F.C.; Liou, E.J.; Chen, P.K.; Noordhoff, M.S. Long-term comparison of the results of four techniques used for bilateral cleft nose repair: A single surgeon’s experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 926e–936e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heijden, P.; Korsten-Meijer, A.G.; van der Laan, B.F.; Wit, H.P.; Goorhuis-Brouwer, S.M. Nasal growth and maturation age in adolescents: A systematic review. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chang, M.H. New growth charts for taiwanese children and adolescents based on world health organization standards and health-related physical fitness. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2010, 51, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhulst, A.; Hol, M.; Vreeken, R.; Becking, A.; Ulrich, D.; Maal, T. Three-dimensional imaging of the face: A comparison between three different imaging modalities. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2018, 38, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ort, R.; Metzler, P.; Kruse, A.L.; Matthews, F.; Zemann, W.; Grätz, K.W.; Luebbers, H.T. The reliability of a three- dimensional photo system- (3dmdface-) based evaluation of the face in cleft lip infants. Plast. Surg. Int. 2012, 2012, 138090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, L.G. (Ed.) Anthropometry of the Head and Neck, 2nd ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chortrakarnkij, P.; Lonic, D.; Lin, H.H.; Lo, L.J. Establishment of a reliable horizontal reference plane for 3-dimensional facial soft tissue evaluation before and after orthognathic surgery. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2017, 78, S139–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhk, J.; Park, J.; Nguyen, A.H. Nasal analysis and anatomy: Anthropometric proportional assessment in asians-aesthetic balance from forehead to chin, part I. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2015, 29, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maal, T.J.; van Loon, B.; Plooij, J.M.; Rangel, F.; Ettema, A.M.; Borstlap, W.A.; Bergé, S.J. Registration of facial 3-dimensional facial photographs for clinical use. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plooij, J.M.; Swennen, G.R.; Rangel, F.A.; Maal, T.J.; Schutyser, F.A.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Bergé, S.J. Evaluation of reproducibility and reliability of 3D soft tissue analysis using 3D stereophotogrammetry. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, L.J.; Kane, A.A.; Chen, Y.R. Simultaneous reconstruction of the secondary bilateral cleft lip and nasal deformity: Abbe flap revisited. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 112, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, J.M.; Alleyne, B.; Gosain, A.K. Secondary cleft nasoplasty at primary school age: Quantitative evaluation of the efficacy of resorbable plates. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allori, A.C.; Mulliken, J.B. Evidence-based medicine: Secondary correction of cleft lip nasal deformity. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 166e–176e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, W.C.; Semb, G.; Nelson, P.; Brattström, V.; Mølsted, K.; Prahl-Andersen, B.; Gundlach, K.K. The Eurocleft project 1996-2000: Overview. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2001, 29, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, B.C.J.; Hung, Y.T.; Wang, R.S.H.; Lo, L.J. Outcome of patients with complete unilateral cleft lip and palate: 20-year follow-up of a treatment protocol. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 359e–367e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


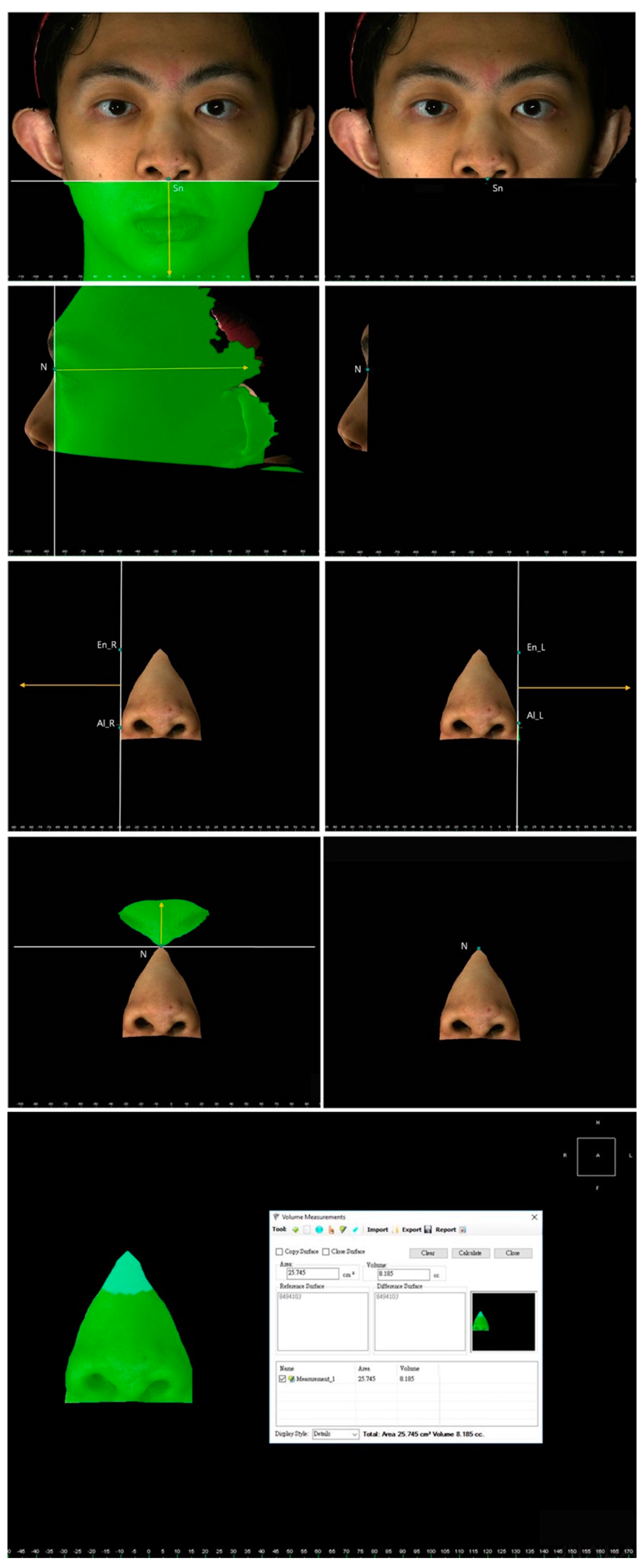

| Parameters | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Landmarks | |
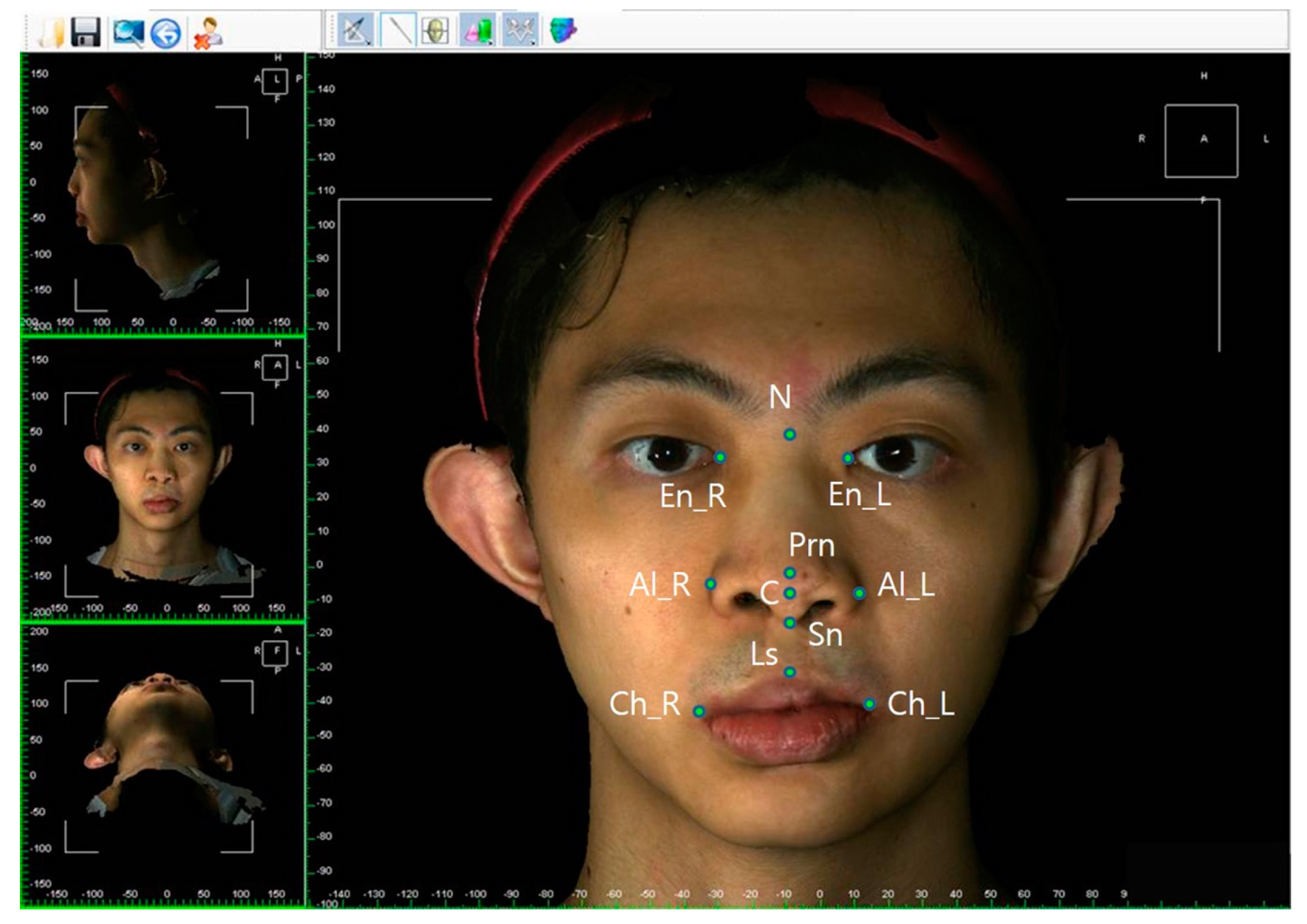
| Nasion (N) | Most depressed midline point superior to the nasal bridge |
| Pronasale (Prn) | Most anterior midpoint of the nasal tip |
| Subnasale (Sn) | Midpoint on the nasolabial soft tissue contour between the columella crest and the upper lip |
| Columellar constructed point (C) | Breakpoint at the end of the tangential line drawn from the Sn along the lower part of columella |
| Alare (Al) | Most lateral point on each alar contour |
| Endocanthion (En) | Soft tissue point located at the inner commissure of each eye fissure |
| Exocanthion (Ex) | Soft tissue point located at the outer commissure of each eye fissure |
| Labial superius (Ls) | Midpoint of the vermilion line of the upper lip |
| Cheilion (Ch) | Point located at each labial commissure |
| Tragion (T) | Soft tissue point located at the upper margin of each tragus |
| Reference planes | |
| T–Ex plane | Line passing through the T and Ex points |
| Soft tissue Frankfurt–Horizontal (FH) plane | Line passing through the T point and 17.6 degrees below the Ex–T plane |
| Linear measurements | |
| Nasal bridge length (NL) | Linear distance between the N and Prn points |
| Nasal height (NH) | Linear distance between the N and Sn points |
| Nasal protrusion (NP) | Linear distance between the Sn and Prn points |
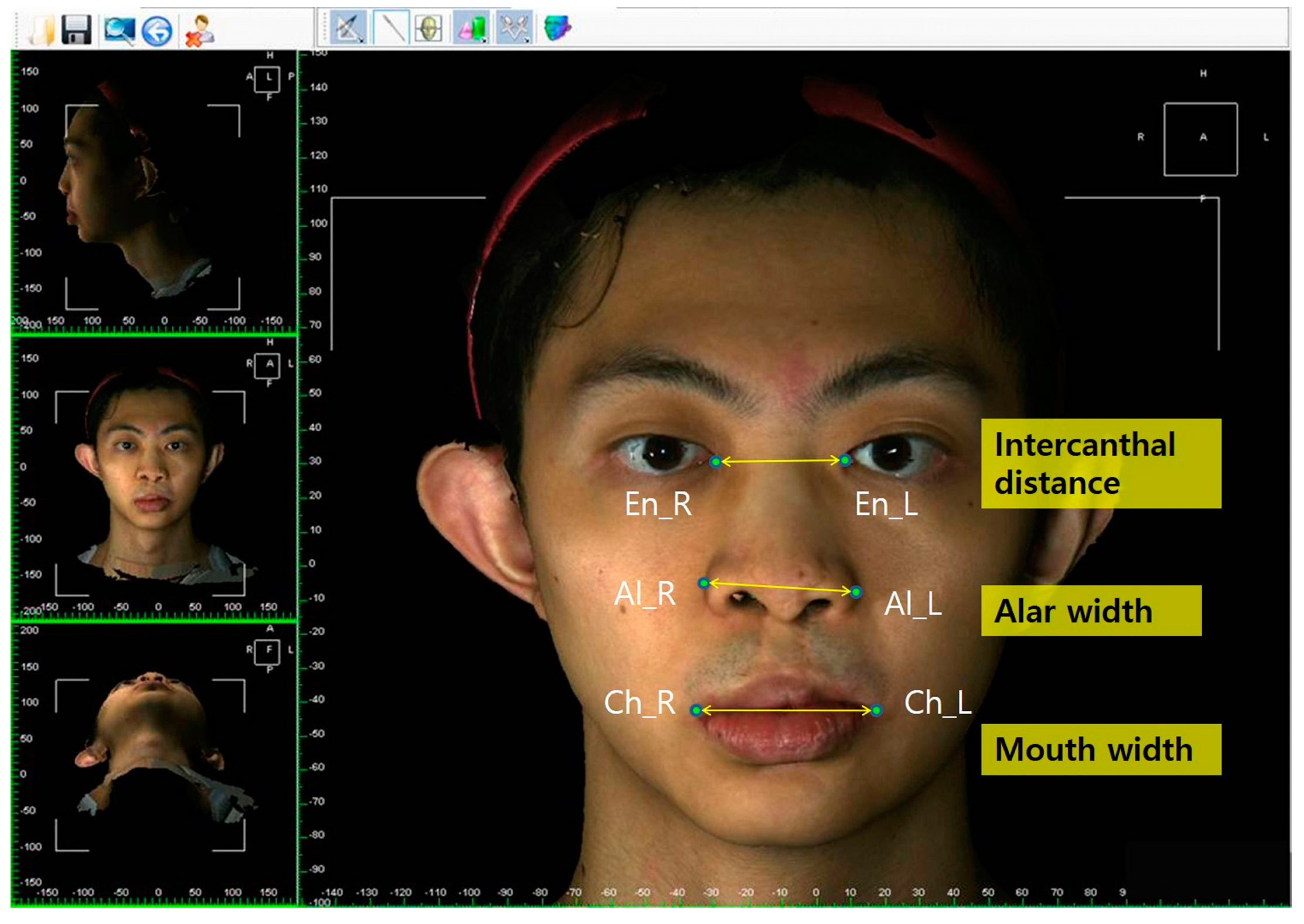
| Alar width (Al–Al) | Linear distance between the right Al and left Al points |
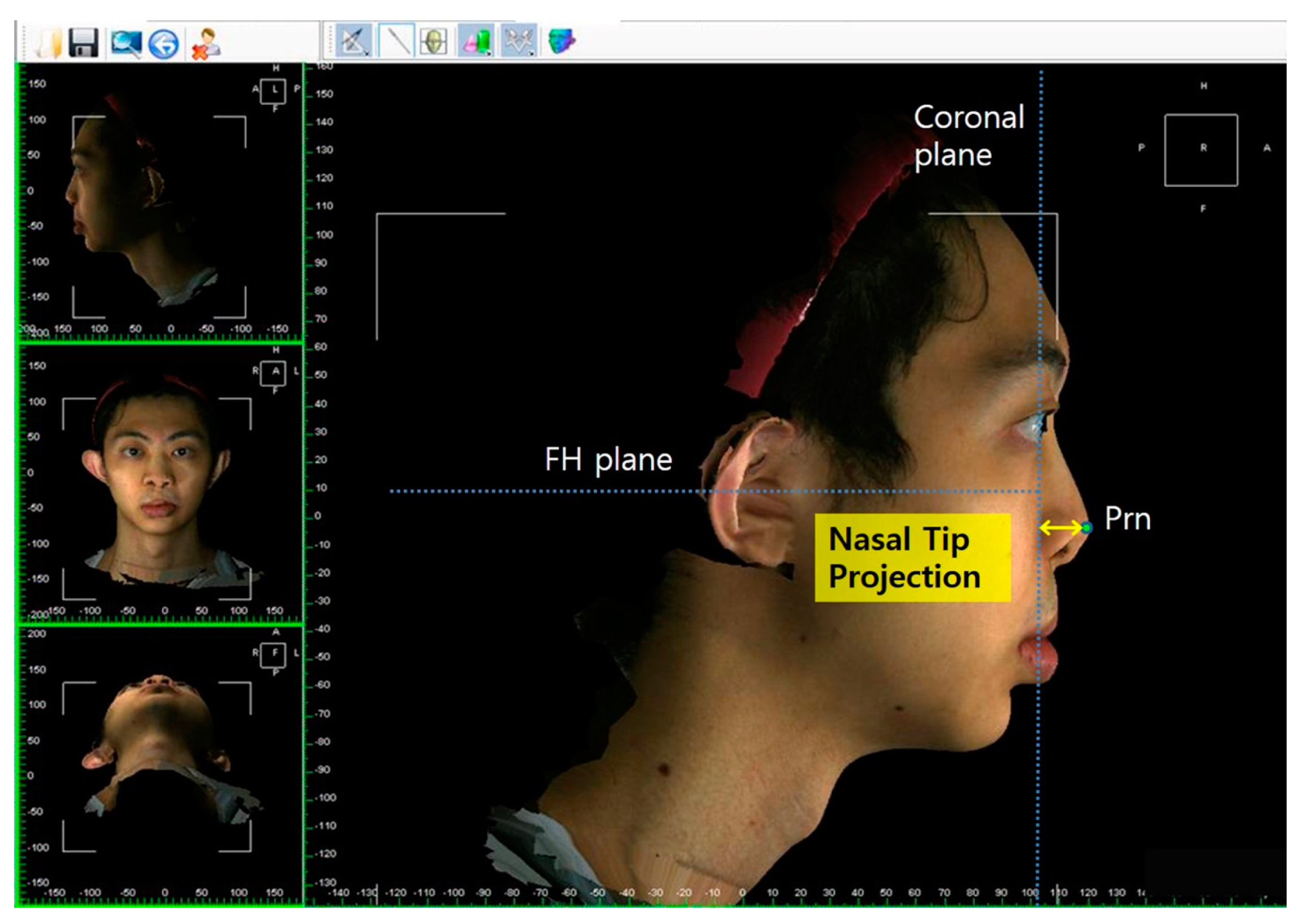
| Nasal tip projection (TP) | Linear distance from coronal plane intersecting the alar facial groove and perpendicular to the FH plane to the Prn point |
| Tip/midline deviation (TD) | Linear distance from sagittal plane intersecting the N point and perpendicular to the FH plane to the Prn point |
| Columellar height (CH) | Linear distance between the midpoint of each nostril’s highest point and the Sn point |
| Dome height (DH) | Linear distance between the midpoint of each nostril’s highest point and the Prn point |
| Intercanthal distance (En–En) | Linear distance between the right En and left En points |
| Mouth width (Ch–Ch) | Linear distance between the right Ch and left Ch points |
| Angular measurements | |
| Nasal dorsum angle | Angulation calculated from intersecting lines drawn from the N to Sn points and from the N to Prn points (Sn–N–Prn) |
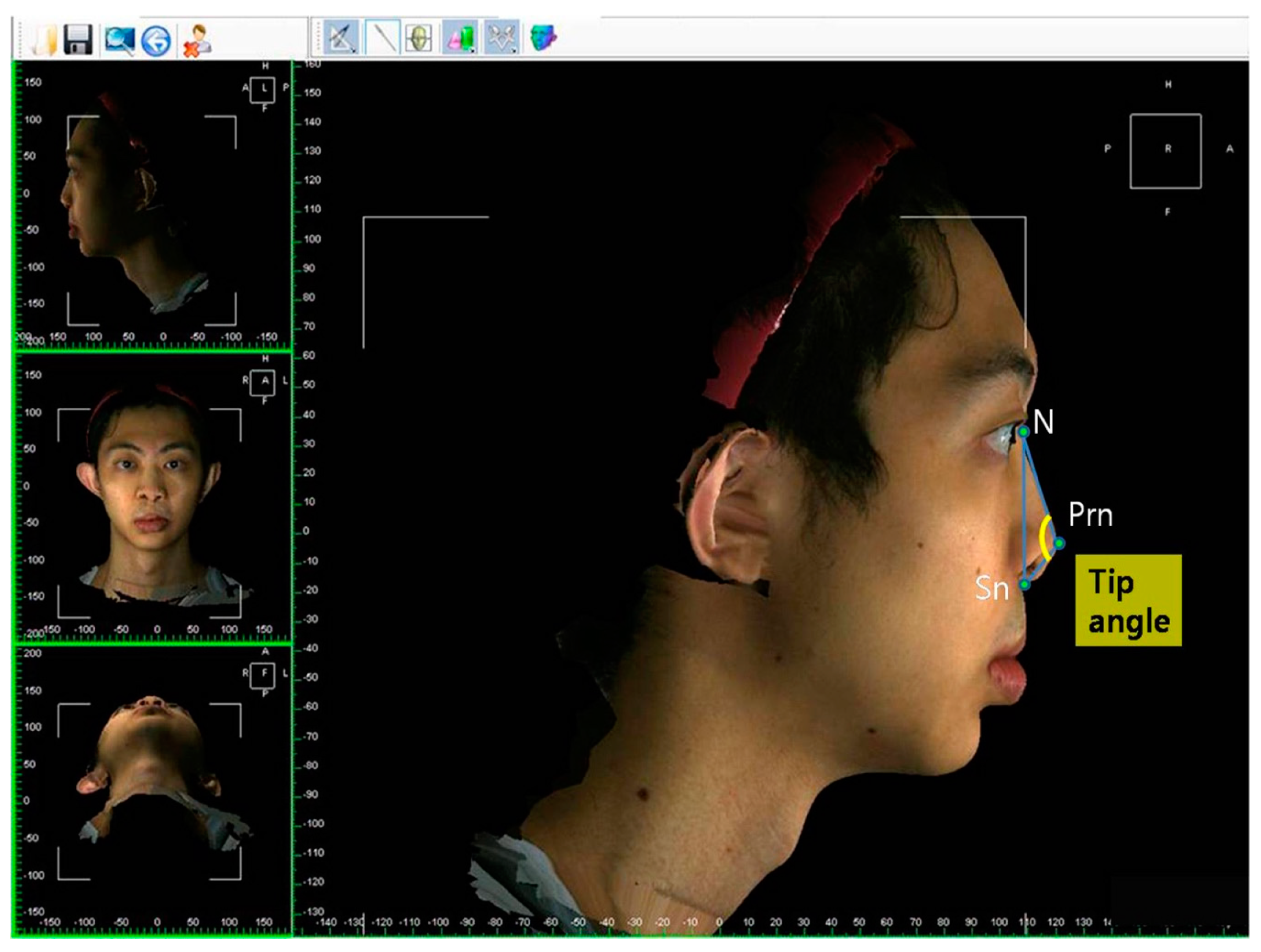
| Nasal tip angle | Angulation calculated from intersecting lines drawn from the N to Prn points and from the Sn to Prn points (N–Prn–Sn) |
| Columellar angle | Angulation calculated from intersecting lines drawn from the N to Sn points and from the Sn to C points (N–Sn–C) |
| Columellar–labial angle | Angulation calculated from intersecting lines drawn from the Sn to C points and from the Sn to Ls points (C–Sn–Ls) |
| Proportional measurements | |
| Nasal tip height ratio | Ratio between the distance from Sn to axial plane intersecting the Prn point and parallel to the FH plane and the distance from the N point to the same axial plane |
| Nasal index | Ratio between Al–Al and NH multiplied by 100 |
| Alar width/intercanthal distance ratio | Ratio between Al–Al and En–En |
| Alar width/mouth width ratio | Ratio between Al–Al and Ch–Ch |
| Dome-to-columella ratio | Ratio between DH and CH |
| Columella height/alar width ratio | Ratio between CH and Al–Al |
| Measurements | Primary Rhinoplasty (n = 9) | Primary Plus Intermediate Rhinoplasty (n = 30) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear (mm) | |||
| Nasal bridge length | 40.72 ± 3.17 | 39.07 ± 3.49 | 0.243 |
| Nasal height | 51.50 ± 4.03 | 50.91 ± 4.31 | 0.777 |
| Nasal protrusion | 20.38 ± 4.22 | 20.40 ± 3.19 | 0.527 |
| Alar width | 42.29 ± 3.48 | 42.36 ± 3.32 | 0.764 |
| Nasal tip projection | 19.92 ± 4.37 | 19.98 ± 3.04 | 0.594 |
| Tip/midline deviation | 1.94 ± 1.33 | 1.38 ± 1.27 | 0.152 |
| Columellar height | 9.57 ± 2.08 | 9.17 ± 2.02 | 0.803 |
| Dome height | 11.75 ± 2.85 | 11.92 ± 2.13 | 0.571 |
| Angular (degrees) | |||
| Nasal dorsum angle | 21.49 ± 3.91 | 21.36 ± 3.77 | 0.764 |
| Nasal tip angle | 111.23 ± 6.26 | 114.32 ± 7.22 | 0.334 |
| Columellar angle | 64.66 ± 7.02 | 62.27 ± 10.32 | 0.110 |
| Columellar–labial angle | 113.17 ± 21.29 | 119.00 ± 13.92 | 0.463 |
| Proportional | |||
| Nasal tip height ratio | 0.34 ± 0.52 | 0.40 ± 0.08 | 0.030 |
| Nasal index | 82.23 ± 5.22 | 83.85 ± 10.20 | 0.790 |
| Alar width/intercanthal distance ratio | 1.10 ± 0.10 | 1.16 ± 0.14 | 0.205 |
| Alar width/mouth width ratio | 0.97 ± 0.11 | 0.96 ± 0.07 | 0.960 |
| Dome-to-columella ratio | 1.23 ± 0.19 | 1.35 ± 0.34 | 0.414 |
| Columella height/alar width ratio | 0.22 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 0.714 |
| Nasal surface area (mm2) | 27.53 ± 6.72 | 26.89 ± 3.76 | 0.689 |
| Nasal volume (mm3) | 9.57 ± 3.95 | 8.82 ± 1.74 | 0.594 |
| Measurements | Male Patients (n = 21) | Female Patients (n = 18) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear (mm) | |||
| Nasal bridge length | 40.75 ± 3.34 | 37.94 ± 3.00 | 0.009 |
| Nasal height | 52.92 ± 3.58 | 48.86 ± 3.87 | 0.002 |
| Nasal protrusion | 21.81 ± 3.64 | 18.73 ± 2.18 | 0.003 |
| Alar width | 44.15 ± 2.61 | 40.24 ± 2.80 | <0.001 |
| Nasal tip projection | 21.80 ± 43.40 | 17.82 ± 1.45 | <0.001 |
| Tip/midline deviation | 1.20 ± 1.24 | 1.87 ± 1.41 | 0.105 |
| Columellar height | 9.87 ± 2.29 | 8.56 ± 1.39 | 0.035 |
| Dome height | 12.81 ± 2.40 | 10.80 ± 1.57 | 0.003 |
| Angular (°) | |||
| Nasal dorsum angle | 22.34 ± 4.14 | 20.29 ± 2.98 | 0.082 |
| Nasal tip angle | 112.55 ± 6.78 | 114.84 ± 7.36. | 0.320 |
| Columellar angle | 65.17 ± 8.74 | 60.09 ± 10.13 | 0.101 |
| Columellar–labial angle | 115.38 ± 18.86 | 120.30 ± 11.19 | 0.322 |
| Proportional | |||
| Nasal tip height ratio | 0.39 ± 0.07 | 0.38 ± 0.08 | 0.694 |
| Nasal index | 83.74 ± 7.12 | 83.16 ± 11.46 | 0.853 |
| Alar width/intercanthal distance ratio | 1.14 ± 0.12 | 1.15 ± 0.15 | 0.892 |
| Alar width/mouth width ratio | 0.97 ± 0.10 | 0.97 ± 0.06 | 0.926 |
| Dome-to-columella ratio | 1.36 ± 0.35 | 1.29 ± 0.26 | 0.501 |
| Columella height/alar width ratio | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.491 |
| Nasal surface area (mm2) | 29.42 ± 4.10 | 24.25 ± 3.25 | <0.001 |
| Nasal volume (mm3) | 10.40 ± 2.37 | 7.36 ± 0.93 | <0.001 |
| Measurements | Cleft Subjects (n = 39) | Normal Subjects (n = 52) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear (mm) | |||
| Nasal bridge length | 39.45 ± 3.45 | 42.19 ± 3.71 | 0.001 |
| Nasal height | 51.05 ± 4.20 | 49.60 ± 3.78 | 0.088 |
| Nasal protrusion | 20.39 ± 3.39 | 17.79 ± 1.63 | <0.001 |
| Alar width | 42.34 ± 3.25 | 38.83 ± 3.03 | <0.001 |
| Nasal tip projection | 20.0 ± 3.40 | 22.98 ± 3.20 | <0.001 |
| Tip/midline deviation | 1.51 ± 1.29 | 1.21 ± 0.94 | 0.209 |
| Columellar height | 9.26 ± 2.01 | 7.98 ± 1.58 | 0.001 |
| Dome height | 11.88 ± 2.27 | 10.47 ± 1.91 | 0.002 |
| Angular (°) | |||
| Nasal dorsum angle | 21.39 ± 3.75 | 20.32 ± 2.09 | 0.115 |
| Nasal tip angle | 113.61 ± 7.05 | 104.27 ± 5.02 | <0.001 |
| Columellar angle | 62.82 ± 9.63 | 72.56 ± 7.46 | <0.001 |
| Columellar-labial angle | 117.65 ± 15.79 | 99.99 ± 10.35 | <0.001 |
| Proportional | |||
| Nasal tip height ratio | 0.39 ± 0.07 | 0.31 ± 0.45 | <0.001 |
| Nasal index | 83.47 ± 9.25 | 78.61 ± 7.37 | 0.009 |
| Alar width/intercanthal distance ratio | 1.15 ± 0.13 | 1.06 ± 0.10 | 0.001 |
| Alar width/mouth width ratio | 0.97 ± 0.08 | 0.82 ± 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Dome-to-columella ratio | 1.32 ± 0.31 | 1.39 ± 0.46 | 0.459 |
| Columella height/alar width ratio | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.216 |
| Nasal surface area (mm2) | 27.04 ± 4.52 | 25.88 ± 4.71 | 0.241 |
| Nasal volume (mm3) | 8.99 ± 2.39 | 8.06 ± 2.31 | 0.062 |
| Measurements | Cleft Subjects (n = 21) | Normal Subjects (n = 25) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear (mm) | |||
| Nasal bridge length | 40.74 ± 3.34 | 44.40 ± 3.01 | <0.001 |
| Nasal height | 52.92 ± 3.60 | 51.87 ± 2.91 | 0.277 |
| Nasal protrusion | 21.81 ± 3.64 | 18.34 ± 1.66 | <0.001 |
| Alar width | 44.15 ± 2.61 | 40.43 ± 2.69 | <0.001 |
| Nasal tip projection | 21.80 ± 3.40 | 25.42 ± 2.40 | <0.001 |
| Tip/midline deviation | 1.20 ± 1.12 | 0.97 ± 0.84 | 0.444 |
| Columellar height | 9.87 ± 2.29 | 7.72 ± 1.51 | <0.001 |
| Dome height | 12.81 ± 2.40 | 11.31 ± 1.66 | 0.021 |
| Angular (°) | |||
| Nasal dorsum angle | 22.34 ± 4.14 | 19.93 ± 1.78 | 0.012 |
| Nasal tip angle | 112.55 ± 6.78 | 104.00 ± 5.41 | <0.001 |
| Columellar angle | 65.17 ± 8.74 | 74.47 ± 8.11 | 0.001 |
| Columellar–labial angle | 115.38 ± 18.86 | 98.41 ± 9.01 | 0.001 |
| Proportional | |||
| Nasal tip height ratio | 0.39 ± 0.72 | 0.30 ± 0.03 | <0.001 |
| Nasal index | 83.74 ± 7.12 | 78.05 ± 5.16 | 0.003 |
| Alar width/intercanthal distance ratio | 1.14 ± 0.12 | 1.08 ± 0.10 | 0.044 |
| Alar width/mouth width ratio | 0.97 ± 0.10 | 0.83 ± 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Dome-to-columella ratio | 1.36 ± 0.35 | 1.53 ± 0.44 | 0.142 |
| Columella height/alar width ratio | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.024 |
| Nasal surface area (mm2) | 29.42 ± 4.10 | 29.33 ± 4.21 | 0.943 |
| Nasal volume (mm3) | 10.4 ± 2.37 | 9.79 ± 2.03 | 0.358 |
| Measurements | Cleft Subjects (n = 18) | Normal Subjects (n = 27) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear (mm) | |||
| Nasal bridge length | 37.94 ± 3.00 | 40.15 ± 3.12 | 0.023 |
| Nasal height | 48.86 ± 3.87 | 47.49 ± 3.26 | 0.209 |
| Nasal protrusion | 18.73 ± 2.18 | 17.28 ± 1.46 | 0.010 |
| Alar width | 40.24 ± 2.80 | 37.35 ± 2.56 | 0.001 |
| Nasal tip projection | 17.82 ± 1.45 | 20.73 ± 1.94 | <0.001 |
| Tip/midline deviation | 1.87 ± 1.41 | 1.43 ± 1.00 | 0.227 |
| Columellar height | 8.56 ± 1.39 | 8.22 ± 1.64 | 0.474 |
| Dome height | 10.80 ± 1.57 | 9.69 ± 1.82 | 0.040 |
| Angular (°) | |||
| Nasal dorsum angle | 20.29 ± 2.98 | 20.69 ± 2.31 | 0.617 |
| Nasal tip angle | 114.84 ± 7.36 | 104.53 ± 4.73 | <0.001 |
| Columellar angle | 60.09 ± 10.13 | 70.79 ± 6.45 | <0.001 |
| Columellar-labial angle | 120.30 ± 11.19 | 101.46 ± 11.42 | <0.001 |
| Proportional | |||
| Nasal tip height ratio | 0.38 ± 0.08 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.004 |
| Nasal index | 83.16 ± 11.46 | 79.13 ± 9.03 | 0.195 |
| Alar width/intercanthal distance ratio | 1.15 ± 0.15 | 1.04 ± 0.10 | 0.013 |
| Alar width/mouth width ratio | 0.97 ± 0.06 | 0.81 ± 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Dome-to-columella ratio | 1.29 ± 0.26 | 1.25 ± 0.44 | 0.726 |
| Columella height/alar width ratio | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 0.600 |
| Nasal surface area (mm2) | 24.25 ± 3.25 | 22.68 ± 2.23 | 0.061 |
| Nasal volume (mm3) | 7.36 ± 0.93 | 6.45 ± 1.03 | 0.004 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, H.J.; Denadai, R.; Lo, L.-J. Long-Term Nasal Growth after Primary Rhinoplasty for Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity: A Three-Dimensional Photogrammetric Study with Comparative Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050602
Seo HJ, Denadai R, Lo L-J. Long-Term Nasal Growth after Primary Rhinoplasty for Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity: A Three-Dimensional Photogrammetric Study with Comparative Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(5):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050602
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Hyung Joon, Rafael Denadai, and Lun-Jou Lo. 2019. "Long-Term Nasal Growth after Primary Rhinoplasty for Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity: A Three-Dimensional Photogrammetric Study with Comparative Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 5: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050602
APA StyleSeo, H. J., Denadai, R., & Lo, L.-J. (2019). Long-Term Nasal Growth after Primary Rhinoplasty for Bilateral Cleft Lip Nose Deformity: A Three-Dimensional Photogrammetric Study with Comparative Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(5), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050602







