Preventive Effect of Cardiotrophin-1 Administration before DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Experimental Model and Study Protocol
- Colitis group (DSS; n = 10): Colitis was induced with 5% DSS (MW 36,000–50,000, MP Biomedical, Solon, OH, USA) in the drinking water through the experiment.
- Colitis + CT-1 treatment group (DSS + CT-1; n = 10): Mice received an i.v. dose of rat CT-1 (200 µg/kg) 2 h before and 2 and 4 days after starting DSS. Rat CT-1 was provided by DRO Biosystems (San Sebastian, Spain).
- Control group (Sham; n = 5): Mice received neither DSS nor CT-1.
2.4. Colitis Severity Quantification
2.5. Histological Studies
2.6. Western Blot (WB) Studies
2.7. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Studies
2.8. Measurement of Cytokine Plasma Levels
2.9. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
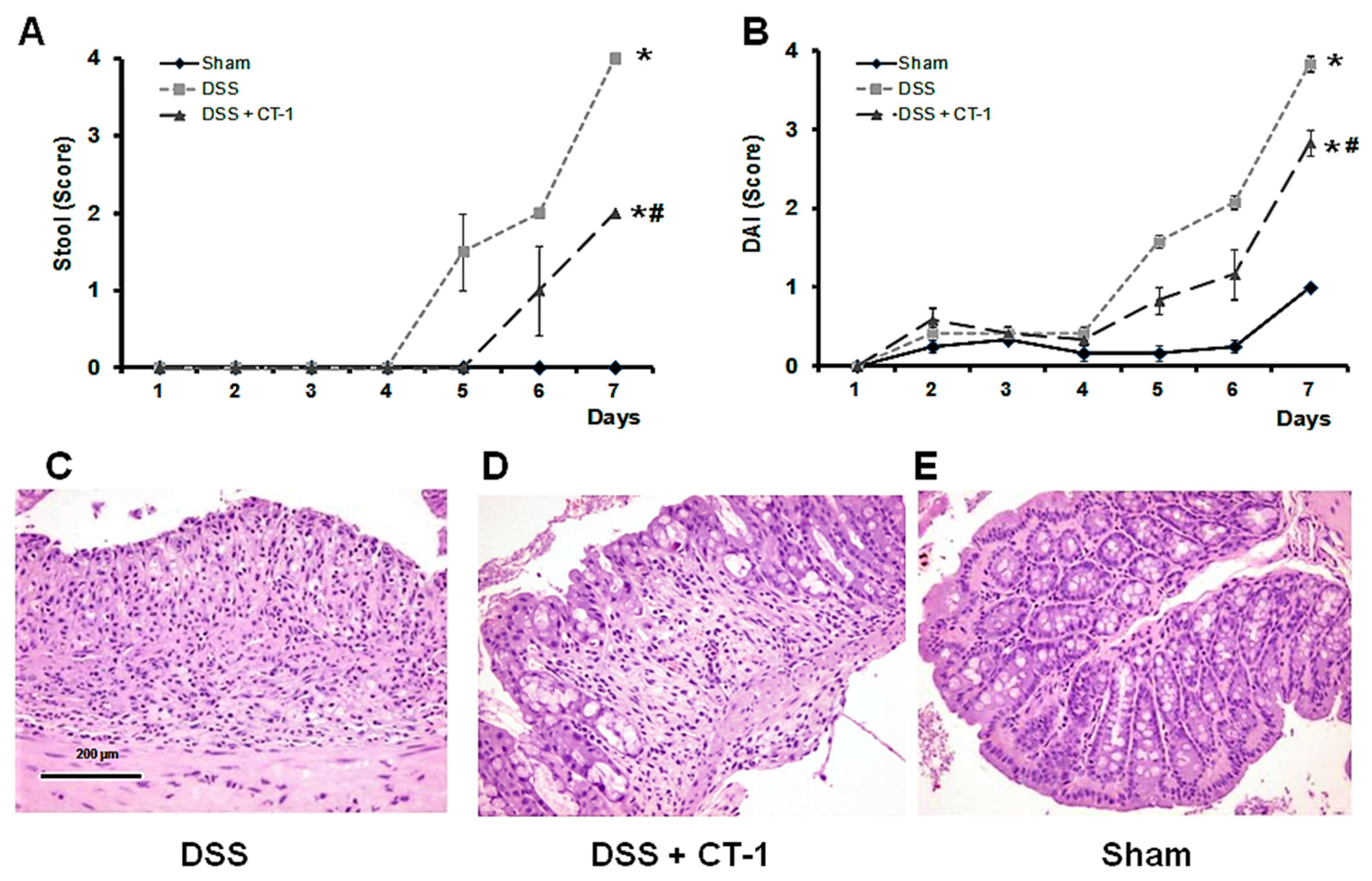
3.1. Evolution of Colitis
3.2. Histological Characterization
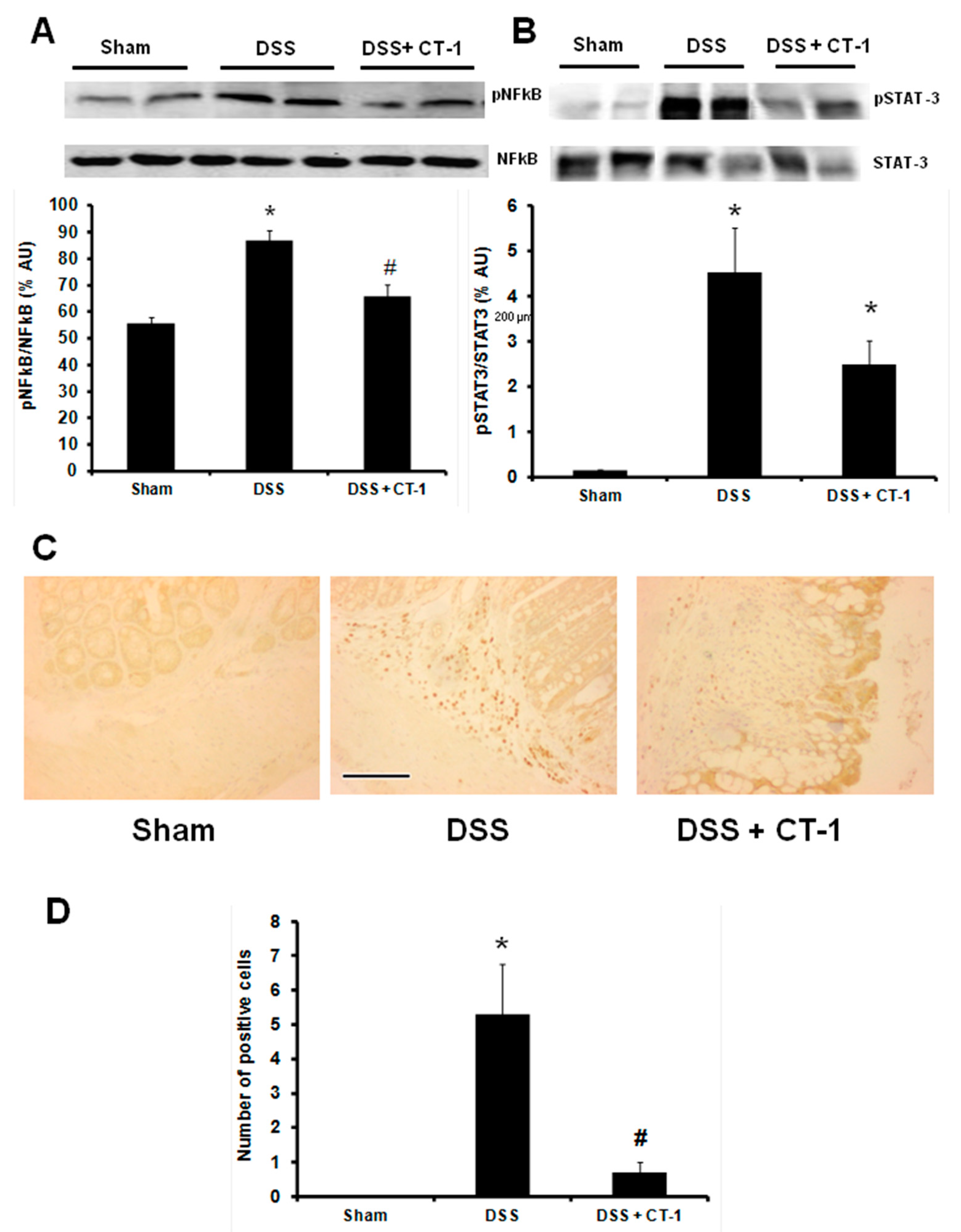
3.3. Evaluation of Colonic Inflammation
3.4. Apoptosis Evaluation
3.5. CT-1 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres, J.; Billioud, V.; Sachar, D.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.F. Ulcerative colitis as a progressive disease: The forgotten evidence. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoivik, M.L.; Moum, B.; Solberg, I.C.; Henriksen, M.; Cvancarova, M.; Bernklev, T.; IBSEN Group. Work disability in inflammatory bowel disease patients 10 years after disease onset: Results from the IBSEN Study. Gut 2013, 62, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burisch, J.; Jess, T.; Martinato, M.; Lakatos, P.L.; ECCO-EpiCom. The burden of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molodecky, N.A.; Soon, I.S.; Rabi, D.M.; Ghali, W.A.; Ferris, M.; Chernoff, G.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Barkema, H.W.; et al. Increasing incidence and prevalence of the inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematic review. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everhart, J.E.; Ruhl, C.E. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States part II: Lower gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.G.; Jess, T. The Changing Landscape of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: East Meets West. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal Bressenot, A.; Riddell, R.H.; Boulagnon-Rombi, C.; Reinisch, W.; Danese, S.; Schreiber, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. The histological assessment of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 42, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Bryant, R.V.; Costello, S.P. Uncovering the cause of ulcerative colitis. JGH Open 2019, 3, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, R.; Colombel, J.F.; Lissoos, T.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. A Treat-to-Target Update in Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 114, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, K.; Feuerstein, J.D. New developments in ulcerative colitis: Latest evidence on management, treatment, and maintenance. Drugs Context 2019, 8, 212572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Feuerstein, J.D.; Binion, D.G.; Tremaine, W.J. AGA technical review on the management of mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 769–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchman, D.S. Cardiotrophin-1: A novel cytokine and its effects in the heart and other tissues. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 85, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Nakajima, K.; Hibi, M. Signaling mechanisms through gp130: A model of the cytokine system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997, 8, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennica, D.; Wood, W.I.; Chien, K.R. Cardiotrophin-1: A multifunctional cytokine that signals via LIF receptor-gp 130 dependent pathways. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996, 7, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, M.; Beraza, N.; Lasarte, J.J.; Baixeras, E.; Alzuguren, P.; Bordet, T.; Prieto, J. Protection against liver damage by cardiotrophin-1: A hepatocyte survival factor up-regulated in the regenerating liver in rats. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, N.; Díez, J.; Fortuño, M.A. Characterization of the protective effects of cardiotrophin-1 against non-ischemic death stimuli in adult cardiomyocytes. Cytokine 2005, 30, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Sola, A.; Moore, J.; Wen, T. Caspase inhibition by cardiotrophin-1 prevents neuronal death in vivo and in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruixing, Y.; Jinzhen, W.; Dezhai, Y.; Jiaquan, L. Cardioprotective role of cardiotrophin-1 gene transfer in a murine model of myocardial infarction. Growth Factors 2007, 25, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Brar, B.K.; Cai, Q.; Stephanou, A.; O’Leary, R.M.; Pennica, D.; Yellon, D.M.; Latchman, D.S. Cardiotrophin-1 (CT-1) can protect the adult heart from injury when added both prior to ischaemia and at reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 53, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez, M.; Berasain, C.; Martinez-Ansó, E.; Bustos, M.; Fortes, P.; Pennica, D.; Avila, M.A.; Prieto, J. Cardiotrophin-1 defends the liver against ischemia-reperfusion injury and mediates the protective effect of ischemic preconditioning. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 2809–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuñon, M.J.; San Miguel, B.; Crespo, I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Larrea, E.; Alvarez, M.; González, I.; Bustos, M.; González-Gallego, J.; Prieto, J. Cardiotrophin-1 promotes a high survival rate in rabbits with lethal fulminant hepatitis of viral origin. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 13124–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiros, Y.; Sánchez-González, P.D.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Morales, A.I.; López-Novoa, J.M. Cardiotrophin-1 administration prevents the renal toxicity of iodinated contrast media in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 132, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cenador, M.B.; Lorenzo-Gomez, M.F.; Herrero-Payo, J.J.; Ruiz, J.; Perez de Obanos, M.P.; Pascual, J.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Garcia-Criado, F.J. Cardiotrophin-1 administration protects from ischemia-reperfusion renal injury and inflammation. Transplantation 2013, 96, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Vicente, V.; Sánchez-Garrido, A.I.; Blanco-Gozalo, V.; Arévalo, M.; García-Sánchez, E.; López-Montañés, D.; Quiros, Y.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Rodríguez-Pérez, A.; López-Novoa, J.M. Cardiotrophin-1 attenuates experimental colitis in mice. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elson, C.O.; Sartor, R.B.; Tennyson, G.S.; Riddell, R.H. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1995, 109, 1344–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, S.; Neufert, C.; Weigmann, B.; Neurath, M.F. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, L.R.; Wang, J.; Le, M. In vitro and in vivo effects of gliotoxin, a fungal metabolite: Efficacy against dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, M.T.; Fuentes-Calvo, I.; Arévalo, M.; Heredia, F.; Santos, E.; Martínez-Salgado, C.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; Nieto, M.A.; López-Novoa, J.M. Deletion of H-Ras decreases renal fibrosis and myofibroblast activation following ureteral obstruction in mice. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Bernstein, C.N.; Khan, K.J.; Abreu, M.T.; Marshall, J.K.; Talley, N.J.; Moayyedi, P. Glucocorticosteroid therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, A.; Patton, P.H.; Chande, N.; McDonald, J.W.; MacDonald, J.K. Azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine for maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, CD000478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, O.H.; Ainsworth, M.A. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for inflammatory bowel disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, O.H. New strategies for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Med. 2014, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fréling, E.; Baumann, C.; Cuny, J.F.; Bigard, M.A.; Schmutz, J.L.; Barbaud, A.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Cumulative incidence of, risk factors for, and outcome of dermatological complications of anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: A 14-year experience. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1186–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rencz, F.; Péntek, M.; Bortlik, M.; Zagorowicz, E.; Hlavaty, T.; Śliwczyński, A.; Diculescu, M.M.; Kupcinskas, L.; Gecse, K.B.; Gulácsi, L.; et al. Biological therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases: Access in Central and Eastern Europe. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, D.N.; Van Assche, G.; Maenhout, B.; Arts, J.; Ferrante, M.; Vermeire, S.; Rutgeerts, P. Incidence of colectomy during long-term follow-up after cyclosporine-induced remission of severe ulcerative colitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombel, J.F.; Sands, B.E.; Rutgeerts, P.; Sandborn, W.; Danese, S.; D’Haens, G.; Panaccione, R.; Loftus, E.V., Jr.; Sankoh, S.; Fox, I.; et al. The safety of vedolizumab for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut 2017, 66, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moresi, V.; Adamo, S.; Berghella, L. The JAK/STAT Pathway in Skeletal Muscle Pathophysiology. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Fiorino, G.; Furfaro, F.; Allocca, M.; Danese, S. Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: Developments from phase I and phase II clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Su, C.; Sands, B.E.; D’Haens, G.R.; Vermeire, S.; Schreiber, S.; Danese, S.; Feagan, B.G.; Reinisch, W.; Niezychowski, W.; et al. Tofacitinib as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1723–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, F. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental and clinical studies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, E.J.; Shames, B.D.; Pennica, D.; O’leary, R.M.; Bensard, D.D.; Cain, B.S.; McIntyre, R.C., Jr. Cardiotrophin-1 attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. J. Surg. Res. 1999, 84, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benigni, F.; Sacco, S.; Pennica, D.; Ghezzi, P. Cardiotrophin-1 inhibits tumor necrosis factor production in the heart and serum of lipopolysaccharide-treated mice and in vitro in mouse blood cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Melero, P.; Luque, A.; Machuca, M.M.; Pérez de Obanos, M.P.; Navarrete, R.; Rodríguez-García, I.C.; Briceño, J.; Iñiguez, M.; Ruiz, J.; Prieto, J.; et al. Cardiotrophin-1 reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury during liver transplant. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 181, e83–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, B.K.; Stephanou, A.; Liao, Z.; O’Leary, R.M.; Pennica, D.; Yellon, D.M.; Latchman, D.S. Cardiotrophin-1 can protect cardiac myocytes from injury when added both prior to simulated ischaemia and at reoxygenation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 51, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanou, A.; Brar, B.; Heads, R.; Knight, R.D.; Marber, M.S.; Pennica, D.; Latchman, D.S. Cardiotrophin-1 induces heat shock protein accumulation in cultured cardiac cells and protects them from stressful stimuli. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1998, 30, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herencia, C.; Almadén, Y.; Ferrín, G.; Martínez-Romero, R.; de la Mata, M.; Ciria, R.; Briceño, F.J.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R. Cardiotrophin-1 decreases liver apoptosis through calpastatin induction. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 193, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués, J.M.; Belza, I.; Holtmann, B.; Pennica, D.; Prieto, J.; Bustos, M. Cardiotrophin-1 is an essential factor in the natural defense of the liver against apoptosis. Hepatology 2007, 45, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-González, M.; Jaques, F.; Rodríguez, S.; Porciuncula, A.; Principe, R.M.; Abizanda, G.; Iñiguez, M.; Escalada, J.; Salvador, J.; Prósper, F.; et al. Cardiotrophin 1 protects beta cells from apoptosis and prevents streptozotocin-induced diabetes in a mouse model. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, G.; Hamanoue, M.; Enokido, Y.; Wyatt, S.; Pennica, D.; Jaffray, E.; Hay, R.T.; Davies, A.M. Cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation promotes the survival of developing neurons. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, T.; Agilli, M. Fecal calprotectin evaluation in patients with ulcerative colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1109–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgut, B.J.; Lemberg, D.A.; Day, A.S.; Leach, S.T. The Value of Fecal Markers in Predicting Relapse in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 5, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T.; Fong, C. The resolution of inflammation: Anti-inflammatory roles for NF-kappaB. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Andres, N.; Rousseau, A.; Akhtar, R.; Calvier, L.; Iñigo, C.; Labat, C.; Zhao, X.; Cruickshank, K.; Díez, J.; Zannad, F.; et al. Cardiotrophin 1 is involved in cardiac, vascular, and renal fibrosis and dysfunction. Hypertension 2012, 60, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Cenador, M.B.; Lopez-Novoa, J.M.; Diez, J.; García-Criado, J.M. Effects and mechanism of organ protection by cardiotrophin-1. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Western Blot | ||
|---|---|---|
| Primary Antibody | Catalog Number | Supplier |
| iNOS | #2977 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| CT-1 | MAB438 | R&D Systems |
| NF-kB | #3034 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| pNF-kB | #3031 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| STAT3 | #9132 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| pSTAT3 | #9145 | Cell Signaling Technology |
| Cleaved caspase 3 | #9661 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| Secondary Antibody | Catalog Number | Supplier |
| Anti-rabbit IgG-HRP | 4052-05 | Southern Biotech. |
| Anti-IgG rat IgG-HRP | sc-2006 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology |
| Anti-mouse IgG-HRP | 1034-05 | Southern Biotech. |
| Immunohistochemistry | Catalog Number | Supplier |
| CD68 | M0814 | Dako Diagnósticos, Spain |
| iNOS | sc-651 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology |
| Cleaved Caspase 3 | #9661 | Cell Signaling Technology |
| Suppliers | ||
| Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, Massachusetts, USA | ||
| R&D Systems, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA | ||
| Santa Cruz Biotechnology, CA, USA | ||
| Southern Biotech., Birmingham, USA | ||
| Dako Diagnósticos, Barcelona, Spain | ||
| Gen | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon (pb) | Tm (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | Fw | AGCACAGAAAGCATGATCCG | 212 | 60 |
| Rv | CTGATGAGAGGGAGGCCATT | |||
| IFN-γ | Fw | TACACACTGCATCTTGGCTTTG | 128 | 57.5 |
| Rv | CTTCCACATCTATGCCACTTGAG | |||
| IL-10 | Fw | ATGCTGCCTGCTCTTACTGACTG | 216 | 58.8 |
| Rv | CCCAAGTAACCCTTAAAGTCCTGC | |||
| IL-17 | Fw | GCTCCAGAAGGCCCTCAGA | 142 | 58.8 |
| Rv | AGCTTTCCCTCCGCATTGA | |||
| GAPDH | Fw | GTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | 153 | 55.9 |
| Rv | GAATTTGCCGTGAGTGGAGT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Garrido, A.I.; Prieto-Vicente, V.; Blanco-Gozalo, V.; Arévalo, M.; Quiros, Y.; López-Montañés, D.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Rodríguez-Pérez, A.; López-Novoa, J.M. Preventive Effect of Cardiotrophin-1 Administration before DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122086
Sánchez-Garrido AI, Prieto-Vicente V, Blanco-Gozalo V, Arévalo M, Quiros Y, López-Montañés D, López-Hernández FJ, Rodríguez-Pérez A, López-Novoa JM. Preventive Effect of Cardiotrophin-1 Administration before DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122086
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Garrido, Ana I., Vanessa Prieto-Vicente, Víctor Blanco-Gozalo, Miguel Arévalo, Yaremi Quiros, Daniel López-Montañés, Francisco J. López-Hernández, Antonio Rodríguez-Pérez, and José M. López-Novoa. 2019. "Preventive Effect of Cardiotrophin-1 Administration before DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122086
APA StyleSánchez-Garrido, A. I., Prieto-Vicente, V., Blanco-Gozalo, V., Arévalo, M., Quiros, Y., López-Montañés, D., López-Hernández, F. J., Rodríguez-Pérez, A., & López-Novoa, J. M. (2019). Preventive Effect of Cardiotrophin-1 Administration before DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(12), 2086. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122086





