Nasopharyngeal Lymphoma: A 22-Year Review of 35 Cases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. ISH of EBERs
2.3. Statistical Analysis
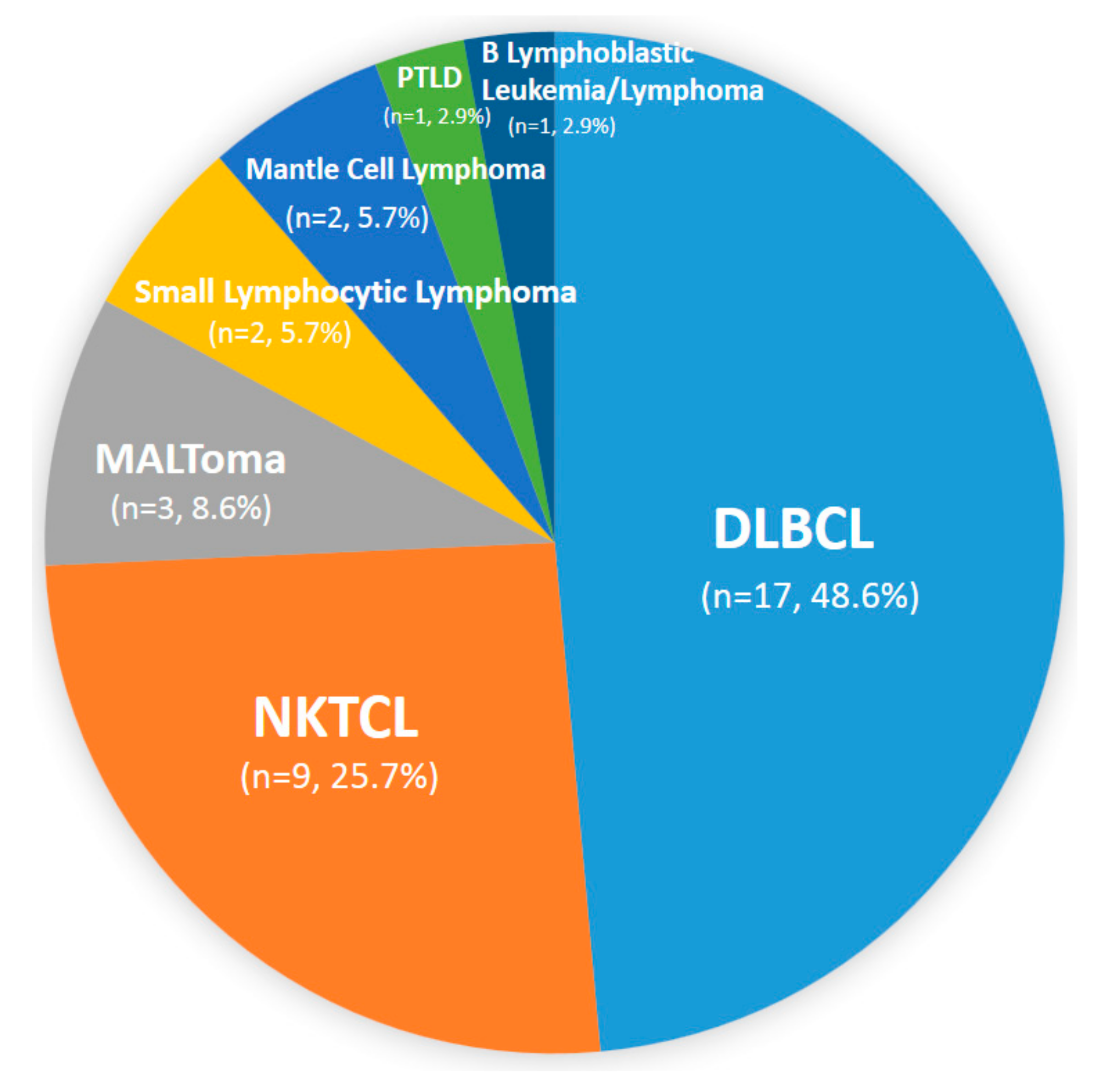
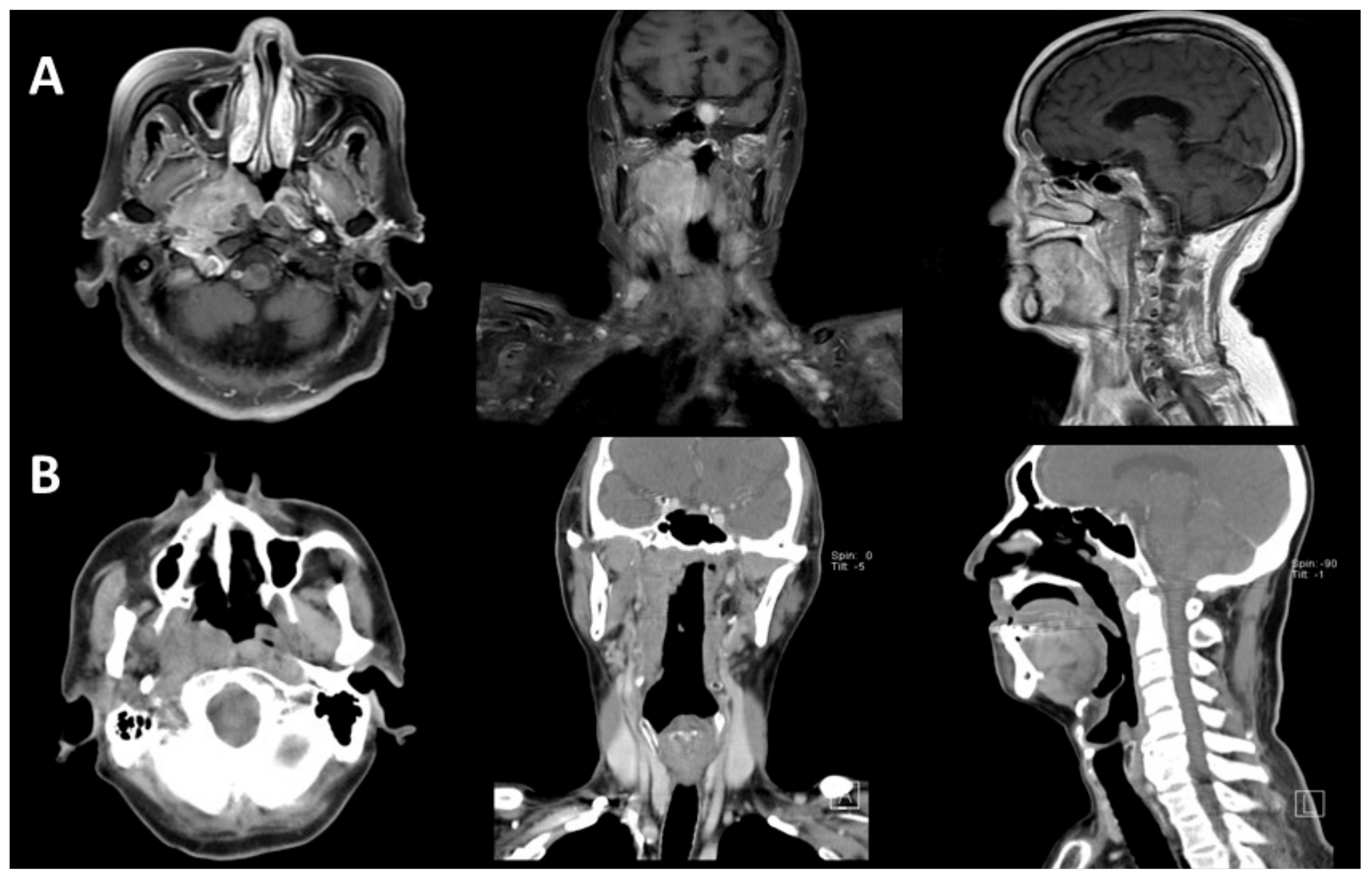
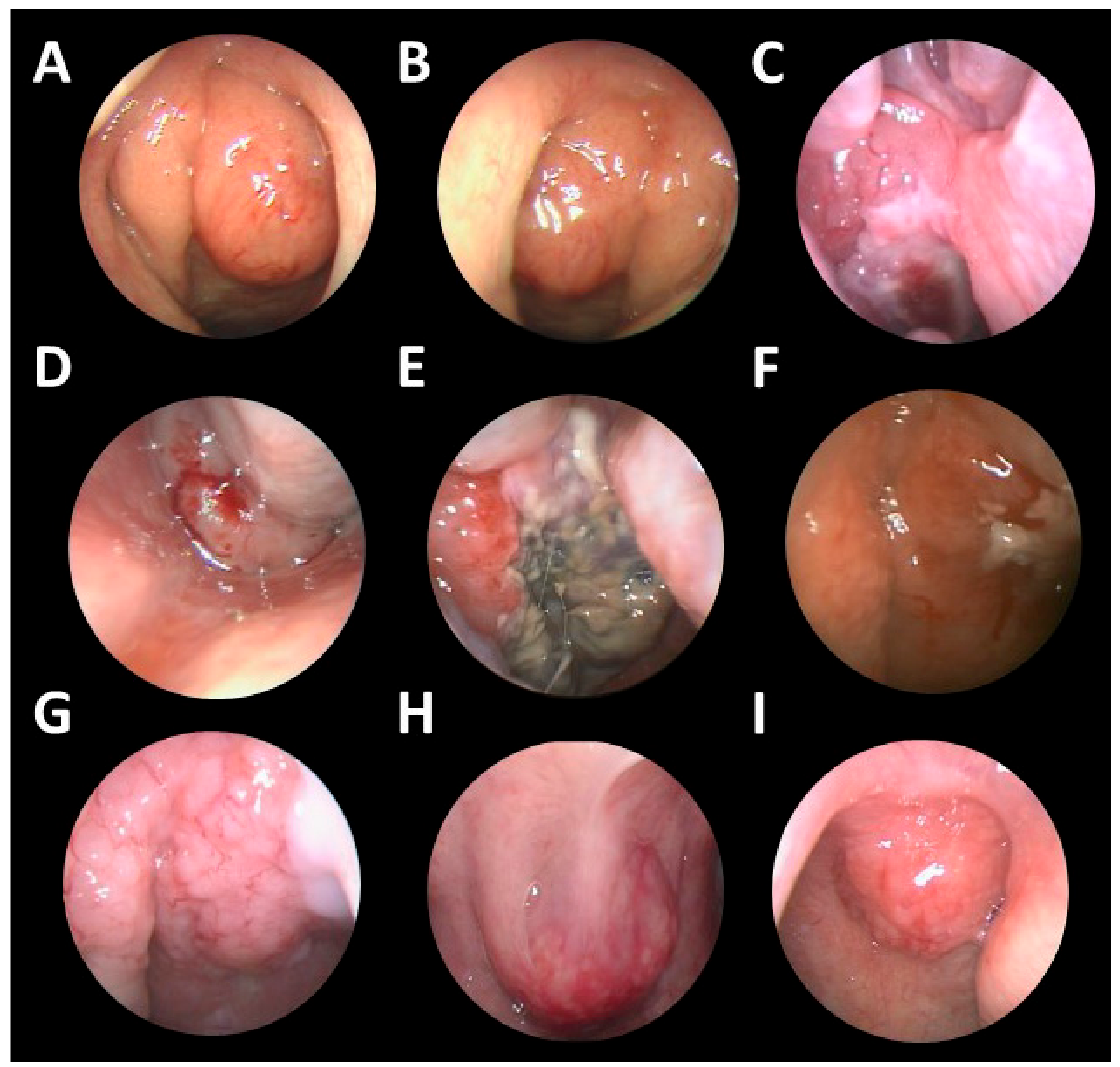
3. Results
3.1. Patients
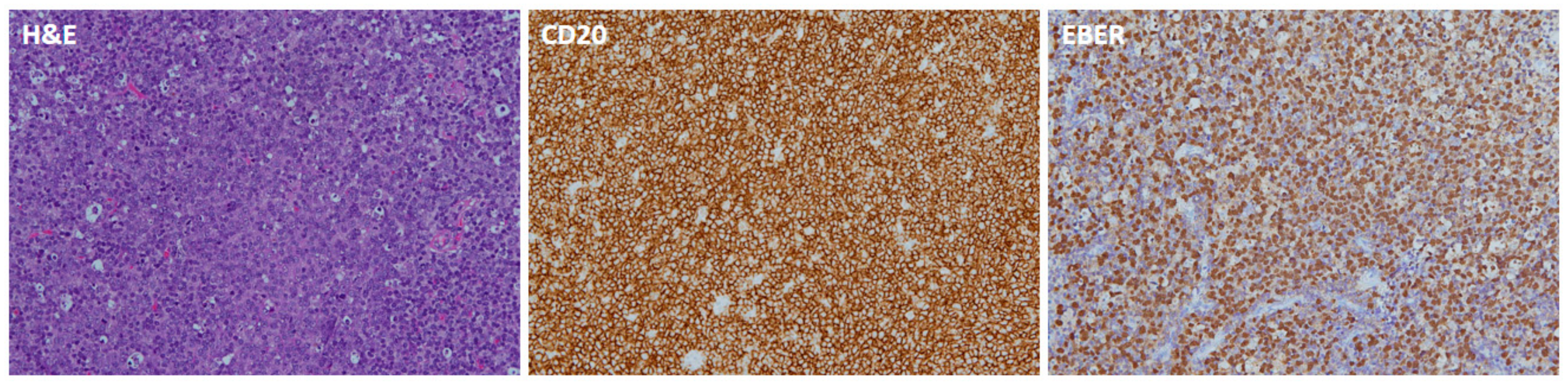
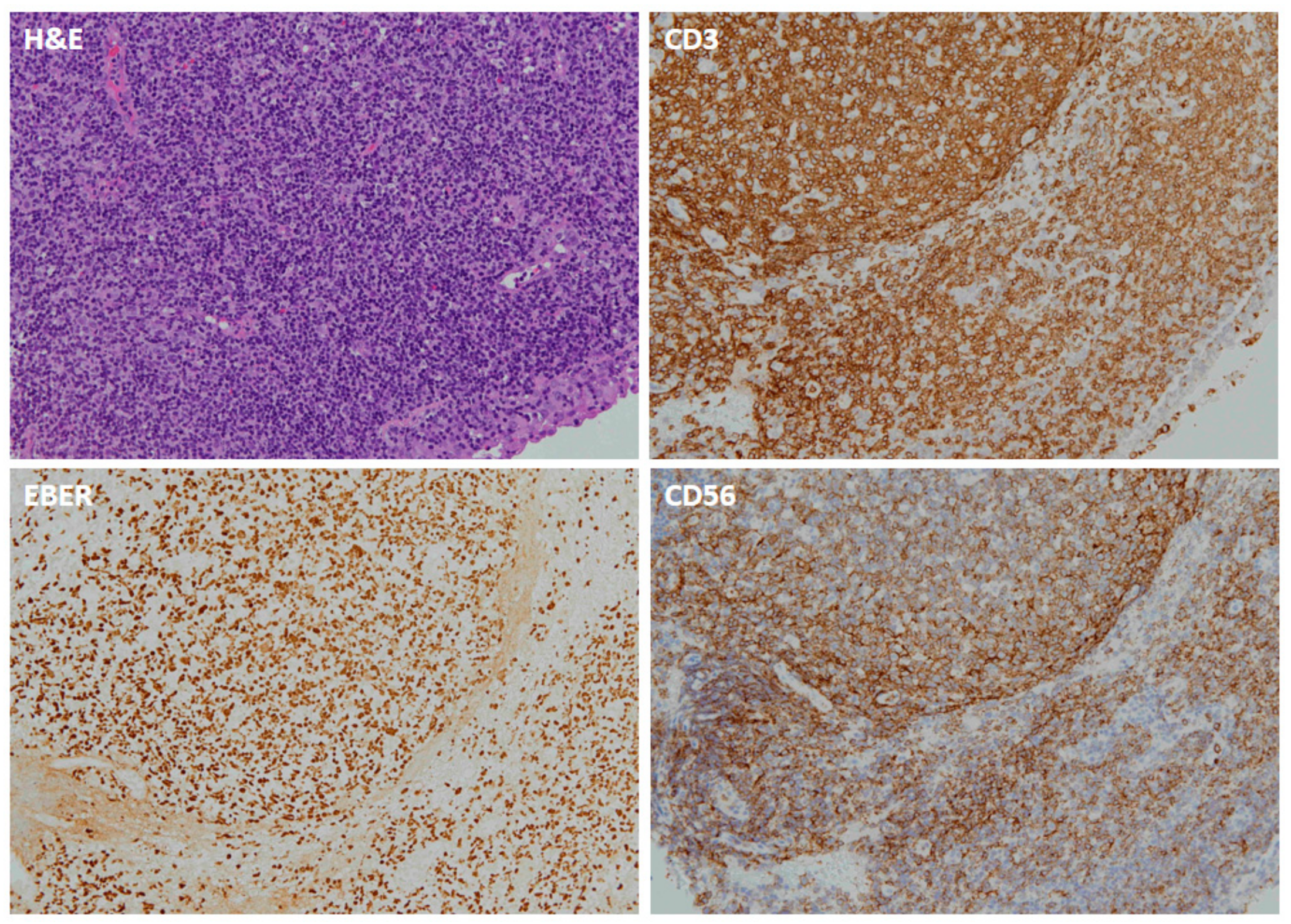
3.2. EBERs
3.3. Treatment Modality
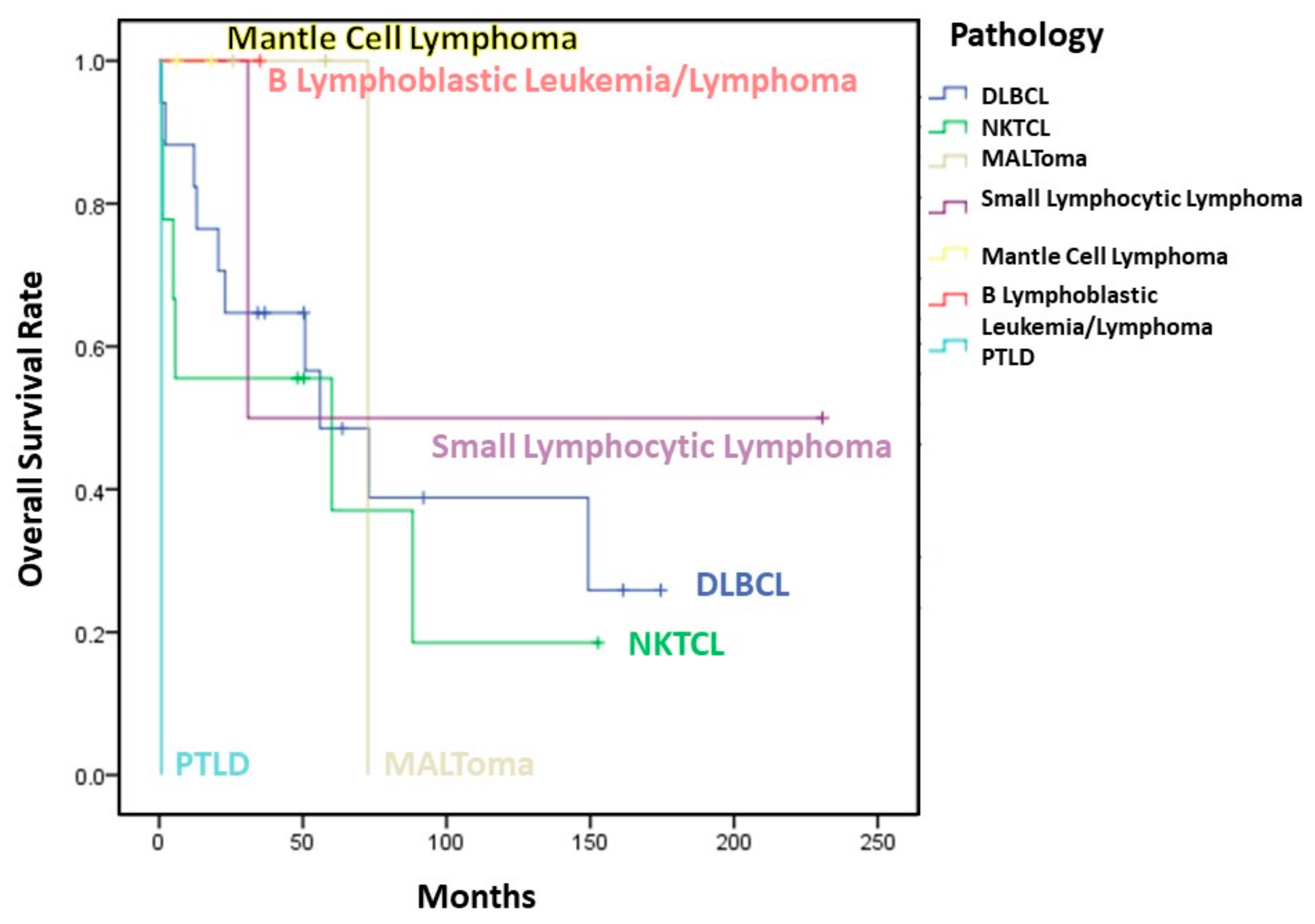
3.4. Survival
3.5. Recurrence
3.6. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.I.; Suen, J.J.; Hui, P.; Tong, M.; Li, W.; Yau, S.H. Primary nasal and nasopharyngeal lymphomas: A comparative study of clinical presentation and treatment outcome. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 1999, 11, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskar, S.; Muckaden, M.A.; Bahl, G.; de Sandeep, R.N.; Gupta, S.; Bakshi, A.; Prabhash, K.; Maru, D.; Gujral, S.; Parikh, P.; et al. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the nasopharynx: Prognostic factors and outcome of 113 Indian patients. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitarnun, W.; Suwiwat, S.; Pradutkanchana, J. Epstein-Barr virus-associated extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the sinonasal tract and nasopharynx in Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2006, 7, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xie, F.Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, H.X.; Xia, Y.F.; Lin, T.Y.; Lu, T.X. Prognosis and treatment strategies of primary B-cell and NK/T-cell nasopharyngeal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma at early stage. Ai Zheng 2006, 25, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Allam, W.; Ismaili, N.; Elmajjaoui, S.; Elgueddari, B.K.; Ismaili, M.; Errihani, H. Primary nasopharyngeal non-Hodgkin lymphomas: A retrospective review of 26 Moroccan patients. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord. 2009, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.Y.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, W.H.; Jin, J.; Wang, S.L.; Liu, Y.P.; Song, Y.W.; Fang, H.; Ren, H.; Liu, Q.F.; et al. Clinical disparity and favorable prognoses for patients with Waldeyer ring extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 37, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owosho, A.A.; Gooden, C.E.; McBee, A.G. Hodgkin lymphoma of the nasopharynx: Case report with review of the literature. Head Neck Pathol. 2015, 9, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.Y.; Kuan, E.C.; Alonso, J.E.; Badran, K.W.; St John, M.A. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal lymphoma in the United States: A population-based analysis of 1119 cases. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Yue, B. Clinical characteristics and prognostic significance of EBER positivity in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Diamond, H.D.; Jaslowitz, B.; Craver, L.F. Lymphosarcoma: A review of 1269 cases. Medicine 1961, 40, 31–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, R.T.; Burke, J.S.; Glatstein, E.; Kaplan, H.S. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Involvement of Waldeyer’s ring. Cancer 1978, 42, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, S.H.; Kapadia, S.B. Primary lymphoma of Waldeyer’s ring: Clinicopathologic study of 68 cases. Cancer 1985, 56, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Epstein-Barr virus: Exploiting the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 1, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruhne, B.; Sompallae, R.; Masucci, M.G. Three Epstein-Barr virus latency proteins independently promote genomic instability by inducing DNA damage, inhibiting DNA repair and inactivating cell cycle checkpoints. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3997–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesri, E.A.; Feitelson, M.A.; Munger, K. Human viral oncogenesis: A cancer hallmarks analysis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A.B.; Bell, A.I. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Ko, Y.H.; Han, A.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, I.G.; Park, Y.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Jung, C.W.; et al. The impact of Epstein-Barr virus status on clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Nakamura, N.; Kojima, M.; Ohmachi, K.; Carreras, J.; Kikuti, Y.Y.; Numata, H.; Ohgiya, D.; Tazume, K.; Amaki, J.; et al. Clinical outcome of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly in the rituximab era. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, W.S. Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly: A concise review and update. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, C.Y.; Papathomas, T.G.; Medeiros, L.J.; Young, K.H. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Blood 2013, 122, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, C.Y.; Li, L.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybkaer, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of epstein-barr virus infection in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, Y.W.; Han, J.H.; Yoon, D.H.; Suh, C.; Huh, J. Epstein-Barr virus positivity is associated with angiogenesis in, and poorer survival of, patients receiving standard treatment for classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, P.P.; Kaplan, H.S.; Musshoff, K.; Smithers, D.W.; Tubiana, M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin’s Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res. 1971, 31, 1860–1861. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, P. Staging and classification of lymphoma. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2005, 35, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Crouch, S.; Lax, S.; Li, J.; Painter, D.; Howell, D.; Patmore, R.; Jack, A.; Roman, E. Lymphoma incidence, survival and prevalence 2004–2014: Sub-type analyses from the UK’s Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yang, Q.; Lu, Z.; He, M.; Gao, L.; Zhu, M.; Sun, L.; Wei, L.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; et al. Distribution of lymphoid neoplasms in China: Analysis of 4638 cases according to the World Health Organization classification. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.J.; Gascoyne, R.D. Classification of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 2008, 22, 781–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, L.Y.; Liang, D.C. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas in Asia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am. 1991, 5, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H.; Kim, C.W.; Park, C.S.; Jang, H.K.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.H.; Ree, H.J.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, S.W.; Huh, J.R. REAL classification of malignant lymphomas in the Republic of Korea: Incidence of recently recognized entities and changes in clinicopathologic features. Hematolymphoreticular Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists. Revised European-American lymphoma. Cancer 1998, 83, 806–812. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.L.; Zhou, M.H.; Lu, X.Y.; Dai, Y.R.; Wu, W.X. Nasopharyngeal and nasal malignant lymphoma: A clinicopathological study of 54 cases. Histopathology 1992, 20, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulfrank, D.; Speelman, T.; Pauwels, C.; Roels, H.; De Schryver, A. Extranodal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the head and neck. Radiother. Oncol. 1987, 8, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, B.J.; Kershaw, J.B. Hodgkin’s disease of the nasopharynx. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1987, 101, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, A.; Berg, R. Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the head and neck. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, T.O.; Buniel, M.C.; Mace, J.C.; El Rassi, E.; Smith, T.L. Lymphoma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: A case series. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2016, 30, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Xie, C.M.; Mo, Y.X.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Huang, Z.L.; Geng, Z.J.; Zheng, L.; Lv, Y.C.; Wu, P.H. Magnetic resonance imaging features of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Are there differences? Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Promotion Administration. Taiwan Cancer Registry Database 2016. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=269&pid=10227 (accessed on 1 April 2019).
- Yamaguchi, M.; Miyazaki, K. Current treatment approaches for NK/T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2017, 57, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Wang, C.W.; Hong, R.L.; Tsai, C.L.; Yao, M.; Tang, J.L.; Lin, C.W.; Cheng, A.L.; Kuo, S.H. Treatment outcomes of and prognostic factors for definitive radiotherapy with and without chemotherapy for Stage I/II nasal extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. J. Radiat. Res. 2017, 58, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.P.; Dahlberg, S.; Cassady, J.R.; Adelstein, D.J.; Spier, C.M.; Grogan, T.M.; LeBlanc, M.; Carlin, S.; Chase, E.; Fisher, R.I. Chemotherapy alone compared with chemotherapy plus radiotherapy for localized intermediate- and high-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviles, A.; Delgado, S.; Ruiz, H.; de la Torre, A.; Guzman, R.; Talavera, A. Treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of Waldeyer’s ring: Radiotherapy versus chemotherapy versus combined therapy. Eur. J. Cancer. B Oral Oncol. 1996, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.W.; Go, S.I.; Kim, S.H.; Hong, J.; Kim, Y.R.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Do, Y.R.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.I.; et al. Clinical outcome and prognosis of patients with primary sinonasal tract diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab-cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone chemotherapy: A study by the Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, J.Z.; Lan, S.M.; Wu, J.X.; Wu, T.; Zhu, S.Y.; Qian, L.T.; Hou, X.R.; Zhang, F.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; et al. Association of improved locoregional control with prolonged survival in early-stage extranodal nasal-type natural killer/t-cell lymphoma. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.J.; Xu, L.M.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Wu, J.X.; Wang, W.; Wu, T.; Lu, B.; et al. Risk-adapted therapy for early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma: Analysis from a multicenter study. Blood 2015, 126, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R. Pathogenesis and treatment of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2014, 51, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, E.; Au-Yeung, R.; Kwong, Y.L. Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of natural killer/T-cell lymphomas. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundo, L.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Picciolini, M.; Lo Bello, G.; Gazaneo, S.; Del Porro, L.; Lazzi, S.; Navari, M.; Onyango, N.; Granai, M.; et al. Unveiling another missing piece in ebv-driven lymphomagenesis: EBV-Encoded microRNAs expression in EBER-negative burkitt lymphoma cases. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundo, L.; Ambrosio, M.; Del Porro, L.; Granai, M.; Mancini, V.; Schiavoni, G.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Falini, B.; Lazzi, S.; Tiacci, E. EBV leaves its mark: New evidence of hypothesis in b-cell lymphomas from non-conventional methods. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 529–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; Campo, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Smeland, E.B.; Giltnane, J.M.; et al. The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, M.A.; Ross, K.N.; Tamayo, P.; Weng, A.P.; Kutok, J.L.; Aguiar, R.C.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Angelo, M.; Reich, M.; Pinkus, G.S.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma outcome prediction by gene-expression profiling and supervised machine learning. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Czuczman, M.S. ABC, GCB, and double-hit diffuse large b-cell lymphoma: Does subtype make a difference in therapy selection? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case Number (n = 35) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | 17–88 (mean 59.57 ± 18.84) | |
| Sex | M/F = 20/15 | |
| Symptoms | ||
| Nasal obstruction | 10 (28.6%) | |
| Epistaxis | 9 (25.7%) | |
| Neck mass | 8 (22.9%) | |
| Purulent Rhinorrhea | 6 (17.1%) | |
| Headache | 5 (14.3%) | |
| B symptoms | 5 (14.3%) | |
| Symptom Duration | 0.5–12 (mean 2.61 ± 2.97) | |
| Location of Disease | ||
| NP only | 22 (62.9%) | |
| NP + neck/distant LN * | 10 (28.6%) | |
| NP + adjacent organ # | 3 (8.6%) | |
| Comorbidity | ||
| HTN | 10 (28.6%) | |
| DM | 6 (17.1%) | |
| CAD | 4 (11.4%) | |
| Lab | ||
| WBC | 2400–167800 (mean 12992) | |
| LDH | 106–1702 (mean 337.7) | |
| EBER | ||
| Positive | 13 (37.1%) | |
| Negative | 19 (54.3%) | |
| NA | 3 (8.6%) | |
| Stage (Ann Arbor) | ||
| I | 12 (34.3%) | |
| II | 15 (42.9%) | |
| IV | 8 (22.9%) | |
| Treatment | ||
| CT | 20 (57.1%) | |
| RT | 1 (2.9%) | |
| CT+RT | 6 (17.1%) | |
| CT+PBSCT | 5 (14.3%) | |
| CT+RT+PBSCT | 2 (5.7%) | |
| No treatment | 1 (2.9%) | |
| Recurrence | 8 (22.9%) | |
| Dead | 19 (54.3%) | |
| DLBCL(n = 17) | NKTCL(n = 9) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | No (%) | No (%) | P value |
| Sex | 0.683 | ||
| male | 9 (52.90%) | 6 (66.70%) | |
| female | 8 (47.10%) | 3 (33.30%) | |
| Age | 61.59+/-22.49 (17-88) | 59.44+/-17.27 (38-81) | 0.806 |
| Duration(months) | 1.53+/-0.86 (0.5-4) | 4.33+/-3.94 (1-12) | 0.009 |
| Stage | 0.324 | ||
| I | 4 (23.50%) | 5 (55.60%) | |
| II | 8 (47.10%) | 3 (33.30%) | |
| IV | 5 (29.40%) | 1 (11.10%) | |
| Location of Disease | 0.822 | ||
| NP only | 11 (64.70%) | 7 (77.80%) | |
| NP+ neck/distant LN * | 4 (23.50%) | 1 (11.10%) | |
| NP+ adjacent organ # | 2 (11.80%) | 1 (11.10%) | |
| EBER † | 0.005 | ||
| Positive | 5 (31.25%) | 7 (100%)† | |
| Negative | 11 (68.75%) | 0 (0%) | |
| B symptoms | 1 (5.90%) | 2 (22.2%) | 0.268 |
| Cervical Node Involvement | 4 (23.50%) | 0 (0%) | 0.263 |
| Treatment | 0.394 | ||
| CT only | 12 (75%) | 5 (55.60%) | |
| CT+RT | 4 (25%) | 4 (44.40%) | |
| Recurrence * | 4 (23.53%) | 1 (11.10%) | 0.628 |
| Dead | 10 (58.82%) | 6 (66.70%) | 1 |
| Overall survival | 25.90% | 16.10% | 0.515 |
| 3-year | 64.70% | 55.60% | 0.505 |
| 5-year | 48.50% | 55.60% | 0.803 |
| 10-year | 38.80% | 18.50% | 0.417 |
| Year | Author | Country | No. | Age | Sex (M/F) | Tumor Pathology | EBER (+) | Treatment | Survival (OS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLBCL | NKTCL | Other | CT | RT | CT + RT | ||||||||
| 1999 | Lei [2] | China | 19 | 51 | 15/4 | 11(57.9%) | 5(26.3%) | 3(15.8%) | NA | 6(32%) | 2(11%) | 11(58%) | 5-Y OS:82% 5-Y DFS:76% |
| 2006 | Laskar [3] | India | 113 | 40 | 79/34 | 94(83.2%) | 0 T-cell | 19(16.8%) | NA | 25(22%) | 0(0) | 86(76%) | 5-Y OS:57.9% 5-Y DFS:55.8% 2 expired before treatment |
| 2006 | Zou [5] | China | 80 | NA | NA | 48(60%) B-cell | 32(40%) | 0 | NA | 31(38.8%) | 7(8.8%) | 42(84%) | 5-Y OS B-cell origin: 69.5% NKTCL: 35.5% 5-Yprogression-free survival: B-cell origin: 53.3% NKTCL: 28.9% |
| 2006 | Mitarnun [4] | Thailand | 42 | 57.2 | 24/18 | 35(83.3%) | 3(7.1%) | 4(9.5%) | 9/42 (21.4%) | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| 2009 | Allam [6] | Morroco | 26 | 52.7 | NA | 13(50%) | 4(15.4%) T cell | 9(34.6%) | NA | 27% | 0(0) | 73% | 1-Y OS:87% 1-Y DFS: 71% DLBCL:2-Y OS:75% |
| 2014 | Wu [7] | China | 61 | 49 all WR | NA | 32(52.5%) | 29(47.5%) | 0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | WR-NKTCL 5-Y OS:68% WR-DLBCL 5-Y OS: 74% |
| 2017 | Han [9] | USA | 1119 | 59.3 | 658/461 | 867(77.5%) B-cell | 67(6.0%) | 185(16.5%) | NA | NA | 452(41.5%) | NA | 2-Y OS:70% 5-Y OS:57% 10-Y OS:45% 2-Y DSS:77% 5-Y DSS:68% 10-Y DSS:62% |
| 2019 | Hsueh | Taiwan | 35 | 59.6 | 20/15 | 17(48.6%) | 9(25.7%) | 9(25.7%) | 13/32 (37.1%) | 25(71.4%) | 1(2.9%) | 8(22.9%) | DLBCL: 3-Y OS:64.7% 5-Y OS:48.5% 10-Y OS:38.8% NKTCL: 3-Y OS:55.6% 5-Y OS:55.6% 10-Y OS:18.5% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsueh, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-F.; Gau, J.-P.; Kuan, E.C.; Ho, C.-Y.; Chiou, T.-J.; Hsiao, L.-T.; Lin, T.-A.; Lan, M.-Y. Nasopharyngeal Lymphoma: A 22-Year Review of 35 Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101604
Hsueh C-Y, Yang C-F, Gau J-P, Kuan EC, Ho C-Y, Chiou T-J, Hsiao L-T, Lin T-A, Lan M-Y. Nasopharyngeal Lymphoma: A 22-Year Review of 35 Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(10):1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101604
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsueh, Chien-Yu, Ching-Fen Yang, Jyh-Pyng Gau, Edward C. Kuan, Ching-Yin Ho, Tzeon-Jye Chiou, Liang-Tsai Hsiao, Ting-An Lin, and Ming-Ying Lan. 2019. "Nasopharyngeal Lymphoma: A 22-Year Review of 35 Cases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 10: 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101604
APA StyleHsueh, C.-Y., Yang, C.-F., Gau, J.-P., Kuan, E. C., Ho, C.-Y., Chiou, T.-J., Hsiao, L.-T., Lin, T.-A., & Lan, M.-Y. (2019). Nasopharyngeal Lymphoma: A 22-Year Review of 35 Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(10), 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8101604






