Waist Circumference and All-Cause Mortality Independent of Body Mass Index in Korean Population from the National Health Insurance Health Checkup 2009–2015
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. The NHIS Database and NHIS Health Checkup Data
Subjects
2.2. Definition of Obesity and Abdominal Obesity
2.3. General Health Behavior and Socio-Demographic Variables
2.4. All-Cause Mortality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; International Association for the Study of Obesity; Health Communications Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Executive Summary of the Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1855–1867. [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Mark, A.E. Elevated body mass index and mortality risk in the elderly. Obes. Rev. 2007, 8, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospective Studies Collaboration; Whitlock, G.; Lewington, S.; Sherliker, P.; Clarke, R.; Emberson, J.; Halsey, J.; Qizilbash, N.; Collins, R.; Peto, R. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults: Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies. Lancet 2009, 373, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.H.; Sull, J.W.; Park, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Ohrr, H.; Guallar, E.; Samet, J.M. Body-mass index and mortality in Korean men and women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, D.S.; Pop-Busui, R.; Park, Y.; Kim, S.G. Body Mass Index and Mortality in the General Population and in Subjects with Chronic Disease in Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study (2002–2010). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, G.W.; Zumoff, B. The relationship of weight-height indices of obesity to body fat content. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, T.L.; Seidell, J.C.; Molarius, A.; van der Kuip, D.; Hofman, A.; Witteman, J.C. A comparison of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as predictors of all-cause mortality among the elderly: The Rotterdam study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institutes of Health. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults—The Evidence Report. Obes. Res. 1998, 6 (Suppl. 2), 51S–209S. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, V.J.; Walters, E.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Solomon, C.G.; Willett, W.C.; Rosner, B.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Manson, J.E. Body fat distribution and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women. The Nurses’ Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, M.B.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Visser, M.; Dekker, J.M.; Seidell, J.C.; Shaw, J.E. Independent and opposite associations of waist and hip circumferences with diabetes, hypertension and dyslipidemia: The AusDiab Study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2004, 28, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Pelt, R.E.; Evans, E.M.; Schechtman, K.B.; Ehsani, A.A.; Kohrt, W.M. Waist circumference vs body mass index for prediction of disease risk in postmenopausal women. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoy, D. Distribution of body fat and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Craig, C.L.; Bouchard, C. Adiposity, adipose tissue distribution and mortality rates in the Canada Fitness Survey follow-up study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahmann, P.H.; Lissner, L.; Gullberg, B.; Berglund, G. A prospective study of adiposity and all-cause mortality: The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study. Obes. Res. 2002, 10, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pischon, T.; Boeing, H.; Hoffmann, K.; Bergmann, M.; Schulze, M.B.; Overvad, K.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Spencer, E.; Moons, K.G.; Tjonneland, A.; et al. General and abdominal adiposity and risk of death in Europe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.A.; MacInnis, R.J.; Peeters, A.; Hopper, J.L.; Giles, G.G.; English, D.R. A comparison of adiposity measures as predictors of all-cause mortality: The Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. Obesity 2007, 15, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, I.; Ascherio, A.; Rimm, E.B.; Giovannucci, E.; Spiegelman, D.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. Adiposity and mortality in men. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigaard, J.; Tjonneland, A.; Thomsen, B.L.; Overvad, K.; Heitmann, B.L.; Sorensen, T.I. Waist circumference, BMI, smoking, and mortality in middle-aged men and women. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folsom, A.R.; Kushi, L.H.; Anderson, K.E.; Mink, P.J.; Olson, J.E.; Hong, C.P.; Sellers, T.A.; Lazovich, D.; Prineas, R.J. Associations of general and abdominal obesity with multiple health outcomes in older women: The Iowa Women’s Health Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, I.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Ross, R. Body mass index is inversely related to mortality in older people after adjustment for waist circumference. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 2112–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, A.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Schatzkin, A.; Mouw, T.; Adams, K.F.; van Eijk, J.T.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Harris, T.B. Waist circumference and mortality. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 167, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Rexrode, K.M.; van Dam, R.M.; Li, T.Y.; Hu, F.B. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: Sixteen years of follow-up in US women. Circulation 2008, 117, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerhan, J.R.; Moore, S.C.; Jacobs, E.J.; Kitahara, C.M.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Adami, H.O.; Ebbert, J.O.; English, D.R.; Gapstur, S.M.; Giles, G.G.; et al. A pooled analysis of waist circumference and mortality in 650,000 adults. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2014, 89, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Patel, A.V.; McCullough, M.L.; Campbell, P.T.; Thun, M.J.; Gapstur, S.M. Waist circumference and all-cause mortality in a large US cohort. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shu, X.O.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y.T.; Zheng, W. Abdominal adiposity and mortality in Chinese women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 46, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.O.; Jung, C.H.; Song, Y.D.; Park, C.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Cha, B.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Ko, K.S.; Lee, B.W. Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the korean national health insurance system. Diabetes Metab. J. 2014, 38, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Service: Health Checkup. Available online: https://nhiss.nhis.or.kr/bd/ay/bdaya001iv.do (accessed on 11 February 2017).
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; Han, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Cho, G.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, H.S.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, C.B.; et al. Appropriate waist circumference cutoff points for central obesity in Korean adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2007, 75, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F. Obesity and Mortality; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- de Hollander, E.L.; Bemelmans, W.J.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Friedrich, N.; Wallaschofski, H.; Guallar-Castillon, P.; Walter, S.; Zillikens, M.C.; Rosengren, A.; Lissner, L.; et al. The association between waist circumference and risk of mortality considering body mass index in 65- to 74-year-olds: A meta-analysis of 29 cohorts involving more than 58 000 elderly persons. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkiewski, M.; Bjorntorp, P.; Sjostrom, L.; Smith, U. Impact of obesity on metabolism in men and women. Importance of regional adipose tissue distribution. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 72, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuk, J.L.; Lee, S.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R. Waist circumference and abdominal adipose tissue distribution: Influence of age and sex. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Pou, K.M.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Liu, C.Y.; Vasan, R.S.; Murabito, J.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Cupples, L.A.; et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: Association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Allison, D.B.; Kotler, D.P.; Ross, R. Body mass index and waist circumference independently contribute to the prediction of nonabdominal, abdominal subcutaneous, and visceral fat. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despres, J.P.; Lemieux, I.; Bergeron, J.; Pibarot, P.; Mathieu, P.; Larose, E.; Rodes-Cabau, J.; Bertrand, O.F.; Poirier, P. Abdominal obesity and the metabolic syndrome: Contribution to global cardiometabolic risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, A.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Williams, K.; Karter, A.J.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Tracy, R.P.; Haffner, S.M. The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2001, 25, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Yannakoulia, M.; Chrysohoou, C.; Stefanadis, C. The implication of obesity and central fat on markers of chronic inflammation: The ATTICA study. Atherosclerosis 2005, 183, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farin, H.M.; Abbasi, F.; Reaven, G.M. Body mass index and waist circumference correlate to the same degree with insulin-mediated glucose uptake. Metabolism 2005, 54, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Shaper, A.G.; Morris, R.W.; Whincup, P.H. Measures of adiposity in the identification of metabolic abnormalities in elderly men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Allison, D.B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Kelley, D.E.; Leibel, R.L.; Nonas, C.; Kahn, R.; Association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, The Obesity Society; American Society for Nutrition; et al. Waist circumference and cardiometabolic risk: A consensus statement from shaping America’s health: Association for Weight Management and Obesity Prevention; NAASO, the Obesity Society; the American Society for Nutrition; and the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snijder, M.B.; van Dam, R.M.; Visser, M.; Seidell, J.C. What aspects of body fat are particularly hazardous and how do we measure them? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 35, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
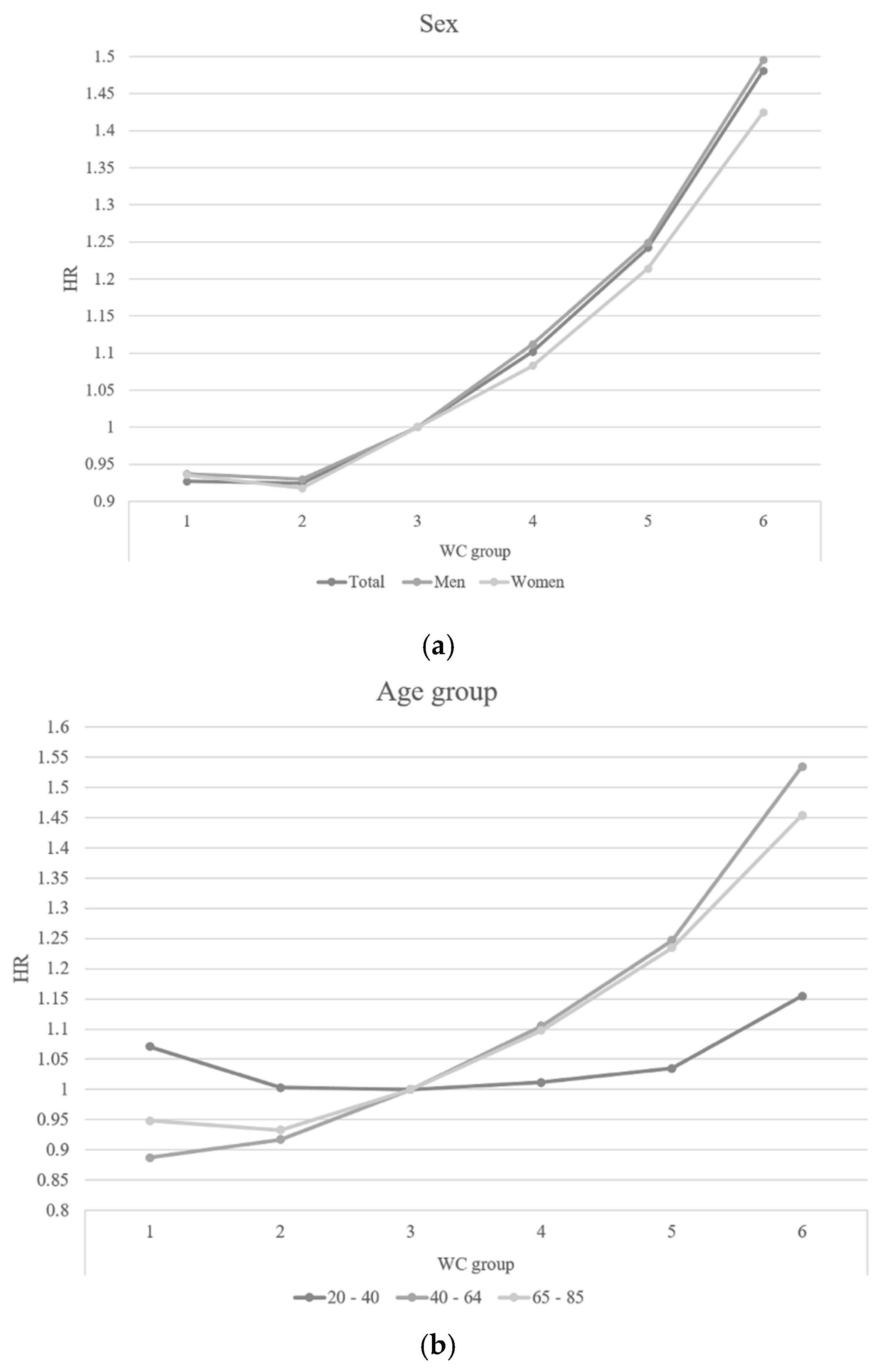
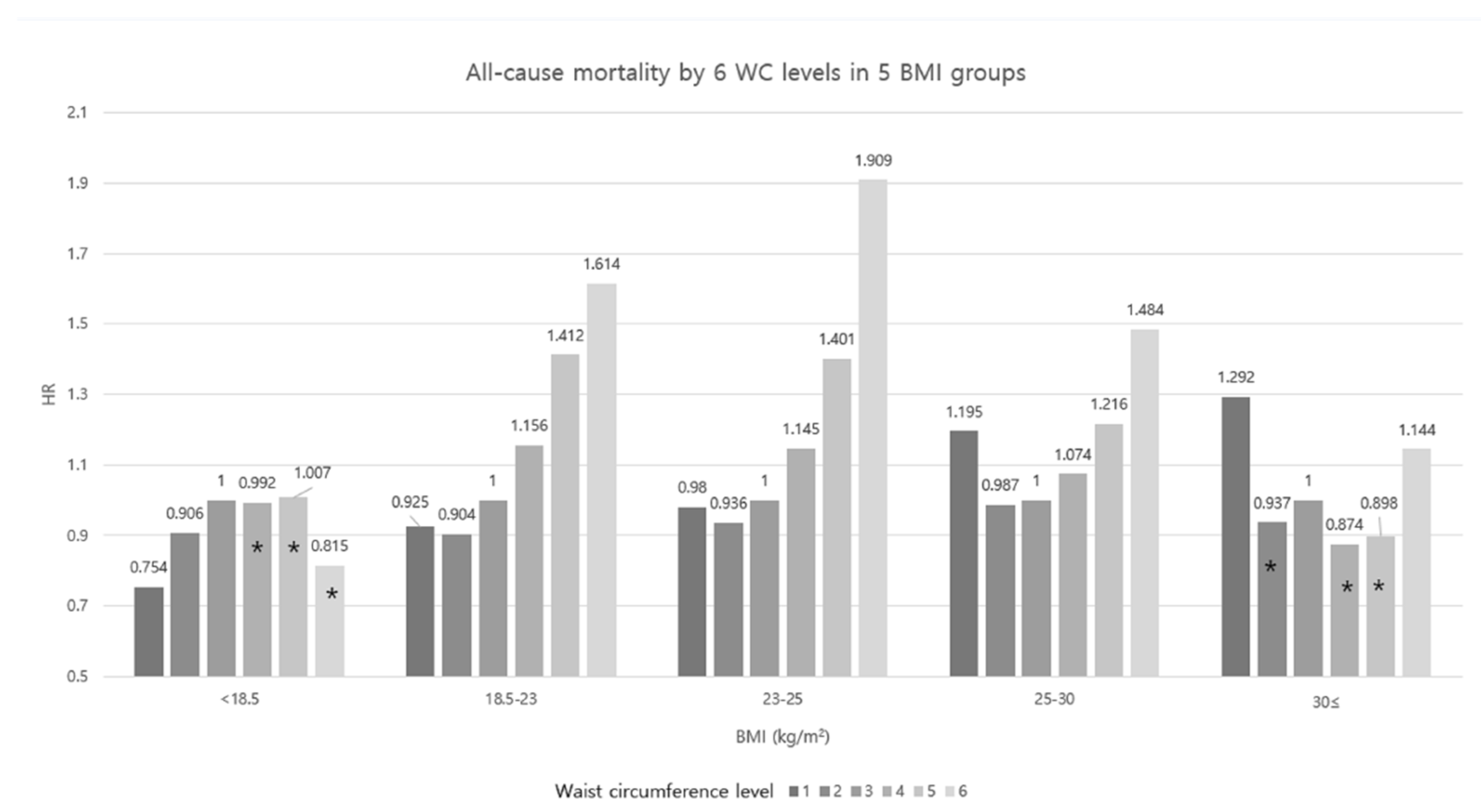
| Waist Circumference Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| N | 8,672,967 | 5,362,342 | 4,538,812 | 2,714,222 | 1,253,456 | 722,079 |
| Men (yes,%) | 3,450,338(39.78) | 3,079,604(57.43) | 2,648,218(58.35) | 1,604,864(59.13) | 679,425(54.2) | 351,401(48.67) |
| Age (year) | 42.69 ± 13.76 | 48.24 ± 13.42 | 50.91 ± 13.44 | 52.43 ± 13.67 | 53.33 ± 14.18 | 52.5 ± 15.11 |
| Age group (yes,%) | ||||||
| 20–40 | 3,596,630(41.47) | 1,384,164(25.81) | 915,952(20.18) | 492,555(18.15) | 225,771(18.01) | 158,788(21.99) |
| 40–64 | 4,399,758(50.73) | 3,297,574(61.5) | 2,842,275(62.62) | 1,651,324(60.84) | 720,342(57.47) | 381,554(52.84) |
| 65–85 | 676,579(7.8) | 680,604(12.69) | 780,585(17.2) | 570,343(21.01) | 307,343(24.52) | 181,737(25.17) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 21.05 ± 2.04 | 23.51 ± 1.89 | 24.99 ± 2.01 | 26.47 ± 2.16 | 28.04 ± 2.37 | 30.68 ± 3.21 |
| <18.5 | 901,949(10.4) | 24,771(0.46) | 6702(0.15) | 2197(0.08) | 638(0.05) | 287(0.04) |
| 18.5–23 | 6,323,446(72.91) | 2,090,324(38.98) | 678,158(14.94) | 125,309(4.62) | 20,215(1.61) | 5471(0.76) |
| 23–25 | 1,213,690(13.99) | 2,156,699(40.22) | 1,637,121(36.07) | 516,685(19.04) | 90,541(7.22) | 14,870(2.06) |
| 25–30 | 230,364(2.66) | 1,080,974(20.16) | 2,167,188(47.75) | 1,925,391(70.94) | 897,990(71.64) | 288,858(40) |
| ≥30 | 3518(0.04) | 9574(0.18) | 49,643(1.09) | 144,640(5.33) | 244,072(19.47) | 412,593(57.14) |
| Smoking (yes,%) | ||||||
| Non | 5,964,846(68.78) | 3,106,503(57.93) | 2,592,749(57.12) | 1,531,141(56.41) | 741,549(59.16) | 446,954(61.9) |
| Former | 786,403(9.07) | 812,076(15.14) | 765,533(16.87) | 481,828(17.75) | 205,172(16.37) | 100,249(13.88) |
| Current | 1,921,718(22.16) | 1,443,763(26.92) | 1,180,530(26.01) | 701,253(25.84) | 306,735(24.47) | 174,876(24.22) |
| Alcohol drinking (yes,%) | ||||||
| Non | 4,784,499(55.17) | 2,741,740(51.13) | 2,368,663(52.19) | 1,433,874(52.83) | 700,834(55.91) | 425,314(58.9) |
| Moderate | 3,422,946(39.47) | 2,178,086(40.62) | 1,756,031(38.69) | 1,006,673(37.09) | 426,554(34.03) | 225,813(31.27) |
| Heavy | 465,522(5.37) | 442,516(8.25) | 414,118(9.12) | 273,675(10.08) | 126,068(10.06) | 70,952(9.83) |
| Regular exercise (yes,%) | 1,405,021(16.2) | 1,027,051(19.15) | 864,575(19.05) | 498,760(18.38) | 216,517(17.27) | 112,544(15.59) |
| Income (Q1) (yes,%) | 1,931,941(22.28) | 1,090,911(20.34) | 911,431(20.08) | 551,669(20.33) | 265,490(21.18) | 163,770(22.68) |
| Urban living (yes,%) | 4,058,601(46.82) | 2,471,135(46.11) | 2,065,373(45.53) | 1,211,852(44.68) | 549,845(43.91) | 31,2001(43.27) |
| Death (yes,%) | 149,733(1.73) | 111,307(2.08) | 106,771(2.35) | 72,606(2.68) | 37,763(3.01) | 24,276(3.36) |
| HR (95% C.I.) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WC Group | N | Death | Duration | Incidence Rate | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
| 1 | 8,672,967 | 149,733 | 46,394,946.4 | 3.22736 | 1.375(1.364,1.386) | 1.328(1.317,1.338) | 0.927(0.919,0.936) |
| 2 | 5,362,342 | 111,307 | 29,089,043.6 | 3.82642 | 1.069(1.06,1.078) | 1.06(1.051,1.069) | 0.925(0.917,0.933) |
| 3 | 4,538,812 | 106,771 | 24,633,745.2 | 4.33434 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2,714,222 | 72,606 | 14,677,575.8 | 4.94673 | 0.993(0.984,1.003) | 0.995(0.985,1.004) | 1.102(1.091,1.113) |
| 5 | 1,253,456 | 37,763 | 6,731,707.3 | 5.60972 | 1.063(1.051,1.076) | 1.061(1.048,1.073) | 1.242(1.226,1.257) |
| 6 | 722,079 | 24,276 | 3,814,427.1 | 6.36426 | 1.262(1.245,1.28) | 1.247(1.23,1.264) | 1.481(1.457,1.505) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, S.M.; Han, K.-D.; Jung, J.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Oh, S.W.; Park, H.S.; Rhee, E.-J.; Lee, W.-Y.; Yoo, S.J. Waist Circumference and All-Cause Mortality Independent of Body Mass Index in Korean Population from the National Health Insurance Health Checkup 2009–2015. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010072
Kim Y-H, Kim SM, Han K-D, Jung J-H, Lee S-S, Oh SW, Park HS, Rhee E-J, Lee W-Y, Yoo SJ. Waist Circumference and All-Cause Mortality Independent of Body Mass Index in Korean Population from the National Health Insurance Health Checkup 2009–2015. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yang-Hyun, Seon Mee Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Seong-Su Lee, Sang Woo Oh, Hye Soon Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, and Soon Jib Yoo. 2019. "Waist Circumference and All-Cause Mortality Independent of Body Mass Index in Korean Population from the National Health Insurance Health Checkup 2009–2015" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010072
APA StyleKim, Y.-H., Kim, S. M., Han, K.-D., Jung, J.-H., Lee, S.-S., Oh, S. W., Park, H. S., Rhee, E.-J., Lee, W.-Y., & Yoo, S. J. (2019). Waist Circumference and All-Cause Mortality Independent of Body Mass Index in Korean Population from the National Health Insurance Health Checkup 2009–2015. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8010072





