Risk and Predisposing Factors for Suicide Attempts in Patients with Migraine and Status Migrainosus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Participants
2.3. Outcome Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
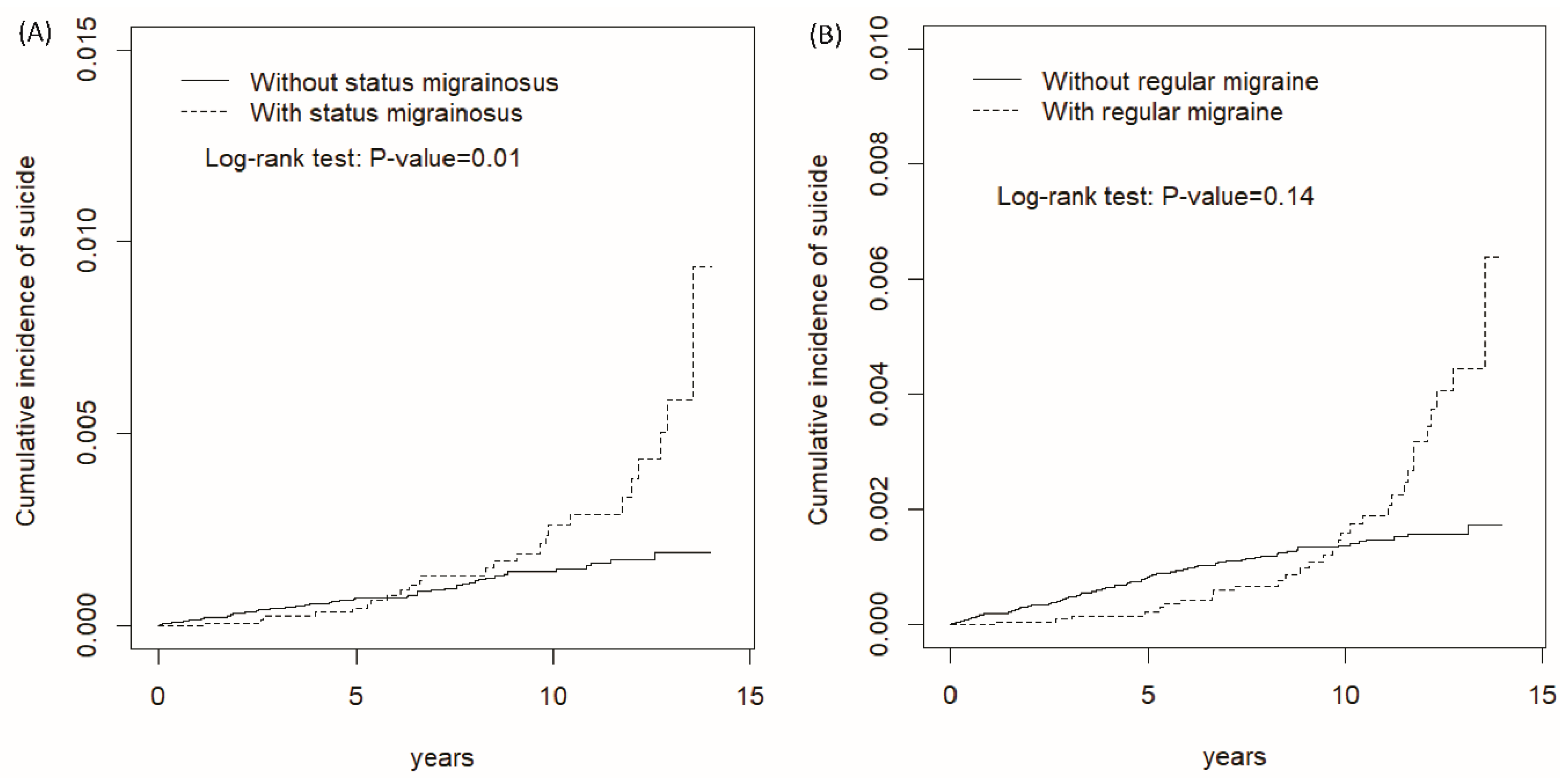
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aHR | adjusted hazard ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database |
| ICD-9-CM | International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification |
References
- Wang, S.J.; Chung, C.S.; Chankrachang, S.; Ravishankar, K.; Merican, J.S.; Salazar, G.; Siow, C.; Cheung, R.T.; Phanthumchinda, K.; Sakai, F. Migraine disability awareness campaign in Asia: Migraine assessment for prophylaxis. Headache 2008, 48, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streel, S.; Donneau, A.F.; Hoge, A.; Albert, A.; Schoenen, J.; Guillaume, M. One-year prevalence of migraine using a validated extended French version of the ID MigraineTM: A Belgian population-based study. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 171, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovner, L.J.; Zwart, J.A.; Hagen, K.; Terwindt, G.M.; Pascual, J. Epidemiology of headache in Europe. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, R.T. Prevalence of migraine, tension-type headache, and other headaches in Hong Kong. Headache 2000, 40, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, R.B.; Stewart, W.F.; Diamond, S.; Diamond, M.L.; Reed, M. Prevalence and burden of migraine in the United States: Data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache 2001, 41, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambarat, C.A.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Johnson, B.D.; Reis, S.E.; Thompson, D.V.; Sharaf, B.L.; Bittner, V.; Sopko, G.; Bairey Merz, C.N.; Pepine, C.J.; et al. Migraine headache and long-term cardiovascular outcomes: An extended follow-up of the women’s ischemia syndrome evaluation. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nović, A.; Kõlves, K.; O’Dwyer, S.; De Leo, D. Migraine and suicidal behaviors: A systematic literature review. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, I.; Kingsbury, M.; Sareen, J.; Bolton, J.; Van Walraven, C. Migraine headache and risk of self-harm and suicide: A population-based study in Ontario, Canada. Headache 2016, 56, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulman, E. Refractory migraine—A review. Headache 2013, 53, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, B.; Dalla Libera, D.; Dalla Costa, G.; Comi, G. Refractory migraine: The role of the physician in assessment and treatment of a problematic disease. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Y.W.; Han, M. Cultural orientation in Southeast Asian American young adults. Cult. Divers. Ethn. Minor. Psychol. 2008, 14, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowdon, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhong, B.; Yamauchi, T. A longitudinal comparison of age patterns and rates of suicide in Hong Kong, Taiwan and Japan and two Western countries. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2017, 31, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Database NHIR. Taiwan. Available online: http://nhird.nhri.org.tw/en/index.html (accessed on 30 December 2017).
- Ministry of Health and Welfare (2017). Taiwan Health and Welfare Report. Available online: http://www.mohw.gov.tw (accessed on 30 December 2017).
- Chen, Y.G.; Lu, C.S.; Lin, T.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Tzeng, H.E.; Tsai, C.H. Risk of fracture in transfusion-naïve thalassemia population: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. Bone 2018, 106, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, I.K.; Hsu, W.H.; Kao, C.H. Risk of acute coronary syndrome and peripheral arterial disease in chronic liver disease and cirrhosis: A nationwide population-based study. Atherosclerosis 2018, 270, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumayer, E.; Plümper, T. Inequalities of income and inequalities of longevity: A cross-country study. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Owolabi, M.O.; Amatya, B.; Hamzat, T.K.; Ogunniyi, A.; Oshinowo, H.; Elmalik, A.; Galea, M.P. Challenges and barriers for implementation of the World Health Organization Global Disability Action Plan in low- and middle-income countries. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.L.; McLean, G.; Park, J.; Martin, D.J.; Connolly, M.; Mercer, S.W.; Smith, D.J. Impact of socioeconomic deprivation on rate and cause of death in severe mental illness. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumbull, P.; Webb, R.; Kapur, N.; Clements, C.; Bergen, H.; Hawton, K.; Ness, J.; Waters, K.; Townsend, E.; Cooper, J. Variation by ethnic group in premature mortality risk following self-harm: A multicentre cohort study in England. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 254. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.L.; Tseng, M.H.; Hu, F.C.; Koh, C.L. Pediatric Evaluation of Disability Inventory: A cross-cultural comparison of daily function between Taiwanese and American children. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2010, 31, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillay, T.; Van Zyl, H.A.; Blackbeard, D. Chronic pain perception and cultural experience. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 113, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.C.; Lim, Y.; Teo, Y.Y.; Goh, R.; Law, H.Y.; Sia, A.T. Ethnic differences in pain perception and patient-controlled analgesia usage for postoperative pain. J. Pain 2008, 9, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Su, J.C.; Carrera, S.; Lin, S.P.; Yi, F. Suppression and interpersonal harmony: A cross-cultural comparison between Chinese and European Americans. J. Couns. Psychol. 2013, 60, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Ang, T.F.A.; Chiang, T.C.; Kaplan, W.A. Growing concerns and controversies to Taiwan National Health Insurance—What are the lessons from mainland China, South Korea and Singapore? Int. J. Health Plan. Manag. 2018, 33, e357–e366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, C.C.; Lin, J.W.; Lin, Y.F.; Hsu, N.C.; Ko, W.J. Evaluating the performance of a hospitalist system in Taiwan: A pioneer study for nationwide health insurance in Asia. J. Hosp. Med. 2011, 6, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Status Migrainosus | p-Value | Regular Migraine | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | No | Yes | |||
| (N = 54,379) | (N = 13,605) | (N = 85,840) | (N = 21,483) | |||
| Sex | 0.95 | 0.95 | ||||
| Female | 40,368(74.2) | 10,096(74.2) | 63,386(73.8) | 15,859(73.8) | ||
| Male | 14,011(25.8) | 3509(25.8) | 22,454(26.2) | 5624(26.2) | ||
| Age stratified (years) | 0.99 | 0.99 | ||||
| ≤49 | 34,928(64.2) | 8740(64.2) | 56,524(65.9) | 14,145(65.8) | ||
| 50–64 | 12,843(23.6) | 3211(23.6) | 19,440(22.7) | 4864(22.6) | ||
| 65+ | 6608(12.2) | 1654(12.2) | 9876(11.5) | 2474(11.5) | ||
| Age, mean ± SD a | 45.6(15.1) | 45.7(14.8) | 0.42 | 44.9(15.2) | 45.1(14.8) | 0.23 |
| Monthly income (NTD) † | 0.01 | 0.001 | ||||
| <15,000 | 20,922(38.5) | 5043(37.1) | 33,192(38.7) | 7959(37.1) | ||
| 15,000–19,999 | 16,626(30.6) | 4211(31.0) | 25,934(30.2) | 6687(31.1) | ||
| ≥20,000 | 16,831(31.0) | 4351(32.0) | 26,714(31.1) | 6837(31.8) | ||
| Urbanization level ‡ | <0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| 1 (highest) | 16,639(30.6) | 3797(27.9) | 26,485(30.9) | 6222(29.0) | ||
| 2 | 16,363(30.1) | 4251(31.3) | 25,727(30.0) | 6642(30.9) | ||
| 3 | 9296(17.1) | 2249(16.5) | 14,692(17.1) | 3486(16.2) | ||
| 4 (lowest) | 12,081(22.2) | 3308(24.3) | 18,936(22.1) | 5133(23.9) | ||
| Occupation category & | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| Office worker | 28,863(53.1) | 7041(51.8) | 45,943(53.5) | 11,283(52.5) | ||
| Laborer | 20,873(38.4) | 5464(40.2) | 32,510(37.9) | 8432(39.3) | ||
| Other | 4643(8.54) | 1100(8.09) | 7387(8.61) | 1768(8.23) | ||
| Comorbidity | ||||||
| Schizophrenia | 511(0.94) | 137(1.01) | 0.47 | 675(0.79) | 184(0.86) | 0.30 |
| Depression | 7214(13.3) | 1810(13.3) | 0.91 | 9918(11.6) | 2494(11.6) | 0.82 |
| Alcohol-related illness | 2045(3.76) | 519(3.81) | 0.77 | 2881(3.36) | 734(3.42) | 0.66 |
| Anxiety | 20,476(37.7) | 5127(37.7) | 0.95 | 30,253(35.2) | 7578(35.3) | 0.93 |
| Mental disorders | 6140(11.3) | 1535(11.3) | 0.98 | 9304(10.8) | 2326(10.8) | 0.96 |
| Insomnia | 37,477(68.9) | 9379(68.9) | 0.96 | 56,314(65.6) | 14,097(65.6) | 0.97 |
| Variable | Event | PY | Rate # | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR $ (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status migrainosus | |||||
| No | 56 | 394,603 | 1.42 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 26 | 99,946 | 2.60 | 1.82(1.15, 2.90) * | 1.81(1.14, 2.89) * |
| Age group (years) | |||||
| ≤49 | 68 | 322,343 | 2.11 | 3.10(1.49, 6.45) ** | 3.27(1.56, 6.87) ** |
| 50–64 | 8 | 117,777 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 65+ | 6 | 54,429 | 1.10 | 1.68(0.58, 4.84) | 1.58(0.55, 4.59) |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 73 | 369,296 | 1.98 | 2.74(1.37, 5.47) ** | 2.67(1.31, 5.43) ** |
| Male | 9 | 125,253 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Monthly income (NTD) † | |||||
| <15,000 | 40 | 171,388 | 2.33 | 3.14(1.68, 5.87) *** | 2.44(1.24, 4.78) ** |
| 15,000−19,999 | 29 | 157,796 | 1.84 | 2.36(1.23, 4.54) * | 1.89(0.98, 3.66) |
| ≥20,000 | 13 | 165,366 | 0.79 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Urbanization level ‡ | |||||
| 1 (highest) | 26 | 148,541 | 1.75 | 1.46(0.71, 3.03) | |
| 2 | 28 | 149,328 | 1.88 | 1.57(0.77, 3.24) | |
| 3 | 10 | 83,682 | 1.20 | 1.00 | |
| 4 (lowest) | 18 | 112,999 | 1.59 | 1.33(0.61, 2.87) | |
| Occupation category & | |||||
| Office worker | 33 | 259,306 | 1.27 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Laborer | 35 | 194,913 | 1.80 | 1.40(0.87, 2.25) | 1.40(0.86, 2.29) |
| Other | 14 | 40,330 | 3.47 | 2.76(1.48, 5.15) ** | 1.88(0.95, 3.69) |
| Comorbidity | |||||
| Schizophrenia | |||||
| No | 79 | 489,986 | 1.61 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 3 | 4563 | 6.57 | 4.14(1.31, 13.1) * | 1.76(0.54, 5.73) |
| Depression | |||||
| No | 54 | 433,365 | 1.25 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 28 | 61,184 | 4.58 | 3.85(2.44, 6.08) *** | 2.15(1.27, 3.65) ** |
| Alcohol-related illness | |||||
| No | 71 | 480,513 | 1.48 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 11 | 14,036 | 7.84 | 5.90(3.11, 11.2) *** | 4.32(2.22, 8.41) *** |
| Anxiety | |||||
| No | 30 | 307,897 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 52 | 186,652 | 2.79 | 2.93(1.87, 4.59) *** | 1.95(1.15, 3.31) * |
| Mental disorders | |||||
| No | 79 | 441,360 | 1.79 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 3 | 53,189 | 0.56 | 0.32(0.10, 1.01) | |
| Insomnia | |||||
| No | 15 | 170,676 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 67 | 323,873 | 2.07 | 2.63(1.50, 4.63) *** | 1.91(1.06, 3.46) * |
| Variable | Event | PY | Rate # | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR $ (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular migraine | |||||
| No | 93 | 659,110 | 1.41 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 32 | 167,185 | 1.91 | 1.35(0.91, 2.02) | 1.34(0.90, 2.00) |
| Age group (years) | |||||
| ≤49 | 105 | 557,763 | 1.88 | 2.20(1.02, 4.72) * | 2.77(1.28, 6.02) * |
| 50–64 | 13 | 185,091 | 0.70 | 0.82(0.33, 2.06) | 0.91(0.36, 2.30) |
| 65+ | 7 | 83,441 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 106 | 616,795 | 1.72 | 1.88(1.16, 3.07) * | 1.77(1.07, 2.93) * |
| Male | 19 | 209,501 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Monthly income (NTD) † | |||||
| <15,000 | 58 | 290,561 | 2.00 | 2.69(1.63, 4.44) *** | 1.92(1.11, 3.30) * |
| 15,000−19,999 | 46 | 260,277 | 1.77 | 2.33(1.39, 3.90) ** | 1.88(1.12, 3.18) * |
| ≥20,000 | 21 | 275,457 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Urbanization level ‡ | |||||
| 1 (highest) | 30 | 251,779 | 1.19 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 48 | 248,120 | 1.93 | 1.62(1.03, 2.56) * | 1.47(0.93, 2.32) |
| 3 | 17 | 138,799 | 1.22 | 1.03(0.57, 1.86) | 0.96(0.53, 1.75) |
| 4 (lowest) | 30 | 187,598 | 1.60 | 1.34(0.81, 2.22) | 1.26(0.75, 2.10) |
| Occupation category & | |||||
| Office worker | 52 | 439,466 | 1.18 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Laborer | 50 | 319,046 | 1.57 | 1.32(0.90, 1.95) | 1.18(0.79, 1.78) |
| Other | 23 | 67,784 | 3.39 | 2.89(1.77, 4.72) *** | 2.19(1.27, 3.77) ** |
| Comorbidity | |||||
| Schizophrenia | |||||
| No | 118 | 820,075 | 1.44 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 7 | 6221 | 11.3 | 7.86(3.67, 16.9) *** | 3.28(1.49, 7.223) ** |
| Depression | |||||
| No | 84 | 739,827 | 1.14 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 41 | 86,469 | 4.74 | 4.30(2.96, 6.25) *** | 2.33(1.51, 3.60) *** |
| Alcohol-related illness | |||||
| No | 114 | 805,688 | 1.41 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 11 | 20,607 | 5.34 | 4.00(2.15, 7.45) *** | 2.61(1.37, 4.96) ** |
| Anxiety | |||||
| No | 49 | 539,650 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 76 | 286,645 | 2.65 | 2.96(2.07, 4.25) *** | 1.87(1.23, 2.86) ** |
| Mental disorders | |||||
| No | 117 | 741,867 | 1.58 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 8 | 84,428 | 0.95 | 0.61(0.30, 1.24) | |
| Insomnia | |||||
| No | 21 | 314,784 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Yes | 104 | 511,512 | 2.03 | 3.26(2.03, 5.22) *** | 2.44(1.49, 4.00) *** |
| Competing-Risks Regression Models | ||
|---|---|---|
| Status Migrainosus | ||
| No | Yes | |
| Status migrainosus | ||
| Crude SHR (95% CI) | 1(Reference) | 2.90(1.77, 4.74) *** |
| Adjusted SHR † (95% CI) | 1(Reference) | 1.99(1.24, 3.18) ** |
| Outcome | Status Migrainosus | Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR $ (95% CI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||||
| Event | Rate # | Event | Rate # | |||
| Liquid or solid poisoning (ICD-9-CM code E950) | 28 | 0.71 | 19 | 1.90 | 2.66(1.49, 4.76) ** | 2.63(1.47, 4.71) ** |
| Charcoal burning and poisoning by gases (ICD-9-CM code E952) | 4 | 0.10 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.98(0.11, 8.77) | 0.96(0.11, 6.60) |
| Hanging (ICD-9-CM code E953) | 1 | 0.03 | 2 | 0.20 | 7.79(0.71, 85.9) | 8.09(0.73, 89.3) |
| Cutting/piercing (ICD-9-CM code E956) | 8 | 0.20 | 1 | 0.10 | 0.50(0.06, 3.96) | 0.55(0.07, 4.43) |
| Jumping from high places (ICD-9-CM code E957) | 2 | 0.05 | 0 | 0.00 | - | - |
| Others (ICD-9-CM codes E951, E954, E955, E958, and E959) | 13 | 0.33 | 3 | 0.30 | 0.91(0.26, 3.19) | 0.93(0.27, 3.26) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harnod, T.; Lin, C.-L.; Kao, C.-H. Risk and Predisposing Factors for Suicide Attempts in Patients with Migraine and Status Migrainosus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7090269
Harnod T, Lin C-L, Kao C-H. Risk and Predisposing Factors for Suicide Attempts in Patients with Migraine and Status Migrainosus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2018; 7(9):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7090269
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarnod, Tomor, Cheng-Li Lin, and Chia-Hung Kao. 2018. "Risk and Predisposing Factors for Suicide Attempts in Patients with Migraine and Status Migrainosus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 7, no. 9: 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7090269
APA StyleHarnod, T., Lin, C.-L., & Kao, C.-H. (2018). Risk and Predisposing Factors for Suicide Attempts in Patients with Migraine and Status Migrainosus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(9), 269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7090269





