The Impact of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Progression to Castration Resistance—Real-World Data from a Romanian Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
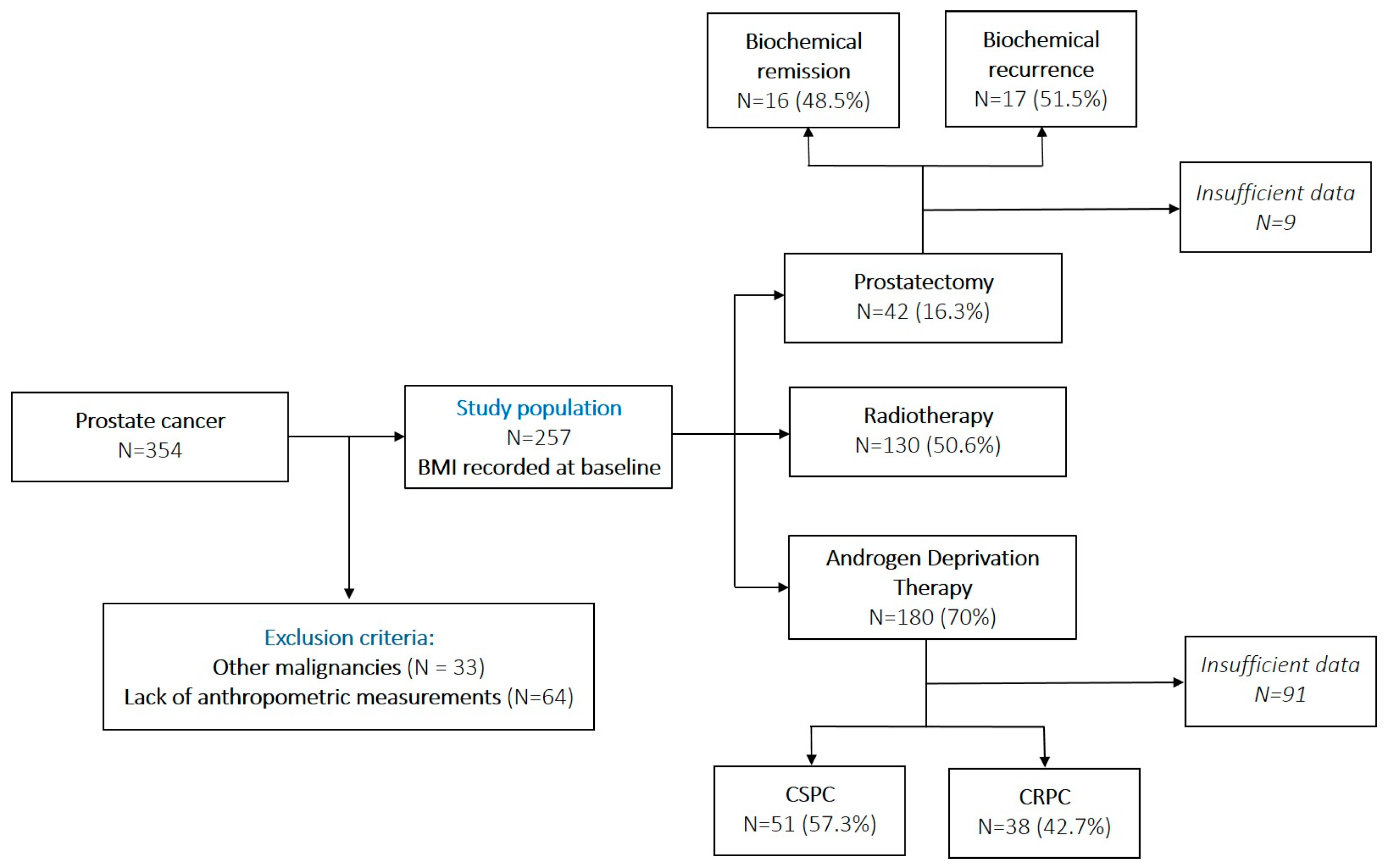
2. Materials and Methods
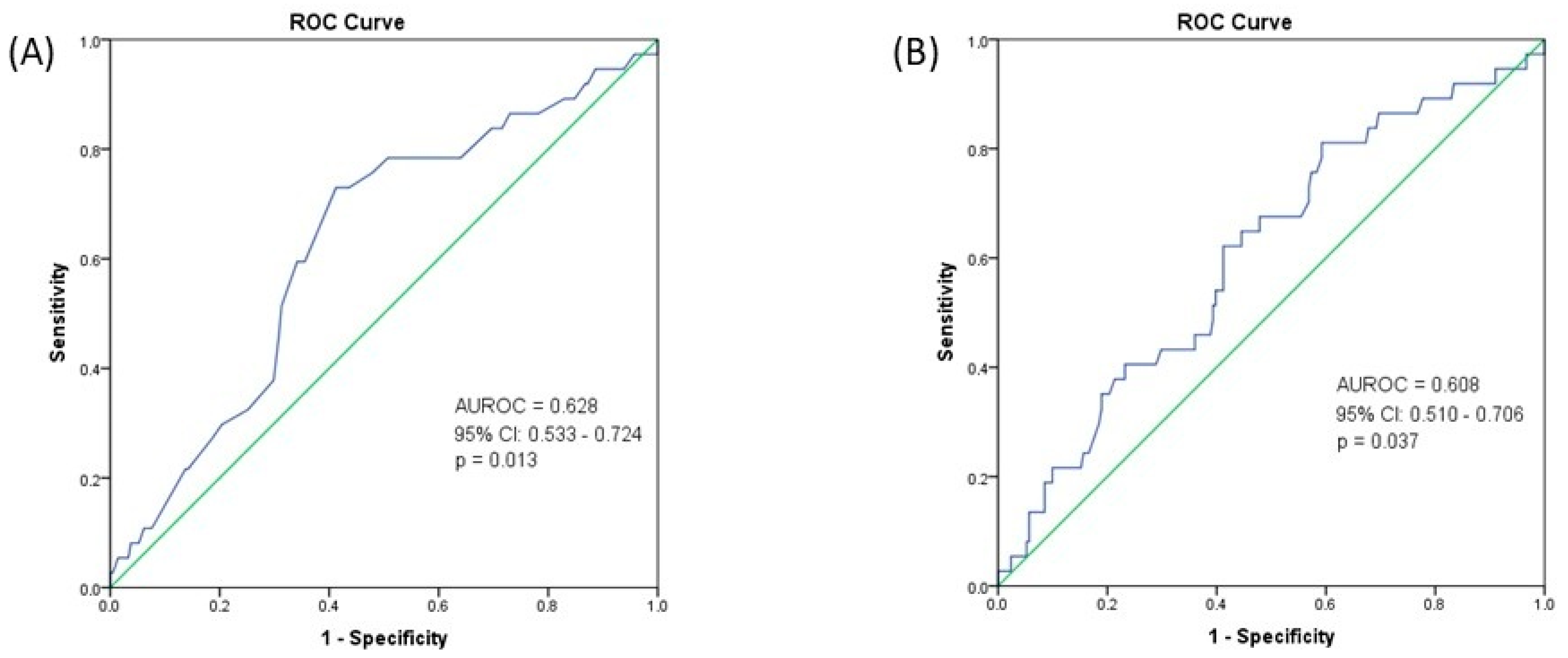
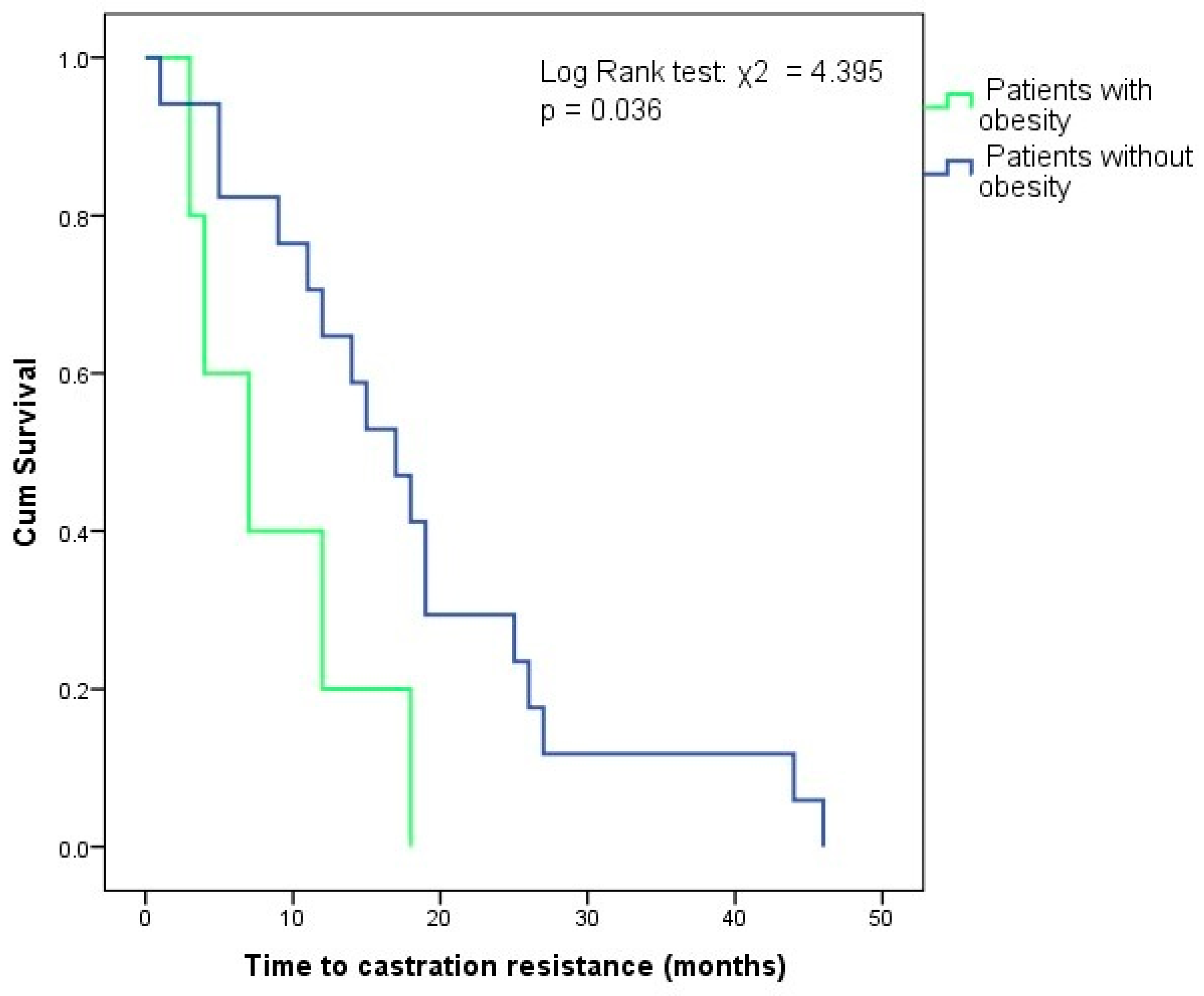
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/publications/i/item/9789289057738 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Bilano, V.; Bixby, H.; Zhou, B.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Taddei, C.; Hajifathalian, K.; Lu, Y.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Body-Mass Index, Underweight, Overweight, and Obesity from 1975 to 2016: A Pooled Analysis of 2416 Population-Based Measurement Studies in 128·9 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2025; World Obesity Federation: London, UK, 2025; Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=23 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and Cancer Risk: Emerging Biological Mechanisms and Perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickman, R.E.; Franco, O.E.; Moline, D.C.; Vander Griend, D.J.; Thumbikat, P.; Hayward, S.W. The Role of the Androgen Receptor in Prostate Development and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Review. Asian J. Urol. 2020, 7, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, C.; Hodges, C. V Studies on Prostatic Cancer. I. The Effect of Castration, of Estrogen and of Androgen Injection on Serum Phosphatases in Metastatic Carcinoma of the Prostate. Cancer Res. 1941, 1, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- EAU Guidelines Office, Arnhem, The Netherlands. Available online: http://uroweb.org/guidelines/compilations-of-all-guidelines/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Discacciati, A.; Orsini, N.; Wolk, A. Body Mass Index and Incidence of Localized and Advanced Prostate Cancer-a Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, A.C.; Howard, L.E.; Moreira, D.M.; Castro-Santamaria, R.; Andriole, G.L.; Freedland, S.J. Obesity Increases the Risk for High-Grade Prostate Cancer: Results from the REDUCE Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 2936–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacci, M.; Russo, G.I.; De Nunzio, C.; Sebastianelli, A.; Salvi, M.; Vignozzi, L.; Tubaro, A.; Morgia, G.; Serni, S. Meta-Analysis of Metabolic Syndrome and Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuzuka, K.; Arai, Y. Metabolic Changes in Patients with Prostate Cancer during Androgen Deprivation Therapy. Int. J. Urol. 2018, 25, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzortzis, V.; Samarinas, M.; Zachos, I.; Oeconomou, A.; Pisters, L.L.; Bargiota, A. Adverse Effects of Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Patients with Prostate Cancer: Focus on Metabolic Complications. Hormones 2017, 16, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Lee Chuy, K.; Yang, J.C.; Bates, M.; Lombardo, M.; Steingart, R.M. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects of Androgen-Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. J. Oncol. Pract. 2018, 14, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunstein, L.Z.; Chen, M.-H.; Loffredo, M.J.; Kantoff, P.W.; D’Amico, A.V. Obesity and the Odds of Weight Gain Following Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Toward a Risk Adapted Approach for ADT Use. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyyounouski, M.K.; Choyke, P.L.; McKenney, J.K.; Sartor, O.; Sandler, H.M.; Amin, M.B.; Kattan, M.W.; Lin, D.W. Prostate Cancer–Major Changes in the American Joint Committee on Cancer Eighth Edition Cancer Staging Manual. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovici, D.; Stanisav, C.; Pricop, M.; Dragomir, R.; Saftescu, S.; Ciurescu, D. Associations between Body Mass Index and Prostate Cancer: The Impact on Progression-Free Survival. Medicina 2023, 59, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.; Moţa, M.; Popa, A.; Moţa, E.; Serafinceanu, C.; Guja, C.; Catrinoiu, D.; Hâncu, N.; Lichiardopol, R.; Bala, C.; et al. Prevalence of Overweight/Obesity, Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome and Atypical Cardiometabolic Phenotypes in the Adult Romanian Population: PREDATORR Study. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2016, 39, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandaglia, G.; Pellegrino, F.; Golozar, A.; De Meulder, B.; Abbott, T.; Achtman, A.; Imran Omar, M.; Alshammari, T.; Areia, C.; Asiimwe, A.; et al. Clinical Characterization of Patients Diagnosed with Prostate Cancer and Undergoing Conservative Management: A PIONEER Analysis Based on Big Data. Eur. Urol. 2024, 85, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañez, L.L.; Hamilton, R.J.; Partin, A.W.; Vollmer, R.T.; Sun, L.; Rodriguez, C.; Wang, Y.; Terris, M.K.; Aronson, W.J.; Presti, J.C.J.; et al. Obesity-Related Plasma Hemodilution and PSA Concentration among Men with Prostate Cancer. JAMA 2007, 298, 2275–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, S.E.; Sjölander, A.; Tillander, A.; Wiklund, F.; Grönberg, H.; Bälter, K. Body Mass Index in Relation to Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen Levels and Prostate Cancer Risk. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, A.T.; Vincent, A.D.; O’Callaghan, M.E.; Martin, S.A.; Sutherland, P.D.; Hoy, A.J.; Butler, L.M.; Wittert, G.A. The Inverse Relationship between Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) and Obesity. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Liu, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z. Body Mass Index in Relation to Prostate-Specific Antigen-Related Parameters. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, Z.; Howard, L.E.; Moreira, D.M.; Andriole, G.L.J.; Terris, M.K.; Freedland, S.J. Association of Obesity-Related Hemodilution of Prostate-Specific Antigen, Dihydrotestosterone, and Testosterone. Prostate 2017, 77, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikesit, D.; Mochtar, C.A.; Umbas, R.; Hamid, A.R.A.H. The Impact of Obesity towards Prostate Diseases. Prostate Int. 2016, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Izquierdo, M.; Pérez de Rojas, J.; Martínez-Ruiz, V.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Sánchez, M.-J.; Khan, K.S.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Prostate Cancer Mortality: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of 280,199 Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Montori, V.M.; Somers, V.K.; Korinek, J.; Thomas, R.J.; Allison, T.G.; Mookadam, F.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Association of Bodyweight with Total Mortality and with Cardiovascular Events in Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Lancet 2006, 368, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, K.; Cao, K.; Yin, P. Association of Overweight and Obesity with Patient Mortality after Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.-C.; Chen, M.-E.; Wu, W.-T.; Kuo, I.-C.; Niu, S.-W.; Lee, J.-J.; Hung, C.-C.; Chang, J.-M.; Hwang, S.-J. Normal Weight and Waist Obesity Indicated by Increased Total Body Fat Associated with All-Cause Mortality in Stage 3-5 Chronic Kidney Disease. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 982519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, Y.; Hasegawa, W.; Yasunaga, H.; Sunohara, M.; Jo, T.; Takami, K.; Matsui, H.; Fushimi, K.; Nagase, T. Paradoxical Association between Body Mass Index and In-Hospital Mortality in Elderly Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Japan. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2014, 9, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Yu, F.; Xu, Q.; Guo, W.; Wu, C.; He, J. Body Mass Index and Mortality in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Boyko, E.J. The Evidence for an Obesity Paradox in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Giovannucci, E.L. The Obesity Paradox in Cancer: Epidemiologic Insights and Perspectives. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2019, 8, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, A.; Shah, Q.N.; Waingankar, N.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Tsao, C.-K.; Necchi, A.; Montorsi, F.; Gallagher, E.J.; Galsky, M.D. The Obesity Paradox in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdtsson, A.; Poon, J.B.; Thorek, D.L.; Mucci, L.A.; Evans, M.J.; Scardino, P.; Abrahamsson, P.-A.; Nilsson, P.; Manjer, J.; Bjartell, A.; et al. Anthropometric Measures at Multiple Times Throughout Life and Prostate Cancer Diagnosis, Metastasis, and Death. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcaro, A.B.; Tafuri, A.; Sebben, M.; Processali, T.; Pirozzi, M.; Amigoni, N.; Rizzetto, R.; Shakir, A.; Cerruto, M.A.; Brunelli, M.; et al. High Body Mass Index Predicts Multiple Prostate Cancer Lymph Node Metastases after Radical Prostatectomy and Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection. Asian J. Androl. 2020, 22, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcaro, A.B.; Tafuri, A.; Sebben, M.; Processali, T.; Pirozzi, M.; Amigoni, N.; Rizzetto, R.; Shakir, A.; Cacciamani, G.E.; Brunelli, M.; et al. Body Mass Index and Prostatic-Specific Antigen Are Predictors of Prostate Cancer Metastases in Patients Undergoing Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy and Extended Pelvic Lymph Node Dissection. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2019, 71, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafuri, A.; Amigoni, N.; Rizzetto, R.; Sebben, M.; Shakir, A.; Gozzo, A.; Odorizzi, K.; De Michele, M.; Gallina, S.; Bianchi, A.; et al. Obesity Strongly Predicts Clinically Undetected Multiple Lymph Node Metastases in Intermediate- and High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients Who Underwent Robot Assisted Radical Prostatectomy and Extended Lymph Node Dissection. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Izquierdo, M.; Pérez de Rojas, J.; Martínez-Ruiz, V.; Arrabal-Polo, M.Á.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Jiménez-Moleón, J.J. Obesity and Biochemical Recurrence in Clinically Localised Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 86,490 Patients. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keto, C.J.; Aronson, W.J.; Terris, M.K.; Presti, J.C.; Kane, C.J.; Amling, C.L.; Freedland, S.J. Obesity Is Associated with Castration-Resistant Disease and Metastasis in Men Treated with Androgen Deprivation Therapy after Radical Prostatectomy: Results from the SEARCH Database. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, J.; Gray, P.K.; Hahn, N.; Hayes, J.; Myers, L.J.; Carney-Doebbeling, C.; Sweeney, C.J. Presence of the Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with Shorter Time to Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, T.; Yang, J.C.; Gao, A.C.; Evans, C.P. Mechanisms of Resistance in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC). Transl. Androl. Urol. 2015, 4, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Wu, S.; Sharkey, C.; Tabatabaei, S.; Wu, C.-L.; Tao, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Strand, D.; Olumi, A.F.; Wang, Z. Obesity-Associated Inflammation Induces Androgenic to Estrogenic Switch in the Prostate Gland. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Galasso, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Bilancio, A.; Perillo, B.; Sinisi, A.A.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Estrogen Receptors in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 67.11 ± 8.05 |
| Weight, median (IQR) (kg) | 84.93 (20) |
| BMI, median (IQR) (kg/m2) | 27.83 (6.02) |
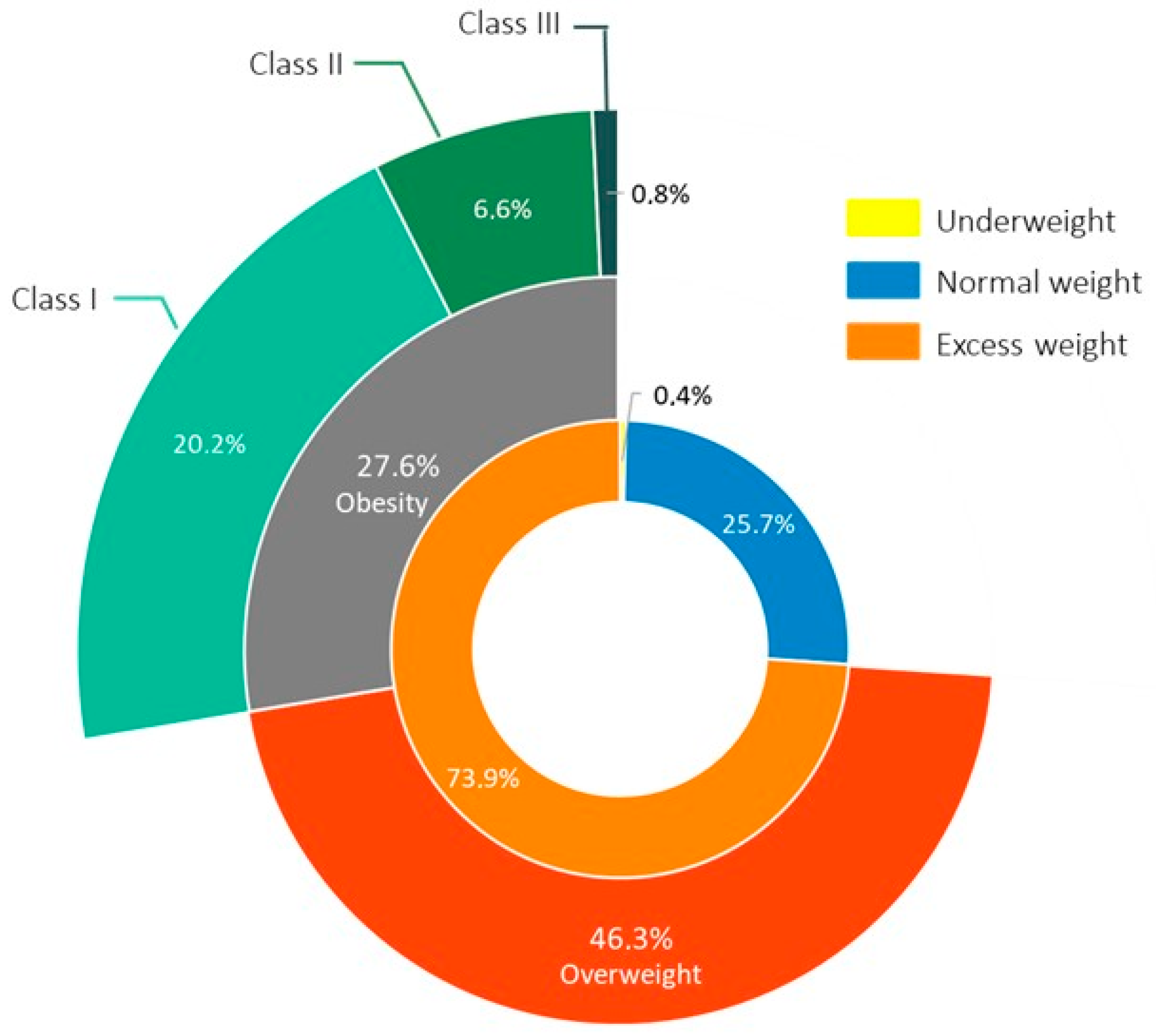
| Obesity, N (%) | 71 (27.6%) |
| Nutritional status, N (%) Underweight Normal weight Overweight Obesity class I Obesity class II Obesity class III | 1 (0.4%) 66 (25.7%) 119 (46.3%) 52 (20.2%) 17 (6.6%) 2 (0.8%) |
| Hypertension, N (%) | 116 (45.1%) |
| Dyslipidemia, N (%) | 35 (13.6%) |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 45 (17.5%) |
| Family history for neoplasia, N (%) | 38 (14.8%) |
| PSA, median (IQR) (ng/mL) | 12.8 (29.4) |
| Gleason Score, median (IQR) | 7 (1) |
| Grade Group, N (%) I II III IV V Missing | 41 (16%) 53 (20.6%) 47 (18.3%) 40 (15.6%) 44 (17.1%) 32 (12.5%) |
| Metastases at diagnosis, N (%) | 59 (23%) |
| 10-year all-cause mortality, % | 14.9% |
| Parameter | Patients with Obesity N = 71 (27.6%) | Patients without Obesity N = 186 (72.4%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 65.25 ± 6.96 | 67.82 ± 8.34 | 0.022 |
| PSA, median (IQR) (ng/mL) | 10.13 (22.71) | 14.75 (34.73) | 0.016 |
| Gleason Score, median (IQR) | 7 (1) | 7 (1) | 0.236 |
| Grade group, N (%) | 0.446 | ||
| I–III | 37 (52.1%) | 104 (55.9%) | |
| IV–V | 26 (36.6%) | 58 (31.2%) | |
| Missing | 8 (11.3%) | 24 (12.9%) | |
| Metastases at diagnosis, N (%) | 12 (16.9) | 47 (25.3) | 0.154 |
| Parameter | M1 N = 59 (23%) | M0 N = 198 (77%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (years) | 67.64 ± 7.98 | 66.94 ± 8.08 | 0.559 |
| 10-year all-cause mortality (%) | 37.5% | 8.3% | <0.001 |
| PSA, median (IQR) (ng/mL) | 52.09 (119) | 11 (16.95) | <0.001 |
| Gleason Score, median (IQR) | 8 (2) | 7 (1) | 0.002 |
| Grade group, N (%) I–III IV–V Missing | 20 (33.9%) 29 (49.2%) 10 (16.9%) | 121 (61.1%) 55 (27.8%) 22 (11.1%) | <0.001 * |
| Weight, median (IQR) (kg) | 76 (16) | 83.5 (21) | 0.001 |
| BMI, median (IQR) (kg/m2) | 26.3 (5.54) | 27.14 (5.98) | 0.033 |
| Obesity, N (%) | 12 (20.3) | 59 (29.8) | 0.154 |
| Parameter | Biochemical Recurrence N = 17 (51.5%) | Biochemical Remission N = 16 (48.5%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, mean ± SD (years) | 64.31 ± 6.51 | 62.31 ± 5.61 | 0.359 |
| Deceased, N (%) | 1 (5.9) | 1 (6.2) | 0.965 |
| PSA at diagnosis, median (IQR) (ng/mL) | 11 (10.83) | 8.21 (5.36) | 0.081 |
| Gleason Score, median (IQR) | 7 (2) | 7 (1) | 0.526 |
| Grade group, N (%) I–III IV–V Missing | 11 (64.7%) 6 (35.3%) - | 11 (68.8%) 4 (25%) 1 (6.2%) | 0.599 |
| Weight at diagnosis, median (IQR) (kg) | 84 (19) | 80 (20) | 0.465 |
| BMI at diagnosis, median (IQR) (kg/m2) | 28.39 (4.94) | 25.22 (5.92) | 0.127 |
| Obesity, N (%) | 7 (41.2) | 3 (18.8) | 0.161 |
| Time to recurrence, median (IQR) (months) | 27.5 (48) | - | - |
| Parameter | CRPC N = 38 (42.7%) | CSPC N = 51 (57.3%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, mean ± SD (years) | 66.45 ± 7 | 67.45 ± 6.83 | 0.499 |
| 10-year all-cause mortality rate (%) | 37.1% | 4.3% | <0.001 |
| PSA at diagnosis, median (IQR) (ng/mL) | 63.53 (132.8) | 14.9 (26.4) | 0.001 |
| Gleason Score, median (IQR) | 8 (2) | 7 (1) | 0.006 |
| Grade group, N (%) I–III IV–V Missing | 10 (26.3%) 21 (55.3%) 7 (18.4%) | 33 (64.7%) 14 (27.5%) 4 (7.8%) | 0.001 |
| Weight at diagnosis, median (IQR) (kg) | 80 (17) | 84 (19) | 0.243 |
| BMI at diagnosis, median (IQR) (kg/m2) | 26.64 (4.28) | 27.31 (6.3) | 0.709 |
| Obesity, N (%) | 7 (18.4) | 18 (35.3) | 0.080 |
| Time to resistance, median (IQR) (months) | 14.5 (14) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mustață, T.; Jinga, D.C.; Lazăr, I.; Martin, S.C.; Sîrbu, A.E.; Fica, S. The Impact of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Progression to Castration Resistance—Real-World Data from a Romanian Center. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093146
Mustață T, Jinga DC, Lazăr I, Martin SC, Sîrbu AE, Fica S. The Impact of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Progression to Castration Resistance—Real-World Data from a Romanian Center. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093146
Chicago/Turabian StyleMustață, Theodor, Dan Corneliu Jinga, Ioana Lazăr, Sorina Carmen Martin, Anca Elena Sîrbu, and Simona Fica. 2025. "The Impact of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Progression to Castration Resistance—Real-World Data from a Romanian Center" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093146
APA StyleMustață, T., Jinga, D. C., Lazăr, I., Martin, S. C., Sîrbu, A. E., & Fica, S. (2025). The Impact of Obesity on Prostate Cancer and Progression to Castration Resistance—Real-World Data from a Romanian Center. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093146







