The Supporting Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Social Aspect
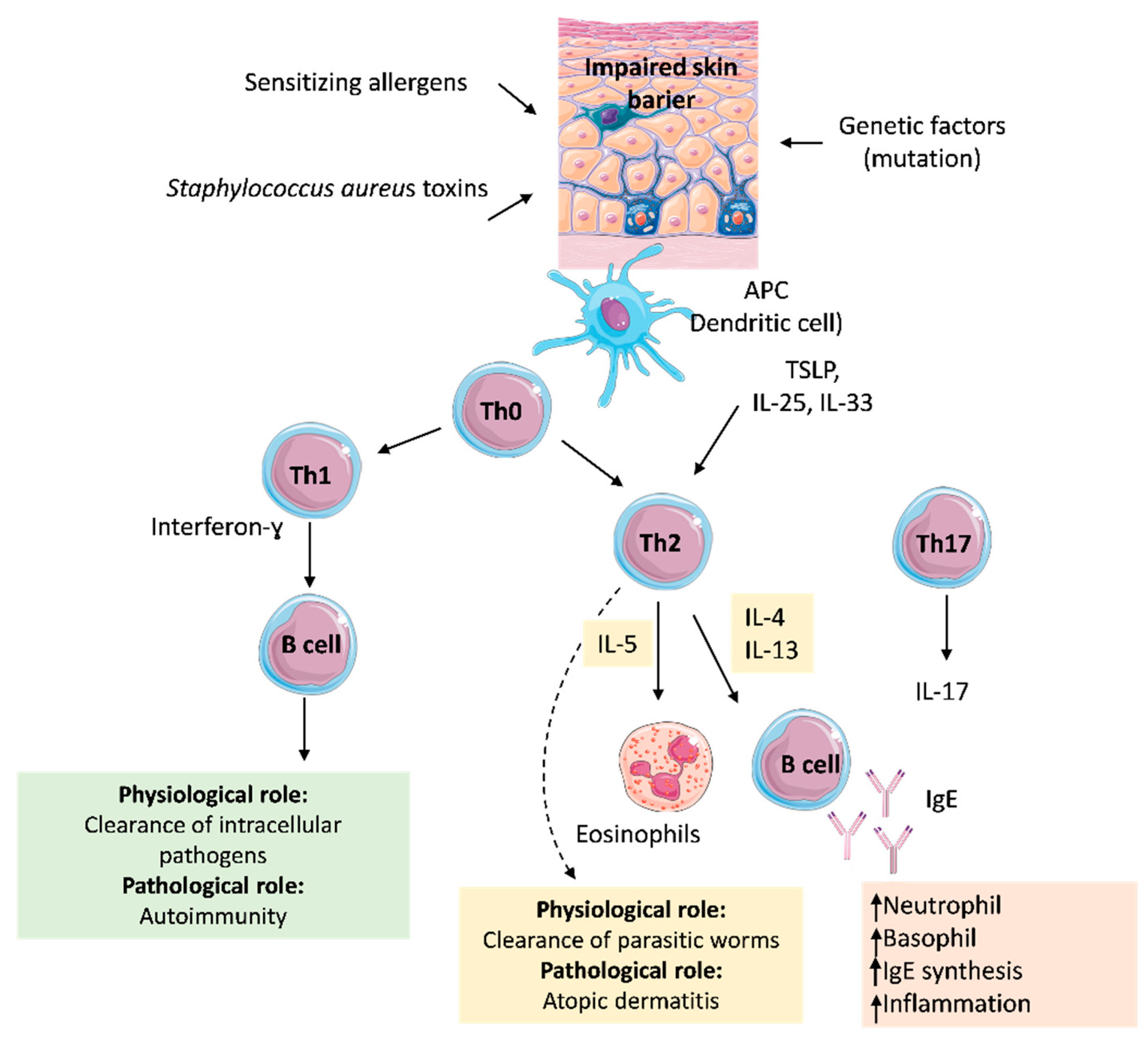
3. Pathomechanism
4. Concomitant Infections
5. Conventional Treatment
5.1. Emollients
5.2. Glucocorticoids and Immunosuppressants
5.3. Biological Treatment
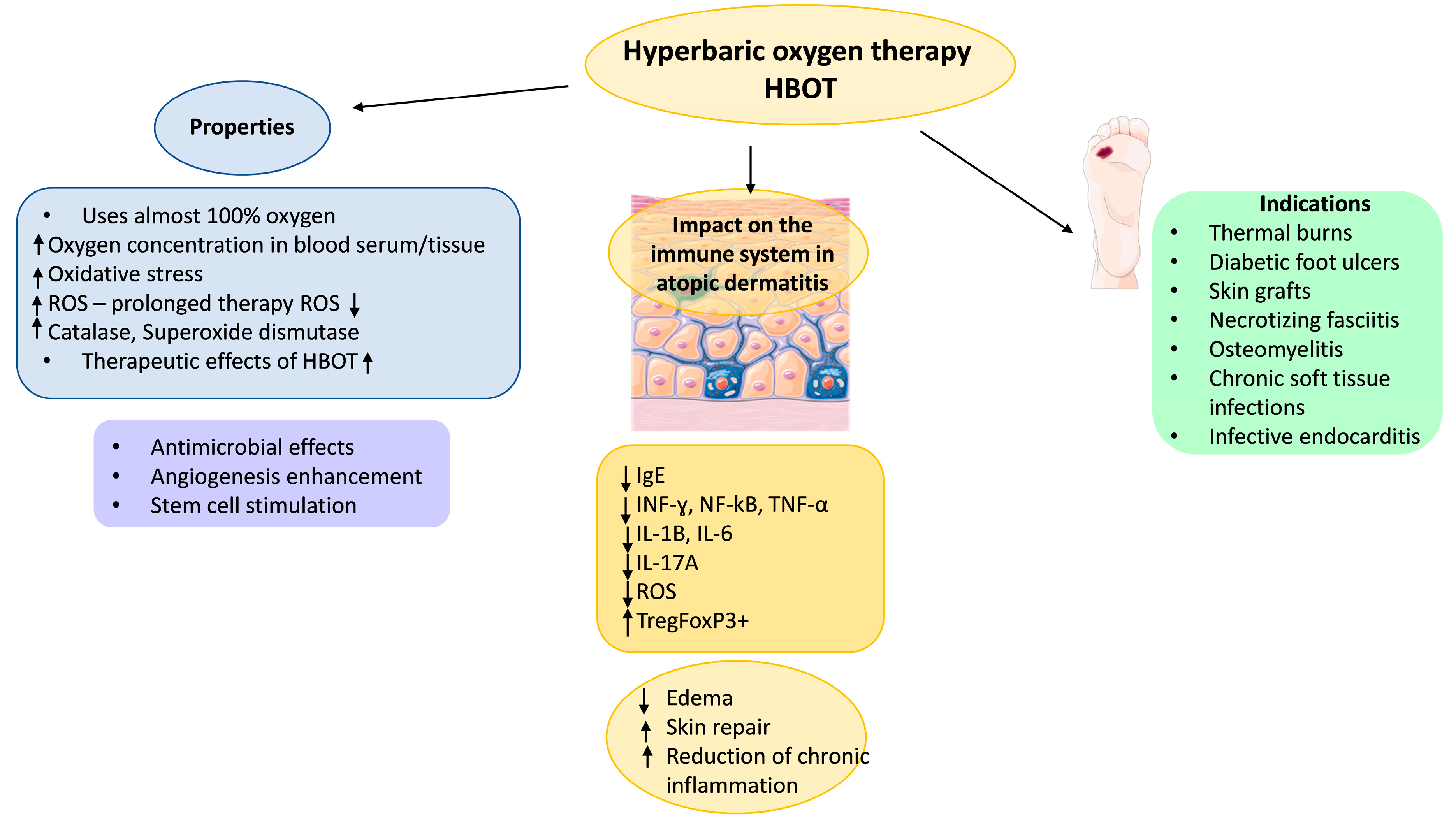
6. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
7. Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis with HBOT
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HBOT | hyperbaric oxygen therapy |
| AD | atopic dermatitis |
| IgE | immunoglobulin E |
| APCs | antigen-presenting cells |
| TSLP | thymic stromal lymphopoietin |
| IL | interleukine |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| EH | eczema herpeticum |
| IFN | interferon |
| TNF | tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SCORAD | scoring atopic dermatitis |
| oSCORAD | objective component of SCORAD |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha |
References
- Qi, S.; Liu, G.; Dong, X.; Huang, N.; Li, W.; Chen, H. Microarray Data Analysis to Identify Differentially Expressed Genes and Biological Pathways Associated with Asthma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatila, T.A. Genetics of Atopic Diseases. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 1998, 10, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautava, S.; Ruuskanen, O.; Ouwehand, A.; Salminen, S.; Isolauri, E. The Hygiene Hypothesis of Atopic Disease—An Extended Version. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Misery, L.; Von Kobyletzki, L.; Armario-Hita, J.C.; Mealing, S.; Redding, M. Unveiling the True Costs and Societal Impacts of Moderate-to-severe Atopic Dermatitis in Europe. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, M.I.; Montefort, S.; Björkstén, B.; Lai, C.K.W.; Strachan, D.P.; Weiland, S.K.; Williams, H. ISAAC Phase Three Study Group Worldwide Time Trends in the Prevalence of Symptoms of Asthma, Allergic Rhinoconjunctivitis, and Eczema in Childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three Repeat Multicountry Cross-Sectional Surveys. Lancet 2006, 368, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, H.A.; Tarmizi, A.I.; Khalid, K.A.; Gajdács, M.; Aslam, A.; Jamshed, S. The Epidemiology and Global Burden of Atopic Dermatitis: A Narrative Review. Life 2021, 11, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarot, S.; Auziere, S.; Gadkari, A.; Girolomoni, G.; Puig, L.; Simpson, E.L.; Margolis, D.J.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Eckert, L. Epidemiology of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults: Results from an International Survey. Allergy 2018, 73, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerta Durango, K.; Chiesa Fuxench, Z.C. Global Burden of Atopic Dermatitis: Examining Disease Prevalence Across Pediatric and Adult Populations World-Wide. Dermatol. Clin. 2024, 42, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raciborski, F.; Jahnz-Rozyk, K.; Kłak, A.; Sybilski, A.J.; Grąbczewska, A.M.; Brzozowska, M.; Śliwczyñski, A.M. Epidemiology and Direct Costs of Atopic Dermatitis in Poland Based on the National Health Fund Register (2008–2017). Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2019, 36, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Marín, H.A.; Silverberg, J.I. Differences between Pediatric and Adult Atopic Dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2022, 39, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bao, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Hong, S.-Z.; Ren, J.; Yang, B.-C.; Wang, P.; Yin, B.; Chu, C.-C.; et al. Global Burden, Incidence and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for Dermatitis: A Systematic Analysis Combined with Socioeconomic Development Status, 1990–2019. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 861053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicras-Mainar, A.; Navarro-Artieda, R.; Carrascosa Carrillo, J.M. Economic Impact of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults: A Population-Based Study (IDEA Study). Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas 2018, 109, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuberbier, T.; Orlow, S.J.; Paller, A.S.; Taïeb, A.; Allen, R.; Hernanz-Hermosa, J.M.; Ocampo-Candiani, J.; Cox, M.; Langeraar, J.; Simon, J.C. Patient Perspectives on the Management of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, A.G.S.; Arents, B.; Fink-Wagner, A.; Seitz, I.A.; Mensing, U.; Wettemann, N.; de Carlo, G.; Ring, J. Out-of-Pocket Costs for Individuals with Atopic Eczema: A Cross-Sectional Study in Nine European Countries. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin Barrier Abnormalities and Immune Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, C.; Yanagihara, S.; Otsuka, A. Innovation in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Emerging Topical and Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitors. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokura, Y.; Phadungsaksawasdi, P.; Ito, T. Atopic Dermatitis as Th2 Disease Revisited. J. Cutan. Immunol. Allergy 2018, 1, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.M.; Lefebvre, D.L.; Dharma, C.; Dai, D.; Lou, W.Y.W.; Subbarao, P.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Sears, M.R.; et al. Predicting the Atopic March: Results from the Canadian Healthy Infant Longitudinal Development Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 601–607.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, L.; Shin, J.I.; López-Sánchez, G.F.; Haro, J.M.; Koyanagi, A.; Kostev, K.; Butler, L.; Barnett, Y.; Oh, H.; Smith, L. Association between Asthma and Work Absence in Working Adults in the United States. J. Asthma 2023, 60, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Deng, X.; Chen, W.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhong, H.; Hao, F. Toll-like Receptor 2 Agonist Pam3CSK4 up-Regulates FcεRI Receptor Expression on Monocytes from Patients with Severe Extrinsic Atopic Dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, J.M.; Paller, A.S. Atopic Dermatitis and the Atopic March. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, S118–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurmond, J.; Stoop, J.N.; Rivellese, F.; Bakker, A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M. Activation of Human Basophils by Combined Toll-like Receptor- and FcεRI-Triggering Can Promote Th2 Skewing of Naive T Helper Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanei, R.; Hasegawa, Y. Immunological Pathomechanisms of Spongiotic Dermatitis in Skin Lesions of Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, M.C.; Yamauchi, P.S. IL-4 and IL-13 Inhibition in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, L.; Shi, V.Y.; Chan, L.S. IL-4 up-Regulates Epidermal Chemotactic, Angiogenic, and pro-Inflammatory Genes and down-Regulates Antimicrobial Genes in Vivo and in Vitro: Relevant in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Cytokine 2013, 61, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Silverberg, J.I. Pathophysiology of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis: Implications for Management in Children. Children 2019, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Dong, C. IL-25 in Allergic Inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisamoto, T.; Suga, H.; Yoshizaki-Ogawa, A.; Sato, S.; Yoshizaki, A. Increased Serum Levels of Tumor Necrosis Factor-like Ligand 1A in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, M. The Role of Th17-Related Cytokines in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymanski, L.; Cios, A.; Lewicki, S.; Szymanski, P.; Stankiewicz, W. Fas/FasL Pathway and Cytokines in Keratinocytes in Atopic Dermatitis—Manipulation by the Electromagnetic Field. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, A.B.; Delevry, D.; Yang, M.; Chuang, C.-C.; Wang, Z.; Bégo-Le-Bagousse, G.; Martins, B.; Wu, E.; Shumel, B.; Wang, J.; et al. Long-Term Effectiveness of Dupilumab in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: Results up to 3 Years from the RELIEVE-AD Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 2107–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oetjen, L.K.; Mack, M.R.; Feng, J.; Whelan, T.M.; Niu, H.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, S.; Trier, A.M.; Xu, A.Z.; Tripathi, S.V.; et al. Sensory Neurons Co-Opt Classical Immune Signaling Pathways to Mediate Chronic Itch. Cell 2017, 171, 217–228.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria-Babí, L.F. Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis: Lessons from Immunology. Dermatol. Pr. Concept. 2022, 12, e2022152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avena-Woods, C. Overview of Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Manag. Care 2017, 23, S115–S123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, V.; Boguniewicz, J.; Boguniewicz, M.; Ong, P.Y. The Infectious Complications of Atopic Dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kindi, A.; Williams, H.; Matsuda, K.; Alkahtani, A.M.; Saville, C.; Bennett, H.; Alshammari, Y.; Tan, S.Y.; O’Neill, C.; Tanaka, A.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Second Immunoglobulin-Binding Protein Drives Atopic Dermatitis via IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 1354–1368.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly, E.; Muller, A.; Lauerma, A.I.; Pivarcsi, A.; Soto, H.; Kemeny, L.; Alenius, H.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.-C.; Meller, S.; Rieker, J.; et al. IL-31: A New Link between T Cells and Pruritus in Atopic Skin Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; Cassidy, S.K.B.; Harrison, O.J.; Ng, W.-I.; Conlan, S.; NISC Comparative Sequencing Program; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A.; Kong, H.H. Staphylococcus Aureus and Staphylococcus Epidermidis Strain Diversity Underlying Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieosilapatham, P.; Kiatsurayanon, C.; Umehara, Y.; Trujillo-Paez, J.V.; Peng, G.; Yue, H.; Nguyen, L.T.H.; Niyonsaba, F. Keratinocytes: Innate Immune Cells in Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 204, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, A.T.; Baba, T.; Chen, X.; Le, T.A.; Kinoshita, H.; Xie, Y.; Kamijo, S.; Hiramatsu, K.; Ikeda, S.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Membrane and Diacylated Lipopeptide Induce Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Keratinocytes through the Toll-like Receptor 2-Toll-like Receptor 6 Pathway. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 985–993, 993.e1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Gao, P.-S.; Grigoryev, D.N.; Rafaels, N.M.; Streib, J.E.; Howell, M.D.; Taylor, P.A.; Boguniewicz, M.; Canniff, J.; Armstrong, B.; et al. Human Atopic Dermatitis Complicated by Eczema Herpeticum Is Associated with Abnormalities in IFN-γ Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 965–973.e1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollenberg, A.; Zoch, C.; Wetzel, S.; Plewig, G.; Przybilla, B. Predisposing Factors and Clinical Features of Eczema Herpeticum: A Retrospective Analysis of 100 Cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 49, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faergemann, J. Atopic Dermatitis and Fungi. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, H.; Heratizadeh, A.; Wichmann, K.; Niebuhr, M.; Crameri, R.; Scheynius, A.; Werfel, T. Malassezia Sympodialis Thioredoxin-Specific T Cells Are Highly Cross-Reactive to Human Thioredoxin in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 92–99.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javad, G.; Taheri Sarvtin, M.; Hedayati, M.T.; Hajheydari, Z.; Yazdani, J.; Shokohi, T. Evaluation of Candida Colonization and Specific Humoral Responses against Candida Albicans in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 849206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjelievskaia, J.; Boytsov, N.; Brouillette, M.A.; Onyekwere, U.; Pierce, E.; Goldblum, O.; Bonafede, M. The Direct and Indirect Costs of Adult Atopic Dermatitis. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2021, 27, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, A.; Yuasa, A.; Yonemoto, N.; Kamei, K.; LoPresti, M.; Murofushi, T.; Ikeda, S. A Systematic Literature Review of Economic Evaluations and Cost Studies of the Treatment of Psoriasis, Atopic Dermatitis, and Chronic Urticaria. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1729–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.; Rind, D.; Chapman, R.; Kumar, V.; Kahn, S.; Carlson, J. Economic Evaluation of Dupilumab for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Cost-Utility Analysis. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2018, 17, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Komura, Y.; Kogure, T.; Kawahara, K.; Yokozeki, H. Economic Assessment of Actual Prescription of Drugs for Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Differences between Dermatology and Pediatrics in Large-Scale Receipt Data. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülpüsch, C.; Weins, A.B.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Reiger, M. A New Era of Atopic Eczema Research: Advances and Highlights. Allergy 2021, 76, 3408–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, K.E.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.H.; Park, Y.M.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.Y. Use of Emollients in Atopic Dermatitis: A Questionnaire Survey Study. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grześk-Kaczyńska, M.; Petrus-Halicka, J.; Kaczyński, S.; Bartuzi, Z.; Ukleja-Sokołowska, N. Should Emollients Be Recommended for the Prevention of Atopic Dermatitis?—New Evidence and Current State of Knowledge. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, R.; Trzeciak, M.; Kaczmarski, M.; Wilkowska, A.; Czarnecka-Operacz, M.; Kowalewski, C.; Rudnicka, L.; Kulus, M.; Mastalerz-Migas, A.; Peregud-Pogorzelski, J.; et al. Atopic Dermatitis. Interdisciplinary Diagnostic and Therapeutic Recommendations of the PTD, PTA, PTP, and PTMR. Part I. Prophylaxis, Topical Treatment, and Phototherapy. Lek. POZ 2019, 5, 335–348. [Google Scholar]
- Cabout, E.; Eymere, S.; Launois, R.; Seité, S.; Delvigne, V.; Taïeb, C.; Reguiai, Z. Cost-Effectiveness of Emollients in the Prevention of Relapse among French Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2021, 101, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncrieff, G.; Lied-Lied, A.; Nelson, G.; Holy, C.E.; Weinstein, R.; Wei, D.; Rowe, S. Cost and Effectiveness of Prescribing Emollient Therapy for Atopic Eczema in UK Primary Care in Children and Adults: A Large Retrospective Analysis of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink. BMC Dermatol. 2018, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchet-Réthoré, S.; Bourdès, V.; Mercenier, A.; Haddar, C.H.; Verhoeven, P.O.; Andres, P. Effect of a Lotion Containing the Heat-Treated Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus Johnsonii NCC 533 on Staphylococcus Aureus Colonization in Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 10, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, K.E.; Chu, D.K.; Schneider, L. Updated Guidelines for Atopic Dermatitis-AAAAI/ACAAI Joint Task Force. JAMA Pediatr. 2024, 178, 961–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, B.U.; Rahman, S.; Dutta, S.; Islam, T.; Nusrat, N.; Chowdhury, K.; Binti Wan Ahmad Fakuradzi, W.F.S.; Haque, M. Management of Atopic Dermatitis: The Role of Tacrolimus. Cureus 2022, 14, e28130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacor, M.L.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Martinelli, N.; Mansueto, P.; Rini, G.B.; Corrocher, R. Comparing Tacrolimus Ointment and Oral Cyclosporine in Adult Patients Affected by Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Bissonnette, R.; Deleuran, M.; Nakahara, T.; Galus, R.; Coleman, A.; Gherardi, G.; Xiao, J.; Dingman, R.; Xu, C.; et al. Dupilumab in Adults with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A 5-Year Open-Label Extension Study. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, M.; So, T.; Duan, W.; Soroosh, P. The Significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-Cell Biology and Immune Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Simpson, E.L.; Reich, K.; Kabashima, K.; Igawa, K.; Suzuki, T.; Mano, H.; Matsui, T.; Esfandiari, E.; Furue, M. An Anti-OX40 Antibody to Treat Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2b Study. Lancet 2023, 401, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.; Briones, J.; Lim, Z.Z.; Chandran, N.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Li, B.K.; Yew, Y.W.; Wee, H.-L. Cost-Effectiveness of Dupilumab and Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis in Singapore. Pharmacoecon Open 2024, 8, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martinez, O.; García-Montero, C.; Callejón-Peláez, E.; Sáez, M.A.; Álvarez-Mon, M.A.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Monserrat, J.; Álvarez-Mon, M.; Bujan, J.; et al. A General Overview on the Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Applications, Mechanisms and Translational Opportunities. Medicina 2021, 57, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, G.; Vezzani, G.; Mrakic Sposta, S.; Rizzato, A.; Enten, G.; Abou-samra, A.; Malacrida, S.; Quartesan, S.; Vezzoli, A.; Camporesi, E. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Ameliorates Osteonecrosis in Patients by Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.D.; Sureda, A.; Batle, J.M.; Tauler, P.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. Scuba Diving Enhances Endogenous Antioxidant Defenses in Lymphocytes and Neutrophils. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teksam, O.; Sabuncuoğlu, S.; Girgin, G.; Özgüneş, H. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Parameters in Children with Carbon Monoxide Poisoning. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, K.; Pontier, J.-M.; Mazur, A.; Buzzacott, P.; Morin, J.; Wang, Q.; Theron, M.; Guerrero, F. Effect of Decompression-Induced Bubble Formation on Highly Trained Divers Microvascular Function. Physiol. Rep. 2013, 1, e00142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, C. Historical Aspects of Hyperbaric Physiology and Medicine. In Respiratory Physiology; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-83962-326-4. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, N.D.; Schwartz, O.; Militianu, D.; Ramon, Y.; Levin, D.; Norman, D.; Melamed, Y.; Shupak, A.; Goldsher, D.; Zinman, C. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy as a Treatment for Stage-I Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2003, 85, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meter, K.W. A Systematic Review of the Application of Hyperbaric Oxygen in the Treatment of Severe Anemia: An Evidence-Based Approach. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2005, 32, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Trends at Prana Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Centre Mumbai, India. NIJS 2019, 10, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, E.-J.; Lee, Y.K.; Kie, J.-H.; Jang, M.H.; Seoh, J.-Y. Hyperoxygenation Attenuated a Murine Model of Atopic Dermatitis through Raising Skin Level of ROS. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oley, M.H.; Oley, M.C.; Aling, D.M.R.; Kalangi, J.A.; Islam, A.A.; Hatta, M.; Patellongi, I.J.; Josh, F.; Faruk, M. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on the Healing of Thermal Burns and Its Relationship with ICAM-1: A Case-Control Study. Ann. Med. Surg. 2021, 61, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatibie, M.J.; Islam, A.A.; Hatta, M.; Moenadjat, Y.; Susilo, R.H.; Rendy, L. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Second-Degree Burn Healing: An Experimental Study in Rabbits. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2019, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D. Efficacy of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Diabetic Foot Ulcers: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian J. Surg. 2022, 45, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Mudgal, S.K.; Jelly, P.; Thakur, K. Efficacy of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Diabetic Foot Ulcer, a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, O.A.; Uridge, A.L.; Hollins, S.; Steeg, K.V. Evaluating the Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Enhancing Skin Graft Outcomes: Mechanisms, Clinical Evidence, and Comparative Efficacy. Oxygen 2024, 4, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Rathored, J. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Future Prospects in Regenerative Therapy and Anti-Aging. Front. Aging 2024, 5, 1368982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Camacho, L.R.; Kormanovski, A.; Del Carmen Castillo-Hernández, M.; Guevara-Balcázar, G.; Lara-Padilla, E. Alterations in Glutathione, Nitric Oxide and 3-Nitrotyrosine Levels Following Exercise and/or Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment in Mice with Diet-Induced Diabetes. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 12, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Wei, H.; Fan, Q. Neuroprotective Effect of Combined Therapy with Hyperbaric Oxygen and Madopar on 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Parkinson’s Disease in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 600, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezgin, D.; Giardina, C.; Perdrizet, G.A.; Hightower, L.E. The Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen on Mitochondrial and Glycolytic Energy Metabolism: The Caloristasis Concept. Cell Stress. Chaperones 2020, 25, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureda, A.; Ferrer, M.D.; Batle, J.M.; Tauler, P.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. Scuba Diving Increases Erythrocyte and Plasma Antioxidant Defenses and Spares NO without Oxidative Damage. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhamodharan, U.; Karan, A.; Sireesh, D.; Vaishnavi, A.; Somasundar, A.; Rajesh, K.; Ramkumar, K.M. Tissue-Specific Role of Nrf2 in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers during Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 138, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, C.-C.; Lin, S.-S.; Yuan, L.-J.; Lu, M.-L.; Ueng, S.W.N.; Yang, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-T.; Lai, P.-L. Upregulation of miR-107 Expression Following Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment Suppresses HMGB1/RAGE Signaling in Degenerated Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resanovic, I.; Gluvic, Z.; Zaric, B.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Jovanovic, A.; Milacic, D.; Isakovic, R.; Isenovic, E.R. Early Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen on Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity/Expression in Lymphocytes of Type 1 Diabetes Patients: A Prospective Pilot Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 2328505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J. Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Combined with Nimodipine on Treatment of Diffuse Brain Injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4651–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiula, M.; Greco, R.; Ferrazzano, L.; Caligiana, A.; Hoxha, K.; Bandini, D.; Longobardi, P.; Spampinato, S.; Tolomelli, A. Integrin-Mediated Adhesive Properties of Neutrophils Are Reduced by Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Patients with Chronic Non-Healing Wound. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0237746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, R.M.; Minter, L.M.; Osborne, B.A.; Granowitz, E.V. Hyperbaric Oxygen Inhibits Stimulus-Induced Proinflammatory Cytokine Synthesis by Human Blood-Derived Monocyte-Macrophages. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 134, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.-C.; Yuan, L.-J.; Chen, L.-H.; Lin, S.-S.; Tsai, T.-T.; Liao, J.-C.; Lai, P.-L.; Chen, W.-J. Beneficial Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen on Human Degenerated Intervertebral Disk Cells via Suppression of IL-1β and P38 MAPK Signal. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Wu, G.; Liang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, C. Hyperbaric Oxygen on Rehabilitation of Brain Tumors after Surgery and Effects on TNF-α and IL-6 Levels. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3277–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wolde, S.D.; Hulskes, R.H.; Weenink, R.P.; Hollmann, M.W.; Van Hulst, R.A. The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygenation on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, G.; Paganini, M.; Giacon, T.A.; Oppio, A.; Vezzoli, A.; Dellanoce, C.; Moro, T.; Paoli, A.; Zanotti, F.; Zavan, B.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, MicroRNA, and Hemoglobin Variations after Administration of Oxygen at Different Pressures and Concentrations: A Randomized Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wolde, S.D.; Hulskes, R.H.; de Jonge, S.W.; Hollmann, M.W.; van Hulst, R.A.; Weenink, R.P.; Kox, M. The Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Markers of Oxidative Stress and the Immune Response in Healthy Volunteers. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 826163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, D. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on 32 Cases of Full-Thickness Skin Grafting for the Repair of Defects on the Hand and Foot. DCC 2018, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Chen, S.-C.; Tsai, S.-C.; Wang, B.-W.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lee, H.-M.; Shyu, K.-G. Hyperbaric Oxygen Induces VEGF Expression through ERK, JNK Andc-Jun/AP-1 Activation in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Villalobos, I.; Casanova-Maldonado, I.; Lois, P.; Prieto, C.; Pizarro, C.; Lattus, J.; Osorio, G.; Palma, V. Hyperbaric Oxygen Increases Stem Cell Proliferation, Angiogenesis and Wound-Healing Ability of WJ-MSCs in Diabetic Mice. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mews, J.; Tomaszewska, A.; Siewiera, J.; Lewicki, S.; Kuczborska, K.; Lipińska-Opałka, A.; Kalicki, B. Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Children with Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Zych, M.; Oliwa, J. Application of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Skin Disease Treatment. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszański, R.; Pachut, M.; Sićko, Z.; Sztaba-Kania, M.; Wilkowska, A. Efficacy of Hyperbaric Oxygenation in Atopic Dermatitis. Bull. Inst. Marit. Trop. Med. Gdyn. 1992, 43, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Olszański, R.; Konarski, M.; Siermontowski, P. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) as a Therapeutic Option for Patients with Atopic Dermatitis (AD)—Own Experiences and Literature Review. Pol. Hyperb. Res. 2017, 60, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennardo, L.; Del Duca, E.; Dastoli, S.; Schipani, G.; Scali, E.; Silvestri, M.; Nisticò, S.P. Potential Applications of Topical Oxygen Therapy in Dermatology. Dermatol. Pr. Concept. 2018, 8, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Gao, L.; Pan, Y.; Fu, Z.; Dou, J.; Huang, J.; Xiang, Y. Effect of ozone on Staphylococcus aureus colonization in patients with atopic dermatitis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018, 43, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doğan, E.; Dinç kaya, H. The Effect of Oxygen on Diaper Dermatitis in Infants: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Neonatal Nurs. 2024, 30, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Yuki, K. SerpinB1 Expression in Th17 Cells Depends on Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewiera, J.; Mews, J.; Królikowska, K.; Kalicki, B.; Jobs, K. Hyperbaric Oxygenation in Pediatrics: Indications in The Light of Evidence–Based Medicine. Dev. Period. Med. 2019, 23, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.M.; Sherif, R.D.; Borab, Z.M.; Ganesh Kumar, N.; Rohrich, R.J. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Aesthetic Medicine and Anti-Aging: A Systematic Review. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simman, R.; Bach, K. Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Cosmetic and Reconstructive Surgery in Ischemic Soft Tissue Wounds: A Case Series. Eplasty 2022, 22, e61. [Google Scholar]
- Chuck, A.W.; Hailey, D.; Jacobs, P.; Perry, D.C. Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Impact of Adjunctive Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 2008, 24, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidia, A.; Laden, G.; Kuhan, G.; Johnson, B.F.; Wilkinson, A.R.; Renwick, P.M.; Masson, E.A.; McCollum, P.T. The Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Ischaemic Diabetic Lower Extremity Ulcers: A Double-Blind Randomised-Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2003, 25, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, R.J.; van Reijen, N.S.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Hoencamp, R.; Koelemay, M.J.; van Hulst, R.A.; Ubbink, D.T. Economic Analysis of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Ischaemic Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2024, 54, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santema, T.B.; Stoekenbroek, R.M.; van Steekelenburg, K.C.; van Hulst, R.A.; Koelemay, M.J.; Ubbink, D.T. Economic Outcomes in Clinical Studies Assessing Hyperbaric Oxygen in the Treatment of Acute and Chronic Wounds. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2015, 45, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camporesi, E.M. Side Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2014, 41, 253–257. [Google Scholar]
- Gawdi, R.; Cooper, J.S. Hyperbaric Contraindications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, A. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in Pregnancy: Maternal and Fetal Outcome. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 43, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, A.C.; Cooper, J.S. Hyperbaric Physiological and Pharmacological Effects of Gases. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
| Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) | |||
| Authors | Group of Patients | Treatment | Significant Observations |
| Mews et al., 2021 [99] | 15 children (3–18 years) with severe AD (SCORAD > 50) | 2.5 ATA, (~250 kPa), 30-day treatment | clinical improvement (reduction in the intensity of pruritus, improvement in sleep quality); |
| significant decrease of IgE in the serum | |||
| Olszański et al., 1992 [101] | 5 patients (8–38 years) with atopic dermatitis | 0.1 MPa pure oxygen, 15 days of treatment | clinical improvement; |
| significant decrease of IgE and the level of C3 and C4 complement | |||
| Olszański et al., 2017 [102] | 10 adult patients (18–44 years) with severe atopic dermatitis who did not respond to standard pharmacotherapy | 10 oxygen exposures at pO2 2.5 ATA each | clinical improvement (local improvement in the dermatological condition, reduction in the experienced itch, reduction in the use of oral antipruritic drugs, i.e., antihistaminic and/or hydroxyzine); |
| significant decrease of IgE and the level of C3 complement | |||
| Topical Oxygen Therapy | |||
| Bennardo et al., 2018 [103] | 24 adult patients with atopic dermatitis (mean age 34 years) with an initial SCORAD disease severity index between 2 and 6. | Ttopical oxygen therapy, 3 sessions of oxygen therapy per week, in total—12 sessions | clinical improvement (decreased SCORAD disease severity index for patients with eczema, and atopic dermatitis showed a decline (the mean score dropped from 3.6 to 2.1 after 12 sessions) |
| Lu et al., 2018 [104] | 12 patients (6–65 years) with moderate or severe AD | ozonated water and smeared with ozonated oil, 7 days of treatment | clinical improvement (decreased SCORAD scores, and pruritus scores, improvementing in sleep quality); a linear correlation between the decreasing percentage of S. aureus S. aureus colony and the declining percentage of SCORAD scores in AD patients |
| Doğan and Dinç Kaya, 2024 [105] | 30 patients (newborns) with diaper dermatitis | oxygen applied for 1 h at each diaper change at a flow rate of 5 L/min and at a concentration of 21% FiO2, which is equivalent to room air. | clinical improvement (administration of oxygen to the diaper dermatitis area reduceds the severity and shorteneds the recovery time of diaper dermatitis) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zwoliński, M.; Hovagimyan, A.; Ignatowicz, J.; Stelmasiak, M.; Lewicka, A.; Bień-Kalinowska, J.; Bałan, B.J.; Lewicki, S. The Supporting Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093138
Zwoliński M, Hovagimyan A, Ignatowicz J, Stelmasiak M, Lewicka A, Bień-Kalinowska J, Bałan BJ, Lewicki S. The Supporting Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093138
Chicago/Turabian StyleZwoliński, Michał, Adrian Hovagimyan, Jakub Ignatowicz, Marta Stelmasiak, Aneta Lewicka, Justyna Bień-Kalinowska, Barbara J. Bałan, and Sławomir Lewicki. 2025. "The Supporting Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093138
APA StyleZwoliński, M., Hovagimyan, A., Ignatowicz, J., Stelmasiak, M., Lewicka, A., Bień-Kalinowska, J., Bałan, B. J., & Lewicki, S. (2025). The Supporting Role of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14093138







