Lipoprotein(a) as a Stroke Biomarker: Pathophysiological Pathways and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Review of Current Literature
3.1. Structure, Genetics, Epidemiology and Quantification of Lp(a)
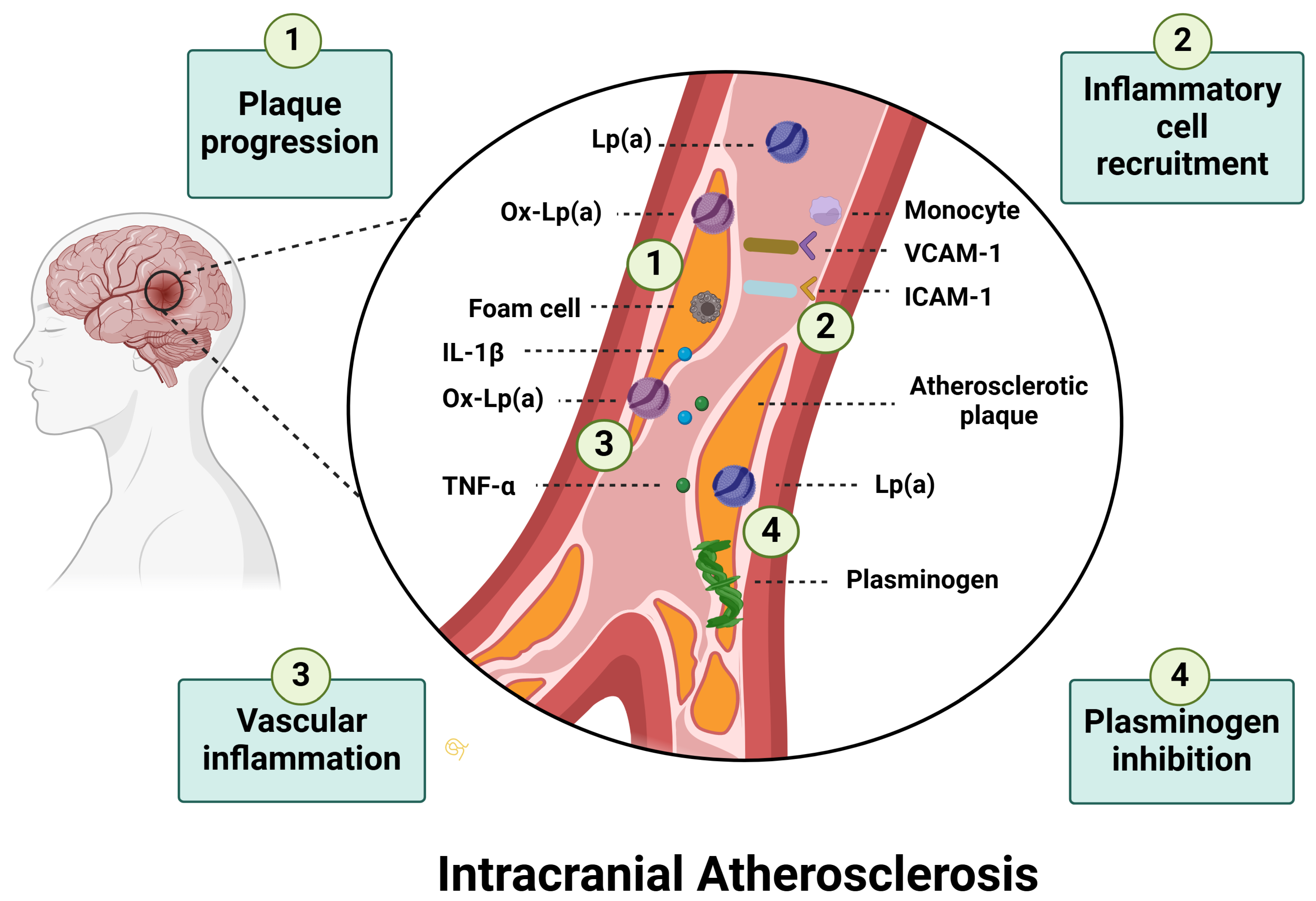
3.2. Pathophysiology in Stroke
3.2.1. Lipoprotein(a) and Ischemic Stroke
3.2.2. Lipoprotein(a) and Ischemic Stroke Subtypes
| Stroke Type | Potential Association with Lp(a) |
|---|---|
| LAA | Elevated Lp(a) is associated with an increased risk of LAA [9]. |
| CE | Elevated Lp(a) is associated with a moderate risk of CE [38]. |
| cSVD | Contradictory findings regarding the association of Lp(a) with cSVD; elevated Lp(a) potentially associated with reduced cSVD risk [39]. |
| Cryptogenic/ESUS | Elevated Lp(a) is associated with a moderate risk of cryptogenic stroke/ESUS [40]. |
| ICH | Contradictory findings regarding the association of Lp(a) with ICH; elevated Lp(a) potentially associated with reduced ICH risk [41]. |
| ICH-CAA | Elevated Lp(a) is associated with potentially protective effects in CAA, based on limited evidence [42]. |
| SAH | Elevated Lp(a) is associated with a moderate risk of SAH, based on preliminary findings [43]. |
Lipoprotein(a) and Large-Artery-Atherosclerosis
Lipoprotein(a) and Small Vessel Disease
Lipoprotein(a) and Cardioembolic Strokes
Lipoprotein(a) and Strokes of Undetermined Etiology
3.2.3. Lipoprotein(a) and Hemorrhagic Stroke
3.2.4. Lipoprotein(a), Post-Stroke Recovery and Stroke Recurrence
3.3. Therapies Targeting Lipoprotein(a)
3.3.1. Existing Strategies
3.3.2. Emerging Therapies
| Therapy Type | Therapy Name | Mechanism of Action | Administration Route | Reduction in Lp(a) Levels | Preclinical or Clinical Trial Phase | Research Question/Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) | Pelacarsen (TQJ230, AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx) | Binds to mRNA and prevents Apo(a) production | Subcutaneous | 30–90% | Phase 3 ongoing (HORIZON trial, NCT04023552) [17] | Whether pelacarsen can reduce the risk of cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, and urgent coronary revascularization requiring hospitalization |
| Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) | Olpasiran (AMG 890) | Degrades LPA mRNA to prevent Apo(a) synthesis | Subcutaneous | Up to 90% | Phase 3 ongoing (OCEAN(a)-Outcomes trial, NCT05581303) [18] | Whether olpasiran can reduce the risk of coronary heart disease death, myocardial infarction, or urgent coronary revascularization |
| Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) | Zerlasiran (SLN360) | Degrades LPA mRNA to prevent Apo(a) synthesis | Subcutaneous | Up to 98% | Phase 2 completed (NCT05537571) [112] | Zerlasiran can reduce Lp(a) levels by more than 80% in patients with ASCVD |
| Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) | Lepodisiran (LY3819469) | Degrades LPA mRNA to prevent Apo(a) synthesis | Subcutaneous | Up to 98% | Phase 1 completed (NCT04914546) [111] | Lepodisiran can be safely tolerated and lead to sustained dose-dependent Lp(a) reductions |
| Small-Molecule Inhibitors | Muvalaplin | Prevents Apo(a) and ApoB-100 interaction | Oral | 45–85% | Phase 2 completed (NCT05563246) [114] | Muvalaplin can reduce Lp(a) levels, but the effects on cardiovascular risk remain unknown |
| Gene Editing | CRISPR-Cas9 | Permanently disrupts the LPA gene | Intravenous | Near elimination in preclinical studies | Preclinical (Non-human primates) [116] | CRISPR-Cas9 can be safe and effective in primates |
3.4. Clinical Applications and Guidance
4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| Apo(a) | Apolipoprotein(a) |
| ApoB-100 | Apolipoprotein B-100 |
| ASOs | Antisense Oligonucleotides |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease |
| BAO | Basilar Artery Occlusion |
| CAA | Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy |
| CAVD | Calcific Aortic Valve Disease |
| CCS | Canadian Cardiovascular Society |
| CCHS | Copenhagen City Heart Study |
| CGPS | Copenhagen General Population Study |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CRISPR-Cas9 | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats–CRISPR-Associated Protein 9 |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| cSVD | Cerebral Small Vessel Disease |
| EAS | European Atherosclerosis Society |
| ECAS | Extracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis |
| ESUS | Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source |
| EVT | Endovascular Therapy |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GBD | Global Burden of Disease |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| ICAD | Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease |
| ICAS | Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis |
| ICH | Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
| ICAM-1 | Intracellular Adhesion Molecule-1 |
| ISNA | In-Stent Neoatherosclerosis |
| KIV | Kringle IV |
| LAA | Large-Artery Atherosclerosis |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein(a) |
| LVO | Large Vessel Occlusion |
| MACE | Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events |
| NLA | National Lipid Association |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| OxPLs | Oxidized Phospholipids |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 |
| PCSK9i | Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors |
| PFO | Patent Foramen Ovale |
| PTAS | Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty and Stenting |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial |
| REGARDS | Reasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke |
| siRNA | Small Interfering RNA |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| TIA | Transient Ischemic Attack |
| TF | Tissue Factor |
| TOAST | Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 |
| VTE | Venous Thromboembolism |
| WSO | World Stroke Organization |
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Brainin, M.; Norrving, B.; Martins, S.O.; Pandian, J.; Lindsay, P.; F Grupper, M.; Rautalin, I. World Stroke Organization: Global Stroke Fact Sheet 2025. Int. J. Stroke 2025, 20, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, W. Cumulative Risk of Stroke Recurrence over the Last 10 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolmos, M.; Christoffersen, L.; Kruuse, C. Recurrent Ischemic Stroke—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flach, C.; Muruet, W.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Bhalla, A.; Douiri, A. Risk and Secondary Prevention of Stroke Recurrence. Stroke 2020, 51, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, C.; Chimowitz, M.I. Stroke Caused by Atherosclerosis of the Major Intracranial Arteries. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Kalra, R.; Callas, P.W.; Alexander, K.S.; Zakai, N.A.; Wadley, V.; Arora, G.; Kissela, B.M.; Judd, S.E.; Cushman, M. Lipoprotein(a) and Risk of Ischemic Stroke in the REGARDS Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampsas, S.; Xenou, M.; Oikonomou, E.; Pantelidis, P.; Lysandrou, A.; Sarantos, S.; Goliopoulou, A.; Kalogeras, K.; Tsigkou, V.; Kalpis, A.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Diseases: From Pathophysiology to Diagnosis and Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.P.; Wang, M.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ng, K.; Kathiresan, S.; Khera, A.V. Lp(a) (Lipoprotein[a]) Concentrations and Incident Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, S.; Kriemler, L.; Dittrich, T.D.; Zietz, A.; Schweizer, J.; Arnold, M.; Peters, N.; Barinka, F.; Jung, S.; Arnold, M.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) as a Blood Marker for Large Artery Atherosclerosis Stroke Etiology: Validation in a Prospective Cohort from a Swiss Stroke Center. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2024, 154, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, T.; Schreiner, P.J.; Morrisett, J.D.; Chambless, L.E.; Rosamond, W.D.; Folsom, A.R. Lipoprotein(a) and Incident Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2006, 37, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Han, L.; Wu, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, T.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhou, C.; Sun, J. Lipoprotein(a) and Stroke: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1178079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Swarnkar, P.; Misra, S.; Nath, M. Lipoprotein(a) Level as a Risk Factor for Stroke and Its Subtype: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendler, J.; Murphy, M.; Yeang, C. Lipoprotein(a) Is a Prevalent yet Vastly Underrecognized Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease. Health Care Curr. Rev. 2024, 12, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nicholls, S.J. Therapeutic Potential of Lipoprotein(a) Inhibitors. Drugs 2024, 84, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Parodi, L.; Frerich, S.; Mayerhofer, E.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Pirruccello, J.P.; Slowik, A.; Rundek, T.; Malik, R.; Dichgans, M.; et al. Genetic Architecture of Stroke of Undetermined Source: Overlap with Known Stroke Etiologies and Associations with Modifiable Risk Factors. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Ference, B.A.; Arsenault, B.J.; Berglund, L.; Dweck, M.R.; Koschinsky, M.; Lambert, G.; Mach, F.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Aortic Stenosis: A European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Statement. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3925–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malick, W.A.; Goonewardena, S.N.; Koenig, W.; Rosenson, R.S. Clinical Trial Design for Lipoprotein(a)-Lowering Therapies: JACC Focus Seminar 2/3. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyovich, A.; Berman, A.N.; Besser, S.A.; Biery, D.W.; Huck, D.M.; Weber, B.; Cannon, C.; Januzzi, J.L.; Booth, J.N., III; Nasir, K.; et al. Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Elevated Lipoprotein(a): Implications for the OCEAN(a)-Outcomes Trial Population. Eur. Heart J. Open 2023, 3, oead077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholzer, C.; Hallman, D.M.; Saha, N.; Sigurdsson, G.; Lackner, C.; Császár, A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Utermann, G. Effects of the Apolipoprotein(a) Size Polymorphism on the Lipoprotein(a) Concentration in 7 Ethnic Groups. Hum. Genet. 1991, 86, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Zychlinski, A.; Kleffmann, T.; Williams, M.J.A.; McCormick, S.P. Proteomics of Lipoprotein(a) Identifies a Protein Complement Associated with Response to Wounding. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, D.G.; Fu, L.; Usher, D.C.; Lavi, E. Detection of Lipoprotein(a) in Intraparenchymal Cerebral Vessels: Correlation with Vascular Pathology and Clinical History. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2001, 71, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemello, K.; Chan, D.C.; Lambert, G.; Watts, G.F. Recent Advances in Demystifying the Metabolism of Lipoprotein(a). Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Soffer, G.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Berglund, L.; Duell, P.B.; Heffron, S.P.; Kamstrup, P.R.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Marcovina, S.M.; Yeang, C.; Koschinsky, M.L.; et al. Lipoprotein(a): A Genetically Determined, Causal, and Prevalent Risk Factor for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, e48–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coassin, S.; Kronenberg, F. Lipoprotein(a) beyond the Kringle IV Repeat Polymorphism: The Complexity of Genetic Variation in the LPA Gene. Atherosclerosis 2022, 349, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, S.; Coassin, S.; Rueedi, R.; Yousri, N.A.; Seppälä, I.; Gieger, C.; Schönherr, S.; Forer, L.; Erhart, G.; Marques-Vidal, P.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Meta-Analysis on Lipoprotein(a) Concentrations Adjusted for Apolipoprotein(a) Isoforms [S]. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkhmaa, B.; Anuurad, E.; Berglund, L. Lipoprotein(a): Impact by Ethnicity and Environmental and Medical Conditions. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmstedt, C.A.; Turan, T.N.; Chimowitz, M.I. Atherosclerotic Intracranial Arterial Stenosis: Risk Factors, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Prabhakaran, S.; Khatri, P.; Liebeskind, D.S. Intracranial Atherosclerotic Disease. Stroke 2019, 50, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, E.; Stefanou, M.-I.; Magoufis, G.; Safouris, A.; Kargiotis, O.; Psychogios, K.; Vassilopoulou, S.; Theodorou, A.; Chondrogianni, M.; Bakola, E.; et al. Prevalence, Diagnosis and Management of Intracranial Atherosclerosis in White Populations: A Narrative Review. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2024, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, J.; Dobiášová, M.; Adler, L.; Francis, M. Gender Differences in Plasma Levels of Lipoprotein(a) in Patients with Angiographically Proven Coronary Artery Disease. Physiol. Res. 2004, 53, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nago, N.; Kayaba, K.; Hiraoka, J.; Matsuo, H.; Goto, T.; Kario, K.; Tsutsumi, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Igarashi, M. Lipoprotein(a) Levels in the Japanese Population: Influence of Age and Sex, and Relation to Atherosclerotic Risk Factors: The Jichi Medical School Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 141, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshotels, M.R.; Sun, C.; Nambi, V.; Virani, S.S.; Matsushita, K.; Yu, B.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Hoogeveen, R.C. Temporal Trends in Lipoprotein(a) Concentrations: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e026762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamstrup, P.R. Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Lipoprotein(a) Concentration and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke, and Nonvascular Mortality. JAMA 2009, 302, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gao, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, H.; Zhou, G.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y. The Relationship Between Serum Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Ischemic Stroke Risk: A Cohort Study in the Chinese Population. Inflammation 2014, 37, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.-A. Prognostic Value of Serum Lipoprotein(a) Levels in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. NeuroReport 2014, 25, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langsted, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Kamstrup, P.R. Elevated Lipoprotein(a) and Risk of Ischemic Stroke. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Shemirani, P.; Chong, M.; Narula, S.; Perrot, N.; Conen, D.; Roberts, J.D.; Thériault, S.; Bossé, Y.; Lanktree, M.B.; Pigeyre, M.; et al. Elevated Lipoprotein(a) and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: An Observational and Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cai, X.; Jing, J.; Wang, S.; Meng, X.; Mei, L.; Yang, Y.; Jin, A.; DongXiao, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Differential Associations of Lipoprotein(a) Level with Cerebral Large Artery and Small Vessel Diseases. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2022, 7, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garagoli, F.; Masson, W.; Barbagelata, L. Association between Elevated Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Vulnerability of Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque: A Systematic Review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, S.; Kotani, K.; Kario, K.; Kayaba, K.; Gotoh, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Kajii, E. Inverse Association between Serum Lipoprotein(a) and Cerebral Hemorrhage in the Japanese Population. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, e54–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Jiang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Qiao, N.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Associations of Lipoprotein(a) Level with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, D.; Zanaty, M.; Roa, J.A.; Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Sabotin, R.; Allan, L.; Samaniego, E.A.; Hasan, D.M. Concentration of Lp(a) (Lipoprotein[a]) in Aneurysm Sac Is Associated with Wall Enhancement of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm. Stroke 2024, 33, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackova, A.; Gdovinova, Z.; Kozarova, M.; Koreň, D.; Lacko, M. Lipoprotein(a) Concentration as a Risk Factor for Ischaemic Stroke and Its Subtypes. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2024, 58, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Ma, T.Y.; Huang, K.; Lu, S.J.; Zhong, J.H.; Li, J.J. Lipoprotein(a)-Related Inflammatory Imbalance: A Novel Horizon for the Development of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2024, 26, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, Y.; Daghem, M.; Tzolos, E.; Meah, M.N.; Doris, M.K.; Moss, A.J.; Kwiecinski, J.; Kroon, J.; Nurmohamed, N.S.; van der Harst, P.; et al. Association of Lipoprotein(a) with Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Jung, H.S.; Bang, O.Y.; Chung, C.S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, G.M. Elevated Serum Lipoprotein(a) as a Potential Predictor for Combined Intracranial and Extracranial Artery Stenosis in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, K.; Denswil, N.P.; Stam, O.C.G.; van Lieshout, J.J.; Daemen, M.J.A.P. Cause and Mechanisms of Intracranial Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2014, 130, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Y.; Fisher, M. Pathological Characteristics. In Intracranial Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment; S.Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ji, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, K. Relationship between Carotid Atherosclerosis and Lipoprotein(a) in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1383771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam-Nolen, D.H.K.; van Dijk, A.C.; van Crombag, G.A.J.C.; Lucci, C.; Kooi, M.E.; Hendrikse, J.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Koudstaal, P.J.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Atherosclerotic Plaque Characteristics in the Carotid Artery: The Plaque at RISK (PARISK) Study. Atherosclerosis 2021, 329, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Qiu, W.; Cai, A.; Kong, B.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, L. The Association of Lipoprotein(a) and Intraplaque Neovascularization in Patients with Carotid Stenosis: A Retrospective Study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Safouris, A.; Kim, D.E.; Alexandrov, A.V. Recent Advances in Primary and Secondary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Stroke. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, Y. Causal Effect of Lp(a) [Lipoprotein(a)] Level on Ischemic Stroke and Alzheimer Disease. Stroke 2019, 50, 3532–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, P.; Imperiale, D.; Fornengo, P.; Bruno, G.; Cassader, M.; Maffeis, P.; Cavallo Perin, P.; Pagano, G.; Bergamasco, B. Higher Lipoprotein(a) Levels in Atherothrombotic than Lacunar Ischemic Cerebrovascular Disease. Neurology 2002, 58, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmark, C.; Dewan, A.; Orsoni, A.; Merki, E.; Miller, E.R.; Shin, M.-J.; Binder, C.J.; Hörkkö, S.; Krauss, R.M.; Chapman, M.J.; et al. A Novel Function of Lipoprotein [a] as a Preferential Carrier of Oxidized Phospholipids in Human Plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2230–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Khan, H.; Nyyssönen, K.; Laukkanen, J.A. Is Lipoprotein(a) Protective of Dementia? Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 31, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Barlingen, H.H.J.J.; Kleinveld, H.A.; Erkelens, D.W.; de Bruin, T.W.A. Lipoprotein Lipase—Enhanced Binding of Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] to Heparan Sulfate Is Improved by Apolipoprotein E (apoE) Saturation: Secretion-Capture Process of ApoE Is a Possible Route for the Catabolism of Lp(a). Metab.—Clin. Exp. 1997, 46, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, S.; Tzourio, C.; Dufouil, C.; Zhu, Y.; Berr, C.; Alpérovitch, A.; Crivello, F.; Mazoyer, B.; Debette, S. Plasma Lipids and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neurology 2014, 83, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, F.F.; Mohamed, G.; Bakry, S.S.; Alqahtani, M.; BinAmir, H.; AlKawi, A.; Alreshaid, A.A.; AlZawahmaha, M.; Alhazzani, A.; Shuaib, A.; et al. Association of White Matter Hyperintensities with Lipoprotein(a) Levels: Insights from a Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1476005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronis, K.N.; Zhao, D.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Alonso, A.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Guallar, E.; Jones, S.R.; Martin, S.S.; Nazarian, S.; Steffen, B.T.; et al. Associations of Lipoprotein(a) Levels with Incident Atrial Fibrillation and Ischemic Stroke: The ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e007372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Zoumi, E.-A.; Rallidis, L.S. Lipoprotein(a) and Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2024, 52, 03000605241264182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lei, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, D. Lipoprotein(a), a Lethal Player in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 812368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisi, M.; Pastore, M.C.; Fiorio, A.; Cameli, M.; Mandoli, G.E.; Righini, F.M.; Cavigli, L.; D’Ascenzi, F.; Focardi, M.; Rubboli, A.; et al. Left Atrial Remodeling in Response to Aortic Valve Replacement: Pathophysiology and Myocardial Strain Analysis. Life 2022, 12, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, M.; Bo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tang, B. Association between Lipoprotein(a) and Thromboembolism in Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehab, O.; Abdollahi, A.; Whelton, S.P.; Wu, C.O.; Ambale-Venkatesh, B.; Post, W.S.; Bluemke, D.A.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lima, J.A.C. Association of Lipoprotein(a) Levels with Myocardial Fibrosis in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 2280–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, K.S.; de Sa Boasquevisque, D.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Taylor, A.; Cheng, A.; Hankey, G.J.; Lee, S.; Fabregas, J.M.; Ameriso, S.F.; Field, T.S.; et al. Evaluating Rates of Recurrent Ischemic Stroke Among Young Adults with Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: The Young ESUS Longitudinal Cohort Study. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Hao, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Xiao, L.; Hao, Y.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) Is Associated with the Progression and Vulnerability of New-Onset Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque. Stroke 2023, 54, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulwa, Z.; Kim, A.; Singh, K.; Kantorovich, A.; Suhail, F. Recurrent Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source in a Patient with Extreme Lipoprotein(a) Levels. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulwa, Z.; Gupta, A. Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: The Role of the Nonstenotic Carotid Plaque. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 382, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Katsanos, A.H.; Köhrmann, M.; Caso, V.; Lemmens, R.; Tsioufis, K.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Bornstein, N.M.; Schellinger, P.D.; Alexandrov, A.V.; et al. Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source: Theoretical Construct or Useful Clinical Tool? Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2019, 12, 1756286419851381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, M.R.; Amarenco, P.; Davis, S.M.; Donnan, G.A. Atheroma of the Aortic Arch: An Important and Poorly Recognised Factor in the Aetiology of Stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, C.A.; Santamarina, E.; Alvarez-Sabín, J. Cryptogenic Stroke, Aortic Arch Atheroma and Patent Foramen Ovale. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 24, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentali, F.; Gessi, V.; Marcucci, R.; Gianni, M.; Grandi, A.M.; Franchini, M. Lipoprotein(a) as a Risk Factor for Venous Thromboembolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of the Literature. Thieme E-J.—Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2017, 43, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, J.; Galli, L.; Schrutka, L.; Haider, P.; Hengstenberg, C.; Gabriel, H.; Krychtiuk, K.; Speidl, W. Lipoprotein(a) Levels in Patients with Cryptogenic Stroke and Persistent Foramen Ovale. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, ehae666-2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtian, A.; Shitole, S.G.; Segal, A.Z.; Leifer, D.; Tracy, R.P.; Rader, D.J.; Devereux, R.B.; Kizer, J.R. Lipoprotein(a) Level, Apolipoprotein(a) Size, and Risk of Unexplained Ischemic Stroke in Young and Middle-Aged Adults. Atherosclerosis 2016, 253, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Daly, D.; Rodriguez Morales, P.; Alabyad, D.; Minja, F.; Lemuel-Clarke, M.; Henriquez, L.; Navalkele, D.; Sperling, L.; Lundberg, G.P.; et al. Abstract TP185: Lipoprotein(a) Levels In Patients with Embolic Stroke Of Undetermined Source And Its Association with Non-Stenotic Atherosclerotic Disease. Stroke 2023, 54, ATP185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, R.; Cui, L.; Qiu, L.; Lin, S.; Peng, B. Association between Lipoprotein(a) Concentration and the Risk of Stroke in the Chinese Han Population: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, A.; Liao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Pentanucleotide TTTTA Repeat Polymorphism of Apolipoprotein(a) Gene and Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Are Associated with Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Chinese. Stroke 2003, 34, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Clarke, R.; Bennett, D.; Guo, Y.; Walters, R.G.; Hill, M.; Parish, S.; Millwood, I.Y.; Bian, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Causal Associations of Blood Lipids with Risk of Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Chinese Adults. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Yao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, B.; Ni, J. Clinical Characteristics of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy and Risk Factors of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Related Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaterra-Pastra, A.; Fernández-de-Retana, S.; Rivas-Urbina, A.; Puig, N.; Benítez, S.; Pancorbo, O.; Rodríguez-Luna, D.; Pujadas, F.; del Mar Freijo, M.; Tur, S.; et al. Comparison of Plasma Lipoprotein Composition and Function in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.; Roberts, G.; Bolger, C.; El Baghdady, A.; Bouchier-Hayes, D.; Farrell, M.; Collins, P. Lipoprotein(a): A Potential Biological Marker for Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, B.; Vishnoi, G.; Goswami, B.; Gowda, S.H.; Chowdhury, D.; Agarwal, S. Lipoprotein(a), Ferritin, and Albumin in Acute Phase Reaction Predicts Severity and Mortality of Acute Ischemic Stroke in North Indian Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, e159–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolescu, B.N.; Berteanu, M.; Dumitru, L.; Dinu, H.; Iliescu, A.; Fărcășanu, I.C.; Oprea, E.; Vlădoiu, S.; Popa, O.; Ianăș, O. Dynamics of Inflammatory Markers in Post-Acute Stroke Patients Undergoing Rehabilitation. Inflammation 2011, 34, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhong, X.; Yuan, K.; Miao, M.; Zhai, Y.; Che, B.; Xu, T.; Xu, X.; Zhong, C. Lipoprotein(a) and Functional Outcome of Acute Ischemic Stroke When Discordant with Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 99, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.S.; Nave, A.H.; Liman, T.G.; Grittner, U.; Endres, M.; Ebinger, M. Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Recurrent Vascular Events After First Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Hao, X.; Zhan, R.; Jiang, X.; Jin, A.; Xue, J.; Cheng, A.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Meng, X.; et al. Effect of Lipoprotein(a) on Stroke Recurrence Attenuates at Low LDL-C (Low-Density Lipoprotein) and Inflammation Levels. Stroke 2022, 53, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosário, M.; Fonseca, A.C. Update on Biomarkers Associated with Large-Artery Atherosclerosis Stroke. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shi, K.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Duan, M.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, T.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.; et al. Correlation between Lipoprotein(a) and Recurrent Ischemic Events Post-Cerebral Vascular Stent Implantation. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Han, Y.; Hu, X.; Jiang, M.; Feng, H.; Fang, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L. Lipoprotein(a) Is Related to In-Stent Neoatherosclerosis Incidence Rate and Plaque Vulnerability: Optical Coherence Tomography Study. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 39, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Kong, W.; Zhang, W. Serum Lipoprotein(a) as Predictive Factor for Early Neurological Deterioration of Acute Ischemic Stroke After Thrombolysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 3791–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidaemias: Lipid Modification to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, G.J.; Thanassoulis, G.; Anderson, T.J.; Barry, A.R.; Couture, P.; Dayan, N.; Francis, G.A.; Genest, J.; Grégoire, J.; Grover, S.A.; et al. 2021 Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Adults. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 1129–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimikas, S.; Gordts, P.L.S.M.; Nora, C.; Yeang, C.; Witztum, J.L. Statin Therapy Increases Lipoprotein(a) Levels. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeit, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Nestel, P.J.; Simes, J.; Tonkin, A.M.; Pedersen, T.R.; Schwartz, G.G.; Olsson, A.G.; Colhoun, H.M.; Kronenberg, F.; et al. Baseline and On-Statin Treatment Lipoprotein(a) Levels for Prediction of Cardiovascular Events: Individual Patient-Data Meta-Analysis of Statin Outcome Trials. Lancet 2018, 392, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, M.; Teng, J. Lipoprotein(a) and Residual Vascular Risk in Statin-Treated Patients with First Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Prospective Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 1004264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmakis, I.; Doundoulakis, I.; Pagiantza, A.; Zafeiropoulos, S.; Antza, C.; Karvounis, H.; Giannakoulas, G. Lipoprotein(a) Reduction with Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukema, J.W.; Zijlstra, L.E.; Bhatt, D.L.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Drexel, H.; Goodman, S.G.; Kim, Y.U.; Pordy, R.; Reiner, Ž.; et al. Effect of Alirocumab on Stroke in ODYSSEY OUTCOMES. Circulation 2019, 140, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Pedersen, T.R.; Saver, J.L.; Sever, P.S.; Keech, A.C.; Bohula, E.A.; Murphy, S.A.; Wasserman, S.M.; Honarpour, N.; Wang, H.; et al. Stroke Prevention with the PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin-Kexin Type 9) Inhibitor Evolocumab Added to Statin in High-Risk Patients with Stable Atherosclerosis. Stroke 2020, 51, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebkar, A.; Reiner, Ž.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Ferretti, G.; Cicero, A.F.G. Effect of Extended-Release Niacin on Plasma Lipoprotein(a) Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Metab.—Clin. Exp. 2016, 65, 1664–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, J.J.; Slee, A.; O’Brien, K.D.; Robinson, J.G.; Kashyap, M.L.; Kwiterovich, P.O.; Xu, P.; Marcovina, S.M. Relationship of Apolipoproteins A-1 and B, and Lipoprotein(a) to Cardiovascular Outcomes: The AIM-HIGH Trial (Atherothrombosis Intervention in Metabolic Syndrome with Low HDL/High Triglyceride and Impact on Global Health Outcomes). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasman, D.I.; Shiffman, D.; Zee, R.Y.L.; Louie, J.Z.; Luke, M.M.; Rowland, C.M.; Catanese, J.J.; Buring, J.E.; Devlin, J.J.; Ridker, P.M. Polymorphism in the Apolipoprotein(a) Gene, Plasma Lipoprotein(a), Cardiovascular Disease, and Low-Dose Aspirin Therapy. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, C.; Wood, M.J.A. Antisense Oligonucleotides: The next Frontier for Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viney, N.J.; van Capelleveen, J.C.; Geary, R.S.; Xia, S.; Tami, J.A.; Yu, R.Z.; Marcovina, S.M.; Hughes, S.G.; Graham, M.J.; Crooke, R.M.; et al. Antisense Oligonucleotides Targeting Apolipoprotein(a) in People with Raised Lipoprotein(a): Two Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Ranging Trials. Lancet 2016, 388, 2239–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Tsamoulis, D.; Koulopoulos, A.; Echavarria Uceta, R.; Guzman, E.; Rallidis, L.S. Novel Pharmacological Therapies for the Management of Hyperlipoproteinemia(a). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Aigner, A. Therapeutic siRNA: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. BioDrugs 2022, 36, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, M.J.; Moriarty, P.M.; Baum, S.J.; Neutel, J.; Hernandez-Illas, M.; Weintraub, H.S.; Florio, M.; Kassahun, H.; Melquist, S.; Varrieur, T.; et al. Preclinical Development and Phase 1 Trial of a Novel siRNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a). Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Rosenson, R.S.; Gencer, B.; López, J.A.G.; Lepor, N.E.; Baum, S.J.; Stout, E.; Gaudet, D.; Knusel, B.; Kuder, J.F.; et al. Small Interfering RNA to Reduce Lipoprotein(a) in Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K.; Watts, G.F.; Koren, M.J.; Fok, H.; Nicholls, S.J.; Rider, D.A.; Cho, L.; Romano, S.; Melgaard, C.; et al. Single Ascending and Multiple-Dose Trial of Zerlasiran, a Short Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a): A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 331, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Linnebjerg, H.; Shen, X.; Wolski, K.; Ma, X.; Lim, S.; Michael, L.F.; Ruotolo, G.; Gribble, G.; Navar, A.M.; et al. Lepodisiran, an Extended-Duration Short Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a): A Randomized Dose-Ascending Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 2075–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wang, Q.; Nicholls, S.J.; Navar, A.M.; Ray, K.K.; Schwartz, G.G.; Szarek, M.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Troquay, R.; Dorresteijn, J.A.N.; et al. Zerlasiran—A Small-Interfering RNA Targeting Lipoprotein(a): A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2024, 332, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Nelson, A.J.; Michael, L.F. Oral Agents for Lowering Lipoprotein(a). Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2024, 35, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, S.J.; Ni, W.; Rhodes, G.M.; Nissen, S.E.; Navar, A.M.; Michael, L.F.; Haupt, A.; Krege, J.H. Oral Muvalaplin for Lowering of Lipoprotein(a): A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2025, 333, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. The New Frontier of Genome Engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 2014, 346, 1258096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerfler, A.M.; Park, S.H.; Assini, J.M.; Youssef, A.; Saxena, L.; Yaseen, A.B.; Giorgi, M.D.; Chuecos, M.; Hurley, A.E.; Li, A.; et al. LPA Disruption with AAV-CRISPR Potently Lowers Plasma Apo(a) in Transgenic Mouse Model: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 27, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baragetti, A.; Da Dalt, L.; Norata, G.D. New Insights into the Therapeutic Options to Lower Lipoprotein(a). Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 54, e14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Ference, B.A.; Staley, J.R.; Freitag, D.F.; Mason, A.M.; Nielsen, S.F.; Willeit, P.; Young, R.; Surendran, P.; Karthikeyan, S.; et al. Association of LPA Variants with Risk of Coronary Disease and the Implications for Lipoprotein(a)-Lowering Therapies: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F.; Mora, S.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Ference, B.A.; Arsenault, B.J.; Berglund, L.; Dweck, M.R.; Koschinsky, M.L.; Lambert, G.; Mach, F.; et al. Frequent Questions and Responses on the 2022 Lipoprotein(a) Consensus Statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Atherosclerosis 2023, 374, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.P.; Jacobson, T.A.; Jones, P.H.; Koschinsky, M.L.; McNeal, C.J.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Orringer, C.E. Use of Lipoprotein(a) in Clinical Practice: A Biomarker Whose Time Has Come. A Scientific Statement from the National Lipid Association. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2022, 16, e77–e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panagiotopoulos, E.; Palaiodimou, L.; Theodorou, A.; Papagiannopoulou, G.; Bakola, E.; Chondrogianni, M.; Psychogios, K.; Kargiotis, O.; Safouris, A.; Vlachopoulos, C.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) as a Stroke Biomarker: Pathophysiological Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092990
Panagiotopoulos E, Palaiodimou L, Theodorou A, Papagiannopoulou G, Bakola E, Chondrogianni M, Psychogios K, Kargiotis O, Safouris A, Vlachopoulos C, et al. Lipoprotein(a) as a Stroke Biomarker: Pathophysiological Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092990
Chicago/Turabian StylePanagiotopoulos, Evangelos, Lina Palaiodimou, Aikaterini Theodorou, Georgia Papagiannopoulou, Eleni Bakola, Maria Chondrogianni, Klearchos Psychogios, Odysseas Kargiotis, Apostolos Safouris, Charalambos Vlachopoulos, and et al. 2025. "Lipoprotein(a) as a Stroke Biomarker: Pathophysiological Pathways and Therapeutic Implications" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092990
APA StylePanagiotopoulos, E., Palaiodimou, L., Theodorou, A., Papagiannopoulou, G., Bakola, E., Chondrogianni, M., Psychogios, K., Kargiotis, O., Safouris, A., Vlachopoulos, C., Giannopoulos, S., Themistocleous, M., Lambadiari, V., Tsivgoulis, G., & Stefanou, M.-I. (2025). Lipoprotein(a) as a Stroke Biomarker: Pathophysiological Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092990








