Challenges and Opportunities of Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC) Therapy in Complex Clinical Scenarios: A Comprehensive Review and Practical Guide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. DOACs Characteristics
3. DOACs in Different Clinical Scenarios
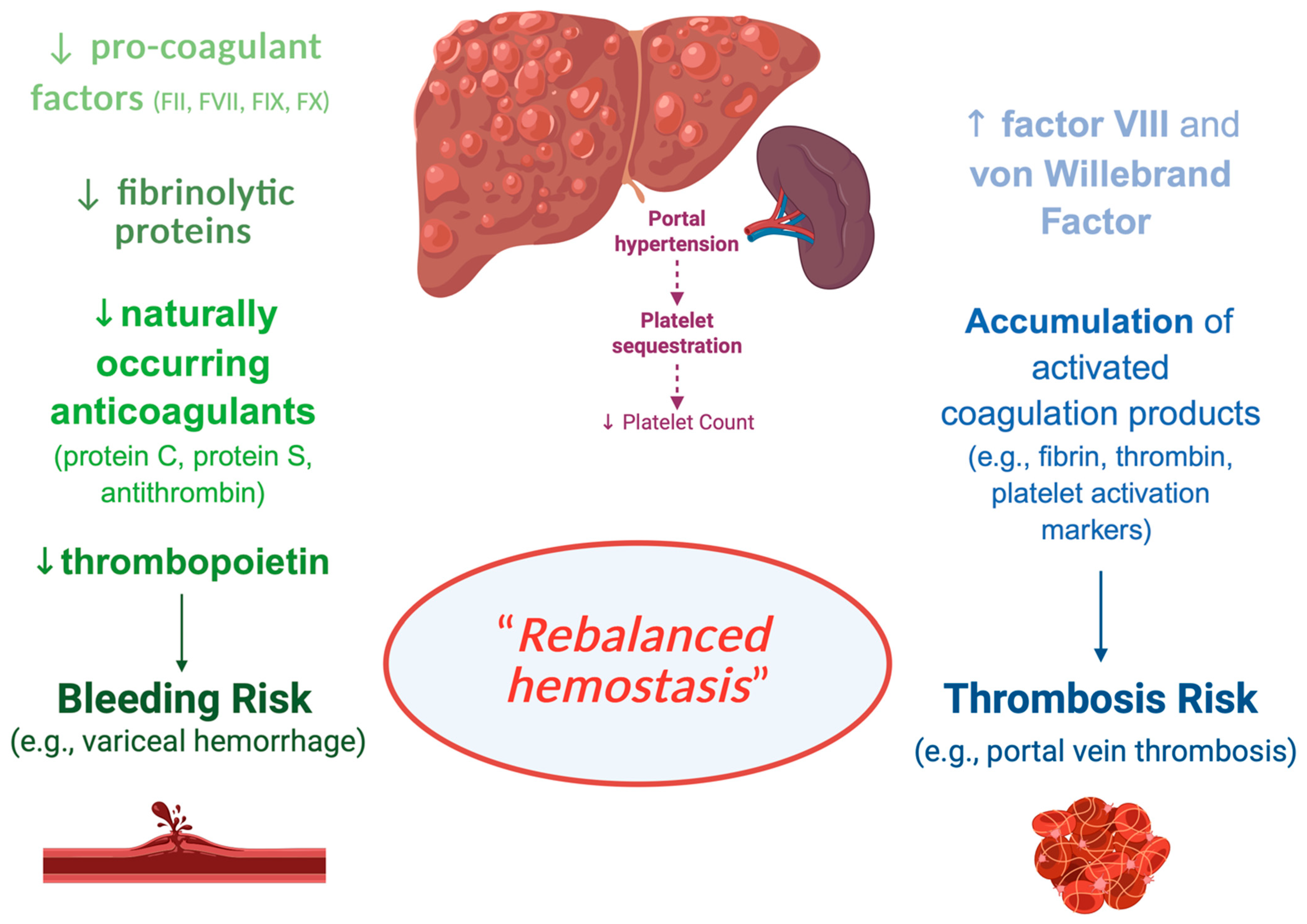
3.1. DOACs in Chronic Liver Diseases
3.2. DOACs in Advanced-Stage Chronic Kidney Disease
3.3. DOACs in Nephrotic Syndrome
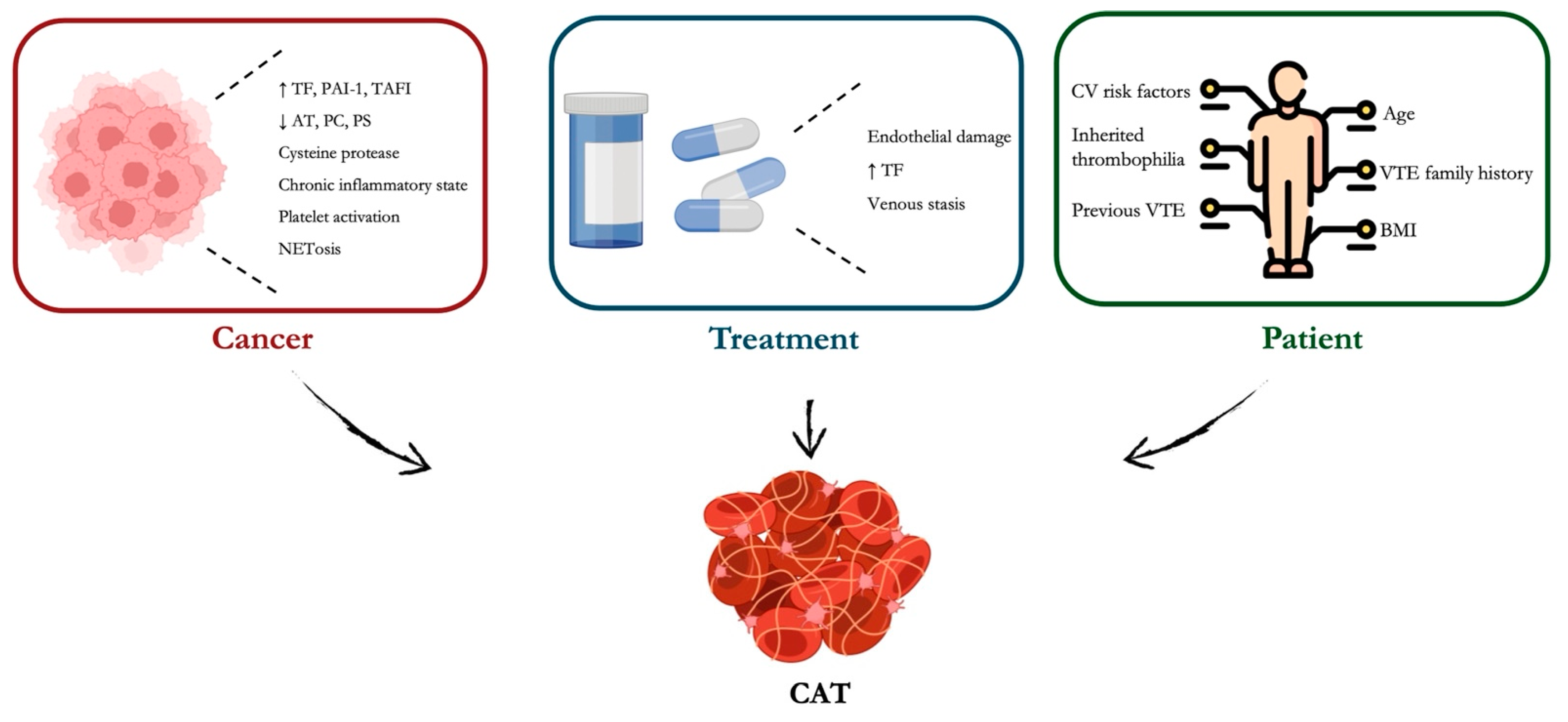
3.4. DOACs in Cancer
3.5. DOACs in Obesity
3.6. DOACs in Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome
3.7. DOACs in Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source
3.8. DOACs in Superficial Venous Thrombosis
3.9. DOACs in Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis
3.10. DOACs in Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis
3.11. DOACs in Pelvic Vein Thrombosis in Women
3.12. DOACs in Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
| Clinical Condition | DOACs | Evidence Strength | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Liver Disease | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban | Moderate [11] | Limited data in Child–Pugh B, contraindicated in Child–Pugh C |
| Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban (cautious use) | Moderate [40,45] | Limited RCTs for stage IV-V CKD and dialysis patients |
| Nephrotic Syndrome | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban | Low [55,56] | Limited pharmacokinetic studies |
| Cancer-Associated Thrombosis | Apixaban, Edoxaban, Rivaroxaban | High [63,74,79] | Increased bleeding risk in GI cancers |
| Obesity | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban | High [89,93] | Caution in BMI > 50 kg/m2 |
| Antiphospholipid Syndrome | Rivaroxaban (not recommended), Apixaban | Low [101,102,103,104] | Contraindicated in triple-positive APS |
| Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source | Rivaroxaban, Dabigatran, Apixaban | Mixed [105,107,109,110] | No significant benefit over aspirin |
| Superficial Venous Thrombosis | Rivaroxaban, Apixaban | Low [114,115,116] | Not first-line; fondaparinux preferred |
| Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban | Low [124,125,126,127] | Limited RCTs |
| Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban | Low [132,133,134,135] | Limited real-world data |
| Pelvic Vein Thrombosis | Rivaroxaban, Apixaban | Low [138] | Extrapolated data from other VTE studies |
| Cerebral Venous Thrombosis | Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban | Moderate [138,139] | Need for larger RCTs |
3.13. DOACs in COVID-19
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, A.; Stecker, E.; Warden, B.A. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Use: A Practical Guide to Common Clinical Challenges. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gorp, R.H.; Schurgers, L.J. New Insights into the Pros and Cons of the Clinical Use of Vitamin K Antagonists (VKAs) Versus Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs). Nutrients 2015, 7, 9538–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ageno, W.; Donadini, M. Breadth of Complications of Long-Term Oral Anticoagulant Care. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2018, 2018, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, G.D.; Ageno, W.; Ansell, J.; Kaatz, S.; Subcommittee on the Control of Anticoagulation of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Recommendation on the Nomenclature for Oral Anticoagulants: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1154–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, T.; Porte, R.J. Rebalanced Hemostasis in Patients with Liver Disease: Evidence and Clinical Consequences. Blood 2010, 116, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aster, R.H. Pooling of Platelets in the Spleen: Role in the Pathogenesis of “Hypersplenic” Thrombocytopenia. J. Clin. Investig. 1966, 45, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, P.; Tarantino, L.; Di Minno, G.; Paternoster, M.; Graziano, V.; Petitto, M.; Nasto, A.; Di Minno, M.N. The Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.N.; Bernal, W. Incidence of Bleeding and Thrombosis in Patients with Liver Disease. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, P.; Tapper, E.B.; Deleuran, T.; Kazankov, K.; Askgaard, G.; Sørensen, H.T.; Vilstrup, H.; West, J. Risk and Outcome of Venous and Arterial Thrombosis in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Danish Nationwide Cohort Study. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2725–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, T.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Magnusson, M.; Roberts, L.; Stanworth, S.; Thachil, J.; Tripodi, A. The Concept of Rebalanced Hemostasis in Patients with Liver Disease: Communication from the ISTH SSC Working Group on Hemostatic Management of Patients with Liver Disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, O.D.; Aronow, H.D.; Hume, A.L.; Shobayo, F.; Matson, K.L.; Barbour, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X. Venous Thromboembolism, Chronic Liver Disease and Anticoagulant Choice: Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants versus Warfarin. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 8, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gottardi, A.; Trebicka, J.; Klinger, C.; Plessier, A.; Seijo, S.; Terziroli, B.; Magenta, L.; Semela, D.; Buscarini, E.; Langlet, P.; et al. Antithrombotic Treatment with Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Splanchnic Vein Thrombosis and Cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffel, J.; Verhamme, P.; Potpara, T.S.; Albaladejo, P.; Antz, M.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; et al. The 2018 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the Use of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1330–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, R.S.; Davitkov, P.; Ko, C.W.; Rajasekhar, A.; Su, G.L.; Sultan, S.; Allen, A.M.; Falck-Ytter, Y. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Coagulation Disorders in Patients with Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 1615–1627.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, E.; Bianchini, M.; Blasi, A.; Denys, A.; Giannini, E.G.; De Gottardi, A.; Lisman, T.; De Raucourt, E.; Ripoll, C.; Rautou, P.E. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on Prevention and Management of Bleeding and Thrombosis in Patients with Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1151–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubitza, D.; Roth, A.; Becka, M.; Alatrach, A.; Halabi, A.; Hinrichsen, H.; Mueck, W. Effect of Hepatic Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Single Dose of Rivaroxaban, an Oral, Direct Factor Xa Inhibitor. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 76, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolato, M.; Paratore, M.; Di Gialleonardo, L.; Marrone, G.; Grieco, A. Direct Oral Anticoagulant Administration in Cirrhotic Patients with Portal Vein Thrombosis: What is the Evidence? World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Xu, X.; De Stefano, V.; Plessier, A.; Noronha Ferreira, C.; Qi, X. Anticoagulation Favors Thrombus Recanalization and Survival in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis: Results of a Meta-Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 495–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisly, S.A.; Mihm, A.E.; Gillette, C.; Davis, K.A.; Tillett, J. Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Mild to Moderate Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 52, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.H.; Dong, W.G.; Tan, X.P.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Efficacy and Safety Study of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Chronic Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 1395–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, C.; Galante, A.; Fasoli, A.; De Gottardi, A. When and How to Use Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Advanced Chronic Liver Disease? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 60, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douros, A.; Cui, Y.; Platt, R.W.; Filion, K.B.; Sebastiani, G.; Renoux, C. Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants Among Patients with Non-Valvular Atrial Fibrillation and Liver Disease: A Multinational Cohort Study. Thromb. Res. 2024, 237, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.R.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, E.K.; Han, K.D.; Jung, J.H.; Cha, M.J.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Liver Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 3295–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitawala, A.A.; Gupta, V. Budd–Chiari Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558941/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Thapa, S.B.; Souza, G.R.; Paravathaneni, M.; Cohen, S.; Mohammed, T.; Laber, D.A. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Budd–Chiari Syndrome. Eur. J. Haematol. 2025, 114, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, N.; Ageno, W. How to Manage Splanchnic Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Liver Disease. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2023, 2023, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senzolo, M.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C. A Major Research Gap: The Use of Anticoagulants in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautou, P.E.; Caldwell, S.H.; Villa, E. Bleeding and Thrombotic Complications in Patients with Cirrhosis: A State-of-the-Art Appraisal. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2110–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, L.; de Raucourt, E.; Valla, D.C.; Villa, E. Anticoagulation in the Cirrhotic Patient. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz Renó, L.; Tustumi, F.; Waisberg, D.R.; Rocha-Santos, V.; Pinheiro, R.S.; Macedo, R.A.; Nacif, L.S.; Ducatti, L.; De Martino, R.B.; Trevisan, A.M.; et al. Venous Thromboembolism in In-Hospital Cirrhotic Patients: A Systematic Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1027882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoul, M.; Aoun, M.; Imani, M.M. The Major Global Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e342–e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, S.; Kaba, R.A.; Delanerolle, G.; Field, B.C.T.; Lip, G.Y.H.; de Lusignan, S. Correct Dosing, Adherence and Persistence of DOACs in Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Heart 2023, 10, e002340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Tanahashi, N.; Momomura, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Goto, S.; Izumi, T.; Koretsune, Y.; Kajikawa, M.; Kato, M.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs. Warfarin in Japanese Patients with Atrial Fibrillation—The J-ROCKET AF Study. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Avezum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Špinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.; Carnicelli, A.P.; Hua, K.; Wallentin, L.; Patel, M.R.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Giugliano, R.P.; Fox, K.A.A.; Hijazi, Z.; Lopes, R.D.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin Across the Spectrum of Kidney Function: Patient-Level Network Meta-Analyses from COMBINE AF. Circulation 2023, 147, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, S.L.; Mavrakanas, T.A.; Harel, Z. Oral Anticoagulation Use in Individuals with Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Review. In Seminars in Nephrology; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2024; p. 151517. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, M.; Scaria, A.; Andrade, J.; Badve, S.V.; Birks, P.; Bota, S.E.; Campain, A.; Djurdjev, O.; Garg, A.X.; Ha, J.; et al. Kidney Function and the Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants vs. Warfarin in Adults with Atrial Fibrillation: A Multicenter Observational Study. Eur. Heart J. Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2023, 9, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, M.R.; Ashton, V.; Moore, K.T.; Shrivastava, S.; Peterson, E.D.; Ammann, E.M. Rivaroxaban versus Warfarin in Patients with Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation and Stage IV–V Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. Heart J. 2020, 223, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, K.; Lamparter, M. Prescription of DOACs in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation at Different Stages of Renal Insufficiency. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 4264–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Akao, M.; Yoshida, T.; Kawata, M.; Okazaki, O.; Akashi, S.; Eshima, K.; Tanizawa, K.; Fukuzawa, M.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Low-Dose Edoxaban in Very Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS Focused Update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuno, T.; Takagi, H.; Ando, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyashita, S.; Valentin, N.; Shimada, Y.J.; Kodaira, M.; Numasawa, Y.; Briasoulis, A.; et al. Oral Anticoagulation for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation on Long-Term Hemodialysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorney, S.D.; Chertow, G.M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Gallup, D.; Dignacco, P.; Mussina, K.; Bansal, N.; Gadegbeku, C.A.; Garcia, D.A.; Garonzik, S.; et al. Apixaban for Patients with Atrial Fibrillation on Hemodialysis: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation 2022, 146, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinecke, H.; Engelbertz, C.; Bauersachs, R.; Breithardt, G.; Echterhoff, H.H.; Gerß, J.; Haeusler, K.G.; Hewing, B.; Hoyer, J.; Juergensmeyer, S.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Apixaban with the Vitamin K Antagonist Phenprocoumon in Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis: The AXADIA-AFNET 8 Study. Circulation 2023, 147, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vriese, A.S.; Caluwé, R.; Van Der Meersch, H.; De Boeck, K.; De Bacquer, D. Safety and Efficacy of Vitamin K Antagonists versus Rivaroxaban in Hemodialysis Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelddal, S.; Hvas, A.M.; Grove, E.L.; Birn, H. Safety and Effectiveness of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Nephrotic Syndrome: A Report of 21 Cases. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meerhaeghe, T.; Cez, A.; Dahan, K.; Esteve, E.; Elalamy, I.; Boffa, J.J.; Ponlot, E. Apixaban Prophylactic Anticoagulation in Patients with Nephrotic Syndrome. TH Open 2022, 6, e299–e303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissar, S.M.; Kuchay, A.A.; Mir, T.H.; Goud, L.N.; Latief, M. Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Nephrotic Syndrome: Our Experience and Literature Review. Indian J. Nephrol. 2024, 34, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, D.J.; de Freitas, D.G.; Little, M.A.; McHugh, T.; Magee, C.; Conlon, P.J.; O’Seaghdha, C.M. Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants as Prophylaxis Against Thromboembolism in the Nephrotic Syndrome. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, A.; Coons, E.M.; Mizuki, B.; Dermady, M.; Stanilova, K.; Casey, A.L.; Alqudsi, M.; Gastanaduy, M.; Elmayan, A.; Bamnolker, A.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Patients with Nephrotic Syndrome: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Pharmacother. 2023, 57, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bardissy, A.; Elshafei, M.N.; Abdelgawad, H.; Mekkawi, R.; Eltahir, A.; Mohammed, A.; Am, A.; Elewa, H. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin for Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis in Nephrotic Syndrome Patients: A Retrospective Study. Thromb. J. 2025, 23, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarniouch, D.M.; Crona, D.J.; Karnabi, P.; Bose, B.; Nachman, P.H.; Carrier, M.; Canney, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Lee, T.; Ramachandran, R.; et al. Anticoagulation for the Prevention of Thrombotic Events in Nephrotic Syndrome. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 3053–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, A.M.; Carrier, M.; Wang, T.F. Primary Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Ambulatory Cancer Patients: Recent Advances and Practical Implications. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2024, 134, 16739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, F.I.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; van Es, N.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Pedersen, L.; Moik, F.; Ay, C.; Büller, H.R.; Sørensen, H.T. Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Blood 2021, 137, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, M.; Abou-Nassar, K.; Mallick, R.; Tagalakis, V.; Shivakumar, S.; Schattner, A.; Kuruvilla, P.; Hill, D.; Spadafora, S.; Marquis, K.; et al. Apixaban to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, C.; Pabinger, I.; Cohen, A.T. Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism: Burden, Mechanisms, and Management. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.P.; Hisada, Y.M.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Reeves, B.N.; Mackman, N. Cancer Therapy-Associated Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretti, A.M.; Scicchitano, P.; La Forgia, D.; De Luca, R.; Campello, E.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Di Nisio, M.; Oliva, S. Prevention of Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)-Associated Vein Thrombosis in Cancer: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorobantu-Lungu, L.R.; Dinca, V.; Gegiu, A.; Spataru, D.; Toma, A.; Welt, L.; Badea, M.F.; Caruntu, C.; Scheau, C.; Savulescu-Fiedler, I. The Relevance of the Virchow Node and Virchow Triad in Renal Cancer Diagnosis. Clin. Pract. 2025, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Efing, J.; Kiesel, L.; Bendas, G.; Götte, M. The Tissue Factor Pathway in Cancer: Overview and Role of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans. Cancers 2023, 15, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzińska, M.; Parodi, A.; Soond, S.M.; Vinarov, A.Z.; Korolev, D.O.; Morozov, A.O.; Daglioglu, C.; Tutar, Y.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr. The Role of Cysteine Cathepsins in Cancer Progression and Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, R.; Hasan, M.M.; Azam, Z.; Grippo, P.J.; Al-Hilal, T.A. The Role of Coagulome in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 200, 115027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayes, J.; Bourne, J.H.; Brill, A.; Watson, S.P. The Dual Role of Platelet–Innate Immune Cell Interactions in Thrombo-Inflammation. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaboury, S.; Wang, K.; O’Sullivan, K.M.; Ooi, J.D.; Ho, G.Y. NETosis as an Oncologic Therapeutic Target: A Mini Review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1170603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Wu, G.; Tan, J.; Xiao, X.; Yang, L.; Saw, P.E. Targeting NETosis: Nature’s Alarm System in Cancer Progression. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Iwaki, T.; Sano, H.; Honkura, N.; Castellino, F.J. Recognition of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor Type 1 as the Primary Regulator of Fibrinolysis. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Koipallil, G.K.; Thomas, N.; Mhaskar, R.; Visweshwar, N.; Laber, D.; Patel, A.; Jaglal, M. Efficacy and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Secondary Prevention of Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskob, G.E.; van Es, N.; Verhamme, P.; Carrier, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Garcia, D.; Grosso, M.A.; Kakkar, A.K.; Kovacs, M.J.; Mercuri, M.F.; et al. Edoxaban for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.M.; Marshall, A.; Thirlwall, J.; Chapman, O.; Lokare, A.; Hill, C.; Hale, D.; Dunn, J.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Hutchinson, C.; et al. Comparison of an Oral Factor Xa Inhibitor with Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Patients with Cancer with Venous Thromboembolism: Results of a Randomized Trial (SELECT-D). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBane, R.D., II; Wysokinski, W.E.; Le-Rademacher, J.G.; Zemla, T.; Ashrani, A.; Tafur, A.; Perepu, U.; Anderson, D.; Gundabolu, K.; Kuzma, C.; et al. Apixaban and Dalteparin in Active Malignancy-Associated Venous Thromboembolism: The ADAM VTE Trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Meyer, G.; Muñoz, A.; Huisman, M.V.; Connors, J.M.; Cohen, A.; Bauersachs, R.; Brenner, B.; Torbicki, A.; et al. Apixaban for the Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, T.; Sueta, D.; Yamamoto, E.; Buckley, C.; Sacchi de Camargo Correia, G.; Aronson, J.; Tallón de Lara, P.; Fujisue, K.; Usuku, H.; Matsushita, K.; et al. Comparing Anticoagulation Strategies for Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Active Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JACC CardioOncol. 2024, 6, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Noble, S.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Soff, G.; Meyer, G.; O’Connell, C.; Carrier, M. Role of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism: Guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1891–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, N.S.; Khorana, A.A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Bohlke, K.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Arcelus, J.I.; Wong, S.L.; Balaban, E.P.; Flowers, C.R.; Francis, C.W.; et al. Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis and Treatment in Patients with Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streiff, M.B.; National Comprehensive Cancer Center Network. The National Comprehensive Cancer Center Network (NCCN) Guidelines on the Management of Venous Thromboembolism in Cancer Patients. Thromb. Res. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S128–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, G.H.; Carrier, M.; Ay, C.; Di Nisio, M.; Hicks, L.K.; Khorana, A.A.; Leavitt, A.D.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Macbeth, F.; Morgan, R.L.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2021 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism: Prevention and Treatment in Patients with Cancer. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 927–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, D.G.; Rebecca, D. The 2022 European Society of Cardiology Cardio-Oncology Guidelines in Focus. Eur. Cardiol. 2023, 18, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Atlas 2023. World Obesity Federation. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-atlas-2023 (accessed on 26 December 2023).
- Hotoleanu, C. Association between Obesity and Venous Thromboembolism. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalliah, C.J.; Sanders, P.; Kottkamp, H.; Kalman, J.M. The Role of Obesity in Atrial Fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.X.; Sullivan, T.; Sun, M.T.; Mahajan, R.; Pathak, R.K.; Middeldorp, M.; Twomey, D.; Ganesan, A.N.; Rangnekar, G.; Roberts-Thomson, K.C.; et al. Obesity and the Risk of Incident, Post-Operative, and Post-Ablation Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis of 626,603 Individuals in 51 Studies. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 1, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, M.J.; Abernethy, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J. Effect of Obesity on the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelkhanova, A.; Oli, P.R.; Shrestha, D.B.; Shtembari, J.; Jha, V.; Shantha, G.; Bodziock, G.M.; Biswas, M.; Zaman, M.O.; Patel, N.K. Safety and Efficacy of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Comparison to Warfarin in Obese Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.A.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Davidson, B.L.; Huisman, M.V.; Sandset, P.M.; Moll, S. Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Obesity for Treatment and Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism: Updated Communication from the ISTH SSC Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coons, J.C.; Albert, L.; Bejjani, A.; Iasella, C.J. Effect of Body Mass Index on the Efficacy and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants: A Retrospective Cohort Study of the Veterans Affairs Population. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algethami, A.; Ahmed, A.M.A.; Ardah, H.; Alsalamah, S.; Alhabs, G.; Al Fraihi, G.; Alanazi, S.; Alharbi, H.; Aljizeeri, A. Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Apixaban vs. Warfarin in Obese Atrial Fibrillation Patients: Propensity Matching Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhu, W. Efficacy and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Across BMI Categories: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 20, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talerico, R.; Pola, R. Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants in Patients at Extremes of Body Weight: A Review of Pharmacological Considerations and Clinical Implications. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2024, 22, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kido, K.; Ngorsuraches, S.; Cavallari, L.H.; Gulseth, M.P. Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Morbidly Obese Patients. Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covert, K.; Branam, D.L. Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulant Use at Extremes of Body Weight: Literature Review and Recommendations. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2020, 77, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tektonidou, M.G.; Andreoli, L.; Limper, M.; Amoura, Z.; Cervera, R.; Costedoat-Chalumeau, N.; Cuadrado, M.J.; Dörner, T.; Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Hambly, K.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Antiphospholipid Syndrome in Adults. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairani, C.D.; Bejjani, A.; Piazza, G.; Jimenez, D.; Monreal, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Pengo, V.; Woller, S.C.; Cortes-Hernandez, J.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants vs. Vitamin K Antagonists in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndromes: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 81, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Denas, G.; Zoppellaro, G.; Padayattil Jose, S.; Hoxha, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Jose, S.P.; Hoxha, A.; Ruffatti, A.; Andreoli, L.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs. Warfarin in High-Risk Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Blood 2018, 132, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordi-Ros, J.; Sáez-Comet, L.; Pérez-Conesa, M.; Vidal, X.; Riera-Mestre, A.; Castro-Salomó, A.; Cuquet-Pedragosa, J.; Ortiz-Santamaria, V.; Mauri-Plana, M.; Solé, C.; et al. Rivaroxaban Versus Vitamin K Antagonist in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Randomized Noninferiority Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastori, D.; Menichelli, D.; Cammisotto, V.; Pignatelli, P. Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the International Guidelines. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 715878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuily, S.; Cohen, H.; Isenberg, D.; Woller, S.C.; Crowther, M.; Dufrost, V.; Wahl, D.; Doré, C.J.; Cuker, A.; Carrier, M.; et al. Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Thrombotic Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Guidance from the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.R.J.; Gomez, K.; Alikhan, R.; Anderson, J.A.M.; Lester, W.; Laffan, M. Addendum to British Society for Haematology Guidelines on Investigation and Management of Antiphospholipid Syndrome, 2012: Use of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortel, T.L.; Neumann, I.; Ageno, W.; Beyth, R.; Clark, N.P.; Cuker, A.; Hutten, B.A.; Jaff, M.R.; Manja, V.; Schulman, S.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism: Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4693–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, R.G.; Catanese, L.; Perera, K.S.; Ntaios, G.; Connolly, S.J. Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: A Systematic Review and Clinical Update. Stroke 2017, 48, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, H.; Josephson, S.A. Anticoagulation in ESUS—Back from the Dead? JAMA Neurol. 2025, 82, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, H.C.; Sacco, R.L.; Easton, J.D.; Granger, C.B.; Bernstein, R.A.; Uchiyama, S.; Kreuzer, J.; Cronin, L.; Cotton, D.; Grauer, C.; et al. Dabigatran for Prevention of Stroke after Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, T.; Keller, T.; Martus, P.; Poli, K.; Serna-Higuita, L.M.; Schreieck, J.; Gawaz, M.; Tünnerhoff, J.; Bombach, P.; Nägele, T.; et al. Apixaban versus Aspirin for Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source. NEJM Evid. 2024, 3, EVIDoa2300235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannam, M.; Al-Qudah, A.M.; Alshaer, Q.N.; Kronmal, R.; Ntaios, G.; Childs, C.A.; Longstreth, W.T.; Alsawareah, A.; Keller, T.; Serna-Higuita, L.M.; et al. Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets Across Subgroups of Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Neurology 2024, 103, e209949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, G.W.; Bernstein, R.; Brachmann, J.; Camm, A.J.; Fromm, P.; Goto, S.; Granger, C.B.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Hylek, E.; Krieger, D.; et al. Reexamination of the Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source Concept. Stroke 2021, 52, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiafico, M.; Costanzo, L. Superficial Venous Thrombosis: A Comprehensive Review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, M.H.; Wakefield, T.W.; Ascher, E.; Caprini, J.A.; Comerota, A.J.; Eklof, B.; Gillespie, D.L.; Greenfield, L.J.; He, A.R.; Henke, P.K.; et al. Acute Venous Disease: Venous Thrombosis and Venous Trauma. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 46 (Suppl. S6), 25S–53S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirmerova, J.; Seidlerova, J.; Chudacek, Z. The Prevalence of Concomitant Deep Vein Thrombosis, Symptomatic or Asymptomatic, Proximal or Distal, in Patients with Symptomatic Pulmonary Embolism. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 24, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Schellong, S.M.; Gerlach, H.; Rabe, E.; Weitz, J.I.; Jersemann, K.; Sahin, K.; Bauersachs, R.; Surprise Investigators. Prevention of Thromboembolic Complications in Patients with Superficial-Vein Thrombosis Given Rivaroxaban or Fondaparinux: The Open-Label, Randomised, Non-Inferiority SURPRISE Phase 3b Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e105–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearon, C.; Carrier, M.; Gu, C.S.; Schulman, S.; Bates, S.M.; Kahn, S.R.; Chagnon, I.; Nguyen, D.T.; Wu, C.; Rudd-Scott, L.; et al. Rivaroxaban Compared to Placebo for the Treatment of Leg Superficial Vein Thrombosis: A Randomized Trial. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearon, C.; Akl, E.A.; Ornelas, J.; Blaivas, A.; Jimenez, D.; Bounameaux, H.; Huisman, M.; King, C.S.; Morris, T.A.; Sood, N.; et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2016, 149, 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, N.; Ageno, W. Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Unusual-Site Venous Thromboembolism. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 5, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Nisio, M.; Camporese, G.; Di Micco, P.; Martini, R.; Ageno, W.; Prandoni, P. Treatment of Superficial Vein Thrombosis: Recent Advances, Unmet Needs and Future Directions. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, A.; Sorella, S.; Fucci, L.; Genoese, A.; Chistolini, A. Treatment with Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) and Secondary Prophylaxis in Patients Affected by Multiple Episodes of Superficial Venous Thrombosis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 122, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffe, H.V.; Kucher, N.; Tapson, V.F.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) FREE Steering Committee. Upper-Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Prospective Registry of 592 Patients. Circulation 2004, 110, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorian, A.; Nahmias, J.T. Upper Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482420/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Porfidia, A.; Agostini, F.; Giarretta, I.; Tonello, D.; Pastori, D.; Pignatelli, P.; Santoliquido, A.; Sartori, M.; Lessiani, G.; Viso-nà, A.; et al. Upper Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis Treated with Direct Oral Anticoagulants: A Multi-Center Real World Experience. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedovati, M.C.; Tratar, G.; Mavri, A.; Mazzetti, M.; Rosa, V.S.; Pierpaoli, L.; Cotugno, M.; Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C. Upper Extremities Deep Vein Thrombosis Treated with Oral Direct Anticoagulants: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 339, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, D.E.; Casanegra, A.I.; Peterson, L.G.; Cochuyt, J.; Hodge, D.O.; Vlazny, D.; McBane, R.D.; Froehling, D.; Wysokinski, W.E. Treatment of upper extremity deep vein thrombosis with apixaban and rivaroxaban. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, S.V.; Klok, F.A.; Stenger, W.J.E.; Mairuhu, A.T.A.; Eikenboom, J.; Fogteloo, J.; Huisman, M.V. Effectiveness and Safety of Apixaban for Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism in Daily Practice. TH Open 2020, 4, e119–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jen-nings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism Developed in Collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lv, M.; Wu, S.; Jiang, S.; Xu, W.; Qian, J.; Chen, M.; Fang, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, J. Editor’s Choice—Severe Bleeding Risks of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in the Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2022, 63, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Li, M.K.; Crowther, M.; Vazquez, S.R. Drug-drug interactions with direct oral anticoagulants associated with adverse events in the real world: A systematic review. Thromb. Res. 2020, 194, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, C.M.; Mead, T. Inferior Vena Caval Thrombosis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537175/ (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Shi, W.; Dowell, J.D. Etiology and Treatment of Acute Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2017, 149, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I. Inferior Vena Cava Thrombosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013009627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, C.; Schuettfort, G.; Weil, Y.; Tirneci, V.; Kasper, A.; Haberichter, B.; Schwonberg, J.; Schindewolf, M.; Lindhoff-Last, E.; Linnemann, B. Thrombosis of the inferior vena cava and malignant disease. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAree, B.J.; O’Donnell, M.E.; Fitzmaurice, G.J.; Reid, J.A.; Spence, R.A.; Lee, B. Inferior vena cava thrombosis: A review of current practice. Vasc. Med. 2013, 18, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihm, A.E.; Bacchus, A.; Harb, K.J.; Menear, R.A.; Nisly, S.A. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for the treatment of inferior vena cava thrombus. Eur. J. Haematol. 2023, 111, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, M. Bleeding Risks Associated with DOACs vs VKAs in IVC Thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 19, 456–465. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilov, S.G.; Moskalenko, Y.P.; Karalkin, A.V.; Alenichev, A.V. Pelvic Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Pelvic Venous Disorders. Phlebology 2024, 39, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; Sawada, K.; Shiomi, M.; Kawano, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Takiuchi, T.; Kodama, M.; Kobayashi, E.; Hashimoto, K.; Mabuchi, S.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Are Effective and Safe for the Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Gynecological Cancers. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 147, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, S.; Shu, L.; Bakradze, E.; Omran, S.S.; Giles, J.A.; Amar, J.Y.; Henninger, N.; Elnazeir, M.; Liberman, A.L.; Moncrieffe, K.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Warfarin in the Treatment of Cerebral Venous Thrombosis (ACTION-CVT): A Multicenter International Study. Stroke 2022, 53, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Saldanha, I.J.; Misquith, C.; Zaidat, B.; Shah, A.; Joudi, K.; Persaud, B.; Khalek, F.A.; Shu, L.; de Havenon, A.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Vitamin K Antagonists in Cerebral Venous Thrombosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2022, 53, 3014–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, N.; Bhinder, J.; Nguyen, J.; Langan, T., Jr.; O’Brien-Irr, M.; Montross, B.; Khan, S.; Sharma, A.M.; Harris, L.M. Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with COVID-19 Infection: Risk Factors, Prevention, and Management. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 34, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roguljić, H.; Arambašić, J.; Ninčević, V.; Kuna, L.; Šesto, I.; Tabll, A.; Smolić, R.; Včev, A.; Primorac, D.; Wu, G.Y.; et al. The Role of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in the Era of COVID-19: Are Antiviral Therapy and Pharmacogenetics Limiting Factors? Croat. Med. J. 2022, 63, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizurini, D.M.; Hottz, E.D.; Bozza, P.T.; Monteiro, R.Q. Fundamentals in COVID-19-Associated Thrombosis: Molecular and Cellular Aspects. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 785738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Willey, J. The Interplay between Inflammation and Thrombosis in COVID-19: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Strategies, and Challenges. Thromb. Update 2022, 8, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Brooks, M.M.; Sciurba, F.C.; Krishnan, J.A.; Bledsoe, J.R.; Kindzelski, A.; Baucom, A.L.; Kirwan, B.A.; Eng, H.; Martin, D.; et al. ACTIV-4B Investigators. Effect of Antithrombotic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes in Outpatients with Clinically Stable Symptomatic COVID-19: The ACTIV-4B Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacciotti, E.; Barile Agati, L.; Calderaro, D.; Aguiar, V.C.R.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; de Oliveira, C.C.C.; Lins Dos Santos, J.; Volpiani, G.G.; Sobreira, M.L.; Joviliano, E.E.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus No Anticoagulation for Post-Discharge Thromboprophylaxis after Hospitalisation for COVID-19 (MICHELLE): An Open-Label, Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorog, D.A.; Gue, Y.X.; Chao, T.F.; Fauchier, L.; Ferreiro, J.L.; Huber, K.; Konstantinidis, S.V.; Lane, D.A.; Marin, F.; Oldgren, J.; et al. Assessment and Mitigation of Bleeding Risk in Atrial Fibrillation and Venous Thromboembolism: A Position Paper from the ESC Working Group on Thrombosis, in Collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Association for Acute CardioVascular Care and the Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society. Europace 2022, 24, 1844–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miceli, G.; Ciaccio, A.M.; Tuttolomondo, A. Challenges and Opportunities of Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC) Therapy in Complex Clinical Scenarios: A Comprehensive Review and Practical Guide. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092914
Miceli G, Ciaccio AM, Tuttolomondo A. Challenges and Opportunities of Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC) Therapy in Complex Clinical Scenarios: A Comprehensive Review and Practical Guide. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092914
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiceli, Giuseppe, Anna Maria Ciaccio, and Antonino Tuttolomondo. 2025. "Challenges and Opportunities of Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC) Therapy in Complex Clinical Scenarios: A Comprehensive Review and Practical Guide" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092914
APA StyleMiceli, G., Ciaccio, A. M., & Tuttolomondo, A. (2025). Challenges and Opportunities of Direct Oral Anticoagulant (DOAC) Therapy in Complex Clinical Scenarios: A Comprehensive Review and Practical Guide. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2914. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092914








