The Influence of Tranexamic Acid (TXA) on Postoperative Infection Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)—A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- P—Population: Adult patients requiring primary total hip arthroplasty.
- -
- I—Intervention: Administration of TXA prior or at the time of surgery, no matter the route of administration.
- -
- C—Comparison: Patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty without the administration of TXA would serve as the control group.
- -
- O—Outcome: The rate of postoperative infections which can be defined as postoperative infection, surgical site infection, or periprosthetic joint infection.
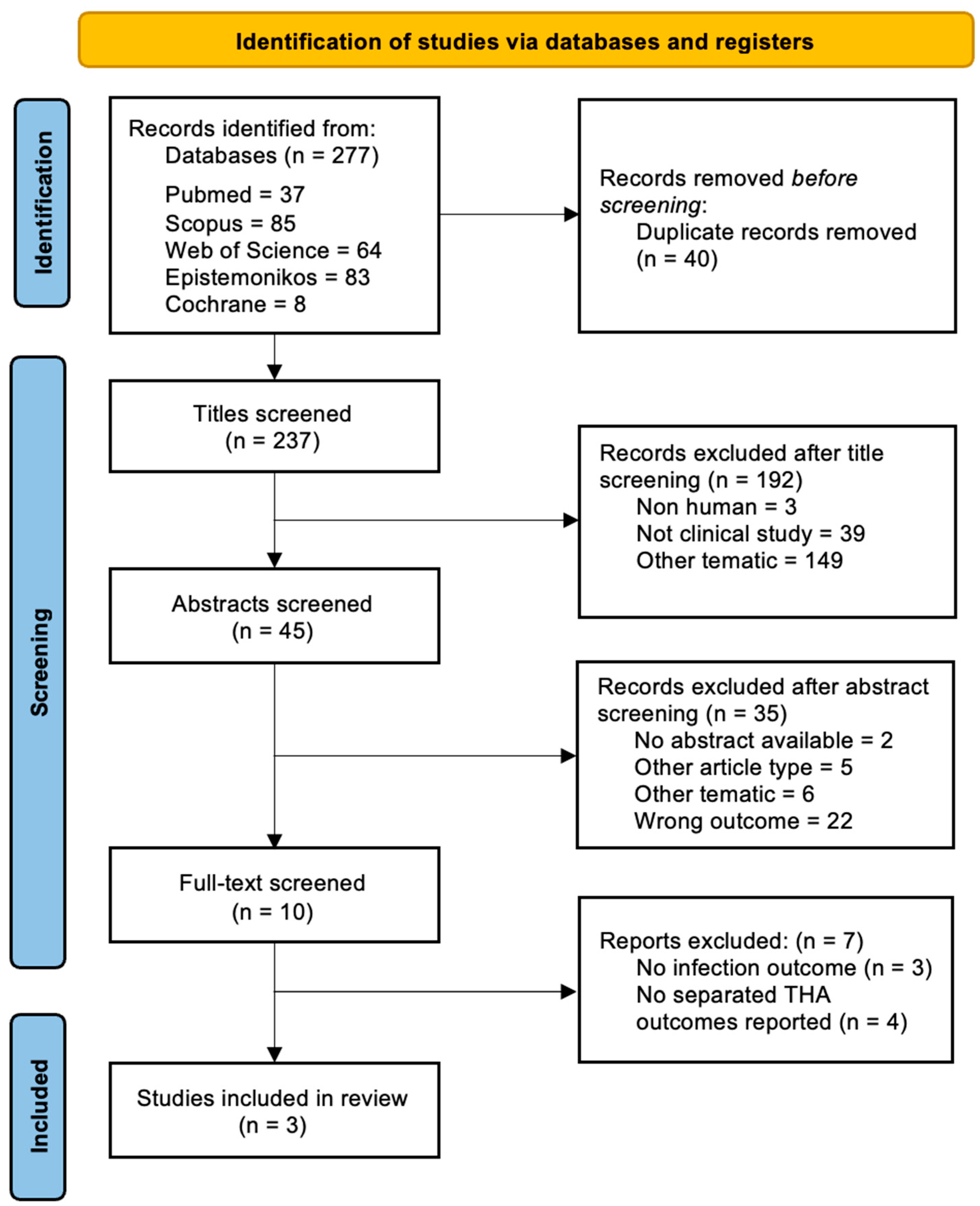
3. Results
3.1. Dosage and Route of Administration
3.2. Surgical Site Infections
3.3. Periprosthetic Joint Infections
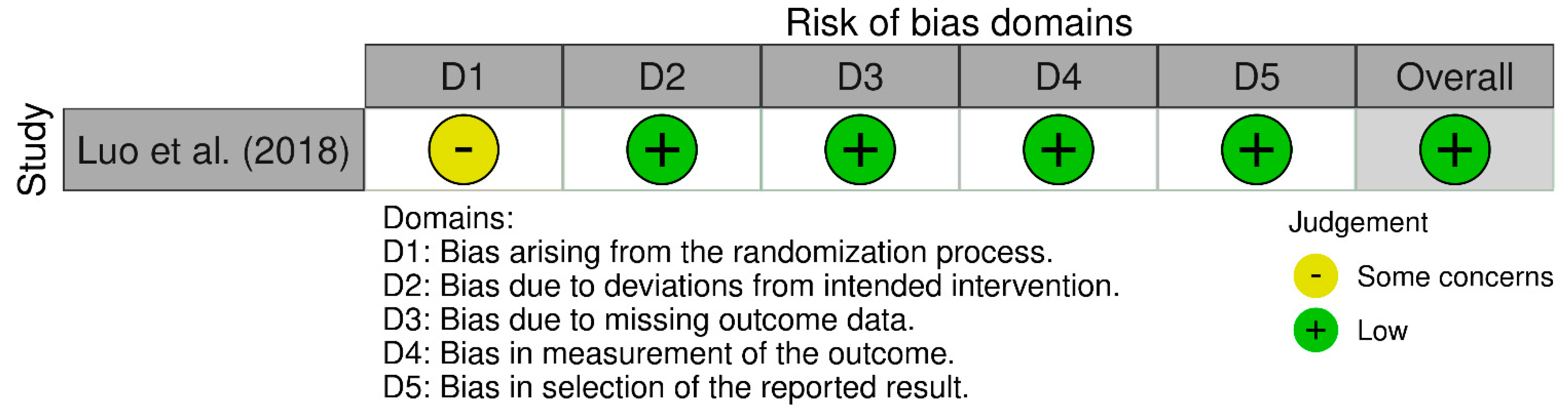
3.4. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, X.; Gong, G.; Han, N.; Liu, M. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Compared with Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Reducing Blood Loss after Primary Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Hu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Ma, J.; Lei, Y.; Pei, F. Comparison of Intravenous versus Topical Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Res. 2017, 153, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, G. A Comparison of Combined Intravenous and Topical Administration of Tranexamic Acid with Intravenous Tranexamic Acid Alone for Blood Loss Reduction after Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 41, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillingham, Y.A.; Ramkumar, D.B.; Jevsevar, D.S.; Yates, A.J.; Shores, P.; Mullen, K.; Bini, S.A.; Clarke, H.D.; Schemitsch, E.; Johnson, R.L.; et al. The Efficacy of Tranexamic Acid in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Network Meta-Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 3083–3089.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prejbeanu, R.; Mioc, M.L.; Deleanu, B.; Balanescu, A.; Al Qatawneh, M.; Malita, D. The Use of Tranexamic Acid in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, B. The Efficacy and Safety of Combined Administration of Intravenous and Topical Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludbrook, G.L. The Hidden Pandemic: The Cost of Postoperative Complications. Curr. Anesthesiol. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birlutiu, R.M.; Stoica, C.I.; Russu, O.; Cismasiu, R.S.; Birlutiu, V. Positivity Trends of Bacterial Cultures from Cases of Acute and Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Prieto, D.; Portillo, M.E.; Puig-Verdié, L.; Alier, A.; Gamba, C.; Guirro, P.; Martínez-Díaz, S.; Horcajada, J.P.; Trampuz, A.; Monllau, J.C. Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Prosthetic Joint Infections: Not a Concern for Intraoperative Cultures. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 86, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.M.; Casey, A.L.; Petrosillo, N.; Hudson, P.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Crosby, C. Impact of Surgical Site Infection on Healthcare Costs and Patient Outcomes: A Systematic Review in Six European Countries. J. Hosp. Infect. 2017, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slim, K.; Nini, E.; Forestier, D.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Panis, Y.; Chipponi, J. Methodological Index for Non-randomized Studies (MINORS): Development and Validation of a New Instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, L.A.; Higgins, J.P.T. Risk-of-bias VISualization (Robvis): An R Package and Shiny Web App for Visualizing Risk-of-bias Assessments. Res. Synth. Methods 2021, 12, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Hsu, A.H.S.; Wu, C.-T.; Tan, T.L.; Wang, J.-W.; Kuo, F.-C. Association between IV and Topical Tranexamic Acid Use and Periprosthetic Joint Infections in Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapaliya, A.; Mittal, M.M.; Ratcliff, T.L.; Mounasamy, V.; Wukich, D.K.; Sambandam, S.N. Usage of Tranexamic Acid for Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Matched Cohort Analysis of 144,344 Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.-Y.; Wang, D.; Meng, W.-K.; Wang, H.-Y.; Pan, H.; Pei, F.-X.; Zhou, Z.-K. Oral Tranexamic Acid Is Equivalent to Topical Tranexamic Acid without Drainage in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Thromb. Res. 2018, 167, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.; Medcalf, R.L.; Cloud, G.C.; Myles, P.S.; Keragala, C.B. Tranexamic Acid for Haemostasis and beyond: Does Dose Matter? Thromb. J. 2023, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbacher, P.; Nguyen, T.-L.; Dorn, P.; Kocher, G.J.; Lutz, J.A. Surgical Site Infections Are Associated With Higher Blood Loss and Open Access in General Thoracic Practice. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 656249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasan, A.; Dworschak, P.; Heyse, T.J.; Malcherczyk, D.; Peterlein, C.D.; Schüttler, K.F.; Lahner, M.; El-Zayat, B.F. Transfusions Increase Complications and Infections after Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: An Analysis of 2760 Cases. Technol. Health Care 2018, 26, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, N.; Bovonratwet, P.; Purtill, J.J.; Bernstein, J.A.; Golden, M.; Grauer, J.N.; Rubin, L.E. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Subsequent Complications of Postoperative Hematomas Requiring Reoperation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2023, 19, 101015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okholm, S.H.; Krog, J.; Hvas, A.-M. Tranexamic Acid and Its Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effect: A Systematic Review. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2022, 48, 568–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Huang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Pan, Y.; He, T.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L. Tranexamic Acid Protects against Implant-Associated Infection by Reducing Biofilm Formation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolin, D.A.; Moverman, M.A.; Menendez, M.E.; Pagani, N.R.; Puzzitiello, R.N.; Kavolus, J.J. A Break-Even Analysis of Tranexamic Acid for Prevention of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J. Orthop. 2021, 26, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.J.; Wilson, L.A.; Liu, J.; Memtsoudis, S.G. Tranexamic Acid Administration Is Associated With a Decreased Odds of Prosthetic Joint Infection Following Primary Total Hip and Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A National Database Analysis. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuhani, W.S.; Alanazi, A.M.; Saeed, A.I.; Alhadlaq, K.H.; Alhoshan, Y.S.; Aljaafri, Z.A. Patient-Related Risk Factors of Prosthetic Joint Infections Following Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty at King Abdulaziz Medical City, a 10-Year Retrospective Study. J. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 18, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaryk, J.; Melus, V.; Vidan, J.; Steno, B. Comparison of Intravenous and Topical Tranexamic Acid in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Acta Chir. Orthop. Traumatol. Cech. 2022, 89, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, N.D.; Haque, T.F.; Piple, A.S.; Mayfield, C.K.; Bouz, G.J.; Mayer, L.W.; Oakes, D.A.; Lieberman, J.R.; Christ, A.B. Tranexamic Acid and Prothrombotic Complications Following Total Hip and Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Population-Wide Safety Analysis Accounting for Surgeon Selection Bias. J. Arthroplast. 2023, 38, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Criteria | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Language | English | Non-English |
| Subjects | Human | Non-human |
| Level of Evidence | Levels I-IV, full text available | Level V, no full text available |
| Procedure | Primary THA | Revision THA for any reason, THA for hip fractures, associated conditions (local bone tumors, coagulation pathology, post-traumatic deformity) |
| Intervention | TXA | no TXA |
| Outcomes | SSI or PJI or other type of infections | SSI or PJI or other type of infections not reported separately |
| Author and Year | Hsu 2024 [15] | Thepalyia 2024 [16] | Luo 2018 [17] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of study | Retrospective cohort | Retrospective cohort | RCT | |
| Level of evidence | III | III | I | |
| All patients | Tot | 1766 | 144,344 | 117 |
| Age (yr) | n/a | 63.4 ± 11.6 * | n/s | |
| Sex M/F * | n/s | 46/52 ** | n/s | |
| Route of administration (comparison) | IV TXA vs. topical vs. no TXA | TXA (n/s) vs. no TXA | Oral TXA vs. topical TXA | |
| Subgroups | Control | 797 | 72,172 | n/a |
| Intervention | 969 | 72,172 | 117 | |
| IV TXA | 777 | n/s | n/a | |
| Oral TXA | n/a | n/s | 59 | |
| Topical TXA | 192 | n/s | 58 | |
| Main Author | Hsu 2024 [15] | Thepalyia 2024 [16] | Luo 2018 [17] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of study | Retrospective cohort | Retrospective cohort | RCT | |||
| Tot Nr. | 1766 | 144,344 | 117 | |||
| Duration of Observation | >12 months | 30 & 90 days | 90 days | |||
| TXA Dosage | IV | 10 mg/kg, 10 min before skin incision | n/s | n/a | ||
| Oral | n/a | n/s | 2 g 2 h preoperatively, and two doses of 1 g postoperatively | |||
| Topical | 1.5–3 g injected intra-articularly or into the drainage tube during surgery | n/s | 3 g in the operating room | |||
| SSI | No TXA | n/a | n/a | n/a | ||
| TXA | Superficial SSI | |||||
| 0.1% p < 0.001 * (30 days) | ||||||
| 0.3%, p < 0.001 * (90 days) | ||||||
| Deep SSI | ||||||
| 0.1% p = 0.228 (30 days) | ||||||
| 0.1%, p = 0.012 * (90 days) | ||||||
| IV TXA | n/a | |||||
| Oral TXA | n/a | |||||
| Topical TXA | n/a | |||||
| PJI | No TXA | 1.3% | n/a | |||
| TXA | 0.6%; p value = 0.209 | 0.6%, p = 0.001 * (30 days) | ||||
| 1.2%, p = 0.019 * (90 days) | ||||||
| IV TXA | 0.8%; p value = 0.426 | n/a | ||||
| Topical TXA | 0%; p value = 0.995 ** | n/a | ||||
| IV TXA—Topical TXA | p value = 0.995 ** | n/a | ||||
| Postoperative Infection | Oral TXA | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | 0 |
| Topical TXA | 0 | |||||
| Conclusion | Favors TXA for PJI but not statical significance | Favors TXA for superficial SSI | Favors TXA for deep SSI | Favors TXA for PJI | No difference between oral vs. topical TXA | |
| Main Author/MINORS Item | Hsu 2024 [15] | Thapaliya 2024 [16] |
|---|---|---|
| Clearly stated aim | 2 | 2 |
| Inclusion of consecutive patients | 0 | 2 |
| Prospective data collection | 2 | 0 |
| Endpoints appropriate to the aim | 2 | 2 |
| Unbiased assessment of endpoints | 0 | 2 |
| Appropriate follow-up period | 2 | 2 |
| Loss to follow-up < 5% | 0 | 2 |
| Prospective calculation of study size | 2 | 2 |
| Total Score (out of 16) | 10 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prejbeanu, R.; Mioc, M.L.; Tsiridis, E.; Kenanidis, E.; Valli, F.; Pasquini, A.; Deleanu, B. The Influence of Tranexamic Acid (TXA) on Postoperative Infection Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)—A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092910
Prejbeanu R, Mioc ML, Tsiridis E, Kenanidis E, Valli F, Pasquini A, Deleanu B. The Influence of Tranexamic Acid (TXA) on Postoperative Infection Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(9):2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092910
Chicago/Turabian StylePrejbeanu, Radu, Mihail Lazar Mioc, Eleftherios Tsiridis, Eustathios Kenanidis, Federico Valli, Andrea Pasquini, and Bogdan Deleanu. 2025. "The Influence of Tranexamic Acid (TXA) on Postoperative Infection Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)—A Systematic Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 9: 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092910
APA StylePrejbeanu, R., Mioc, M. L., Tsiridis, E., Kenanidis, E., Valli, F., Pasquini, A., & Deleanu, B. (2025). The Influence of Tranexamic Acid (TXA) on Postoperative Infection Rates Following Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA)—A Systematic Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(9), 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14092910






