Complement in Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney Graft: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice
Abstract
1. Introduction
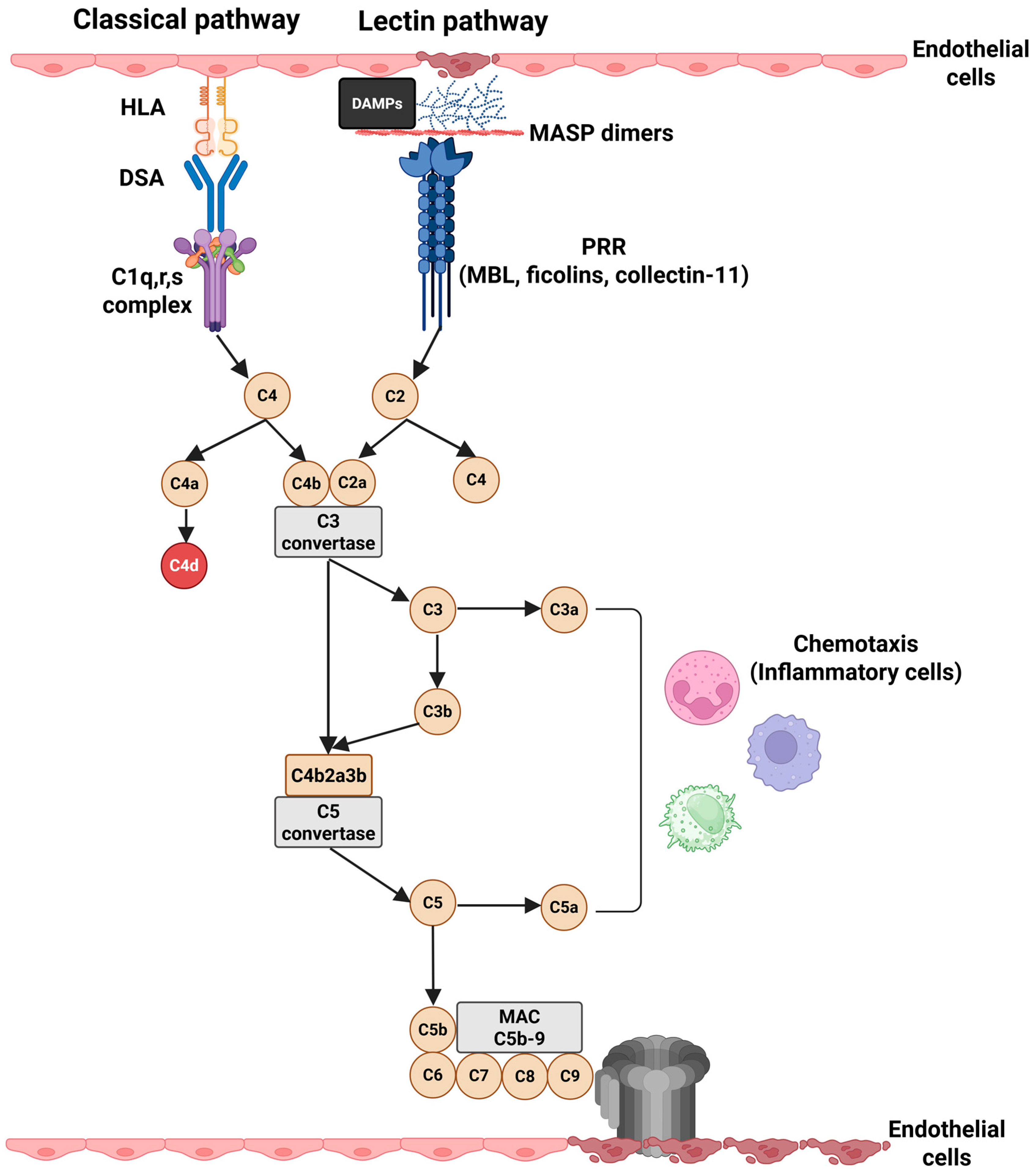
2. Complement System in Kidney Transplantation
3. The Role of Complement in the Pathophysiology of AMR
4. Histological Features of AMR and Complement
5. Complement Inhibition in the Treatment of AMR
5.1. Clinical Evidence for Terminal Complement Blockade in AMR
5.2. Clinical Evidence for Proximal Complement Blockade in AMR
6. Novel Therapies and Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Axelrod, D.A.; Schnitzler, M.A.; Xiao, H.; Irish, W.; Tuttle-Newhall, E.; Chang, S.-H.; Kasiske, B.L.; Alhamad, T.; Lentine, K.L. An Economic Assessment of Contemporary Kidney Transplant Practice. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, M.; Mirocha, J.; Reinsmoen, N.L.; Vo, A.A.; Choi, J.; Kahwaji, J.M.; Peng, A.; Villicana, R.; Jordan, S.C. Differences in Pathologic Features and Graft Outcomes in Antibody-Mediated Rejection of Renal Allografts Due to Persistent/Recurrent versus de Novo Donor-Specific Antibodies. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellarés, J.; De Freitas, D.G.; Mengel, M.; Reeve, J.; Einecke, G.; Sis, B.; Hidalgo, L.G.; Famulski, K.; Matas, A.; Halloran, P.F. Understanding the Causes of Kidney Transplant Failure: The Dominant Role of Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Nonadherence. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Cabrales, C.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Gimeno, J.; Sánchez-Güerri, I.; Bermejo, S.; Sierra, A.; Burballa, C.; Mir, M.; Crespo, M.; et al. Renal Graft Survival According to Banff 2013 Classification in Indication Biopsies. Nefrologia 2016, 36, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, O.; Loupy, A.; Hidalgo, L.; Duong van Huyen, J.-P.; Higgins, S.; Viglietti, D.; Jouven, X.; Glotz, D.; Legendre, C.; Lefaucheur, C.; et al. Antibody-Mediated Rejection Due to Preexisting versus De Novo Donor-Specific Antibodies in Kidney Allograft Recipients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, J.M.; Panzer, S.E.; Le Quintrec, M. The Role of Complement in Antibody Mediated Transplant Rejection. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorohan, B.M.; Ismail, G.; Leca, N.; Tacu, D.; Obrișcă, B.; Constantinescu, I.; Baston, C.; Sinescu, I. Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies in Kidney Transplantation: An Evidence-Based Comprehensive Review. Transplant. Rev. 2020, 34, 100573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorohan, B.M.; Baston, C.; Tacu, D.; Bucșa, C.; Tincu, C.; Vizireanu, P.; Sinescu, I.; Constantinescu, I. Non-HLA Antibodies in Kidney Transplantation: Immunity and Genetic Insights. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.; Connelly, C.; Moldakhmetova, S.; Sheerin, N.S. Complement Activation and Kidney Transplantation; a Complex Relationship. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasowska, B.A. Mechanisms Involved in Antibody- and Complement-Mediated Allograft Rejection. Immunol. Res. 2010, 47, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinstock, C.A.; Mannon, R.B.; Budde, K.; Chong, A.S.; Haas, M.; Knechtle, S.; Lefaucheur, C.; Montgomery, R.A.; Nickerson, P.; Tullius, S.G.; et al. Recommended Treatment for Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus From the Transplantion Society Working Group. Transplantation 2020, 104, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Kirkiles-Smith, N.C.; Deng, Y.H.; Formica, R.N.; Moeckel, G.; Broecker, V.; Bow, L.; Tomlin, R.; Pober, J.S. Eculizumab Therapy for Chronic Antibody-Mediated Injury in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viglietti, D.; Gosset, C.; Loupy, A.; Deville, L.; Verine, J.; Zeevi, A.; Glotz, D.; Lefaucheur, C. C1 Inhibitor in Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection Nonresponsive to Conventional Therapy in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglarnia, A.R.; Huber-Lang, M.; Mohlin, C.; Ekdahl, K.N.; Nilsson, B. The Multifaceted Role of Complement in Kidney Transplantation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarsiero, D.; Aiello, S. The Complement System in Kidney Transplantation. Cells 2023, 12, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.; Jiang, L.; Stacks, S.; Lin, H.; Parajuli, N. Aberrant Activation of the Complement System in Renal Grafts Is Mediated by Cold Storage. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2021, 320, F1174–F1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, N.M.; Venema, L.H.; Arykbaeva, A.S.; Meter-Arkema, A.H.; Ottens, P.J.; van Kooten, C.; Mollnes, T.E.; Alwayn, I.P.J.; Leuvenink, H.G.D.; Pischke, S.E. Complement Is Activated During Normothermic Machine Perfusion of Porcine and Human Discarded Kidneys. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 831371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, J.; Bloks, V.W.; Daha, M.R.; Van Der Most, P.J.; Sanjabi, B.; Van Der Vlies, P.; Snieder, H.; Ploeg, R.J.; Krikke, C.; Leuvenink, H.G.D.; et al. Hypoxia and Complement-and-Coagulation Pathways in the Deceased Organ Donor as the Major Target for Intervention to Improve Renal Allograft Outcome. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppelaars, F.; Seelen, M.A. Complement-Mediated Inflammation and Injury in Brain Dead Organ Donors. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 84, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszek, D.; Mazanowska, O.; Kościelska-Kasprzak, K.; Kamińska, D.; Lepiesza, A.; Chudoba, P.; Myszka, M.; Żabińska, M.; Klinger, M. Functional Activity of the Complement System in Deceased Donors in Relation to Kidney Allograft Outcome. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, M.; Rosso, G.; Bertoni, E. Update on Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Kidney Transplantation: Pathogenesis and Treatment. World J. Transplant. 2015, 5, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.X.; Qi, S.; Lasaro, M.A.; Bouchard, K.; Dow, C.; Moore, K.; Wu, Z.; Barama, A.; Xu, J.; Johnson, K.; et al. Targeting Complement Pathways During Cold Ischemia and Reperfusion Prevents Delayed Graft Function. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langewisch, E.; Mannon, R.B. Chronic Allograft Injury. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiske, B.L.; Kalil, R.S.; Lee, H.S.; Rao, K.V. Histopathologic Findings Associated with a Chronic, Progressive Decline in Renal Allograft Function. Kidney Int. 1991, 40, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Liu, C.; Farrar, C.A.; Ma, L.; Dong, X.; Sacks, S.H.; Li, K.; Zhou, W. Collectin-11 Promotes the Development of Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, S.; Sahu, R.K.; Bontha, S.V.; Mass, V.; Taylor, R.P.; Megyesi, J.; Thielens, N.M.; Portilla, D. Complement C1r Serine Protease Contributes to Kidney Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F1293–F1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Wu, W.; Wu, K.-Y.; Cao, B.; Qiang, C.; Li, K.; Sacks, S.H.; Zhou, W. The C5a/C5aR1 Axis Promotes Progression of Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, D.; Xavier, S. Role of Intracellular Complement Activation in Kidney Fibrosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2880–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honsová, E.; Lodererová, A.; Viklický, O.; Boucek, P. BK-Virus Nephropathy and Simultaneous C4d Positive Staining in Renal Allografts. Cesk. Patol. 2005, 41, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Higdon, L.E.; Tan, J.C.; Maltzman, J.S. Infection, Rejection, and the Connection. Transplantation 2023, 107, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.B.; Fishman, J.A. Immunosuppressive Agents and Infectious Risk in Transplantation: Managing the “Net State of Immunosuppression”. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1302–e1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Reed, E.F. Effect of Antibodies on Endothelium: Minireview. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 2459–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R. Donor-Specific Antibodies in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkash, E.A.; Colvin, R.B. Pathology: Diagnostic Challenges in Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djamali, A.; Kaufman, D.B.; Ellis, T.M.; Zhong, W.; Matas, A.; Samaniego, M. Diagnosis and Management of Antibody-Mediated Rejection: Current Status and Novel Approaches. Am. J. Transplant. 2014, 14, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, P.W.; Allison, M.E.; Akkaraju, S.; Goodnow, C.C.; Fearon, D.T. C3d of Complement as a Molecular Adjuvant: Bridging Innate and Acquired Immunity. Science 1996, 271, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xu, C.; Fu, Y.X.; Holers, V.M.; Molina, H. Expression of Complement Receptors 1 and 2 on Follicular Dendritic Cells Is Necessary for the Generation of a Strong Antigen-Specific IgG Response. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 5273–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, S.F.; Lukacs-Kornek, V.; Kuligowski, M.P.; Pitcher, L.A.; Degn, S.E.; Turley, S.J.; Carroll, M.C. Complement-Dependent Transport of Antigen into B Cell Follicles. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandendriessche, S.; Cambier, S.; Proost, P.; Marques, P.E. Complement Receptors and Their Role in Leukocyte Recruitment and Phagocytosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 624025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frémeaux-Bacchi, V.; Legendre, C.M. The Emerging Role of Complement Inhibitors in Transplantation. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Puttarajappa, C.; Shapiro, R.; Tan, H.P. Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplantation: A Review. J. Transplant. 2012, 2012, 193724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regele, H.; Böhmig, G.A.; Habicht, A.; Gollowitzer, D.; Schillinger, M.; Rockenschaub, S.; Watschinger, B.; Kerjaschki, D.; Exner, M. Capillary Deposition of Complement Split Product C4d in Renal Allografts Is Associated with Basement Membrane Injury in Peritubular and Glomerular Capillaries: A Contribution of Humoral Immunity to Chronic Allograft Rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupy, A.; Haas, M.; Roufosse, C.; Naesens, M.; Adam, B.; Afrouzian, M.; Akalin, E.; Alachkar, N.; Bagnasco, S.; Becker, J.U.; et al. The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): Updates on and Clarification of Criteria for T Cell– and Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, M.; Roufosse, C.; Haas, M.; Lefaucheur, C.; Mannon, R.B.; Adam, B.A.; Aubert, O.; Böhmig, G.A.; Callemeyn, J.; Clahsen-van Groningen, M.; et al. The Banff 2022 Kidney Meeting Report: Reappraisal of Microvascular Inflammation and the Role of Biopsy-Based Transcript Diagnostics. Am. J. Transplant. 2024, 24, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feucht, H.E.; Felber, E.; Gokel, M.J.; Hillebrand, G.; Nattermann, U.; Brockmeyer, C.; Held, E.; Riethmüller, G.; Land, W.; Albert, E. Vascular Deposition of Complement-Split Products in Kidney Allografts with Cell-Mediated Rejection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 86, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.B.; Schneeberger, E.E.; Pascual, M.A.; Saidman, S.L.; Williams, W.W.; Tolkoff-Rubin, N.; Cosimi, A.B.; Colvin, R.B. Complement Activation in Acute Humoral Renal Allograft Rejection: Diagnostic Significance of C4d Deposits in Peritubular Capillaries. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 2208–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.A.; Loupy, A.; Segev, D.L. Antibody-Mediated Rejection: New Approaches in Prevention and Management. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupy, A.; Hill, G.S.; Suberbielle, C.; Charron, D.; Anglicheau, D.; Zuber, J.; Timsit, M.O.; Duong, J.P.; Bruneval, P.; Vernerey, D.; et al. Significance of C4d Banff Scores in Early Protocol Biopsies of Kidney Transplant Recipients with Preformed Donor-Specific Antibodies (DSA). Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Colvin, R.B.; Daha, M.R.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Haas, M.; Nickeleit, V.; Salmon, J.E.; Sis, B.; Zhao, M.H.; Bruijn, J.A.; et al. Pros and Cons for C4d as a Biomarker. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roufosse, C.; Simmonds, N.; Clahsen-Van Groningen, M.; Haas, M.; Henriksen, K.J.; Horsfield, C.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Perkowska-Ptasińska, A.; Rabant, M.; et al. A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 2018, 102, 1795–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M. C4d-Negative Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Renal Allografts: Evidence for Its Existence and Effect on Graft Survival. Clin. Nephrol. 2011, 75, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sis, B.; Jhangri, G.S.; Bunnag, S.; Allanach, K.; Kaplan, B.; Halloran, P.F. Endothelial Gene Expression in Kidney Transplants with Alloantibody Indicates Antibody-Mediated Damage despite Lack of C4d Staining. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 2312–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellarés, J.; Reeve, J.; Loupy, A.; Mengel, M.; Sis, B.; Skene, A.; De Freitas, D.G.; Kreepala, C.; Hidalgo, L.G.; Famulski, K.S.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Human Kidney Transplants. Am. J. Transplant. 2013, 13, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.; Afzali, B.; Dominy, K.M.; Chapman, E.; Gill, R.; Hidalgo, L.G.; Roufosse, C.; Sis, B.; Mengel, M. Multiplexed Color-Coded Probe-Based Gene Expression Assessment for Clinical Molecular Diagnostics in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Human Renal Allograft Tissue. Clin. Transplant. 2016, 30, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegall, M.D.; Diwan, T.; Raghavaiah, S.; Cornell, L.D.; Burns, J.; Dean, P.G.; Cosio, F.G.; Gandhi, M.J.; Kremers, W.; Gloor, J.M. Terminal Complement Inhibition Decreases Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Sensitized Renal Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, L.D.; Schinstock, C.A.; Gandhi, M.J.; Kremers, W.K.; Stegall, M.D. Positive Crossmatch Kidney Transplant Recipients Treated with Eculizumab: Outcomes beyond 1 Year. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinstock, C.A.; Bentall, A.J.; Smith, B.H.; Cornell, L.D.; Everly, M.; Gandhi, M.J.; Stegall, M.D. Long-Term Outcomes of Eculizumab-Treated Positive Crossmatch Recipients: Allograft Survival, Histologic Findings, and Natural History of the Donor-Specific Antibodies. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, W.H.; Mamode, N.; Montgomery, R.A.; Stegall, M.D.; Ratner, L.E.; Cornell, L.D.; Rowshani, A.T.; Colvin, R.B.; Dain, B.; Boice, J.A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Eculizumab in the Prevention of Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Living-Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients Requiring Desensitization Therapy: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 2876–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.E.; Magro, C.M.; Singer, A.L.; Segev, D.L.; Haas, M.; Hillel, A.T.; King, K.E.; Kraus, E.; Lees, L.M.; Melancon, J.K.; et al. The Use of Antibody to Complement Protein C5 for Salvage Treatment of Severe Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehade, H.; Rotman, S.; Matter, M.; Girardin, E.; Aubert, V.; Pascual, M. Eculizumab to Treat Antibody-Mediated Rejection in a 7-Year-Old Kidney Transplant Recipient. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e551–e555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelken, B.; Arpali, E.; Görcin, S.; Kocak, B.; Karatas, C.; Demiralp, E.; Turkmen, A. Eculizumab for Treatment of Refractory Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Patients: A Single-Center Experience. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.; Kumar, V.; Mompoint-Williams, D.; Reed, R.D.; MacLennan, P.A.; Stegner, K.; Locke, J.E. Dosing Eculizumab for Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplantation: A Case Report. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfranco, L.; Joly, M.; Del Bello, A.; Esposito, L.; Cognard, N.; Perrin, P.; Moulin, B.; Kamar, N.; Caillard, S. Eculizumab for Thrombotic Microangiopathy Associated with Antibody-Mediated Rejection after ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation. Case Rep. Transplant. 2017, 2017, 3197042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.K.; Bentall, A.; Dean, P.G.; Shaheen, M.F.; Stegall, M.D.; Schinstock, C.A. Use of Eculizumab for Active Antibody-Mediated Rejection That Occurs Early Post-Kidney Transplantation: A Consecutive Series of 15 Cases. Transplantation 2019, 103, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Baskin, E.; Karakayali, F.Y.; Gemici, A.; Gulleroglu, K.; Yilmaz, A.C.; Moray, G.; Haberal, M. Use of Eculizumab in Pediatric Patients with Late Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 20, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, N.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.N.; Shin, H.S.; Jung, Y.; Rim, H.; Rennke, H.G.; Chandraker, A. Lack of Efficacy and Safety of Eculizumab for Treatment of Antibody-Mediated Rejection Following Renal Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2022, 54, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglarnia, A.-R.; Nilsson, B.; Nilsson, T.; von Zur-Mühlen, B.; Wagner, M.; Berne, C.; Wanders, A.; Magnusson, A.; Tufveson, G. Prompt Reversal of a Severe Complement Activation by Eculizumab in a Patient Undergoing Intentional ABO-Incompatible Pancreas and Kidney Transplantation. Transpl. Int. 2011, 24, e61–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, Z.A.; Collins, T.E.; Schlueter, A.J.; Raife, T.I.; Holanda, D.G.; Nair, R.; Reed, A.I.; Thomas, C.P. Case Report: Eculizumab Rescue of Severe Accelerated Antibody-Mediated Rejection after ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplant. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 3033–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Roncero, F.; Suñer, M.; Bernal, G.; Cabello, V.; Toro, M.; Pereira, P.; Angel Gentil, M. Eculizumab Treatment of Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Renal Transplantation: Case Reports. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 2690–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noone, D.; Al-Matrafi, J.; Tinckam, K.; Zipfel, P.F.; Herzenberg, A.M.; Thorner, P.S.; Pluthero, F.G.; Kahr, W.H.A.; Filler, G.; Hebert, D.; et al. Antibody Mediated Rejection Associated with Complement Factor H-Related Protein 3/1 Deficiency Successfully Treated with Eculizumab. Am. J. Transplant. 2012, 12, 2546–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Arpali, E.; Demiralp, E.; Yelken, B.; Karatas, C.; Gorcin, S.; Gorgulu, N.; Uzunalan, M.; Turkmen, A.; Kalayoglu, M. Eculizumab for Salvage Treatment of Refractory Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Patients: Case Reports. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghirardo, G.; Benetti, E.; Poli, F.; Vidal, E.; Della Vella, M.; Cozzi, E.; Murer, L. Plasmapheresis-Resistant Acute Humoral Rejection Successfully Treated with Anti-C5 Antibody. Pediatr. Transplant. 2014, 18, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbach, M.; Suberbielle, C.; Brochériou, I.; Ridel, C.; Mesnard, L.; Dahan, K.; Rondeau, E.; Hertig, A. Report of the Inefficacy of Eculizumab in Two Cases of Severe Antibody-Mediated Rejection of Renal Grafts. Transplantation 2014, 98, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orandi, B.J.; Zachary, A.A.; Dagher, N.N.; Bagnasco, S.M.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M.; Van Arendonk, K.J.; Gupta, N.; Lonze, B.E.; Alachkar, N.; Kraus, E.S.; et al. Eculizumab and Splenectomy as Salvage Therapy for Severe Antibody-Mediated Rejection after HLA-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2014, 98, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.A.; Orandi, B.J.; Racusen, L.; Jackson, A.M.; Garonzik-Wang, J.M.; Shah, T.; Woodle, E.S.; Sommerer, C.; Fitts, D.; Rockich, K.; et al. Plasma-Derived C1 Esterase Inhibitor for Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection Following Kidney Transplantation: Results of a Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Am. J. Transplant. 2016, 16, 3468–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandary, F.; Jilma, B.; Mühlbacher, J.; Wahrmann, M.; Regele, H.; Kozakowski, N.; Firbas, C.; Panicker, S.; Parry, G.C.; Gilbert, J.C.; et al. Anti-C1s Monoclonal Antibody BIVV009 in Late Antibody-Mediated Kidney Allograft Rejection—Results from a First-in-Patient Phase 1 Trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.; Lefaucheur, C.; Jordan, S.C. Update on C1 Esterase Inhibitor in Human Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.A.; Zeevi, A.; Choi, J.; Cisneros, K.; Toyoda, M.; Kahwaji, J.; Peng, A.; Villicana, R.; Puliyanda, D.; Reinsmoen, N.; et al. A Phase I/II Placebo-Controlled Trial of C1-Inhibitor for Prevention of Antibody-Mediated Rejection in HLA Sensitized Patients. Transplantation 2015, 99, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlbacher, J.; Jilma, B.; Wahrmann, M.; Bartko, J.; Eskandary, F.; Schörgenhofer, C.; Schwameis, M.; Parry, G.C.; Gilbert, J.C.; Panicker, S.; et al. Blockade of HLA Antibody-Triggered Classical Complement Activation in Sera From Subjects Dosed With the Anti-C1s Monoclonal Antibody TNT009-Results from a Randomized First-in-Human Phase 1 Trial. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, U.; Altuner, U.; Pavenstädt, H.; Reuter, S. First Report on Successful Conversion of Long-Term Treatment of Recurrent Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Eculizumab to Ravulizumab in a Renal Transplant Patient. Transpl. Int. 2022, 35, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Gödel, M.; Mahmud, M.; Fischer, L.; Huber, T.B.; Kluger, M.A.; Grahammer, F. Ravulizumab in Preemptive Living Donor Kidney Transplantation in Hereditary Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Transplant. Direct 2022, 8, e1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, S.C.; Kucher, K.; Bagger, M.; Hockey, H.-U.; Wagner, K.; Ammerman, N.; Vo, A. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Significantly Reduces Exposure of Concomitantly Administered Anti-C5 Monoclonal Antibody Tesidolumab. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 2581–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, A.B.; Lovasik, B.P.; Faber, D.A.; Burlak, C.; Breeden, C.; Estrada, J.L.; Reyes, L.M.; Vianna, R.M.; Tector, M.F.; Tector, A.J. Anti-C5 Antibody Tesidolumab Reduces Early Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Prolongs Survival in Renal Xenotransplantation. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooden, B.; Tarragon, B.; Navarro-Torres, M.; Bomback, A.S. Complement Inhibitors for Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, II29–II39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigooka, H.; Katsumata, H.; Saiga, K.; Tokita, D.; Motoi, S.; Matsui, C.; Suzuki, Y.; Tomimatsu, A.; Nakatani, T.; Kuboi, Y.; et al. Novel Complement C5 Small-Interfering RNA Lipid Nanoparticle Prolongs Graft Survival in a Hypersensitized Rat Kidney Transplant Model. Transplantation 2022, 106, 2338–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Fitch, Z.W.; Schroder, P.M.; Choi, A.Y.; Manook, M.; Yoon, J.; Song, M.; Yi, J.S.; Khandelwal, S.; Arepally, G.M.; et al. C3 Complement Inhibition Prevents Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Prolongs Renal Allograft Survival in Sensitized Non-Human Primates. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomback, A.S.; Daina, E.; Remuzzi, G.; Kanellis, J.; Kavanagh, D.; Pickering, M.C.; Sunder-Plassmann, G.; Walker, P.D.; Wang, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pegcetacoplan in Kidney Transplant Recipients With Recurrent Complement 3 Glomerulopathy or Primary Immune Complex Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2025, 10, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Recipient-Related Factors | Donor-Related Factors | Transplant-Related Factors |
|---|---|---|
Comorbidities
| Donor type
| Graft preservation
|
Cause of CKD
| Comorbidities
| Ischemia times
|
Type of dialysis
| Immunosuppression
|
| Author (Year) | Study Type | Patients No. | Transplant Type | AMR Time (Post-KT) | AMR Type | Eculizumab No. of Doses | Other Treatments | Response | Graft Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locke et al. (2009) [59] | Case report | 1 | HLAi | D10 | Active AMR, C4d+ | 1 | PE, IVIG, anti-CD20 | Yes | No |
| Biglarnia et al. (2011) [67] | Case report | 1 | ABOi | D9 | Active AMR, C4d+ | 2 | IA | Yes | No |
| Stewart et al. (2012) [68] | Case report | 1 | ABOi | D4 | Refractory active AMR, C4d+ | 8 | PE, IVIG, splenectomy | Yes (partially) | No |
| Gonzalez-Roncero et al. (2012) [69] | Case report | 2 | 1st-Retransplant, HLAi; 2nd-first KT; | 1st-D7; 2nd-D8; | 1st-Active AMR, vascular thrombosis, C4d+; 2nd-Active AMR, TMA, C4d+; | 1st-1; 2nd-1; | 1st-PE, IVIG, anti-CD20 2nd-PE, IVIG, anti-CD20; | 1st-Yes; 2nd-Yes; | 1st-No; 2nd-No; |
| Noone et al. (2012) [70] | Case report | 1 | Retransplant (highly sensitized) | D15 | Refractory chronic active AMR, TMA, C4d+ | 2 | PE, IVIG, anti-CD20 | Yes (partially) | No |
| Kocak et al. (2013) [71] | Case report | 2 | 1st-Retransplant (sensitized); 2nd-First KT (sensitized); | 1st-D8; 2nd-D5; | 1st-Active AMR, TMA, severe vascular lesions, C4d+; 2nd-Mixed acute rejection, C4d+; | 1st-5; 2nd-5; | 1st-PE, IVIG, anti-CD20; 2nd-IVIG, anti-CD20; | 1st-Yes; 2nd-No; | 1st-No; 2nd-Yes; |
| Ghirardo et al. (2014) [72] | Case report | 1 | Retransplant (highly sensitized) | D42 | Active AMR, C4d+ | 4 | PE, IVIG, anti-CD20 | Yes; 1 year graft biopsy showed complete resolution of AMR; | No |
| Burbach et al. (2014) [73] | Case report | 2 | 1st-First KT (sensitized); 2nd-Retransplant (sensitized); | 1st-12 months; 2nd-1 month; | 1st-Chronic active AMR, C4d−; 2nd-Active AMR, C4d−; | 1st-N/A; 2nd-15; | 1st-PE, IVIG, anti-CD20; 2nd-IA, IVIG; | 1st-No; 2nd-Yes (temporary); | 1st-Yes 2nd-Yes |
| Orandi et al. (2014) [74] | Retrospective | 24 (14/24-Sple-nectomy; 5/24-Eculi-zumab+ splenectomy; 5/24-Eculi-zumab) | HLA/ABOi | Median: 6 days (5–9) | Active and chronic AMR, C4d+ | Median: 12.5 (4–17) | PE, IVIG, anti-CD20 | Similar mean SCr across the groups at 1-year after KT; Transplant glomerulopathy at follow-up biopsies: 70% (Splenectomy group), 20% (Eculizumab+ splenectomy group), 100% (Eculizumab group); | 22.1—Splenectomy group; 0—Eculizumab + splenectomy group; 70—Eculizumab group; |
| Chehade et al. (2015) [60] | Case report | 1 | Retransplant (highly sensitized) | D4 | Active AMR, C4d+, borderline TCMR; | 2 | PE, IVIG, ATG | Yes; 2 months graft biopsy showed complete resolution of AMR; | No |
| Yelken et al. (2015) [61] | Case series | 8 | 2/8-Retransplant; 4/8-Sensitized patients; | 3/8-first 3 days; 5/8-between 8 and 18 months; | 5/8-Acute AMR 6/8-C4d+ 1/8-TMA | N/A | PE, IVIG, RTX, ATG, | 4/8-Yes | 4/8-Yes |
| Smith et al. (2016) [62] | Case report | 2 | ABOi | 1st-D7; 2nd-D5; | 1st-Active AMR, C4d+; 2nd-Active AMR, C4d+; | 1st-2; 2nd-4; | PE, IVIG, anti-CD20, splenectomy; | 1st-Yes; 1 year graft biopsy showed complete resolution of AMR; 2nd-Yes (partially); 1 month biopsy showed partial resolution of the histological lesions of AMR; | 1st-No; 2nd-No; |
| Lanfranco et al. (2017) [63] | Case report | 2 | ABOi | 1st-D13; 2nd-D12 | 1st-Active AMR, C4d+, TMA, vascular thrombosis; 2nd-Acute AMR, Cd4+, TMA; | 1st-6; 2nd-6; | 1st-PE, IA; 2nd-PE, IA; | 1st-No; 2nd-Yes; | 1st-Yes; 2nd-No; |
| Kulkarni et al. (2017) [12] | Pilot RCT | 15 (Treatment group: 10 patients—6 months of Eculizumab and 6 months of observation; Control group: 5 patients—observation only) | Chronic AMR, de novo DSA MFI > 1100, | N/A | Chronic AMR, C4d+ (20%) | 14 | N/A | Stable graft function and non-significant mean eGFR difference between groups at 6 months:−1.52 (8.80 to 5.76) | No reduction in ENDAT with complement inhibition on protocol biopsies at 1 year |
| Tan et al. (2019) [64] | Retrospective | 15 | Sensitized patients (80%) + B-FCXM (66%) | Median: 10days (7–11) | Early active AMR, C4d+ | Median: 5 | PE (80%), splenectomy (6.7%) | Improvement of kidney function; AMR resolution (83.3%) within 4–6 months; | No |
| Siddiqui et al. (2022) [65] | Case report | 2 | Unsensitized patients | 1st-11 months; 2nd-24months; | Late active AMR, C4d+ | 1st-2; 2nd-2; | 1st-PE, IVIG, anti-CD20; 2nd-PE, IVIG, anti-CD20; | 1st-Yes; 2nd-Yes; | 1st-No; 2nd-No; |
| Heo et al. (2022) [66] | RCT, open label | 11 (Eculizumab arm: 7 patients; SOC arm: 4 patients) | Sensitized patients (81.8%); Retransplant (27.3%) | Median: 1628 days (1–5495) | Active and chronic active AMR, C4d+ | 7 (if DSA < 50% of baseline DSA; 9 (if DSA > 50% of baseline); | PE, IVIG, anti-CD20, bortezomib, ATG | Lack of efficacy in AMR treatment and in prevention of acute AMR to chronic AMR progression or transplant glomerulopathy | No |
| Author (Year) | Study Type | Sample Size | AMR Type | Intervention | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viglietti et al. (2016) [13] | Single-arm, pilot | 6 | Active AMR unresponsive to SOC therapy | C1-INH 2000 U/day for 3 days, then twice weekly added to high dose IVIG for 6 months; | eGFR improvement from 38.7 ± 17.9 to 45.2 ± 21.3 mL/min/1.73 m2 (p = 0.0277); No changes in histological feature, except a decrease in the C4d deposition rate from 5/6 to 1/6 (p = 0.0455); Change in DSA C1q status from 6/6 to 1/6 (p = 0.0253); AE: 1 DVT; |
| Montgomery et al. (2016) [75] | Phase 2b, multicenter double-blind RCT pilot study | 18 | Active and chronic active AMR | C1-INH arm (n = 9)—7 doses over a 2-week period, with an initial IV infusion of 5000 U on day 1, followed by 2500 U IV on days 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13 added to SOC (PE, IVIG ± RTX); Placebo arm (n = 9); | Graft survival at D20 between groups was not different; Six-month biopsies (n = 14): Transplant glomerulopathy in 0/7 (C1-INH arm) and 3/7 (Placebo arm); PP significantly depleted endogenous functional C1-INH levels; No discontinuations, graft losses, deaths, or study drug—related serious AEs; |
| Eskandary et al. (2018) [76] | Non-randomized, phase 1b trial | 10 | Late active or chronic active AMR | Anti-C1s monoclonal antibody—4 weekly doses (60 mg/kg); | No serious AEs were observed during the 7 weeks of follow-up; Sutimlimab profoundly blocks CP activity in both serum and renal tissue; 5/8 C4d+ KTR switch to a C4d− status and 2/8 KTR had a significant decrease in C4d score; No change in microcirculation inflammation, gene expression patterns, DSA levels, or kidney function; |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorohan, B.M.; Tacu, D.; Gîngu, C.; Guler-Margaritis, S.; Obrișcă, B.; Tănăsescu, M.-D.; Ismail, G.; Baston, C. Complement in Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney Graft: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082810
Sorohan BM, Tacu D, Gîngu C, Guler-Margaritis S, Obrișcă B, Tănăsescu M-D, Ismail G, Baston C. Complement in Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney Graft: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082810
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorohan, Bogdan Marian, Dorina Tacu, Constantin Gîngu, Silviu Guler-Margaritis, Bogdan Obrișcă, Maria-Daniela Tănăsescu, Gener Ismail, and Cătălin Baston. 2025. "Complement in Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney Graft: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082810
APA StyleSorohan, B. M., Tacu, D., Gîngu, C., Guler-Margaritis, S., Obrișcă, B., Tănăsescu, M.-D., Ismail, G., & Baston, C. (2025). Complement in Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Kidney Graft: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082810





