Which Surrogate Marker of Insulin Resistance Among Those Proposed in the Literature Better Predicts the Presence of Non-Metastatic Bladder Cancer?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Anthropometric Evaluation
2.3. Clinical Assessment
2.4. Diagnostic Criteria of Bladder Cancer
2.5. Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and Their Calculation
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
4. Predictions
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bladder Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/bladder-cancer-statistics (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Halaseh, S.A.; Halaseh, S.; Alali, Y.; Ashour, M.E.; Alharayzah, M.J. A Review of the Etiology and Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: All You Need to Know. Cureus 2022, 14, e27330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmadinezhad, M.; Arshadi, M.; Hesari, E.; Sharafoddin, M.; Azizi, H.; Khodamoradi, F. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and its components with bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Epidemiol. Health 2022, 44, e2022050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Feng, D.; Song, P.; Yang, Y.; Wei, W.; Li, L. Is metabolic syndrome associated with high tumor grade and stage of bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2188–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lu, Y.; Tao, J. Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity as Risk Factors for Bladder Cancer Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 699732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- van den Brandt, P.A. Diabetes and the risk of bladder cancer subtypes in men and women: Results from the Netherlands Cohort Study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 39, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzschneider, K.M.; Kahn, S.E. Review: The role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4753–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Iiritano, S.; Nocera, A.; Possidente, K.; Nevolo, M.T.; Ventura, V.; Foti, D.; Chiefari, E.; Brunetti, A. Insulin resistance and cancer risk: An overview of the pathogenetic mechanisms. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 789174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Màrmol, J.M.; Carlsson, M.; Raun, S.H.; Grand, M.K.; Sørensen, J.; Lang Lehrskov, L.; Richter, E.A.; Norgaard, O.; Sylow, L. Insulin resistance in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Oncol. 2023, 62, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, G.; Crocetto, F.; Di Vito, C.; Creta, M.; Martino, R.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Pesce, S.; Napolitano, L.; Capone, D.; Imbimbo, C. Association of NAFLD and Insulin Resistance with Non Metastatic Bladder Cancer Patients: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, J.K. Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp to assess insulin sensitivity in vivo. Methods Protocols 2009, 560, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, S.M.; Miettinen, H.; Stern, M.P. The homeostasis model in the San Antonio Heart Study. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdas Nayak, V.K.; Satheesh, P.; Shenoy, M.T.; Kalra, S. Triglyceride Glucose (TyG) Index: A surrogate biomarker of insulin resistance. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2022, 72, 986–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er, L.K.; Wu, S.; Chou, H.H.; Hsu, L.A.; Teng, M.S.; Sun, Y.C.; Ko, Y.L. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index is a simple and clinically useful surrogate marker for insulin resistance in nondiabetic individuals. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneu, P.; Văcărescu, C.; Drăgan, S.R.; Cirin, L.; Lazăr-Höcher, A.I.; Cozgarea, A.; Faur-Grigori, A.A.; Crișan, S.; Gaiță, D.; Luca, C.T.; et al. The Triglyceride/HDL Ratio as a Surrogate Biomarker for Insulin Resistance. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yamauchi, K.; Sato, Y.; Nakasone, Y.; Aizawa, T. Comparison of HOMA-IR, HOMA-β% and disposition index between US white men and Japanese men in Japan in the ERA JUMP study: Was the calculation of disposition index legitimate? Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1679–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Chavolla, O.Y.; Almeda-Valdes, P.; Gomez-Velasco, D.; Viveros-Ruiz, T.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Romo-Romo, A.; Sánchez-Lázaro, D.; Meza-Oviedo, D.; Vargas-Vázquez, A.; Campos, O.A.; et al. METS-IR, a novel score to evaluate insulin sensitivity, is predictive of visceral adiposity and incident type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulmichl, K.; Hatunic, M.; Højlund, K.; Jotic, A.; Krebs, M.; Mitrakou, A.; Porcellati, F.; Tura, A.; Bergsten, P.; Forslund, A.; et al. Modification and Validation of the Triglyceride-to-HDL Cholesterol Ratio as a Surrogate of Insulin Sensitivity in White Juveniles and Adults without Diabetes Mellitus: The Single Point Insulin Sensitivity Estimator (SPISE). Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Jee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jin, S.M.; Suh, S.; Bae, J.C.; Kim, S.W.; Chung, J.H.; Min, Y.K.; Lee, M.S.; et al. Non-HDL-cholesterol/HDL-cholesterol is a better predictor of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance than apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 2678–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.T.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.T.; Xie, X. Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP): A novel predictive indicator for the coronary artery disease in postmenopausal women. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piccinelli, M.; Tessari, E.; Bortolomasi, M.; Piasere, O.; Semenzin, M.; Garzotto, N.; Tansella, M. Efficacy of the alcohol use disorders identification test as a screening tool for hazardous alcohol intake and related disorders in primary care: A validity study. BMJ 1997, 314, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tofthagen, C. Threats to validity in retrospective studies. J. Adv. Pr. Oncol. 2012, 3, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Walsh, J.W.; Hoffstad, O.J.; Sullivan, M.O.; Margolis, D.J. Association of diabetic foot ulcer and death in a population-based cohort from the United Kingdom. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Kidney Foundation. Available online: https://www.kidney.org/ (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/bladder-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/staging.html (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Statology. Available online: https://www.statology.org/friedman-test-stata/ (accessed on 19 October 2024).
- Fluss, R.; Faraggi, D.; Reiser, B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decision Curve Analysis. Available online: https://www.danieldsjoberg.com/dca-tutorial/dca-tutorial-stata.html#Case-Control_Designs (accessed on 21 October 2024).
- Lebovitz, H.E.; Banerji, M.A. Treatment of insulin resistance in diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 490, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitner, B.P.; Siebel, S.; Akingbesote, N.D.; Zhang, X.; Perry, R.J. Insulin and cancer: A tangled web. Biochem. J. 2022, 479, 583–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ferro, M.; Vartolomei, M.D.; Russo, G.I.; Cantiello, F.; Farhan, A.R.A.; Terracciano, D.; Cimmino, A.; Di Stasi, S.; Musi, G.; Hurle, R.; et al. An increased body mass index is associated with a worse prognosis in patients administered BCG immunotherapy for T1 bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endukuru, C.K.; Gaur, G.S.; Yerrabelli, D.; Sahoo, J.; Vairappan, B. Response: Cut-off Values and Clinical Utility of Surrogate Markers for Insulin Resistance and Beta-Cell Function to Identify Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components among Southern Indian Adults. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Lv, W.; Pan, Y. Causal associations of insulin resistance with coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke: A Mendelian randomization analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, L.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Bao, H.; Cheng, X.; Li, P. Association Between the Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and Chronic Kidney Disease in Chinese Hypertensive Patients. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 831648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gao, J.; Xie, C.; Tian, C.; Gao, T. Association between triglyceride glucose index and cognitive decline: A meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 359, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Moon, S.Y.; Koh, M.; Kang, Y.; Lee, J.Y. Association between Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and the Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choi, C.H.; Moon, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y. The Relationship between Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and Occurrence of Colorectal Adenoma in Individuals under 50 Years Old: A Single-Center Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, C.; Cheng, W.; Plum, P.S.; Köppe, J.; Gockel, I.; Thieme, R. Association between four insulin resistance surrogates and the risk of esophageal cancer: A prospective cohort study using the UK Biobank. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Jia, X.; Hu, C.; Qi, H.; Lin, H.; Zheng, R.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; et al. Association between triglyceride glucose index and breast cancer in 142,184 Chinese adults: Findings from the REACTION study. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1321622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zha, B.; Cai, A.; Wang, G. Relationship between obesity indexes and triglyceride glucose index with gastrointestinal cancer among the US population. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 43, 102760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yan, X.; Gao, Y.; Tong, J.; Tian, M.; Dai, J.; Zhuang, Y. Association Between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Risk in Chinese Population. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 585388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karin, M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Huang, H.; Fang, S.; Hang, Q. ROS: A “booster” for chronic inflammation and tumor metastasis. Biochim. Biophys Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, M.S.; Evans, M.D.; Dizdaroglu, M.; Lunec, J. Oxidative DNA damage: Mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1195–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppa, M.; Uribarri, J.; Vlassara, H. Aging and glycoxidant stress. Hormones 2008, 7, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wautier, M.P.; Chappey, O.; Corda, S.; Stern, D.M.; Schmidt, A.M.; Wautier, J.L. Activation of NADPH oxidase by AGE links oxidant stress to altered gene expression via RAGE. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E685–E694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conover, C.A.; Lee, P.D.; Kanaley, J.A.; Clarkson, J.T.; Jensen, M.D. Insulin regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in obese and nonobese humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 74, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Zwahlen, M.; Minder, C.; O’Dwyer, S.T.; Shalet, S.M.; Egger, M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: Systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulstone, E.; Prince, S.; Zaccheo, O.; Burns, J.L.; Harper, J.; Jacobs, C.; Church, D.; Hassan, A.B. Insulin-like growth factor ligands, receptors, and binding proteins in cancer. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, S.H.; Hanum, N.; Grotenhuis, A.J.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; van der Heijden, A.G.; Aben, K.K.; Mysorekar, I.U.; Kiemeney, L.A. Recurrent urinary tract infection and risk of bladder cancer in the Nijmegen bladder cancer study. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schwartz, L.; Salamon, K.; Simoni, A.; Eichler, T.; Jackson, A.R.; Murtha, M.; Becknell, B.; Kauffman, A.; Linn-Peirano, S.; Holdsworth, N.; et al. Insulin receptor signaling engages bladder urothelial defenses that limit urinary tract infection. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, F.; Mao, S.; Wang, R.; Chen, H.; Ran, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, P.; Yan, Y.; Li, W.; et al. Bladder cancer-associated microbiota: Recent advances and future perspectives. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- El-Mosalamy, H.; Salman, T.M.; Ashmawey, A.M.; Osama, N. Role of chronic E. coli infection in the process of bladder cancer- an experimental study. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2012, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abd-El-Raouf, R.; Ouf, S.A.; Gabr, M.M.; Zakaria, M.M.; El-Yasergy, K.F.; Ali-El-Dein, B. Escherichia coli foster bladder cancer cell line progression via epithelial mesenchymal transition, stemness and metabolic reprogramming. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nardelli, C.; Aveta, A.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Tripodi, L.; Russo, F.; Imbimbo, C.; Castaldo, G.; Pastore, L. Microbiome Profiling in Bladder Cancer Patients Using the First-morning Urine Sample. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2023, 59, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hussein, A.A.; Elsayed, A.S.; Durrani, M.; Jing, Z.; Iqbal, U.; Gomez, E.C.; Singh, P.K.; Liu, S.; Smith, G.; Tang, L.; et al. Investigating the association between the urinary microbiome and bladder cancer: An exploratory study. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 370.e9–370.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H.; Meyer, K.; Lulla, A.; Lewis, C.E.; Carnethon, M.R.; Schreiner, P.J.; Sidney, S.; Shikany, J.M.; Meirelles, O.; Launer, L.J. Gut microbiome and stages of diabetes in middle-aged adults: CARDIA microbiome study. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Persu, C.; Ciofu, I.; Petrescu, A.; Chirca, N.; Cauni, V. Bladder Wall Structure Alterations in Patients Treated with Botulinum Toxin for Detrusor Overactivity–A Morphological Study. In Vivo 2023, 37, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Peng, X.F.; Meng, X.Y.; Wei, C.; Xing, Z.H.; Huang, J.B.; Fang, Z.F.; Hu, X.Q.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zhou, S.H. The association between metabolic syndrome and bladder cancer susceptibility and prognosis: An updated comprehensive evidence synthesis of 95 observational studies involving 97,795,299 subjects. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6263–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kahn, H.S. The “lipid accumulation product” performs better than the body mass index for recognizing cardiovascular risk: A population-based comparison. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2005, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Epstein, E.J.; Osman, J.L.; Cohen, H.W.; Rajpathak, S.N.; Lewis, O.; Crandall, J.P. Use of the estimated glucose disposal rate as a measure of insulin resistance in an urban multiethnic population with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2280–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Patients (n) | BC (n = 123) | No BC (n = 86) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age years (median/IQR) | 70 (62–76) | 70 (61/77) | 0.56 * |
| Gender M/F (n) | 100/76 | 76/10 | 0.17 ^ |
| BMI | 26.4 (24.1–29) | 25.9 (24–28.7) | 0.37 * |
| BMI 18.5–24.9/25–29.9 /> 30 (n) | 39/59,721 | 33/43/10 | 0.44 ^ |
| Smoking yes/no/FMs (n) | 59/15/48 | 23/17/46 | 0.007 ^ |
| T2DM yes/no/prediabetes (n) | 32/52/36 | 18/46/22 | 0.25 ^ |
| Hypertension yes/no (n) | 74/49 | 56/30 | 0.46 ^ |
| Kidney failure yes/no (n) | 9/197 | 3/83 | 0.24 ^ |
| Dyslipidemia yes/no (n) | 86/37 | 70/16 | 0.061 ^ |
| Total cholesterol mg/dL (median/IQR) | 180 (153–206) | 175 (147–203) | 0.55 * |
| HDL-cholesterol mg/dL (median/IQR) | 46 (41–54) | 47.5 (41–57) | 0.6 * |
| LDL-cholesterol mg/dL (median/IQR) | 117 (91.5–142) | 113 (88–139) | 0.57 * |
| Triglycerides mg/dL (median/IQR) | 110 (80–144) | 96 (70–128) | 0.02 * |
| FPG mg/dL (median/IQR) | 95 (88–109) | 95.5 (85–110) | 0.62 * |
| Insulin mIU/L (median/IQR) | 9.4 (5.9–14.2) | 9.3 (6.9–11.7) | 0.37 * |
| Uric acid mg/dL (median/IQR) | 5.8 (4.9–6.8) | 5.85 (5.2–6.5) | 0.73 * |
| Creatinine mg/dL (median/IQR) | 0.96 (0.82–1.19) | 0.96 (0.85–1.12) | 0.9 * |
| Surrogate Markers IR Patients (n) | Total Population (n = 209) | BC Group (n = 123) | No BC Group (n = 86) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOMA-IR median (IQR) | 2.27 (1.53–3.18) | 2.34 (1.48–3.67) | 2.18 (1.57–2.85 | 0.17 * |
| HOMA-B median (IQR) | 1.98 (1.32–2.79) | 1.38 (0.91–2.94) | 1.88 (1.32–2.77) | 0.41 * |
| DI median (IQR) | 0.99 (0.85–1.16) | 1.01 (0.85–1.15) | 0.99(0.84–1.25) | 0.40 * |
| MetS-IR Mean +/− SD | 1.04 +/− 0.29 | 1.71 +/− 0.7 ° | 1.74 +/− 0.8 ° | 0.03 ° |
| SPISE median (IQR) | 6.15 (5.36–7.21) | 5.88 (5.24–7.21) | 6.45 (5.58–7.27) | 0.08 * |
| TyG median (IQR) | 8.5 (8.18–8.83) | 8.58 (8.27–8.89) | 8.42 (8.05–8.74) | 0.02 * |
| TyG-BMI median (IQR) | 223 (201–243) | 228 (202–249) | 219 (201–235) | 0.08 * |
| TG/HDL-C ratio median (IQR) | 2.22 (1.43–2.95) | 2.35 (1.59–3.21) | 1.96 (1.36–2.85) | 0.05 * |
| non-HDL/HDL ratio median (IQR) | 2.65 (2.17–3.38) | 2.8 (2.26–3.38) | 2–52 (1.09–3.45) | 0.2 * |
| LCI median (IQR) | 40,283 (23,864–74,315) | 47,051 (26,795–80,527) | 35,925 (21,249–73,155) | 0.18 * |
| d.v. | BC (Yes/No) | Odds Ratio | Std. Err. | z | p > |z| | 95% CI | Pseudo R2 | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
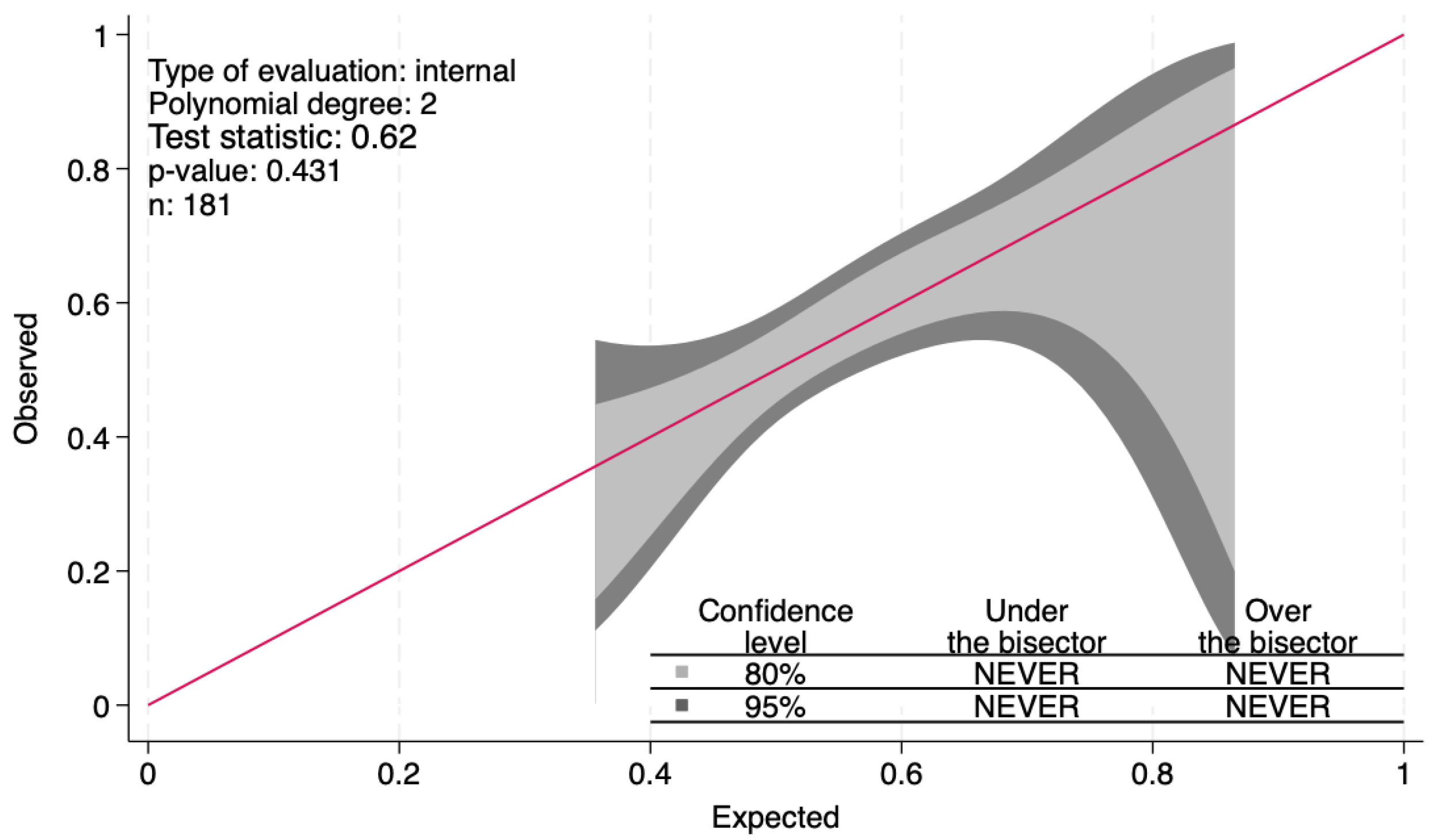
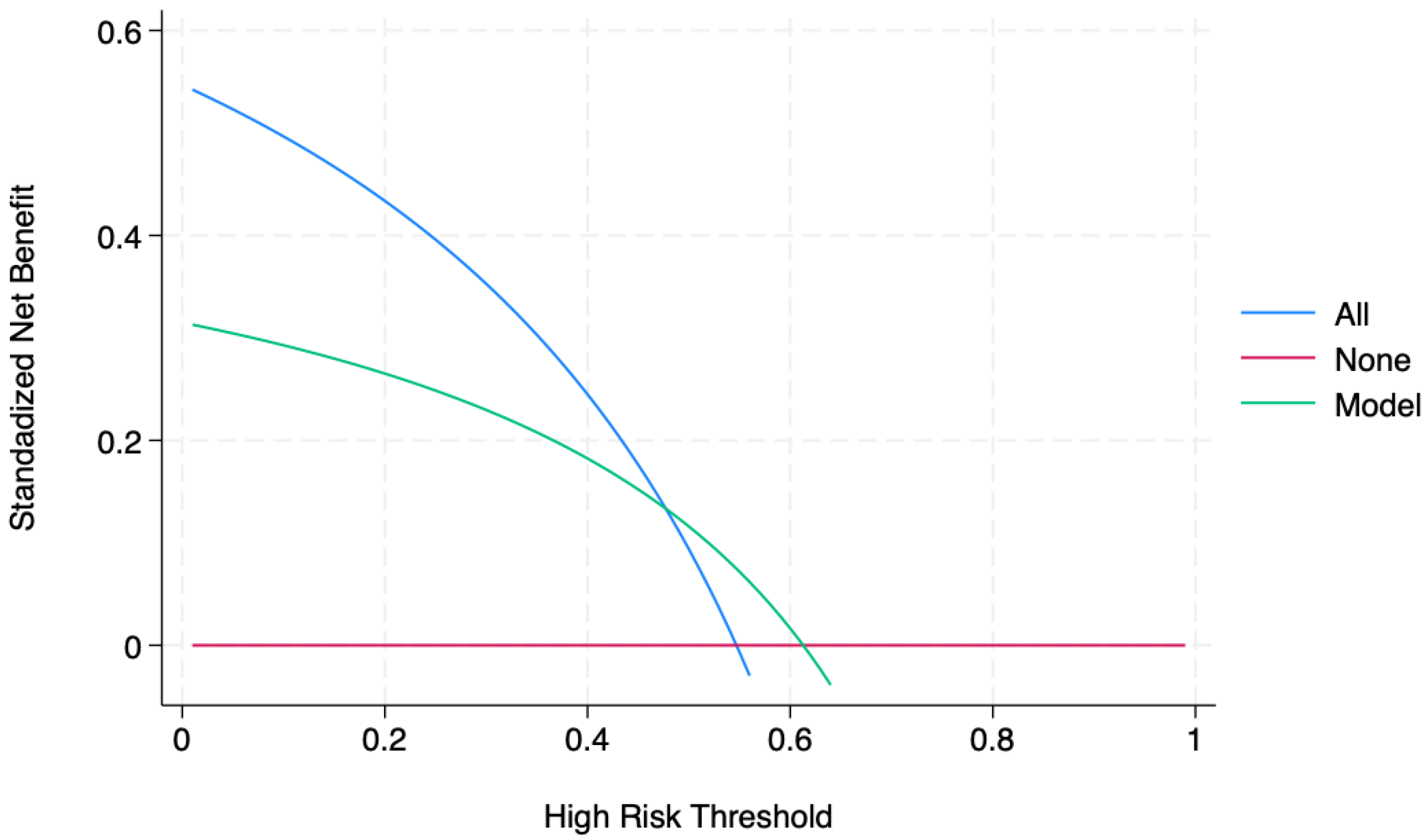
| i.v. | TyG | 2.10 | 0.67 | 2.34 | 0.02 | 1.13–3.91 | 0.022 | 181 |
| i.v | TyG-BMI | 1.01 | 0.00 | 1.57 | 0.12 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.01 | 179 |
| i.v | TG/HDL-C ratio | 1.21 | 0.13 | 1.73 | 0.08 | 0.97–1.50 | 0.017 | 178 |
| i.v | MetS-IR | 0.01 | 0.03 | −2.11 | 0.04 | 0.00–0.74 | 0.018 | 179 |
| i.v | DI | 0.54 | 0.30 | −1.10 | 0.27 | 0.18–1.61 | 0.00 | 156 |
| i.v | HOMA-B | 1.16 | 0.11 | 1.49 | 0.14 | 0.96–1.40 | 0.01 | 207 |
| i.v | HOMA-IR | 1.24 | 0.14 | 1.88 | 0.06 | 0.99–1.55 | 0.018 | 156 |
| i.v | SPISE | 0.84 | 0.09 | −1.59 | 0.11 | 0.68–1.04 | 0.01 | 176 |
| i.v | non HDL/HDLratio | 1.22 | 0.19 | 1.29 | 0.20 | 0.90–1.65 | 0.00 | 179 |
| i.v. | LCI | 1.00 | 0.00 | 1.72 | 0.08 | 0.99–1.0 | 0.016 | 175 |
| IR Markers | OR | Robust SE | z | p | 95% CI | Pseudo R2 | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TyG > 65 years | 1.56 | 0.70 | 0.99 | 0.32 | 0.65–3.76 | 0.00 | 115 |
| TyG = <65 years | 2.96 | 1.47 | 2.19 | 0.03 | 1.12–7.83 | 0.06 | 66 |
| MetS-IR > 65 years | 0.08 | 0.24 | −0.85 | 0.40 | 0.00–26.49 | 0.00 | 113 |
| MetS-IR = <65 years | 0.002 | 0.01 | −2.08 | 0.04 | 0.00–0.69 | 0.05 | 66 |
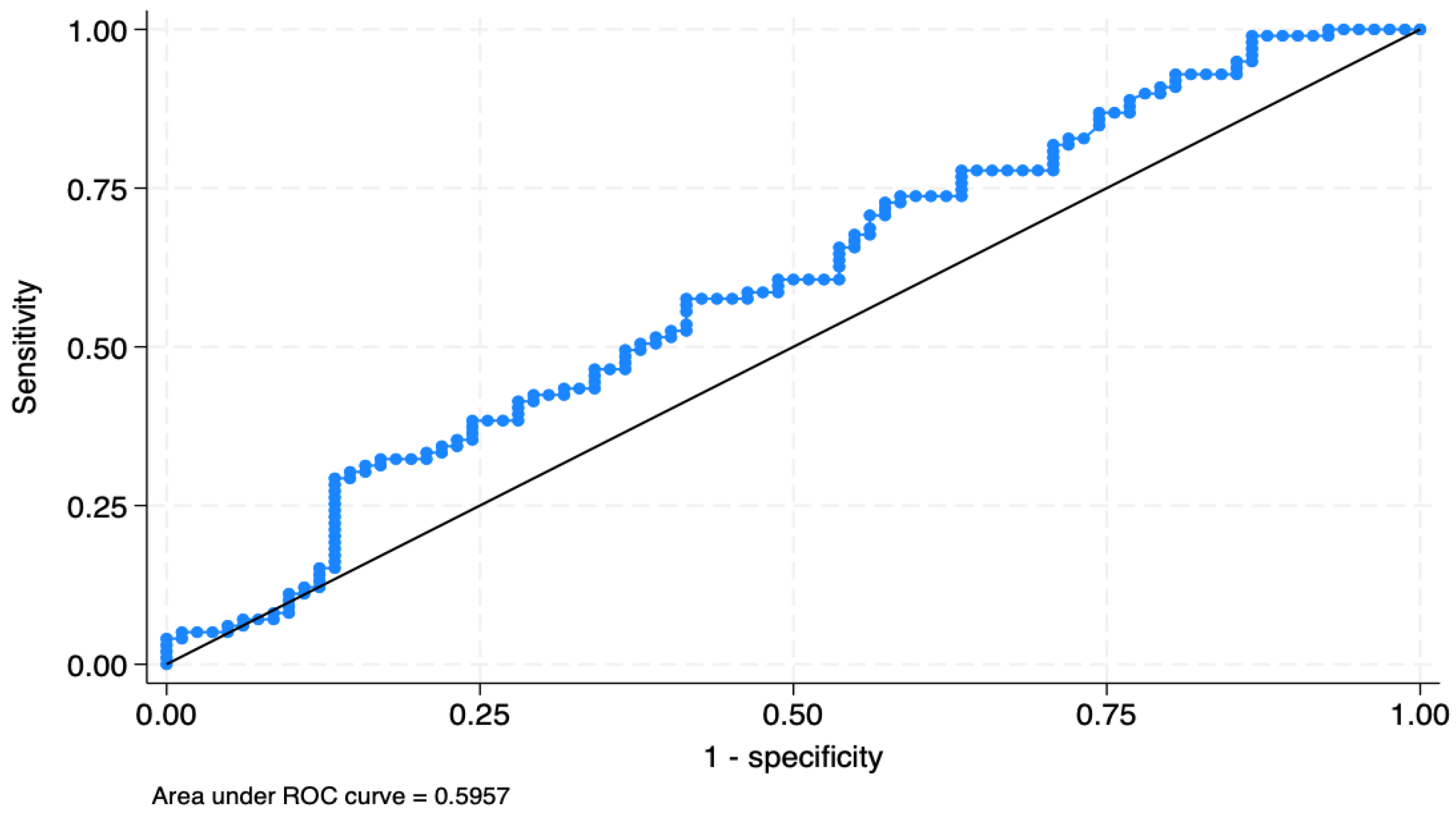
| Patients Classified | True BC | True No BC | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | n = 75 | n = 52 | n = 127 |
| Negative | n = 24 | n = 30 | n = 54 |
| Total | n = 99 | n = 82 | n = 181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarantino, G.; Imbimbo, C.; Ferro, M.; Bianchi, R.; La Rocca, R.; Lucarelli, G.; Lasorsa, F.; Busetto, G.M.; Finati, M.; Pastore, A.L.; et al. Which Surrogate Marker of Insulin Resistance Among Those Proposed in the Literature Better Predicts the Presence of Non-Metastatic Bladder Cancer? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082636
Tarantino G, Imbimbo C, Ferro M, Bianchi R, La Rocca R, Lucarelli G, Lasorsa F, Busetto GM, Finati M, Pastore AL, et al. Which Surrogate Marker of Insulin Resistance Among Those Proposed in the Literature Better Predicts the Presence of Non-Metastatic Bladder Cancer? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(8):2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082636
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarantino, Giovanni, Ciro Imbimbo, Matteo Ferro, Roberto Bianchi, Roberto La Rocca, Giuseppe Lucarelli, Francesco Lasorsa, Gian Maria Busetto, Marco Finati, Antonio Luigi Pastore, and et al. 2025. "Which Surrogate Marker of Insulin Resistance Among Those Proposed in the Literature Better Predicts the Presence of Non-Metastatic Bladder Cancer?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 8: 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082636
APA StyleTarantino, G., Imbimbo, C., Ferro, M., Bianchi, R., La Rocca, R., Lucarelli, G., Lasorsa, F., Busetto, G. M., Finati, M., Pastore, A. L., Al Salhi, Y., Fuschi, A., Terracciano, D., Giampaglia, G., Falabella, R., Barone, B., Fusco, F., Del Giudice, F., & Crocetto, F. (2025). Which Surrogate Marker of Insulin Resistance Among Those Proposed in the Literature Better Predicts the Presence of Non-Metastatic Bladder Cancer? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(8), 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14082636