Combined Surgically Induced Macular Detachment and Autologous Internal Limiting Membrane Transplantation for Refractory Full Thickness Macular Hole
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design: Interventional Case Series
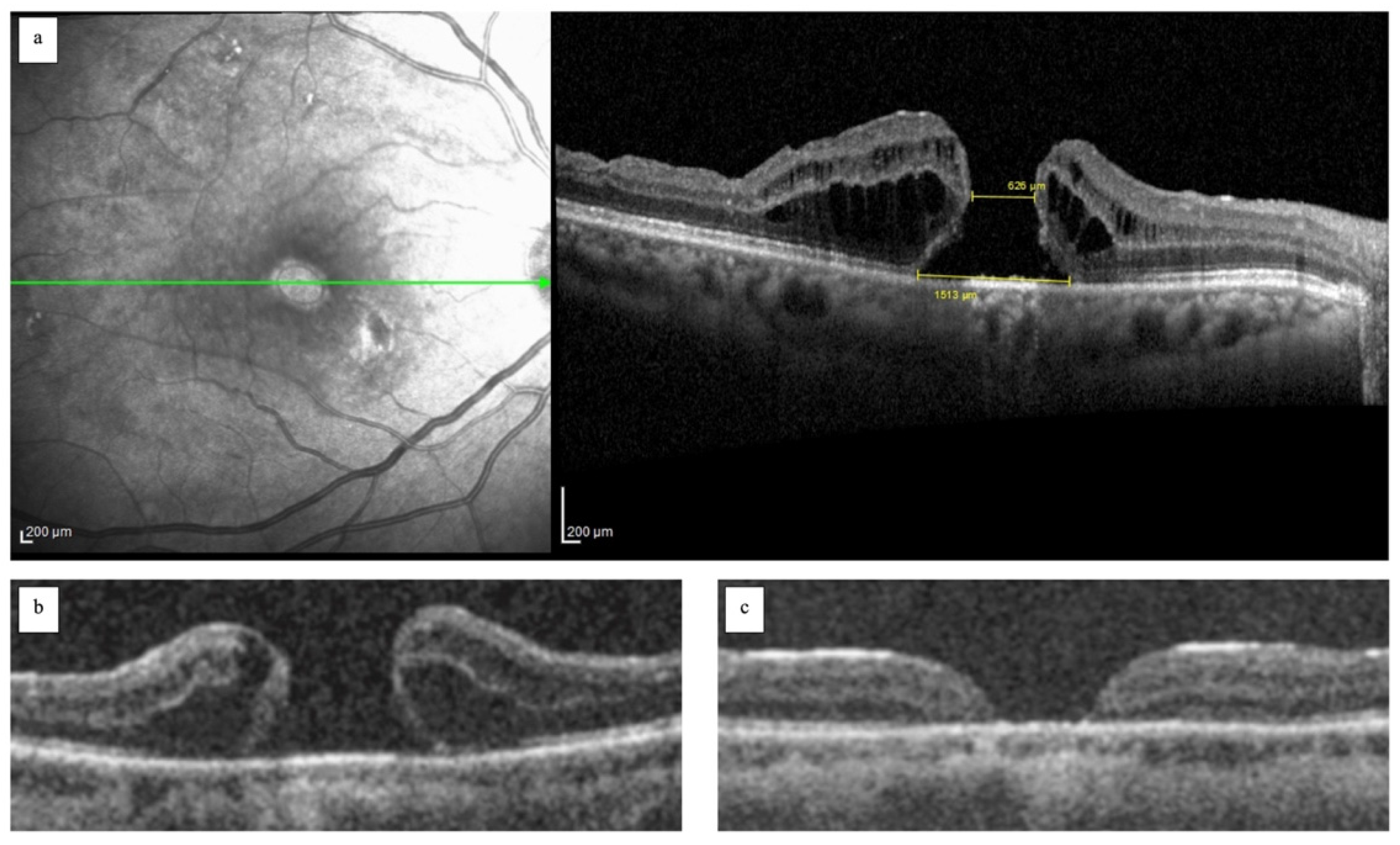
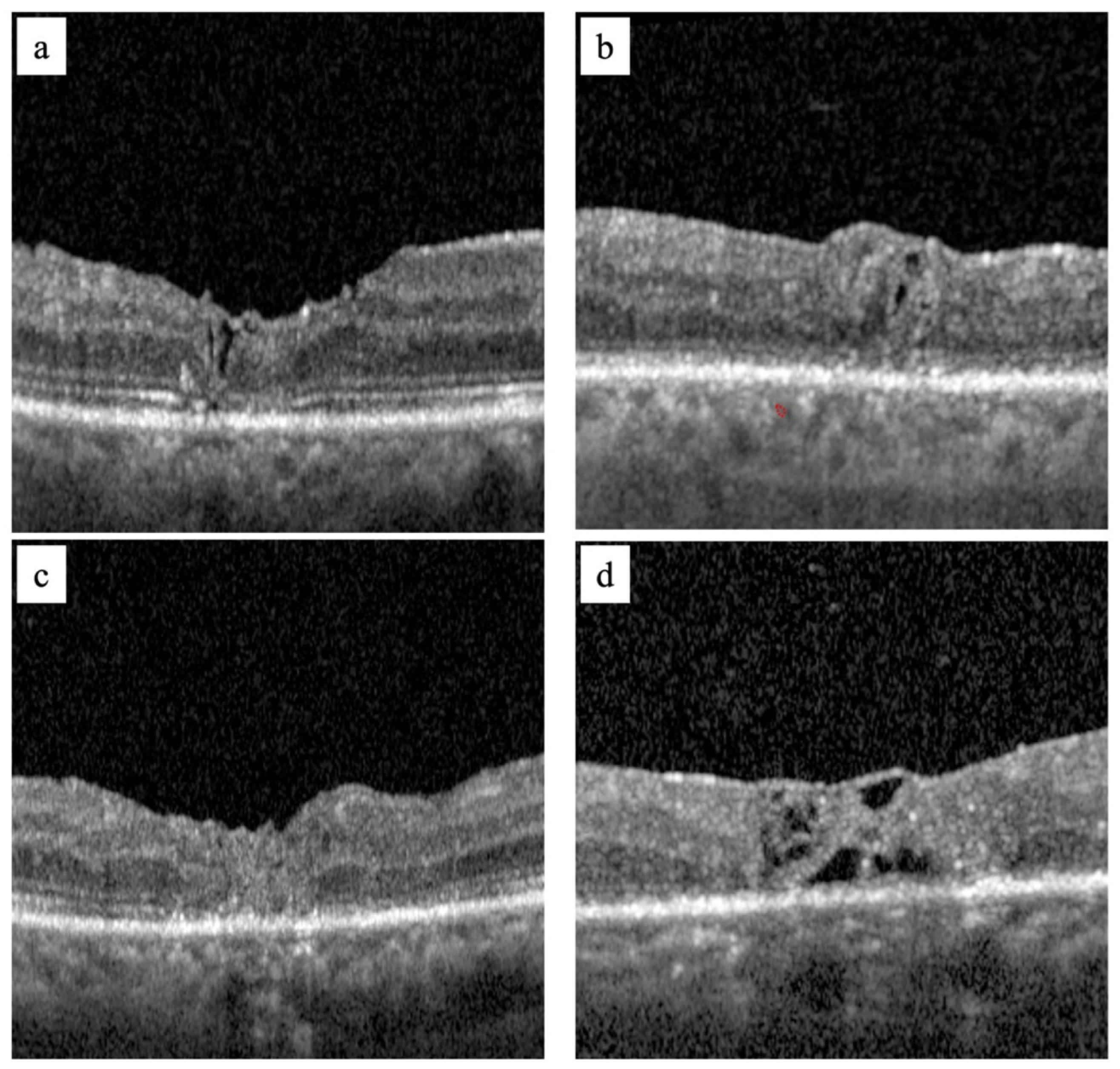
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
- (1)
- it combines and enhances the effect of two well-known surgical procedures by adding them together synergically;
- (2)
- it offers a new approach to the treatment of refractory FTMH, which would be useful in triggering retinal healing towards the complete restoration of the foveal tissue.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waich’ng, S.; Patton, N.; Ahmed, M.; Ivanova, T.; Baumann, C.; Charles, S.; Jalil, A. The Manchester large macular hole study: Is it time to reclassify large macular holes? Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 195, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, C.; Eckardt, U.; Groos, S.; Luciano, L.; Reale, E. Removal of the internal limiting membrane in macular holes. Clin. Morphol. Find. Ophthalmol. 1997, 94, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, H.L., Jr. Macular hole surgery with and without internal limiting membrane peeling. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, K.; Furukawa, M.; Ogino, N.; Uemura, A.; Demizu, S.; Larson, E. Vitreous surgery with and without internal limiting membrane peeling for macular hole repair. Retina 2004, 24, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, A.K.; Lai, T.Y.; Wong, V.W. Idiopathic macular hole surgery in Chinese patients: A randomised study to compare indocyanine green-assisted internal limiting membrane peeling with no internal limiting membrane peeling. Hong Kong Med. J. 2005, 11, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, U.C.; Kroyer, K.; Sander, B.; Larsen, M.; Henning, V.; Villumsen, J.; la Cour, M. Value of internal limiting membrane peeling in surgery for idiopathic macular hole stage 2 and 3: A randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, K.S.; Lois, N.; Scott, N.W.; Burr, J.; Cook, J.; Boachie, C.; Tadayoni, R.; la Cour, M.; Christensen, U.; Kwok, A.K. Vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane peeling versus no peeling for idiopathic full-thickness macular hole. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhao, J. Factors Associated with Anatomic Failure and Hole Reopening after Macular Hole Surgery. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 2021, 7861180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, D.; EI-Kannishy, A.; Kamel, R.; Abou Samra, W. Correlation between en face optical coherence tomography defects of the inner retinal layers and ganglion cell inner plexiform layer analysis after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic full thickness macular hole. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Almony, A.; Nudleman, E.; Shah, G.K.; Blinder, K.J.; Eliott, D.B.; Mittra, R.A.; Tewari, A. Techniques, rationale, and outcomes of internal limiting membrane peeling. Retina 2012, 32, 877–891. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, X. Modified internal limiting membrane flap technique for large chronic macular hole: Two case reports. Medicine 2022, 101, e28412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.K.; Chang, A.A.; Beaumont, P.E. The macular hole: Report of an Australian surgical series and meta-analysis of the literature. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2000, 28, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ip, M.S.; Baker, B.J.; Duker, J.S.; Reichel, E.; Baumal, C.R.; Gangnon, R.; Puliafito, C.A. Anatomical outcomes of surgery for idiopathic macular hole as determined by optical coherence tomography. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shpak, A.A.; Shkvorchenko, D.O.; Sharafetdinov, I.; Yukhanova, O.A. Predicting anatomical results of surgical treatment of idiopathic macular hole. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 9, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steel, D.H.; Chen, Y.; Latimer, J.; White, K.; Avery, P.J. Does Internal Limiting Membrane Peeling Size Matter? J. VitreoRetinal Dis. 2017, 1, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- D’Souza, M.J.J.; Chaudhary, V.; Devenyi, R.; Kertes, P.J.; Lam, W.-C. Re-operation of idiopathic full-thickness macular holes after initial surgery with internal limiting membrane peel. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, M.J.M.; Steel, D.H.M.; Yorston, D.F.; Hind, J.F.; El-Faouri, M.F.; Jalil, A.F.; Tyagi, P.F.; Wickham, L.F.; Laidlaw, A.H.M. Outcome of revision procedures for failed primary macular hole surgery. Retina 2021, 41, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Frisina, R.; Gius, I.; Tozzi, L.; Midena, E. Refractory full thickness macular hole: Current surgical management. Eye 2022, 36, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valldeperas, X.; Wong, D. Is it worth reoperating on macular holes? Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenkamp, J.; Kraus, J.; Framme, C.; Jackson, T.L.; Roider, J.; Gabel, V.-P.; Sachs, H.G. Retreatment of full-thickness macular hole: Predictive value of optical coherence tomography. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 91, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paques, M.; Chastang, C.; Mathis, A.; Sahel, J.; Massin, P.; Dosquet, C.; Korobelnik, J.-F.; Le Gargasson, J.-F.; Gaudric, A. Effect of autologous platelet concentrate in surgery for idiopathic macular hole: Results of a multicenter, double-masked, randomized trial. Platelets in macular hole surgery group. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoerauf, H.; Klüter, H.; Joachimmeyer, E.; Roider, J.; Framme, C.; Schlenke, P.; Kirchner, H.; Lagua, H. Results of vitrectomy and the no-touch-technique using autologous adjuvants in macular hole treatment. Int. Ophthalmol. 2001, 24, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, S.; William, A.; Voykov, B.; Ziemssen, F.; Bartz-Schmidt, K.U.; Spitzer, M.S. Anatomical and visual outcomes of autologous thrombocyte serum concentrate in the treatment of persistent full-thickness idiopathic macular hole after ILM peeling with brilliant blue G and membrane blue dual. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purtskhvanidze, K.; Frühsorger, B.; Bartsch, S.; Hedderich, J.; Roider, J.; Treumer, F. Persistent full-thickness idiopathic macular hole: Anatomical and functional outcome of revitrectomy with autologous platelet concentrate or autologous whole blood. Ophthalmologica 2017, 239, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, A.; Wojcik, E.J. Macular detachment for treatment of persistent macular hole. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging 2011, 42, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, H.D.; Kuang, K.; Kang, F.; Head, M.W.; Fishbarg, J. Macular holes: Migratory gaps and vitreous as obstacles to glial closure. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1997, 235, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, A.; Iandiev, I.; Pannicke, T.; Wurm, A.; Hollborn, M.; Wiedemann, P.; Osborne, N.N.; Reichenbach, A. Cellular signaling and factors involved in Muller cell gliosis: Neuroprotective and detrimental effects. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 28, 423–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, J.D. Idiopathic senile macular hole. Its early stages and pathogenesis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1988, 106, 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Premi, E.; Donati, S.; Azzi, L.; Porta, G.; Metrangolo, C.; Fontanel, L.; Morescalchi, F.; Azzolini, C. Macular holes: Main clinical presentations, diagnosis, and therapies. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 2022, 2270861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Kadir, M.A.; Lim, L.T. Update on surgical management of complex macular holes: A review. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2021, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikbova, G.; Oshitari, T.; Baba, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Mori, K. Pathogenesis and management of macular hole: Review of current advances. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 3467381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographic Parameters of Patients (14 Eyes of 14 Patients) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age years | mean ± [range] | 69.2 ± 4.8 [59–79] |
| Gender female/male | number (%) | 6/8 (42.9/57.1) |
| Eye right/left | number (%) | 6/8 (42.9/57.1) |
| Pre-operative Clinical Data | ||
| Axial length (AL) Millimeters (mm) | mean ± [range] | 24.6 ± 1.2 [22.9–26.3] |
| Best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) (logarithm of minimum angle of resolution) | mean ± [range] | 1.1 ± 0.1 [1.4–1] |
| Pre-operative Tomographic Data of FTMH | ||
| Base diameter μm | mean ± [range] | 760.2 ± 219.8 [368–1120] |
| Minimum diameter μm | mean ± [range] | 316.9 ± 126.4 [134–450] |
| Morphology of FTMH cuff/flat pattern | number (%) | 7/7 (50/50) [134–450] |
| Time of surgery | mean ± [range] | 2.3 ± 1.8 [1–6] |
| Post-operative BCVA (6th month) (logarithm of minimum angle of resolution) | mean ± [range] | 0.48 ± 0.3 [1.1–0.3] |
| Post-operative Morphological Parameters (6th month of follow-up) | ||
| FTMH closure rate yes-no | number (%) | 14/0 (100/0) |
| Foveal profile Regular/flat/inverted | number (%) | 7/5/2 (50/35/14.3) |
| Intact outer retinal layers yes-no | number (%) | 12/2 (85.7/14.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frisina, R.; Di Leo, L.; Gallo Afflitto, I.; Vulpetti, A.; Motta, L.; De Salvo, G. Combined Surgically Induced Macular Detachment and Autologous Internal Limiting Membrane Transplantation for Refractory Full Thickness Macular Hole. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062123
Frisina R, Di Leo L, Gallo Afflitto I, Vulpetti A, Motta L, De Salvo G. Combined Surgically Induced Macular Detachment and Autologous Internal Limiting Membrane Transplantation for Refractory Full Thickness Macular Hole. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(6):2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062123
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrisina, Rino, Laura Di Leo, Ilenia Gallo Afflitto, Andrea Vulpetti, Lorenzo Motta, and Gabriella De Salvo. 2025. "Combined Surgically Induced Macular Detachment and Autologous Internal Limiting Membrane Transplantation for Refractory Full Thickness Macular Hole" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 6: 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062123
APA StyleFrisina, R., Di Leo, L., Gallo Afflitto, I., Vulpetti, A., Motta, L., & De Salvo, G. (2025). Combined Surgically Induced Macular Detachment and Autologous Internal Limiting Membrane Transplantation for Refractory Full Thickness Macular Hole. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(6), 2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14062123








