Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease in Germany: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Practices Ahead of the Release of the German Recommendations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Outcomes
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Symptoms and Laboratory Findings: Initial Diagnosis vs. Current Status
3.2. Drug Therapies and Satisfaction with Treatment
3.3. Disease Activity: Initial Diagnosis vs. Current Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fautrel, B.; Mitrovic, S.; De Matteis, A.; Bindoli, S.; Antón, J.; Belot, A.; Bracaglia, C.; Constantin, T.; Dagna, L.; Di Bartolo, A.; et al. EULAR/PReS recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Still’s disease, comprising systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still’s disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1614–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, A.; Bindoli, S.; De Benedetti, F.; Carmona, L.; Fautrel, B.; Mitrovic, S. Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still’s disease are the same disease: Evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses informing the 2023 EULAR/PReS recommendations for the diagnosis and management of Still’s disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1748–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Jamilloux, Y.; Iwaz, J.; Seve, P. Adult-onset Still’s disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suda, T.; Zoshima, T.; Takeji, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Mizushima, I.; Yamada, K.; Nakashima, A.; Yachie, A.; Kawano, M. Elderly-onset Still’s disease complicated by macrophage activation syndrome: A case report and review of the literature. Intern. Med. 2020, 59, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Feist, E.; Canon-Garcia, V.; Rabijns, H.; Toennessen, K.; Bartlett, C.; Gregg, E.; Miller, P.; McGonagle, D. Burden of adult-onset Still’s disease: A systematic review of health-related quality of life, utilities, costs and resource use. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 63, 152264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, S.; Schroeder, B.; Alfaki, M. Mortality, length of stay and cost of hospitalization among patients with adult-onset Still’s disease: Results from the National Inpatient Sample 2016-2019. Diseases 2024, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bywaters, E.G. Still’s disease in the adult. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1971, 30, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaras, S.; Goetzke, C.C.; Kallinich, T.; Feist, E. Adult-onset Still’s disease: Clinical aspects and therapeutic approach. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Colafrancesco, S.; Alessandri, C.; Minniti, A.; Perricone, C.; Iaiani, G.; Palazzo, D.; Valesini, G. Interleukin 18: A biomarker for differential diagnosis between adult-onset Still’s disease and sepsis. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feist, E.; Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B. Mechanisms, biomarkers and targets for adult-onset Still’s disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Föll, D.; Wittkowski, H.; Hinze, C. Das Still-Syndrom als biphasische Erkrankung: Aktuelle Erkenntnisse zur Pathogenese und neue therapeutische Ansätze [Still’s disease as biphasic disorder: Current knowledge on pathogenesis and novel treatment approaches]. Z. Rheumatol. 2020, 79, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cush, J.J.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Christy, W.C.; Herbert, D.C.; Cooperstein, L.A. Adult-onset Still’s disease. Clinical course and outcome. Arthritis Rheum. 1987, 30, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, P.; Kontzias, A.; Hur, P.; Rodha, K.; Ramakrishna, G.S.; Nakasato, P. Adult-onset Still’s disease in focus: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and unmet needs in the rra of targeted therapies. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.A. Roles of interactions between toll-like receptors and their endogenous ligands in the pathogenesis of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still’s disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigrovic, P.A. Review: Is there a window of opportunity for treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis? Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, R.; Kernder, A.; Blank, N.; Ernst, D.; Henes, J.; Keyßer, G.; Klemm, P.; Krusche, M.; Meinecke, A.; Rech, J.; et al. Implementation of the new DGRh S2e guideline on diagnostics and treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease in Germany. Implications for clinical practice in rheumatology. Z. Rheumatol. 2024; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispin, J.C.; Martinez-Banos, D.; Alcocer-Varela, J. Adult-onset Still disease as the cause of fever of unknown origin. Medicine 2005, 84, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautner, J. Makrophagenaktivierungssyndrom—Eine seltene Komplikation bei adultem Morbus Still. Rheuma Plus 2020, 19, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlecken, N.T.; Schmidt, R.E. Adulter Morbus Still, Fieber, Diagnose und Therapie [Adult onset Still’s disease, fever, diagnosis and therapy]. Z. Rheumatol. 2012, 71, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M. Macrophage activation syndrome associated with adult-onset Still’s disease. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 2007, 30, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rigante, D.; Emmi, G.; Fastiggi, M.; Silvestri, E.; Cantarini, L. Macrophage activation syndrome in the course of monogenic autoinflammatory disorders. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saper, V.E.; Chen, G.; Deutsch, G.H.; Guillerman, R.P.; Birgmeier, J.; Jagadeesh, K.; Canna, S.; Schulert, G.; Deterding, R.; Xu, J.; et al. Emergent high fatality lung disease in systemic juvenile arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Bruno, F.; Berardicurti, O.; Acanfora, C.; Pavlych, V.; Palumbo, P.; Conforti, A.; Carubbi, F.; Di Cola, I.; Di Benedetto, P.; et al. Lung involvement in macrophage activation syndrome and severe COVID-19: Results from a cross-sectional study to assess clinical, laboratory and artificial intelligence-radiological differences. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantarogh, S.; Vilaiyuk, S.; Tim-Aroon, T.; Worawichawong, S. Clinical improvement of renal amyloidosis in a patient with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis who received tocilizumab treatment: A case report and literature review. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pouchot, J.; Sampalis, J.S.; Beaudet, F.; Carette, S.; Décary, F.; Salusinsky-Sternbach, M.; Hill, R.O.; Gutkowski, A.; Harth, M.; Myhal, D.; et al. Adult Still’s disease: Manifestations, disease course, and outcome in 62 patients. Medicine 1991, 70, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, M.; Schiller, M.; Krienke, S.; Heyder, P.; Lorenz, H.; Blank, N. Clinical manifestations but not cytokine profiles differentiate adult-onset Still’s disease and sepsis. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyoncu, U.; Kasifoglu, T.; Omma, A.; Bes, C.; Cinar, M.; Emmungil, H.; Kucuksahin, O.; Akar, S.; Aksu, K.; Yildiz, F.; et al. Derivation and validation of adult Still Activity Score (SAS). Jt. Bone Spine 2023, 90, 105499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindoli, S.; De Matteis, A.; Mitrovic, S.; Fautrel, B.; Carmona, L.; De Benedetti, F. Efficacy and safety of therapies for Still’s disease and macrophage activation syndrome (MAS): A systematic review informing the EULAR/PReS guidelines for the management of Still’s disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1731–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia Marques, M.; Balay-Dustrude, E.; Bracaglia, C.; Twilt, M.; Onel, K.; Appenzeller, S.; Dedeoglu, F.; Eloseily, E.; Martinez Jimenez, P.; Trachtman, R.; et al. Reporting of clinical features and outcome measures in Still’s disease: A systematic literature review of sJIA and AOSD cohorts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76 (Suppl. S9), 0402. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reporting-of-clinical-features-and-outcome-measures-in-stills-disease-a-systematic-literature-review-of-sjia-and-aosd-cohorts/ (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Ruscitti, P.; Stamm, T.; Ritschl, V.; Mitrovic, S.; Girard-Guyonvarc’h, C.; Alexanderson, H.; Barten, B.; Bostrøm, C.; Fell, D.; Gattorno, M.; et al. The development of the EULAR Score for the definition of disease activity in adult-onset Still’s sisease; The “DAVID” Project [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76 (Suppl. S9), 2030. Available online: https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-development-of-the-eular-score-for-the-definition-of-disease-activity-in-adult-onset-stills-disease-the-david-project/ (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Leavis, H.L.; van Daele, P.L.A.; Mulders-Manders, C.; Michels, R.; Rutgers, A.; Legger, E.; Bijl, M.; Hak, E.A.; Lam-Tse, W.K.; Bonte-Mineur, F.; et al. Management of adult-onset Still’s disease: Evidence- and consensus-based recommendations by experts. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vordenbäumen, S.; Feist, E.; Rech, J.; Fleck, M.; Blank, N.; Haas, J.-P.; Kötter, I.; Krusche, M.; Chehab, G.; Hoyer, B.; et al. DGRh-S2e-Leitlinie: Diagnostik und Therapie des adulten Still-Syndroms (AOSD). Z. Rheumatol. 2022, 81, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ohta, A.; Tsunematsu, T.; Kasukawa, R.; Mizushima, Y.; Kashiwagi, H.; Kashiwazaki, S.; Tanimoto, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ota, T.; et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J. Rheumatol. 1992, 19, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lebrun, D.; Mestrallet, S.; Dehoux, M.; Golmard, J.L.; Granger, B.; Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Arnaud, L.; Grateau, G.; Pouchot, J.; Fautrel, B. Validation of the Fautrel Classification Criteria for Adult-Onset Still’s Disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2018, 47, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, S.; Dagna, L.; Salvo, F.; Aiello, P.; Baldissera, E.; Sabbadini, M.G. Adult onset Still’s disease: Clinical presentation in a large cohort of Italian patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalyoncu, U.; Solmaz, D.; Emmungil, H.; Yazici, A.; Kasifoglu, T.; Kimyon, G.; Balkarli, A.; Bes, C.; Ozmen, M.; Alibaz-Oner, F.; et al. Response rate of initial conventional treatments, disease course, and related factors of patients with adult-onset Still’s disease: Data from a large multicenter cohort. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 69, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, P.; Natoli, V.; Consolaro, A.; Caorsi, R.; Rosina, S.; Giancane, G.; Naddei, R.; Di Cola, I.; Di Muzio, C.; Berardicurti, O.; et al. Disparities in the prevalence of clinical reatures between systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and adult-onset Still’s disease. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4124–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fautrel, B.; Patterson, J.; Bowe, C.; Arber, M.; Glanville, J.; Mealing, S.; Canon-Garcia, V.; Fagerhed, L.; Rabijns, H.; Giacomelli, R. Systematic review on the use of biologics in adult-onset Still’s disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 58, 152139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Summary of Opinion (Post Authorization): Ilaris (Canakinumab). 23 June 2016. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop/chmp-post-authorisation-summary-positive-opinion-ilaris_en.pdf-1 (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Sobi. Kineret® (anakinra) approved in the EU for the treatment of Still’s disease. 11 April 2018. Available online: https://www.sobi.com/sites/sobi/files/pr/201804107653-1.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Kernder, A.; Filla, T.; Friedrich, R.; Blank, N.; Ernst, D.; Henes, J.; Keyßer, G.; Klemm, P.; Krusche, M.; Meinecke, A.; et al. First-line biological vs. conventional therapy in adult-onset Still’s disease: A multicentre, retrospective, propensity weighted analysis. Lancet Rheum. 2025; Manuscript accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Gregg, E.; Canon-Garcia, V.; Rabijns, H.; Toennessen, K.; Bartlett, K.; Graziadio, S. Care pathway analysis and evidence gaps in adult-onset Still’s disease: Interviews with experts from the UK, France, Italy, and Germany. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1257413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, C.H.; Holzinger, D.; Lainka, E.; Haas, J.P.; Speth, F.; Kallinich, T.; Rieber, N.; Hufnagel, M.; Jansson, A.F.; Hedrich, C.; et al. PRO-KIND SJIA project collaborators. Practice and consensus-based strategies in diagnosing and managing systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Germany. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2018, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravelli, A.; Consolaro, A.; Horneff, G.; Laxer, R.M.; Lovell, D.J.; Wulffraat, N.M.; Akikusa, J.D.; Al-Mayouf, S.M.; Antón, J.; Avcin, T.; et al. Treating juvenile idiopathic arthritis to target: Recommendations of an international task force. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Tal, T.; Ryan, M.E.; Feldman, B.M.; Bingham, C.A.; Burnham, J.M.; Batthish, M.; Bullock, D.; Ferraro, K.; Gilbert, M.; Gillispie-Taylor, M.; et al. Consensus approach to a treat-to-target strategy in juvenile idiopathic arthritis care: Report From the 2020 PR-COIN Consensus Conference. J. Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onel, K.B.; Horton, D.B.; Lovell, D.J.; Shenoi, S.; Cuello, C.A.; Angeles-Han, S.T.; Becker, M.L.; Cron, R.Q.; Feldman, B.M.; Ferguson, P.J.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Therapeutic approaches for oligoarthritis, temporomandibular joint arthritis, and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ter Haar, N.M.; van Dijkhuizen, E.H.P.; Swart, J.F.; van Royen-Kerkhof, A.; El Idrissi, A.; Leek, A.P.; de Jager, W.; de Groot, M.C.H.; Haitjema, S.; Holzinger, D.; et al. Treatment to target using recombinant interleukin-1 receptor antagonist as first-line monotherapy in new-onset systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Results from a five-year follow-up study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Minden, K.; Hospach, A.; Foeldvari, I.; Weller-Heinemann, F.; Trauzeddel, R.; Huppertz, H.I.; Horneff, G. Treat-to-target study for improved outcome in polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, E.; Hogan, D.; Trost, B.; Kusalik, A.J.; Boire, G.; Cabral, D.A.; Campillo, S.; Chédeville, G.; Chetaille, A.L.; Dancey, P.; et al. Clinical and associated inflammatory biomarker features predictive of short-term outcomes in non-systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glerup, M.; Kessel, C.; Foell, D.; Berntson, L.; Fasth, A.; Myrup, C.; Nordal, E.; Rypdal, V.; Rygg, M.; Arnstad, E.D.; et al. Nordic Study Group of Paediatric Rheumatology (NoSPeR). Inflammatory biomarkers predicting long-term remission and active disease in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A population-based study of the Nordic JIA cohort. RMD Open 2024, 10, e004317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vastert, S.J.; Jamilloux, Y.; Quartier, P.; Ohlman, S.; Osterling Koskinen, L.; Kullenberg, T.; Franck-Larsson, K.; Fautrel, B.; de Benedetti, F. Anakinra in children and adults with Still’s disease. Rheumatology 2019, 58 (Suppl. S6), vi9–vi22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindoli, S.; Baggio, C.; Doria, A.; Sfriso, P. Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD): Advances in understanding pathophysiology, genetics and emerging treatment options. Drugs 2024, 84, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

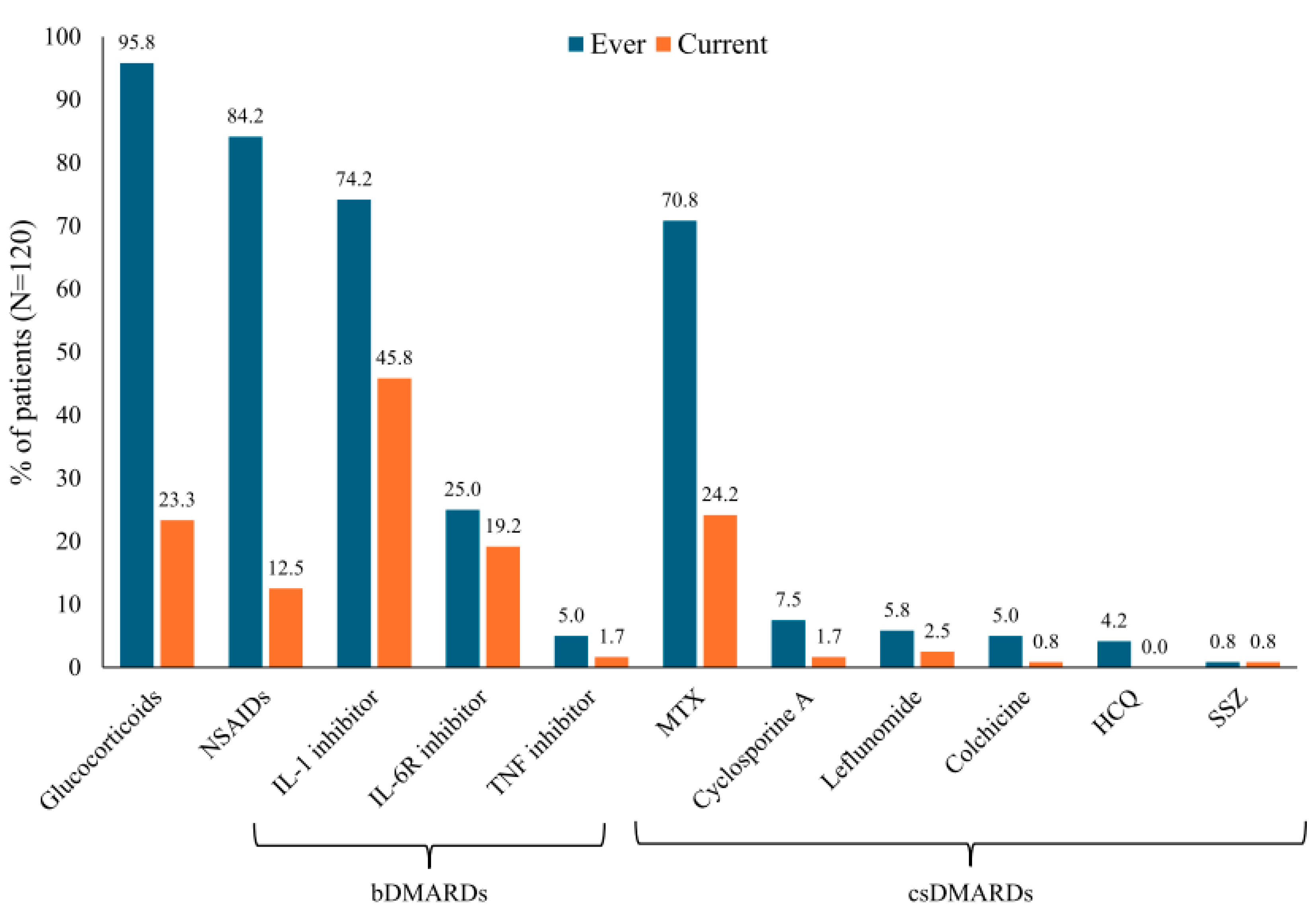
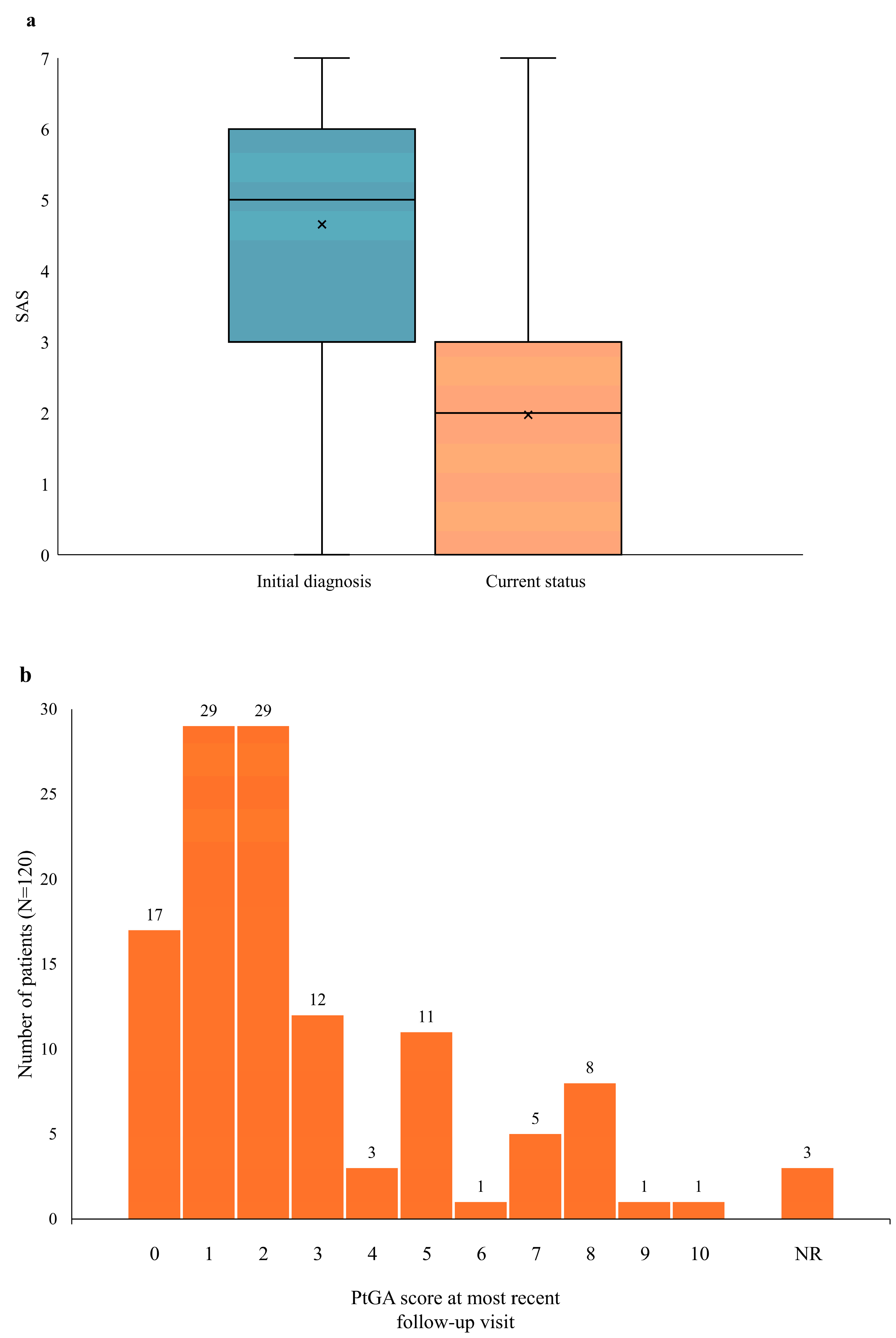
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| N | 120 |
| Age at initial diagnosis, years a | |
| Mean (SD) | 41.4 (16.8) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | 40 (27, 55) |
| Age at most recent visit, years a | |
| Mean (SD) | 50.7 (16.2) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | 51 (36, 62) |
| Sex (as categorized by physician) | |
| Female | 67 (55.8%) |
| Male | 53 (44.2%) |
| Reason for visit | |
| Regular follow-up following earlier AOSD diagnosis | 86 (71.7%) |
| Disease recurrence | 34 (28.3%) |
| Disease course | |
| Monocyclic | 25 (20.8%) |
| Polycyclic | 66 (55.0%) |
| Chronic | 29 (24.1%) |
| Current complications and comorbidities | |
| Hypertension | 20 (16.7%) |
| MAS | 12 (10.0%) |
| Osteoporosis | 10 (8.3%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 8 (6.7%) |
| Time since diagnosis for most recent visit, years a | |
| Mean (SD) | 9.4 (6.9) |
| Median (Q1, Q3) | 9 (4, 11) |
| Pouchot score at initial diagnosis a | |
| Mean (SD) | 5.1 (2.0) |
| Median (IQR) | 5 (4, 6.5) |
| Outcome | p Value * |
|---|---|
| Signs and symptoms | |
| Abdominal pain | <0.001 |
| Arthralgia | 0.129 |
| Cough | <0.001 |
| Fever | 0.178 |
| Hepatomegaly | <0.001 |
| Large-joint involvement | <0.001 |
| Lymphadenopathy | <0.001 |
| Shortness of breath | <0.001 |
| Small-joint involvement | <0.001 |
| Sore throat | <0.001 |
| Splenomegaly | <0.001 |
| Swollen joints | <0.001 |
| Thoracic pain | <0.001 |
| Measures of disease activity | |
| Ferritin > 350 ng/mL | 0.416 |
| Neutrophils > 65% | 0.002 |
| Still’s Activity Score | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schoenau, V.; Wendel, S.; Tascilar, K.; Henes, J.; Feist, E.; Baerlecken, N.T.; Popp, F.; Schmidt-Haendle, M.; Hellmich, B.; Kötter, I.; et al. Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease in Germany: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Practices Ahead of the Release of the German Recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030981
Schoenau V, Wendel S, Tascilar K, Henes J, Feist E, Baerlecken NT, Popp F, Schmidt-Haendle M, Hellmich B, Kötter I, et al. Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease in Germany: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Practices Ahead of the Release of the German Recommendations. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):981. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030981
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchoenau, Verena, Sarah Wendel, Koray Tascilar, Joerg Henes, Eugen Feist, Niklas Thomas Baerlecken, Florian Popp, Matthias Schmidt-Haendle, Bernhard Hellmich, Ina Kötter, and et al. 2025. "Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease in Germany: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Practices Ahead of the Release of the German Recommendations" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030981
APA StyleSchoenau, V., Wendel, S., Tascilar, K., Henes, J., Feist, E., Baerlecken, N. T., Popp, F., Schmidt-Haendle, M., Hellmich, B., Kötter, I., Andreica, I., & Rech, J. (2025). Patients with Adult-Onset Still’s Disease in Germany: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Practices Ahead of the Release of the German Recommendations. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030981







