Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes, Treatment Interactions, and Emerging Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
Pulmonary Hypertension and Depression: A Common and Complex Coexistence
2. Objectives
3. Study Selection
4. Prevalence and Impact of Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension
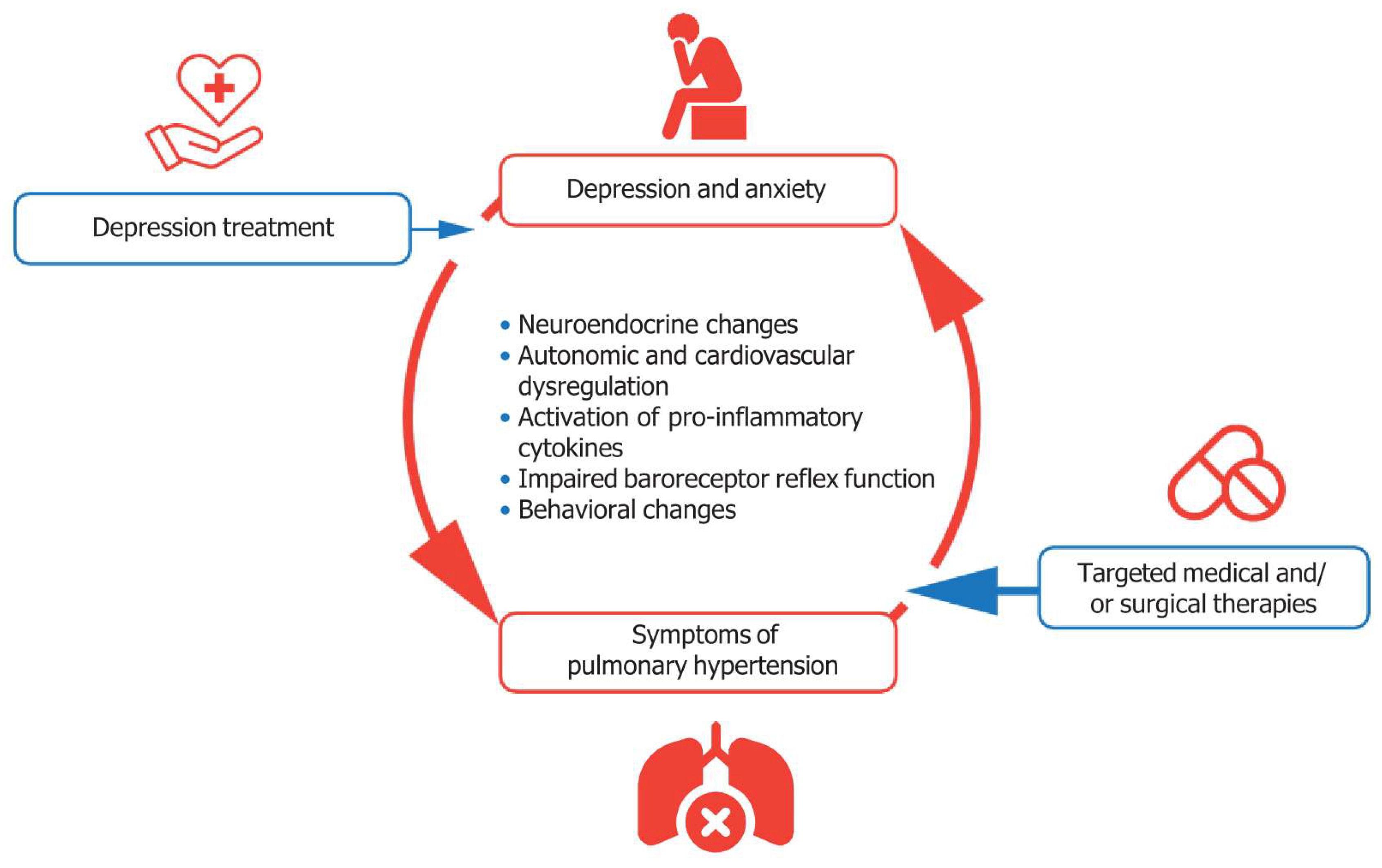
5. Mechanistic Insights into the Relationship Between Pulmonary Hypertension and Depression
6. Therapeutic Interactions Between Pulmonary Hypertension and Depression Treatments
6.1. CYP450 System in PAH and Depression Therapies
6.2. CYP3A4 and Its Role in PAH Therapy
6.3. CYP2D6: A Target of Potent Inhibition by Antidepressants
6.4. CYP2C8 and Prostacyclin Analogues
6.5. Non-CYP Mediated Interactions in PAH Therapy
6.6. Antidepressant Selection in PAH Patients
6.7. Implications for Clinical Practice
7. Strategies for Optimizing Mental Health Management in Pulmonary Hypertension Care
8. Emerging Technologies for Mental Health Management in Pulmonary Hypertension
Cost Efficiency in Pulmonary Hypertension Care
9. Limitations
10. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: Developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on rare respiratory diseases (ERN-LUNG). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Humbert, M.; Souza, R.; Idrees, M.; Kawut, S.M.; Sliwa-Hahnle, K.; Jing, Z.C.; Gibbs, J.S. A global view of pulmonary hypertension. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 306–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, C. Anxiety and depression in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: Results from a Chinese survey. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3124–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeuffer, E.; Krannich, H.; Halank, M.; Wilkens, H.; Kolb, P.; Jany, B.; Held, M. Anxiety, Depression, and Health-Related QOL in Patients Diagnosed with PAH or CTEPH. Lung 2017, 195, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, K.M.; Meltendorf, T.; Fuge, J.; Kamp, J.C.; Park, D.-H.; Richter, M.J.; Gall, H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Ferrari, P.; Schmiedel, R. Prevalence of mental disorders and impact on quality of life in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 667602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takita, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Fujisawa, D.; Kataoka, M.; Kawakami, T.; Doorenbos, A.Z. Depression, anxiety and psychological distress in patients with pulmonary hypertension: A mixed-methods study. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2021, 8, e000876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeuffer-Jovic, E.; Joa, F.; Halank, M.; Krannich, J.H.; Held, M. Anxiety, Depression and Quality of Life in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Comparison of Incident and Prevalent Cases. Respiration 2022, 101, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussotti, M.; Sommaruga, M. Anxiety and depression in patients with pulmonary hypertension: Impact and management challenges. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenard, J.L.; Munjas, B.A.; Adams, J.L.; Suttorp, M.; Maglione, M.; McGlynn, E.A.; Gellad, W.F. Depression and medication adherence in the treatment of chronic diseases in the United States: A meta-analysis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2011, 26, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Wen, Y.; Shi, F.; Wang, J. Anxiety and Depression in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Northwest China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 758120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larisch, A.; Neeb, C.; de Zwaan, M.; Pabst, C.; Tiede, H.; Ghofrani, A.; Olsson, K.; Hoeper, M.; Kruse, J. Mental distress and wish for psychosomatic treatment of patients with pulmonary hypertension. Psychother. Psychosom. Med. Psychol. 2014, 64, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcroix, M.; Howard, L. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: The burden of disease and impact on quality of life. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2015, 24, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norell, P.N.; Ivarsson, B.; Selin, M.; Kjellström, B. Prevalence of potential drug-drug interactions with disease-specific treatments in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A registry study. Pulm. Circ. 2022, 12, e12114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hoang, H.B.; Yang, J.Z.; Papamatheakis, D.G.; Poch, D.S.; Alotaibi, M.; Lombardi, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Kim, N.H.; Fernandes, T.M. Drug-Drug Interactions in the Management of Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Chest 2022, 162, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Chou, P.H.; Lin, K.H. The effects of treatment via telemedicine interventions for patients with depression on depressive symptoms and quality of life: A systematic review and meta-ranalysis. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, S.A.; Mathews, N.; Kunik, M.E. Telemedicine interventions for medication adherence in mental illness: A systematic review. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2020, 62, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- eHealth, WHOGOF. Telemedicine: Opportunities and Developments in Member States: Report on the Second Global Survey on eHealth; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, K.E.; Willman, C.; Winn, R. Optimizing the Use of Telemedicine in Oncology Care: Postpandemic OpportunitiesTelehealth in Cancer Care. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.B.; Gonzalez, B.D.; Turner, K.; Alishahi Tabriz, A.; Rollison, D.E.; Robinson, E.; Naso, C.; Wang, X.; Spiess, P.E. Estimated Carbon Emissions Savings with Shifts From In-Person Visits to Telemedicine for Patients with Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2253788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, A.; Smith, J.; Hibble, A. Does telemedicine reduce the carbon footprint of healthcare? A systematic review. Future Healthc. J. 2021, 8, e85–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindrane, R.; Patel, J. The environmental impacts of telemedicine in place of face-to-face patient care: A systematic review. Future Healthc. J. 2022, 9, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagkaris, C.; Hoian, A.V.; Ahmad, S.; Essar, M.Y.; Campbell, L.W.; Grobusch, L.; Angelopoulos, T.; Kalaitzidis, K. Using telemedicine for a lower carbon footprint in healthcare: A twofold tale of healing. J. Clim. Change Health 2021, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, C.; Mehta, N.; Sejo, C.; Qureshi, L.; Moyer, M.; Valentino, V.; Saleh, J. Telemedicine and the environment: Life cycle environmental emissions from in-person and virtual clinic visits. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellowlees, P.M.; Chorba, K.; Burke Parish, M.; Wynn-Jones, H.; Nafiz, N. Telemedicine can make healthcare greener. Telemed. J. E-Health 2010, 16, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcillo Serra, C.; Aroca Tanarro, A.; Cummings, C.M.; Jimenez Fuertes, A.; Tomás Martínez, J.F. Impact on the reduction of CO2 emissions due to the use of telemedicine. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollister, D.H.; Beutz, M.; McLaughlin, V.; Rumsfeld, J.; Masoudi, F.A.; Tripputi, M.; Yaeger, T.; Weintraub, P.; Badesch, D.B. Depressive symptoms in pulmonary arterial hypertension: Prevalence and association with functional status. Psychosomatics 2010, 51, 339.e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, B.; Gräfe, K.; Ufer, C.; Kroenke, K.; Grünig, E.; Herzog, W.; Borst, M.M. Anxiety and depression in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Psychosom. Med. 2004, 66, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, A.S.; Lim, O.Z.H.; Ho, Y.J.; Kong, G.; Lim, G.E.H.; Ng, C.H.; Ho, C.; Ho, R.; Lim, Y.; Kuntjoro, I.; et al. Prevalence, Risk Factors and Intervention for Depression and Anxiety in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 765461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarzyńska, K.; Świątoniowska-Lonc, N.; Dudek, K.; Jonas, K.; Kopeć, G.; Gajek, J.; Jankowska-Polańska, B. Quality of life of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension: A meta-analysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 4983–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dering, M.-R.; Lepsy, N.; Fuge, J.; Meltendorf, T.; Hoeper, M.M.; Heitland, I.; Kamp, J.C.; Park, D.-H.; Richter, M.J.; Gall, H.; et al. Prevalence of Mental Disorders in Patients With Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 821466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Sahni, S.; Vijayan, V.K.; Talwar, A. Depression in pulmonary arterial hypertension: An undertreated comorbidity. Lung India 2016, 33, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, S.; Xie, W.; Wan, J.; Kuang, T.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, C. The impact and financial burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension on patients and caregivers: Results from a national survey. Medicine 2017, 96, e6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watzker, A.; Alsumali, A.; Ferro, C.; Dieguez, G.; Park, C.; Lautsch, D.; El-Kersh, K. Economic Burden Associated with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the United States. Pharmacoeconomics 2025, 43, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikirica, M.; Iorga, S.R.; Bancroft, T.; Potash, J. The economic burden of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in the US on payers and patients. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2014, 14, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgeson, S.A.; Menon, D.; Helmi, H.; Vadlamudi, C.; Moss, J.E.; Zeiger, T.K.; Burger, C.D. Psychosocial and Financial Burden of Therapy in USA Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Diseases 2020, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, L.; Suehs, C.M.; Marin, G.; Boissin, C.; Gamez, A.S.; Vachier, I.; Molinari, N.; Bourdin, A. Health-related quality of life and disease progression in pulmonary arterial hypertension patients: A 3-year study. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, G.H.; Thompson, A.R.; Armstrong, I.; Novakova, B.; Beail, N. Coping styles associated with depression, health anxiety and health-related quality of life in pulmonary hypertension: Cross-sectional analysis. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e062564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, A.; Larive, A.B.; Horn, E.M.; DuBrock, H.M.; Mehra, R.; Jacob, M.S.; Hemnes, A.R.; Leopold, J.A.; Radeva, M.K.; Hill, N.S.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life Across the Spectrum of Pulmonary Hypertension. Chest 2024, 165, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzheim, D.; Klose, H.; Pinado, F.P.; Ehlken, N.; Nagel, C.; Fischer, C.; Ghofrani, A.; Rosenkranz, S.; Seyfarth, H.J.; Halank, M.; et al. Anxiety and depression disorders in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, J.; Park, D.H.; von Lengerke, T.; Richter, M.J.; Gall, H.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Kamp, J.C.; Hoeper, M.M.; Olsson, K.M. Impact of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension on Employment, Work Productivity, and Quality of Life - Results of a Cross-Sectional Multi-Center Study. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 781532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batal, O.; Khatib, O.F.; Bair, N.; Aboussouan, L.S.; Minai, O.A. Sleep quality, depression, and quality of life in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Lung 2011, 189, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Cardenas-Garcia, J.; Mohapatra, P.R.; Talwar, A. Depression in pulmonary arterial hypertension and interstitial lung diseases. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 6, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grippo, A.J.; Johnson, A.K. Stress, depression and cardiovascular dysregulation: A review of neurobiological mechanisms and the integration of research from preclinical disease models. Stress 2009, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez-Roa, S.; Ciarka, A.; Najem, B.; Vachiery, J.L.; Naeije, R.; van de Borne, P. Increased sympathetic nerve activity in pulmonary artery hypertension. Circulation 2004, 110, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaker, R.H.; Agam, G. Major depressive disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, A.; Vrugt, B.; Brock, M.; Speich, R.; Ulrich, S.; Huber, L.C. Inflammatory cytokines in pulmonary hypertension. Respir. Res. 2014, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paula-Ribeiro, M.; Ribeiro, I.C.; Aranda, L.C.; Silva, T.M.; Costa, C.M.; Ramos, R.P.; Ota-Arakaki, J.; Cravo, S.L.; Nery, L.E.; Stickland, M.K.; et al. Cardiac baroreflex dysfunction in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension at rest and during orthostatic stress: Role of the peripheral chemoreflex. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985 2021, 131, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.J.; Vorla, M.; Kalra, D.K. Molecular Pathways in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matura, L.A.; Shou, H.; Fritz, J.S.; Smith, K.A.; Vaidya, A.; Pinder, D.; Archer-Chicko, C.; Dubow, D.; Palevsky, H.I.; Sommers, M.S.; et al. Physical Activity and Symptoms in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Chest 2016, 150, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciracì, R.; Tirone, G.; Scaglione, F. The impact of drug-drug interactions on pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, A.M.; Dang, C.H. Basic review of the cytochrome p450 system. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2013, 4, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.G.; Kloner, R.A. Drug interactions with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors used for the treatment of erectile dysfunction or pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 2010, 122, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venitz, J.; Zack, J.; Gillies, H.; Allard, M.; Regnault, J.; Dufton, C. Clinical pharmacokinetics and drug-drug interactions of endothelin receptor antagonists in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 1784–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.; Fay, M. Cytochrome P450 drug interactions: Are they clinically relevant? Aust. Prescr. 2001, 24, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsky, R.L.; Gaman, E.A.; Obach, R.S. Examination of 209 drugs for inhibition of cytochrome P450 2C8. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narechania, S.; Malesker, M.A. Drug Interactions Associated With Therapies for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Pharm. Technol. 2022, 38, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.G.; Ijadi-Maghsoodi, R.; Shadravan, S.; Moore, E.; Mensah, M.O., 3rd; Docherty, M.; Aguilera Nunez, M.G.; Barcelo, N.; Goodsmith, N.; Halpin, L.E.; et al. Community Interventions to Promote Mental Health and Social Equity. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harandi, T.F.; Taghinasab, M.M.; Nayeri, T.D. The correlation of social support with mental health: A meta-analysis. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 5212–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, S. Mental Health Prevention and Promotion-A Narrative Review. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 898009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryers, T.; Melzer, D.; Jenkins, R. Social inequalities and the common mental disorders: A systematic review of the evidence. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2003, 38, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.; Bhugra, D.; Bebbington, P.; Brugha, T.; Farrell, M.; Coid, J.; Fryers, T.; Weich, S.; Singleton, N.; Meltzer, H. Debt, income and mental disorder in the general population. Psychol. Med. 2008, 38, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, C.; Breen, A.; Flisher, A.J.; Kakuma, R.; Corrigall, J.; Joska, J.A.; Swartz, L.; Patel, V. Poverty and common mental disorders in low and middle income countries: A systematic review. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, H.; Wilson, M. Why Living with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Requires a Holistic Approach: A Patient and Clinician Perspective. Pulm. Ther. 2023, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, N.; Barberà, J.A.; Frost, A.E.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Hoeper, M.M.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Peacock, A.J.; Simonneau, G.; Vachiery, J.L.; Grünig, E.; et al. Initial Use of Ambrisentan plus Tadalafil in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, T.; Adzerikho, I.; Channick, R.N.; Delcroix, M.; Galiè, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Jansa, P.; Jing, Z.C.; Le Brun, F.O.; Mehta, S.; et al. Macitentan and morbidity and mortality in pulmonary arterial hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitbon, O.; Channick, R.; Chin, K.M.; Frey, A.; Gaine, S.; Galiè, N.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Hoeper, M.M.; Lang, I.M.; Preiss, R.; et al. Selexipag for the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Badesch, D.B.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Gomberg-Maitland, M.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Preston, I.R.; Souza, R.; Waxman, A.B.; Grünig, E.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of Sotatercept for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Camacho, A.; Moreno-Jiménez, B. Depression and Anxiety in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Optimism. Psychosomatics 2018, 59, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Tang, J.; Chen, C.; Tan, L.; Wu, Z.; Yu, F.; Wang, X. Progressive muscle relaxation improves anxiety and depression of pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 792895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Visger, T.T.; Thrane, S.E.; Klatt, M.D.; Dabbs, A.D.; Chlan, L.L.; Tan, A.; Happ, M.B. The Impact of Urban Zen Integrative Therapy on Symptoms and Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Palliat. Med. 2020, 23, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matura, L.A.; Fargo, J.; Fritz, J.S.; Smith, K.A.; Vaidya, A.; Pinder, D.; Archer-Chicko, C.; Palevsky, H.I.; Pack, A.I.; Sommers, M.S.; et al. Slow-paced respiration therapy to treat symptoms in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Heart Lung 2017, 46, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, T.; Bahr, F.; Herrmann, P.; Luethje, L.; Heusser, K.; Hasenfuss, G.; Bernardi, L.; Andreas, S. Slow breathing reduces sympathoexcitation in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilo, G.; Revera, M.; Bussotti, M.; Bonacina, D.; Styczkiewicz, K.; Caldara, G.; Giglio, A.; Faini, A.; Giuliano, A.; Lombardi, C.; et al. Effects of slow deep breathing at high altitude on oxygen saturation, pulmonary and systemic hemodynamics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, M.C.; Valenza-Peña, G.; Torres-Sánchez, I.; González-Jiménez, E.; Conde-Valero, A.; Valenza-Demet, G. Effectiveness of controlled breathing techniques on anxiety and depression in hospitalized patients with COPD: A randomized clinical Trial. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, L.; Porta, C.; Spicuzza, L.; Bellwon, J.; Spadacini, G.; Frey, A.W.; Yeung, L.Y.; Sanderson, J.E.; Pedretti, R.; Tramarin, R. Slow breathing increases arterial baroreflex sensitivity in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation 2002, 105, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Calderon, J.; Casuso-Holgado, M.J.; Muñoz-Fernandez, M.J.; Garcia-Muñoz, C.; Heredia-Rizo, A.M. Yoga-based interventions may reduce anxiety symptoms in anxiety disorders and depression symptoms in depressive disorders: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 1442–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.; Bobonis Babilonia, M.; Naso, C.; Nguyen, O.; Gonzalez, B.D.; Oswald, L.B.; Robinson, E.; Elston Lafata, J.; Ferguson, R.J.; Alishahi Tabriz, A.; et al. Health Care Providers’ and Professionals’ Experiences with Telehealth Oncology Implementation During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e29635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzi, G.; Papa, S.; Mariani, M.V.; Scoccia, G.; Filomena, D.; Malerba, C.; Adamo, F.I.; Caputo, A.; De Lazzari, C.; De Lazzari, B.; et al. Telehealth: A winning weapon to face the COVID-19 outbreak for patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 145, 107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Sahay, S.; Shlobin, O.; Soto, F.J.; Mathai, S.C.; Melendres-Groves, L.; Mullin, C.J.; Levine, D.J.; Kay, D.; Highland, K.; et al. Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on the management of pulmonary hypertension. Respir. Med. 2023, 206, 107061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Takeyasu, R.; Furukawa, A.; Takada, H.; Takechi, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Kawamura, A. How COVID-19 Affected the Introduction of Telemedicine and Patient Reported Outcomes Among Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension―A Report From a Referral Center in Japan―. Circ. Rep. 2020, 2, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley Milks, M.; Sahay, S.; Benza, R.L.; Farber, H.W. Risk assessment in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension in the era of COVID 19 pandemic and the telehealth revolution: State of the art review. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telematics, WHOGCoH. A Health Telematics Policy in Support of WHO’s Health-for-All Strategy for Global Health Development: Report of the WHO Group Consultation on Health Telematics, 11–16 December, Geneva, 1997; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, M.; D’Avanzato, C.; King, B.T. Telehealth treatment of patients with major depressive disorder during the COVID-19 pandemic: Comparative safety, patient satisfaction, and effectiveness to prepandemic in-person treatment. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 323, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.M.; Clark, J.; Greenwood, H.; Krzyzaniak, N.; Cardona, M.; Peiris, R.; Sims, R.; Glasziou, P. Telehealth v. face-to-face provision of care to patients with depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2022, 52, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulkes, N.Z.; Davis, K.; Kay, B.; Riemann, B.C. Comparing efficacy of telehealth to in-person mental health care in intensive-treatment-seeking adults. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 145, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, R.P.; Hill, J.W.; Lickert, C.A.; Wade, R.L.; Cole, M.R.; Tsang, Y.; Drake, W., 3rd. Medication adherence, hospitalization, and healthcare resource utilization and costs in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension treated with endothelin receptor antagonists or phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894019880086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellström, B.; Sandqvist, A.; Hjalmarsson, C.; Nisell, M.; Näsman, P.; Ivarsson, B. Adherence to disease-specific drug treatment among patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00299–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikowski, E.M.; Swabe, G.; Chan, S.Y.; Magnani, J.W. Association Between Copayment and Adherence to Medications for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e026620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, C.; Sloan, D.; Gregor, P.; Sullivan, F.; Detmer, D.; Kahan, J.P.; Oortwijn, W.; MacGillivray, S. What is eHealth (4): A scoping exercise to map the field. J. Med. Internet Res. 2005, 7, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Garcia, M.C.; Fatehi, F.; Varnfield, M.; Ding, H.; Karunanithi, M.; Yang, I.; Cordina, R.; Feenstra, J. Use of eHealth in the management of pulmonary arterial hypertension: Review of the literature. BMJ Health Care Inform. 2020, 27, e100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashi, N.; Karunanithi, M.; Fatehi, F.; Ding, H.; Walters, D. Remote monitoring of patients with heart failure: An overview of systematic reviews. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benza, R.L.; Doyle, M.; Lasorda, D.; Parikh, K.S.; Correa-Jaque, P.; Badie, N.; Ginn, G.; Airhart, S.; Franco, V.; Kanwar, M.K.; et al. Monitoring Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Using an Implantable Hemodynamic Sensor. Chest 2019, 156, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, S.; Kanwar, M.; Benza, R.; Raina, A. Long Term Safety and Outcomes Utilizing the CardioMEMS Device in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2022, 41 (Suppl. 4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpay, L.; van der Boog, P.; Dumaij, A. An empowerment-based approach to developing innovative e-health tools for self-management. Health Inform. J. 2011, 17, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramm, J.M.; Nieboer, A.P. Disease management: The need for a focus on broader self-management abilities and quality of life. Popul. Health Manag. 2015, 18, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, M.; Santos, J.; Takane, M. mHealth: New Horizons for Health Through Mobile Technologies; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Varnfield, M.; Karunanithi, M.; Lee, C.-K.; Honeyman, E.; Arnold, D.; Ding, H.; Smith, C.; Walters, D.L. Smartphone-based home care model improved use of cardiac rehabilitation in postmyocardial infarction patients: Results from a randomised controlled trial. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2014, 100, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemnes, A.R.; Silverman-Lloyd, L.G.; Huang, S.; MacKinnon, G.; Annis, J.; Whitmore, C.S.; Mallugari, R.; Oggs, R.N.; Hekmat, R.; Shan, R.; et al. A Mobile Health Intervention to Increase Physical Activity in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Chest 2021, 160, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, H.; Brewis, M.; Church, C.; Johnson, M. Towards telemedicine in pulmonary hypertension: Assessing the feasibility of remote quality of life and exercise capacity assessment. Pulm. Circ. 2022, 12, e12144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbomo, A.; Tsang, Y.; Mallampati, R.; Panjabi, S. The direct and indirect health care costs associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension among commercially insured patients in the United States. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2022, 28, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgoyne, D.S. Reducing economic burden and improving quality of life in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Manag. Care 2021, 27 (Suppl. 3), S53–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokkerbol, J.; Adema, D.; Cuijpers, P.; Reynolds, C.; Schulz, R.; Weehuizen, R.; Smit, F. Improving the Cost-Effectiveness of a Healthcare System for Depressive Disorders by Implementing Telemedicine: A Health Economic Modeling Study. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Off. J. Am. Assoc. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 22, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egede, L. Telehealth intervention for depression reduces costs. PharmacoEconomics Outcomes News 2018, 812, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaiana, G.; Mastrangelo, J.; Hendrikx, S.; Barbui, C. A Systematic Review of the Use of Telepsychiatry in Depression. Community Ment. Health J. 2021, 57, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Appleton, R.; Kalocsanyiova, E.; Gkaintatzi, E.; McCrone, P. Are remote mental healthcare interventions cost-effective? A systematic review of economic evaluations of remote mental healthcare. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsell, A.; Krzanowski, J.; Page, L.; Cuthbert, S.; Harvey, G. What mental health professionals and organisations should do to address climate change. BJPsych Bull. 2021, 45, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kramer, M.; Rosenkranz, S.; Kramer, T. Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes, Treatment Interactions, and Emerging Technologies. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030982
Kramer M, Rosenkranz S, Kramer T. Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes, Treatment Interactions, and Emerging Technologies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030982
Chicago/Turabian StyleKramer, Mira, Stephan Rosenkranz, and Tilmann Kramer. 2025. "Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes, Treatment Interactions, and Emerging Technologies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030982
APA StyleKramer, M., Rosenkranz, S., & Kramer, T. (2025). Depression in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcomes, Treatment Interactions, and Emerging Technologies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030982





