Adolescent Obesity and Charlson Comorbidity Index in Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
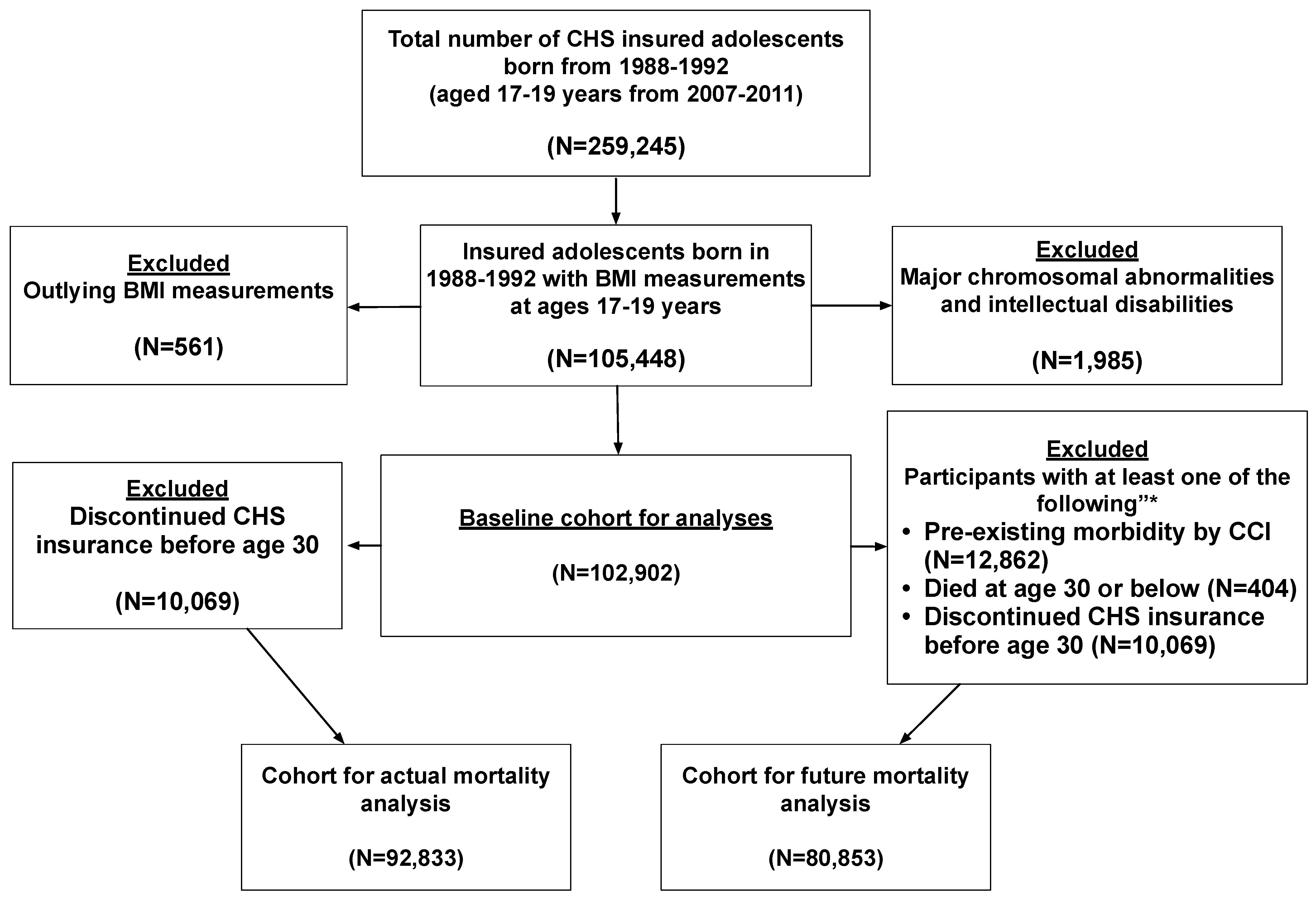
2. Methods
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Association of Adolescent Weight Categories with CCI at Age 30
3.2. Association of Weight Categories with All-Cause Mortality
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Strengths
4.2. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Twig, G.; Zucker, I.; Afek, A.; Cukierman-Yaffe, T.; Bendor, C.D.; Derazne, E.; Lutski, M.; Shohat, T.; Mosenzon, O.; Tzur, D.; et al. Adolescent Obesity and Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, E.; Bjerregaard, L.G.; Gamborg, M.; Vaag, A.A.; Sorensen, T.I.A.; Baker, J.L. Childhood body mass index and development of type 2 diabetes throughout adult life-A large-scale danish cohort study. Obesity 2017, 25, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, R.K.; Magnussen, C.G.; Sabin, M.A.; Cheung, M.; Juonala, M. Development of hypertension in overweight adolescents: A review. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2015, 6, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, S.; Khalili, D.; Asgari, S.; Fahimfar, N.; Hadaegh, F.; Tohidi, M.; Azizi, F. Predictors of early adulthood hypertension during adolescence: A population-based cohort study. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, L.; Li, P. Body Mass Index and Its Change from Adolescence to Adulthood Are Closely Related to the Risk of Adult Metabolic Syndrome in China. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 8888862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, K.E.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kwon, H.; Park, D.J.; Cho, B.; Choi, H.C.; et al. Adolescent overweight and obesity and the risk of papillary thyroid cancer in adulthood: A large-scale case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furer, A.; Afek, A.; Sommer, A.; Keinan-Boker, L.; Derazne, E.; Levi, Z.; Tzur, D.; Tiosano, S.; Shina, A.; Glick, Y.; et al. Adolescent obesity and midlife cancer risk: A population-based cohort study of 2.3 million adolescents in Israel. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, I.; Zloof, Y.; Bardugo, A.; Tsur, A.M.; Lutski, M.; Cohen, Y.; Cukierman-Yaffe, T.; Minsky, N.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; et al. Obesity in late adolescence and incident type 1 diabetes in young adulthood. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zuo, J.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J.; Chen, C.; Xiang, E.; Li, H.; Cheng, X.; Chen, P. Childhood obesity leads to adult type 2 diabetes and coronary artery diseases: A 2-sample mendelian randomization study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, A.; Twig, G. The Impact of Childhood and Adolescent Obesity on Cardiovascular Risk in Adulthood: A Systematic Review. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardugo, A.; Fishman, B.; Libruder, C.; Tanne, D.; Ram, A.; Hershkovitz, Y.; Zucker, I.; Furer, A.; Gilon, R.; Chodick, G.; et al. Body Mass Index in 1.9 Million Adolescents and Stroke in Young Adulthood. Stroke 2021, 52, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.T.; Krenek, A.; Magge, S.N. Childhood Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsur, A.M.; Akavian, I.; Landau, R.; Derazne, E.; Tzur, D.; Vivante, A.; Grossman, E.; Rotem, R.S.; Fishman, B.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; et al. Adolescent Body Mass Index and Early Chronic Kidney Disease in Young Adulthood. JAMA Pediatr. 2024, 178, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendor, C.D.; Bardugo, A.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Afek, A.; Twig, G. Cardiovascular morbidity, diabetes and cancer risk among children and adolescents with severe obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horesh, A.; Tsur, A.M.; Bardugo, A.; Twig, G. Adolescent and Childhood Obesity and Excess Morbidity and Mortality in Young Adulthood-a Systematic Review. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twig, G.; Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Furer, A.; Levine, H.; Derazne, E.; Goldberger, N.; Haklai, Z.; Levy, M.; Afek, A.; Leiba, A.; et al. Adolescent Body Mass Index and Cardiovascular Disease-Specific Mortality by Midlife. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3011–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdz, D.; Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Wojcik, M.; Borghi, C.; Gabbianelli, R.; Mazur, A.; Herceg-Cavrak, V.; Lopez-Valcarcel, B.G.; Brzezinski, M.; Lurbe, E.; et al. Obesity and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: From Childhood to Adulthood. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Pathophysiological Molecular Mechanisms of Obesity: A Link between MAFLD and NASH with Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyo, J.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, T.J.; Min, Y.W.; Min, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Rhee, P.L.; Yoo, H.; et al. Obesity and Risk of Peptic Ulcer Disease: A Large-Scale Health Check-Up Cohort Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, J.S.; Khan, S.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Sidney, S. Changes in Mortality in Top 10 Causes of Death from 2011 to 2018. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2021, 36, 2517–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, A.; Haelyon, U.; Krolik, E.; Sack, J. Comparison of body weight and height of Israeli schoolchildren with the Tanner and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention growth charts. Pediatrics 2001, 108, E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overweight and Obesity. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Charlson, M.E.; Carrozzino, D.; Guidi, J.; Patierno, C. Charlson Comorbidity Index: A Critical Review of Clinimetric Properties. Psychother. Psychosom. 2022, 91, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, A.R. Clinimetrics; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Albertsen, P.C.; Fryback, D.G.; Storer, B.E.; Kolon, T.F.; Fine, J. The impact of co-morbidity on life expectancy among men with localized prostate cancer. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bari, M.; Virgillo, A.; Matteuzzi, D.; Inzitari, M.; Mazzaglia, G.; Pozzi, C.; Geppetti, P.; Masotti, G.; Marchionni, N.; Pini, R. Predictive validity of measures of comorbidity in older community dwellers: The Insufficienza Cardiaca negli Anziani Residenti a Dicomano Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeuser, L.; Herzog, P.; Ayub, A.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Noldus, J.; Cone, E.B.; Mossanen, M.; Trinh, Q.-D. Comparison of co morbidity indices for prediction of morbidity and mortality after major surgical procedures. Am. J. Surg. 2021, 222, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraccaro, P.; Kontopantelis, E.; Sperrin, M.; Peek, N.; Mallen, C.; Urban, P.; Buchan, I.E.; Mamas, M.A. Predicting mortality from change-over-time in the Charlson comorbidity index: A retrospective cohort study in a data-intensive UK health system. Medicine 2016, 95, e4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicas, K.M.; Jones, A.A.; Thornton, A.E.; Petersson, A.; Livingston, E.; Waclawik, K.; Panenka, W.J.; Barr, A.M.; Lang, D.J.; Vila-Rodriguez, F.; et al. Cognitive decline and mortality in a community-based sample of homeless and precariously housed adults: 9-year prospective study. BJPsych Open 2020, 6, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luben, R.; Hayat, S.; Wareham, N.; Pharoah, P.P.; Khaw, K.T. Sociodemographic and lifestyle predictors of incident hospital admissions with multimorbidity in a general population, 1999–2019: The EPIC-Norfolk cohort. BMJ Open. 2020, 10, e042115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.X.; Huang, Y.Q.; Xie, J.W.; Wang, J.B.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.Y.; Cao, L.L.; Lin, M.; Tu, R.; Huang, Z.N.; et al. Association of the age-adjusted Charlson Comorbidity Index and systemic inflammation with survival in gastric cancer patients after radical gastrectomy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.W.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, W.T.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, S.-C.; Kim, W.-J.; Hwang, E.C.; Kang, S.H.; Hong, S.-H.; Chung, J.; et al. The age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index as a predictor of overall survival of surgically treated non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Chou, A.C.C.; Nadkarni, N.; Ng, C.E.Q.; Chong, Y.S.; Howe, T.S.; Koh, J.S.B. Charlson Comorbidity Index Predicts 5-Year Survivorship of Surgically Treated Hip Fracture Patients. Geriatr. Orthop. Surg. Rehabil. 2018, 9, 2151459318806442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.C.; Ciol, M.A. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeweiss, S.; Seeger, J.D.; Maclure, M.; Wang, P.S.; Avorn, J.; Glynn, R.J. Performance of comorbidity scores to control for confounding in epidemiologic studies using claims data. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 154, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, H.; van Klaveren, D.; Kogame, N.; Chichareon, P.; Modolo, R.; Tomaniak, M.; Ono, M.; Kawashima, H.; Takahashi, K.; Capodanno, D.; et al. Statistical methods for composite endpoints. EuroIntervention 2021, 16, e1484–e1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.Y.; Donner, A. Extension of the modified Poisson regression model to prospective studies with correlated binary data. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2013, 22, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, M.; Llewellyn, A.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.H.; Lv, J.J.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, X.T.; Yin, M.Y. Global burden of asthma in young adults in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: Systematic analysis of the Global burden of disease study 2019. Prev. Med. Rep. 2024, 37, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Shan, Y.; Wang, X.; Shan, X. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the related risk factors among healthy adults: A cross-sectional study in Chongqing, China. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1127489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsson, O.; Vesterinen, T.; Arola, J.; Aberg, F.; Nissinen, M.J. Coexistence of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and autoimmune or toxic liver disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 36, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller-Thomson, E.; Howden, K.E.N.; Fuller-Thomson, L.R.; Agbeyaka, S. A Strong Graded Relationship between Level of Obesity and COPD: Findings from a National Population-Based Study of Lifelong Nonsmokers. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 6149263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.E.; Que, L.G. Obesity and Asthma. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 43, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, A.E.; Peters, U. The effect of obesity on lung function. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2018, 12, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigham, E.P.; Anderson, J.A.; Brook, R.D.; Calverley, P.M.; Celli, B.R.; Cowans, N.J.; Crim, C.; Diserens, J.E.; Martinez, F.J.; McCormack, M.C.; et al. Challenging the obesity paradox: Extreme obesity and COPD mortality in the SUMMIT trial. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00902-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Chun-Yan, N.; Hong-Xin, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wen, W.; Yu, T. Association of Adolescent Obesity with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Related Risk Factors in Xi’an, China. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, M.; Peng, X.; Sun, X.; Yan, J. Relationship between obesity related indicators and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Pediatr. 2023, 12, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakonmaki, N.; Zedde, M.; Sarkanen, T.; Martinez-Majander, N.; Tuohinen, S.; Sinisalo, J.; Ryodi, E.; Autere, J.; Hedman, M.; Junttola, U.; et al. Obesity and the Risk of Cryptogenic Ischemic Stroke in Young Adults. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. Off. J. Natl. Stroke Assoc. 2022, 31, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Geng, J.H.; Wu, P.Y.; Huang, J.C.; Hu, H.M.; Chen, S.C.; Kuo, C.H. High Obesity Indices Are Associated with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, but Low Obesity Indices Are Associated with Peptic Ulcer Disease in a Large Taiwanese Population Study. Obes. Facts. 2024, 17, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, T. Genetic liability to obesity and peptic ulcer disease: A Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, M.R.; Khalili, H.; Huang, E.S.; Chan, A.T. Measures of adiposity are associated with increased risk of peptic ulcer. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1688–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savulescu-Fiedler, I.; Mihalcea, R.; Dragosloveanu, S.; Scheau, C.; Baz, R.O.; Caruntu, A.; Scheau, A.E.; Caruntu, C.; Benea, S.N. The Interplay between Obesity and Inflammation. Life 2024, 14, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tune, J.D.; Goodwill, A.G.; Sassoon, D.J.; Mather, K.J. Cardiovascular consequences of metabolic syndrome. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempesis, I.G.; Varrias, D.; Sagris, M.; Attaran, R.R.; Altin, E.S.; Bakoyiannis, C.; Palaiodimos, L.; Dalamaga, M.; Kokkinidis, D.G. Obesity and Peripheral Artery Disease: Current Evidence and Controversies. Curr. Obes. Rep. Sep. 2023, 12, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmans, M.D.; Kromhout, D.; de Lezenne Coulander, C. The impact of body mass index of 78,612 18-year old Dutch men on 32-year mortality from all causes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1988, 41, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorge, T.; Engeland, A.; Tverdal, A.; Smith, G.D. Body mass index in adolescence in relation to cause-specific mortality: A follow-up of 230,000 Norwegian adolescents. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twig, G.; Yaniv, G.; Levine, H.; Leiba, A.; Goldberger, N.; Derazne, E.; Ben-Ami Shor, D.; Tzur, D.; Afek, A.; Shamiss, A.; et al. Body-Mass Index in 2.3 Million Adolescents and Cardiovascular Death in Adulthood. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treister-Goltzman, Y.; Nemet, D.; Menashe, I. The Association of Weight Categories in Adolescence with Cardiovascular Morbidity in Young Adult Israeli Arabs-A Nationwide Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.A.; McDonough, D.J.; Ryu, S.; Zhou, W.; Oginni, J.; Gao, Z. Comparative effectiveness of school-based obesity prevention programs for children and adolescents: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1504279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhatib, A.; Obita, G. Childhood Obesity and Its Comorbidities in High-Risk Minority Populations: Prevalence, Prevention and Lifestyle Intervention Guidelines. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, W.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Xu, J.; Berenson, G.S. Relation of childhood obesity/cardiometabolic phenotypes to adult cardiometabolic profile: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, S142–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Li, W.; Wen, C.P.; Yang, M.; Ning, X.; Hu, K.; Wu, X. Dyslipidemia progression and increased lung cancer risk: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 39, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Weight Category | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight (N = 4172) | Normal (N = 57,867) | Overweight (N = 8883) | Obesity (N = 7958) | Class 2 Obesity (N = 1381) | Class 3 Obesity (N = 592) | p | Total Population (N = 80,853) | |
| Age of BMI measurement, years | ||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 18.0 (0.7) | 18.2 (0.8) | 18.2 (0.9) | 18.0 (0.7) | 18.2 (0.9) | 18.2 (0.9) | <0.001 | 18.1 (0.8) |
| Median (IQR) | 17.9 (1.1) | 18.0 (1.4) | 18.0 (1.5) | 17.8 (1.1) | 18.0 (1.4) | 18.1 (1.5) | 17.9 (1.3) | |
| Sex (male) | ||||||||
| N (%) | 2195 (52.6) | 26,176 (45.2) | 4097 (46.1) | 4180 (52.5) | 672 (48.7) | 296 (50.0) | <0.001 | 37,616 (46.5) |
| Ethnicity N (%) | ||||||||
| Jewish | 2635 (63.2) | 25,513 (44.1) | 3757 (42.3) | 3865 (48.6) | 708 (51.3) | 330 (55.7) | <0.001 | 36,808 (45.5) |
| Arab | 1537 (36.8) | 32,354 (55.9) | 5126 (57.7) | 4093 (51.4) | 673 (48.7) | 262 (44.3) | 44,045 (54.5) | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 16.8 (1.0) | 21.3 (2.0) | 26.5 (1.3) | 30.5 (2.1) | 36.9 (1.4) | 44.6 (4.6) | <0.001 | 23.0 (4.6) |
| Median (IQR) | 16.9 (1.2) | 21.2 (3.2) | 26.4 (1.6) | 30.3 (3.3) | 36.6 (2.3) | 43.1 (4.8) | 22.0 (45.0) | |
| BMI percentile | ||||||||
| Mean (SD) | 2.4 (1.4) | 43.5 (23.5) | 89.7 (3.0) | 97.8 (1.5) | 99.3 (1.2) | 99.3 (1.3) | <0.001 | 53.2 (31.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 2.5 (2.3) | 44.6 (38.8) | 90.0 (5.1) | 98.0 (2.6) | 99.9 (0.1) | 100 (0.0) | 51.2 (57.9) | |
| Socio-economic level | ||||||||
| N (%): | 438 (10.5) | 5229 (9.0) | 674 (7.6) | 622 (7.8) | 87 (6.3) | 42 (7.1) | <0.001 | 7092 (8.8) |
| High | 2250 (53.9) | 25,659 (44.3) | 3888 (43.8) | 3805 (47.8) | 678 (49.1) | 308 (52.0) | 36,588 (45.3) | |
| Middle | 1160 (27.8) | 22,032 (38.1) | 3509 (39.5) | 2913 (36.6) | 511 (37.0) | 200 (33.8) | 30,325 (37.5) | |
| Low | 324 (7.8) | 4947 (8.5) | 812 (9.1) | 618 (7.8) | 105 (7.6) | 42 (7.1) | 6847 (8.5) | |
| missing | ||||||||
| District of residency | ||||||||
| N (%): | 843 (20.2) | 7571 (13.1) | 1002 (11.3) | 1112 (13.8) | 189 (13.7) | 88 (14.9) | <0.001 | 10,805 (13.4) |
| Central | 609 (14.6) | 10,554 (18.2) | 1574 (17.7) | 1241 (15.6) | 215 (15.6) | 71 (12.0) | 14,264 (17.6) | |
| Northern | 756 (18.1) | 11,942 (20.6) | 1834 (20.6) | 1647 (20.7) | 264 (19.1) | 119 (20.1) | 16,562 (20.5) | |
| Haifa | 527 (12.6) | 8281 (14.3) | 1321 (14.9) | 1205 (15.1) | 223 (16.1) | 87 (14.7) | 11,644 (14.4) | |
| Sharon-Shomron | 371 (8.9) | 3889 (6.7) | 588 (6.6) | 563 (7.1) | 77 (5.6) | 58 (9.8) | 5546 (6.9) | |
| Dan-PT | 322 (7.7) | 6913 (11.9) | 1266 (14.3) | 1052 (13.2) | 227 (16.4) | 83 (14.0) | 9863 (12.2) | |
| Jerusalem Southern | 744 (17.8) | 8698 (15.0) | 1298 (14.6) | 1138 (14.3) | 186 (13.5) | 86 (14.5) | 12,150 (15.0) | |
| Missing | 0 (0.0) | 19 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 19 (0.0) | |
| Weight Category | Total Population (N = 80,853) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight (N = 4172) | Normal (N = 57,867) | Overweight (N = 8883) | Obesity (N = 7958) | Class 2 Obesity (N = 1381) | Class 3 Obesity (N = 592) | ||
| |||||||
| Charlson score ≥ 1 | |||||||
| N (%) | 600 (14.38) | 9762 (16.87) | 2042 (22.99) | 2188 (27.49) | 469 (33.96) | 229 (38.68) | 15,281 (18.90) |
| Charlson score ≥ 3 | |||||||
| N (%) | 21 (0.50) | 430 (0.74) | 111 (1.25) | 122 (1.53) | 44 (3.19) | 19 (3.21) | 747 (0.92) |
| Charlson score a | |||||||
| Mean (SD) | 1.22 (0.60) | 1.26 (0.63) | 1.28 (0.65) | 1.33 (0.67) | 1.42 (0.88) | 1.38 (0.73) | 1.28 (0.65) |
| Median (IQR) | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (0) |
| Association of weight category in adolescence with Charlson score at age 30 | |||||||
| RR (95% CI) p-value | 0.83 (0.76–0.90) <0.001 | Reference | 1.39 (1.32–1.46) <0.001 | 1.71 (1.63–1.80) <0.001 | 2.26 (2.05–2.49) <0.001 | 2.51 (2.17–2.90) <0.001 | |
| aRR b (95% CI) p-value | 0.85 (0.78–0.93) <0.001 | 1.39 (1.32–1.46) <0.001 | 1.76 (1.68–1.84) <0.001 | 2.30 (2.08–2.53) <0.001 | 2.59 (2.24–2.98) <0.001 | ||
| aRR c (95% CI) p-value | 1.00 (0.92–1.09) 0.940 | 1.11 (1.05–1.17) <0.001 | 1.17 (1.11–1.24) <0.001 | 1.22 (1.09–1.35) <0.001 | 1.14 (0.98–1.33) 0.090 | ||
| |||||||
| Population | 2195 | 26,176 | 4097 | 4180 | 672 | 296 | 37,616 |
| Charlson score ≥ 1 | |||||||
| N (%) | 258 (11.75) | 3510 (13.41) | 743 (18.14) | 955 (22.85) | 201 (29.91) | 113 (38.18) | 5780 (15.37) |
| Charlson score ≥ 3 | |||||||
| N (%) | 12 (0.55) | 175 (0.67) | 42 (1.03) | 57 (1.36) | 19 (2.83) | 10 (3.38) | 315 (0.84) |
| Association of weight category in adolescence with Charlson score at age 30 | |||||||
| RR (95% CI) p-value | 0.86 (0.76–0.98) 0.021 | Reference | 1.36 (1.25–1.48) <0.001 | 1.74 (1.61–1.88) <0.001 | 2.35 (1.99–2.77) <0.001 | 3.13 (2.50–3.93) <0.001 | |
| aRR b (95% CI) p-value | 0.87 (0.76–0.98) 0.029 | 1.36 (1.25–1.47) <0.001 | 1.74 (1.61–1.88) <0.001 | 2.37 (2.01–2.79) <0.001 | 3.14 (2.50–3.94) <0.001 | ||
| aRR c (95% CI) p-value | 1.01 (0.88–1.15) 0.894 | 1.11 (1.02–1.21) 0.014 | 1.19 (1.09–1.30) <0.001 | 1.26 (1.05–1.51) 0.010 | 1.37 (1.07–1.76) 0.011 | ||
| |||||||
| Population | 1977 | 31,691 | 4786 | 3778 | 709 | 296 | 43,237 |
| Charlson score ≥ 1 | |||||||
| N (%) | 342 (17.30) | 6243 (19.70) | 1299 (27.14) | 1233 (32.63) | 268 (37.80) | 116 (39.19) | 9501 (21.97) |
| Charlson score ≥ 3 | |||||||
| N (%) | 9 (0.46) | 255 (0.80) | 69 (1.44) | 65 (1.72) | 25 (3.53) | 9 (3.04) | 432 (1.00) |
| Association of weight category in adolescence with Charlson score at age 30 | |||||||
| RR (95% CI) p-value | 0.84 (0.75–0.93) 0.001 | Reference | 1.41 (1.33–1.50) <0.001 | 1.77 (1.66–1.88) <0.001 | 2.24 (1.98–2.53) <0.001 | 2.13 (1.76–2.57) <0.001 | |
| aRR b (95% CI) p-value | 0.84 (0.75–0.94) 0.002 | 1.41 (1.33–1.50) <0.001 | 1.77 (1.66–1.88) <0.001 | 2.24 (1.99–2.53) <0.001 | 2.14 (1.77–2.58) <0.001 | ||
| aRR c (95% CI) p-value | 1.00 (0.90–1.12) 0.946 | 1.10 (1.03–1.17) 0.002 | 1.15 (1.07–1.23) <0.001 | 1.17 (1.03–1.34) 0.018 | 0.94 (0.76–1.14) 0.513 | ||
| Weight Category | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Normal | Overweight | Obesity | Class 2 Obesity | Class 3 Obesity | Total | |
| Adolescents in the category (N) | 4826 | 65,816 | 10,324 | 9445 | 1638 | 739 | 92,833 |
| Cases of death, N (%) | 27 (0.6) | 266 (0.4) | 47 (0.4) | 50 (0.5) | 13 (0.8) | 1 (0.1) | 404 (0.4) |
| Age at death, years, Mean (SD) | 25.0 (3.2) | 24.4 (3.5) | 25.7 (3.3) | 24.1 (3.2) | 24.8 (3.7) | 28.3 (-) | 24.6 (3.4) |
| Adult BMI, kg/m2, Mean (SD) | 20.6 (3.8) | 24.8 (4.6) | 30.1 (5.0) | 34.1 (5.8) | 40.1 (6.0) | 44.3 (-) | 26.6 (6.3) |
| RR (95% CI) p-value | 1.38 (0.91–2.02) 0.107 | Reference | 1.13 (0.82–1.52) 0.452 | 1.31 (0.96–1.75) 0.080 | 1.91 (1.04–3.20) 0.023 | 0.33 (1.02–1.48) 0.275 | |
| aRR a (95% CI) p-value | 1.30 (0.86–1.90) 0.190 | 1.11 (0.81–1.50) 0.502 | 1.22 (0.89–1.64) 0.191 | 1.79 (0.98–3.00) 0.040 | 0.32 (0.02–1.43) 0.259 | ||
| aRR b (95% CI) p-value | 1.15 (0.69–1.83) 0.564 | 1.60 (1.11–2.27) 0.010 | 1.71 (1.12–2.57) 0.011 | 3.18 (1.48–6.35) 0.002 | 0.75 (0.04–3.69) 0.785 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Treister-Goltzman, Y.; Menashe, I.; Nemet, D. Adolescent Obesity and Charlson Comorbidity Index in Young Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030873
Treister-Goltzman Y, Menashe I, Nemet D. Adolescent Obesity and Charlson Comorbidity Index in Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(3):873. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030873
Chicago/Turabian StyleTreister-Goltzman, Yulia, Idan Menashe, and Dan Nemet. 2025. "Adolescent Obesity and Charlson Comorbidity Index in Young Adults" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 3: 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030873
APA StyleTreister-Goltzman, Y., Menashe, I., & Nemet, D. (2025). Adolescent Obesity and Charlson Comorbidity Index in Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(3), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14030873






