Non-Fistulizing Perianal Disease in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical Significance, Pathogenesis, and Management Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Epidemiology and Natural History
4. Classification
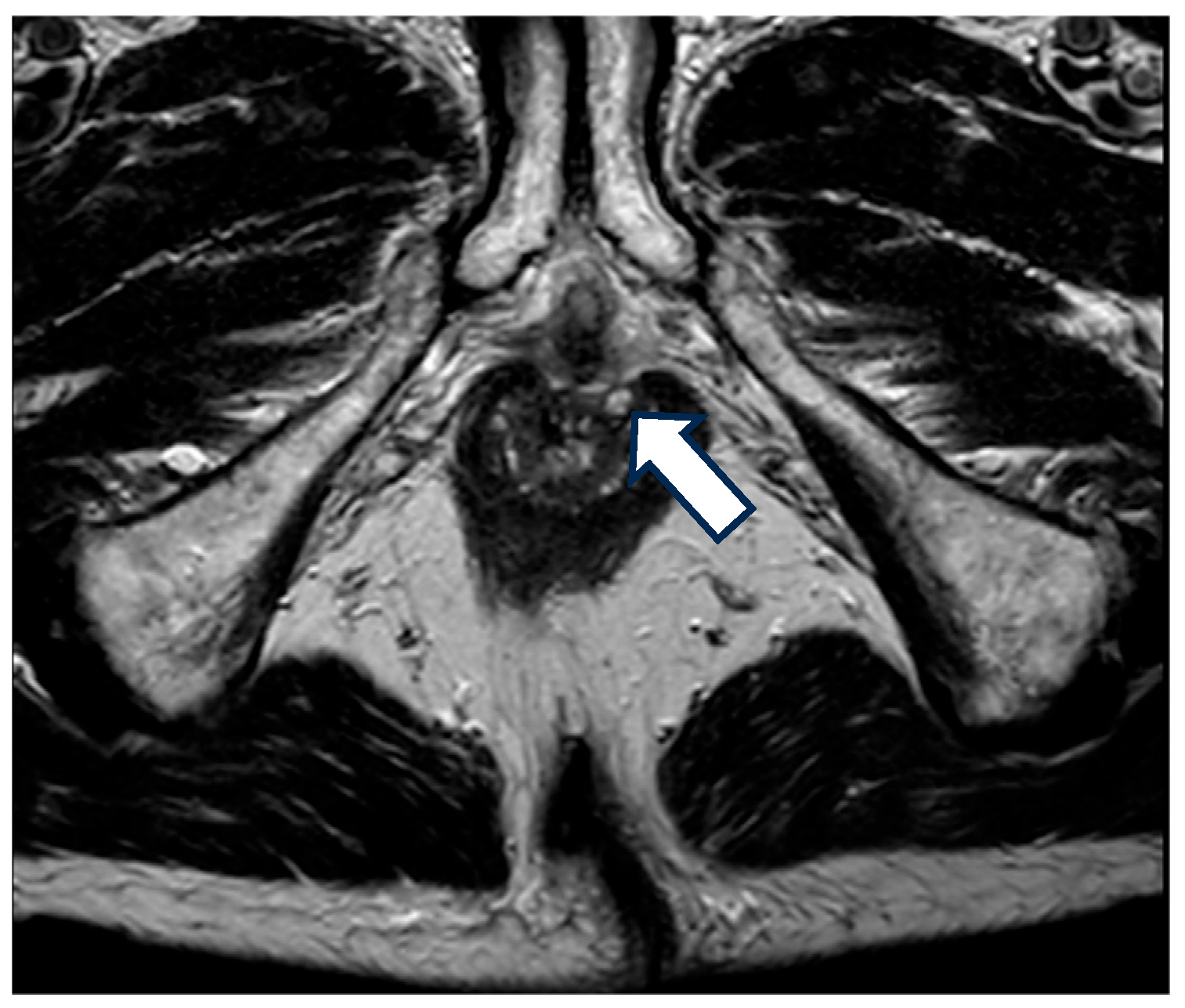
5. Diagnosis
6. Clinical Manifestations and Management
6.1. Fissures
6.1.1. Medical Treatment
6.1.2. Surgical Treatment
6.2. Ulcers
6.2.1. Medical Treatment
6.2.2. Other Treatment Options
6.2.3. Surgical Treatment
6.3. Skin Tags
Surgical Treatment
6.4. Strictures
6.4.1. Medical Treatment
6.4.2. Surgical or Endoscopic Treatment
6.5. Biologic Therapy
6.6. Anal Cancer
6.7. Hemorrhoids
6.8. Management Strategy
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGA | American Gastroenterological Association |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance |
| PCD | Perianal Crohn’s disease |
| PDAI | Perianal Disease Activity Index |
| EUA | Examination under anesthesia |
References
- Munster, L.J.; Hanna, L.N.; Hart, A.L.; Tozer, P.J.; Buskens, C.J.; Van Der Bilt, J.D.W. Diagnosing Crohn’s disease in presumed cryptoglandular perianal fistulas: An expert Delphi consensus on early identification of patients at risk of Crohn’s disease in perianal fistulas (PREFAB). J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, jjaf002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keighley, M.R.B.; Allan, R.N. Current status and influence of operation on perianal Crohn’s disease. Int. J. Color. Dis. 1986, 1, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, B.G.; Culp, C.E.; Beart, R.W.; Ilstrup, D.M.; Ready, R.L.; Wolff Bg, R.N. Anorectal Crohn’s Disease A Long-term Perspective. Dis. Colon Rectum 1985, 28, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, R.G.; Hawk, W.A.; Turnbull, R.B. Clinical Patterns in Crohn’s Disease: A Statistical Study of 615 Cases. Gastroenterology 1975, 68, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamina, M.; Minozzi, S.; Warusavitarne, J.; Buskens, C.J.; Chaparro, M.; Verstockt, B.; Kopylov, U.; Yanai, H.; Vavricka, S.R.; Sigall-Boneh, R.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, 18, 1556–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, S.; Victor, F.; Brian, F.; Stephen, H. AGA Technical Review on Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1508–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadev, S.; Young, J.M.; Selby, W.; Solomon, M.J. Quality of life in perianal Crohn’s disease: What do patients consider important? Dis. Colon Rectum 2011, 54, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegbola, S.O.; Dibley, L.; Sahnan, K.; Wade, T.; Verjee, A.; Sawyer, R.; Mannick, S.; McCluskey, D.; Yassin, N.; Phillips, R.K.S.; et al. Burden of disease and adaptation to life in patients with Crohn’s perianal fistula: A qualitative exploration. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keljo, D.J.; Markowitz, J.; Langton, C.; Lerer, T.; Bousvaros, A.; Carvalho, R.; Crandall, W.; Evans, J.; Griffiths, A.; Kay, M.; et al. Course and treatment of perianal disease in children newly diagnosed with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.; Present, D.; Cohen, Z. An Approach to Perirectal Disease in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 1999, 5, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- Rutgeerts, P. Review article: Treatment of perianal fistulizing Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenhorst, T.; Brochard, C.; Bretagne, J.-F.; Boughen, G.; Siproudhis, L. Crohn’s disease: Is there any link between anal and luminal phenotypes? Int. J. Color. Dis. 2016, 31, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouguen, G.; Siproudhis, L.; Bretagne, J.F.; Bigard, M.A.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Nonfistulizing perianal Crohn’s disease: Clinical features, epidemiology, and treatment. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Loftus, E.V.; Tremaine, W.J.; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Sandborn, W.J. Perianal Crohn’s disease findings other than fistulas in a population-based cohort. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2012, 18, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglinton, T.W.; Barclay, M.L.; Gearry, R.B.; Frizelle, F.A. The spectrum of perianal crohn’s disease in a population-based cohort. Dis. Colon Rectum 2012, 55, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Sánchez, E.R.; Solá Fernández, A.; Pérez Palacios, D.; Núñez Ortiz, A.; de la Cruz Ramírez, M.D.; Leo Carnerero, E.; Salado, C.T.; Justiniano, J.M.H. Perianal Crohn’s disease: Clinical implications, prognosis and use of resources. Rev. Esp. Enferm Dig. 2022, 114, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakase, H.; Watanabe, K.; Shinzaki, S.; Takatsu, N.; Fujii, T.; Okamoto, R.; Matsuoka, K.; Yamada, A.; Kunisaki, R.; et al. Diagnosis and Clinical Features of Perianal Lesions in Newly Diagnosed Crohn’s Disease: Subgroup Analysis from Inception Cohort Registry Study of Patients with Crohn’s Disease (iCREST-CD). J. Crohn’s Colitis 2023, 17, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglinton, T.W.; Gearry, R.B. Clinical factors predicting disease course in Crohn’s disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 6, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogacnik, J.S.; Salgado, G. Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2019, 32, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, S.B.; Loftus, E.V. The natural history of perianal Crohn’s disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2007, 39, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siproudhis, L.; Mortaji, A.; Mary, J.-Y.; Juguet, F.; Bretagne, J.-F.; Gosselin, M. siproudhis1997. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 9, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figg, R.E.; Church, J.M. Perineal Crohn’s disease: An indicator of poor prognosis and potential proctectomy. Dis. Colon Rectum 2009, 52, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, S.; Cúrdia Gonçalves, T.; Dias de Castro, F.; Magalhães, J.; Rosa, B.; Moreira, M.J.; Cotter, J. Perianal Crohn’s disease–association with significant inflammatory activity in proximal small bowel segments. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.E. Clinical Classification of Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 1992, 35, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horaist, C.; De Parades, V.; Abramowitz, L.; Benfredj, P.; Bonnaud, G.; Bouchard, D.; Fathallah, N.; Sénéjoux, A.; Siproudhis, L.; Staumont, G.; et al. Elaboration and validation of Crohn’s disease anoperineal lesions consensual definitions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5371–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, E.J. Usual therapy improves perianal Crohn’s disease as measured by a new disease activity index. McMaster IBD Study Group. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1995, 20, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera-Castro, L.; Ferre-Aracil, C.; Garcia-Garcia-De-Paredes, A.; Rodriguez-De-Santiago, E.; Lopez-Sanroman, A. Management of complex perianal crohn’s disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losco, A.; Vigano, C.; Conte, D.; Cesana, B.M.; Basilisco, G. Assessing the activity of perianal Crohn’s disease: Comparison of clinical indices and computer-assisted anal ultrasound. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniel, P.; Resent, D.H.; Aul Utgeerts, P.R.; Tephan Argan, S.T.; Tephen HAnauer, S.B.; Loyd Ayer, L.M.; Van Ogezand, R.H.; Sands, B.E.; Braakman, T.; DeWoody, K.L.; et al. Infliximab for the treatment of fistulas in patients with Crohn’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Pelly, T.; Anand, E.; Hanna, L.; Shakweh, E.; Joshi, S.; Lung, P.; Hart, A.; Tozer, P. Time to classify: A narrative and scoping review of the old and the new classifications of perianal Crohn’s disease. Tech. Coloproctol. 2025, 29, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bolshinsky, V.; Church, J. Management of Complex Anorectal and Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2019, 32, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juncadella, A.C.; Alame, A.M.; Sands, L.R.; Deshpande, A.R. Perianal crohn’s disease: A review. Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuerstein, J.D.; Ho, E.Y.; Shmidt, E.; Singh, H.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Terdiman, J.P.; Sultan, S.; Cohen, B.L.; Chachu, K.; Day, L.; et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Medical Management of Moderate to Severe Luminal and Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2496–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, P.; Michael Keighley, S.R.; Robert Allan, E.N.; Henry Thompson, E.; John Alexander-Williams, E. Natural History of Perianal Crohn’s Disease Ten Year Follow-Up: A Plea for Conservatism. Am. J. Surg. 1980, 140, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzik, T.; Taylor, S.; Allocca, M.; Burisch, J.; Ellul, P.; Iacucci, M.; Maaser, C.; Baldin, P.; Bhatnagar, G.; Ben-Horin, S.; et al. ECCO-ESGAR-ESP-IBUS Guideline on Diagnostics and Monitoring of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Part 1. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2025, 19, jjaf106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panes, J.; Bouhnik, Y.; Reinisch, W.; Stoker, J.; Taylor, S.A.; Baumgart, D.C.; Danese, S.; Halligan, S.; Marincek, B.; Matos, C.; et al. Imaging techniques for assessment of inflammatory bowel disease: Joint ECCO and ESGAR evidence-based consensus guidelines. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2013, 7, 556–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garros, A.; Siproudhis, L.; Tchoundjeu, B.; Rohou, T.; Brochard, C.; Wallenhorst, T.; Bretagne, J.-F.; Bouguen, G. Magnetic resonance imaging and clinical assessments for perianal Crohn’s disease: Gain and limits. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, D.M.; Schwartz, D.A. Managing Perianal Crohn’s disease. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012, 14, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.A.; Williams, G.T.; Hughes, L.E.; Rhodes, J. The histology of anal skin tags in Crohn’s disease: An aid to confirmation of the diagnosis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 1989, 4, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, D.; Abramowitz, L.; Bouguen, G.; Brochard, C.; Dabadie, A.; De Parades, V.; Eléouet-Kaplan, M.; Fathallah, N.; Faucheron, J.-L.; Maggiori, L.; et al. Crohn’s disease: French recommendations for clinical practice. Tech. Coloproctol. 2017, 21, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonheur, J.L.; Braunstein, J.; Korelitz, B.I.; Panagopoulos, G. Anal skin tags in inflammatory bowel disease: New observations and a clinical review. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.; Bleier, J.S. Surgical treatment of anorectal crohn disease. Clin. Colon Rectal Surg. 2013, 26, 090–099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleshner, P.R.; Schoetz, D.J.; Roberts, P.L.; Murray, J.J.; Coller, J.A.; Veidenheimer, M.C. Anal Fissure in Crohn’s Disease: A Plea For Aggressive Management. Dis. Colon Rectum 1995, 38, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegbola, S.O.; Pisani, A.; Sahnan, K.; Tozer, P.; Ellul, P.; Warusavitarne, J. Medical and surgical management of perianal crohn’s disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouguen, G.; Trouilloud, I.; Siproudhis, L.; Oussalah, A.; Bigard, M.A.; Bretagne, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Long-term outcome of non-fistulizing (ulcers, stricture) perianal Crohn’s disease in patients treated with infliximab. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 30, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallenhorst, T.; Brochard, C.; Le Balch, E.; Bodere, A.; Garros, A.; Merlini-l’Heritier, A.; Bouguen, G.; Siproudhis, L. Anal ulcerations in Crohn’s disease: Natural history in the era of biological therapy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, A.; Zaghiyan, K.; Fleshner, P. Anorectal Crohn’s Disease. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 99, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; George, B.D.; McCMortensen, N.J. Surgical therapy of perianal Crohn’s disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2007, 39, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkomir, A.F.; Luchtefeld, M.A. Surgery for Symptomatic Hemorrhoids and Anal Fissures in Crohn’s Disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 1993, 36, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosnes, J.; Bourrier, A.; Laharie, D.; Nahon, S.; Bouhnik, Y.; Carbonnel, F.; Allez, M.; Dupas, J.; Reimund, J.; Savoye, G.; et al. Early administration of azathioprine vs conventional management of Crohn’s disease: A randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 758–765.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédéric Colombel, J.; Sandborn, W.J.; Reinisch, W.; Mantzaris, G.J.; Kornbluth, A.; Rachmilewitz, D.; Lichtiger, S.; D’Haens, G.; Diamond, R.H.; Broussard, D.L.; et al. Infliximab, Azathioprine, or Combination Therapy for Crohn’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.J.; Mcleod, R.S.; O’connor, B.I.; Steinhart, A.H.; Greenberg, G.R.; Cohen, Z. Combination ciprofloxacin and metronidazole in severe perianal Crohn’s disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1992, 7, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Ng, S.C.; Durdey, P.; Burt, C.; Torkington, J.; Rao, P.K.D.; Mayberry, J.; Moshkovska, T.; Stone, C.D.; Carapeti, E.; et al. Randomized clinical trial of metronidazole ointment versus placebo in perianal Crohn’s disease. Br. J. Surg. 2010, 97, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, E.E.; Nicholson, T.J.; Armstrong, D. Efficacy of topical metronidazole (10 percent) in the treatment of anorectal Crohn’s disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2005, 48, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A.L.; Plamondon, S.; Kamm, M.A. Topical tacrolimus in the treatment of perianal Crohn’s disease: Exploratory randomized controlled trial. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombel, J.-F.; Mathieu, D.; Bouault, A.-J.-M.; Lesage, X.; Zavadil, P.; Quandalle, P.; Cortot, A. Hyperbaric Oxygenation in Severe Perineal Crohn’s Disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 1995, 38, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyer, C.M.; Brandt, L.J. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Perineal Crohn’s Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, M.R.; Féres Filho, O.; Tamaki, C.M.; Perazzoli, C.; Bernardes, M.V.A.A.; Parra, R.S.; da Rocha, J.J.R.; Féres, O. Adjunctive hyperbaric oxygen therapy promotes successful healing in patients with refractory crohn’s disease. Acta Cir. Bras. 2016, 31, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, Y.P.; Schoetz, D.J.; Murray, J.J.; Roberts, P.L.; Coller, J.A. Perianal Crohn’s Disease Results of Local Surgical Treatment. Dis. Colon Rectum 1996, 39, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korelitz, B.I. Anal Skin Tags: An Overlooked Indicator of Crohn’s Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, K.W.; Langman, M.J.S.; Da Cruz, D.J. Malignant transformation of anal skin tags in Crohn’s disease. Gut 1984, 25, 1124–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lightner, A.L.; Click, B.; Yamamoto, T.; Spinelli, A.; Kotze, P. Management of Isolated Anal Strictures in Crohn’s Disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2020, 63, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, L.; Moreira, L.F.; Andrews, H.; Allan, R.N.; Alexander-Willims, J.; Keighley, M.R.B. Natural history and treatment of anorectaI strictures complicating Crohn’s disease. Br. J. Surg. 1988, 75, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochard, C.; Siproudhis, L.; Wallenhorst, T.; Cuen, D.; D’Halluin, P.N.; Garros, A.; Bretagne, J.; Bouguen, G. Anorectal stricture in 102 patients with Crohn’s disease: Natural history in the era of biologics. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander-Williams, J.; Allan, A.; Morel, P.; Hawker, P.; Dykes, P.W.; O’Connor, H. The therapeutic dilatation of enteric strictures due to Crohn’s disease Consultant Surgeon Senior Surgical Registrar. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1986, 68, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Michelassi, F.; Melis, M.; Rubin, M.; Hurst, R.D. Surgical treatment of anorectal complications in Crohn’s disease. Surgery 2000, 128, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Kochhar, G.; Navaneethan, U.; Liu, X.; Farraye, F.A.; Gonzalez-Lama, Y.; Bruining, D.; Pardi, D.S.; Lukas, M.; Bortlik, M.; et al. Role of interventional inflammatory bowel disease in the era of biologic therapy: A position statement from the Global Interventional IBD Group. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, C.; Scarpa, M.; Faggian, D.; Romanato, G.; De Pellegrin, A.; Filosa, T.; Prando, D.; Polese, L.; Scopelliti, M.; Pilon, F.; et al. Cytokine network in chronic perianal crohn’s disease and indeterminate colitis after colectomy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2007, 11, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, C.; Scarpa, M.; Faggian, D.; Pozza, A.; Navaglia, F.; D’Incà, R.; Hoxha, P.; Romanato, G.; Polese, L.; Sturniolo, G.C.; et al. Cytokine network in rectal mucosa in perianal Crohn’s disease: Relations with inflammatory parameters and need for surgery. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wewer, M.D.; Zhao, M.; Nordholm-Carstensen, A.; Weimers, P.; Seidelin, J.B.; Burisch, J. The incidence and disease course of perianal crohn’s disease: A danish nationwide cohort study, 1997–2015. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Rowan, C.; Brockmans, E.D.; Law, C.C.Y.; Giselbrecht, E.; Ang, C.; Khaitov, S.; Sachar, D.; Polydorides, A.D.; Winata, L.S.-H.; et al. Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease–Associated Anorectal and Fistula Cancers: Systematic Review and Expert Consensus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 23, 927–945.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, A.; Sparrow, M.P. Perianal Crohn’s disease: Still more questions than answers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 4260–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, T.; Monteiro, S.; Barros, L.; Silva, J. Perianal disease in inflammatory bowel disease: Broadening treatment and surveillance strategies for anal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 3373–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjö Dahl, R.I.; Myrelid, P.; Sö, J.D. Anal and rectal cancer in Crohn’s disease. Color. Dis. 2003, 5, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ugo, S.; Franceschilli, L.; Cadeddu, F.; Leccesi, L.; Blanco, G.D.V.; Calabrese, E.; Milito, G.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Gaspari, A.L.; Sileri, P. Medical and surgical treatment of haemorrhoids and anal fissure in Crohn’s disease: A critical appraisal. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, P.J.; Ritchie, J.K. Treatment of hemorrhoids in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Surg. Gynecol. Obs. 1960, 152, 839. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, A.T.; Davis, B.R.; Bhama, A.R.; Fang, S.H.; Dawes, A.J.; Feingold, D.L.; Lightner, A.L.; Paquette, I.M.; On behalf of the Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hemorrhoids. Dis. Colon Rectum 2024, 67, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Author | Study Design | Country | CD Phenotypes | Population (n) | Time of Follow-Up | Skin Tags | Fissures | Ulcers | Strictures | Hemorrhoids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Peyrin-Biroulet et al., 2012) [14] | Single-center; Retrospective | United States of America | All phenotypes | 310 | 30 year calculated cumulative risk | 32.2% | 16% | 8.4% | 17.5% | NR |
| (Eglinton et al., 2012) [15] | Single-center; Retrospective | New Zealand | All phenotypes | 715 | Median 9 years [IQR 2 months–45 years] | 11.1% | 32.6% 1 | 32.6% 1 | 7.4% | 1.6% |
| (Martínez Sánchez et al., 2022) [16] | Single-center; Retrospective | Spain | All phenotypes | 430 | 12 years | 4.6% | 30.1% | NR | 15% | NR |
| (Yamamoto et al., 2023) [17] | Multi-center; Prospective | Japan | All phenotypes | 673 | At the time of diagnosis | 19.1% | 18.5% | 11.1% | 4.6% | NR |
| (Wallenhorst et al., 2016) [12] | Single-center; Prospective | France | All phenotypes | 282 | 5 years | NR | NR | 54.6% -Superficial ulcer U1 n = 17; -Cavitating ulcer U2 n = 17; | 17.4% -Short stricture S1 n = 32; -Long stricture S2 n = 17; | NR |
| The Cardiff Classification | ||
| U. Ulceration | F. Fistula/Abscess | S. Stricture |
|
|
|
| Subsidiary Classification (A.P.D.) | ||
| A. Associated Anal Conditions | P. Proximal Intestinal Disease | D. Disease Activity (in Anal Lesions) |
| 0. None 1. Hemorrhoids 2. Malignancy 3. Other(specify) | 0. No proximal disease 1. Contiguous rectal disease 2. Colon (rectum spared) 3. Small intestine 4. Investigation incomplete | 1. Active 2. Inactive 3. Inconclusive |
| Simplified Clinical Classification of PCD | ||
| U. Ulceration | F. Fistula/Abscess | S. Stricture |
| 0. Not present | 0. Not present | 0. Not present |
| 1. Superficial fissure | 1. Low/superficial | 1. Spasm/membranous |
| 2. Cavitating ulcer | 2. High/complex | 2. Severe fibrotic |
| Lesion | Clinical Presentation | Physical Examination Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Fissure | Sharp or burning pain during defecation, possibly lingering afterwards; Rectal bleeding; Pruritus; May be asymptomatic. | Linear/oval ulceration usually limited to dentate line. Multiple and atypically located raises suspicion of association with CD; Can have tenderness to palpation; Chronic cases may show sentinel tag or hypertrophied papilla. |
| Ulcer | Severe, persistent pain; Anal discharge; Rectal bleeding. | Irregular, deep mucosal defect with indurated edges, granulation tissue, or purulent base; Often off-midline and may involve anoderm, anal canal, or perianal skin. |
| Skin Tag | Usually asymptomatic; May cause discomfort, pruritus, or hygiene issues. | Two types described:
|
| Stricture | Pain or difficulty during defecation; Feeling of incomplete evacuation; Narrow or ribbon-like stools; Rectal bleeding; Anal discharge; May be asymptomatic. | Narrowed anal canal or tight fibrotic ring; Possible scarring; Resistance or pain on digital examination or anoscope/endoscope insertion. |
| Hemorrhoids | Painless rectal bleeding; Pruritus; Mucous discharge; Prolapse; Acute pain if thrombosed. | External hemorrhoids: bluish and swelling on anal canal. Internal hemorrhoids: pink-red cushions on anoscopy or visible if prolapsed, reducible or not. |
| Anal Cancer | Persistent pain, bleeding, discharge; Systemic symptoms if advanced. | Ulcerated, indurated lesion or palpable mass; Non-healing fissure/ulcer; Chronic or long stricture; Possible fixation and regional lymphadenopathy. Superficial inguinal lymphadenopathy can be palpable on physical examination. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abreu Marques, I.; Cúrdia Gonçalves, T.; Macedo, C.; Campelo, P.; Cotter, J. Non-Fistulizing Perianal Disease in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical Significance, Pathogenesis, and Management Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248811
Abreu Marques I, Cúrdia Gonçalves T, Macedo C, Campelo P, Cotter J. Non-Fistulizing Perianal Disease in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical Significance, Pathogenesis, and Management Strategies. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(24):8811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248811
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbreu Marques, Inês, Tiago Cúrdia Gonçalves, Cláudia Macedo, Pedro Campelo, and José Cotter. 2025. "Non-Fistulizing Perianal Disease in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical Significance, Pathogenesis, and Management Strategies" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 24: 8811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248811
APA StyleAbreu Marques, I., Cúrdia Gonçalves, T., Macedo, C., Campelo, P., & Cotter, J. (2025). Non-Fistulizing Perianal Disease in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical Significance, Pathogenesis, and Management Strategies. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(24), 8811. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14248811







