When Rewiring Fails—The Enduring Role of the Pectoralis Major Flap in Sternal Wound Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting and Population
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Variables and Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chello, C.; Lusini, M.; Nenna, A.; Nappi, F.; Spadaccio, C.; Satriano, U.M.; Cardetta, F.; Mastroianni, C.; Chello, M. Deep Sternal Wound Infection (DSWI) and Mediastinitis After Cardiac Surgery: Current Approaches and Future Trends in Prevention and Management. Surg. Technol. Int. 2020, 36, 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, A.M.; Lyytikäinen, O.; Klemets, P.; Huotari, K.; Anttila, V.-J.; Werkkala, K.A.; Valtonen, M. Mediastinitis after more than 10,000 cardiac surgical procedures. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2006, 82, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazelrigg, S.R.; Wellons, H.; Schneider, J.; Kolm, P. Wound complications after median sternotomy. Relationship to internal mammary grafting. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1989, 98, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khashkhusha, A.; Butt, S.; Abdelghaffar, M.; Wang, W.; Rajananthanan, A.; Roy, S.; Khurshid, B.N.; Zeinah, M.; Harky, A. Sternal Wound Reconstruction Following Deep Sternal Wound Infection: Past, Present and Future: A Literature Review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauermann, W.J.; Sampathkumar, P.; Thompson, R.L. Sternal wound infections. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2008, 22, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perezgrovas-Olaria, R.; Audisio, K.; Cancelli, G.; Rahouma, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Soletti, G.J.; Chadow, D.; Demetres, M.; Girardi, L.N.; Gaudino, M. Deep Sternal Wound Infection and Mortality in Cardiac Surgery: A Meta-analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 115, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwnica-Worms, W.; Azoury, S.C.; Kozak, G.; Nathan, S.; Stranix, J.T.; Colen, D.; Othman, S.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Serletti, J.; Kovach, S. Flap Reconstruction for Deep Sternal Wound Infections: Factors Influencing Morbidity and Mortality. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 109, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiraldi, L.; Jabbour, G.; Centofanti, P.; Giordano, S.; Abdelnour, E.; Gonzalez, M.; Raffoul, W.; di Summa, P.G. Deep sternal wound infections: Evidence for prevention, treatment, and reconstructive surgery. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2019, 46, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chu, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Yu, H.; Shen, C. Review on risk factors, classification, and treatment of sternal wound infection. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2023, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, B.; Qu, C.; Liu, L.; Song, Y. Analysis of Risk Factors for Sternal Wound Infection After Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5249–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xie, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ooi, O.C.; Luo, H. Association between HbA1c and deep sternal wound infection after coronary artery bypass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.H.; Maganti, M.; Weisel, R.D.; Borger, M.A. Prevention and management of deep sternal wound infection. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 16, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chu, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, B.; Gao, M.; Yuan, H.; Shen, C. A study on the preoperative risk factors for primary healing failure in the reconstruction of deep sternal wound infection with platelet-rich plasma and negative pressure trauma therapy. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 3457–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahi, G.; Koohsari, E.; Hosseini, S.S. Fungal and bacterial co-infection in the superficial and deep sternal wound after open cardiac surgery. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2023, 15, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, D.M.S.; Deininger, M.O.; de Oliveira, O.G.; de Freitas, J.A.; Deininger, E.d.G. Deep Sternal Wound Infection After Beating Heart Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery with Routine Use of Skeletonized Bilateral Internal Thoracic Artery. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2023, 38, e20210607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Cheng, N.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Risk factors for sternal wound infection after median sternotomy: A nested case-control study and time-to-event analysis. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancari, F.; Gatti, G.; Rosato, S.; Mariscalco, G.; Pappalardo, A.; Onorati, F.; Faggian, G.; Salsano, A.; Santini, F.; Ruggieri, V.G.; et al. Preoperative risk stratification of deep sternal wound infection after coronary surgery. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.B.; Thourani, V.H.; Naka, Y.; Grubb, K.J.; Grehan, J.; Patel, N.; Guy, T.S.; Landolfo, K.; Gerdisch, M.; Bonnell, M.; et al. Randomized, multicenter trial comparing sternotomy closure with rigid plate fixation to wire cerclage. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 153, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, E.A.; Culliford, A.T.; Krieger, K.H.; Kloth, D.; Press, R.; Baumann, F.G.; Spencer, F.C. A survey of 77 major infectious complications of median sternotomy: A review of 7949 consecutive operative procedures. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1985, 40, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingerden, J.J.V.; Lapid, O.; Boonstra, P.W.; de Mol, B.A.J.M. Muscle flaps or omental flap in the management of deep sternal wound infection. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 13, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.M.; Yu, C.-M.; Yao, W.-T.; Chen, Y.-F.; Lee, A.-L.; Liu, Y.-C.; Tu, C.-P.; Huang, W.-C.; Tung, K.-Y.; Tsai, M.-F. Efficacy and safety of pectoralis muscle flap combined rectus abdominis muscle sheath fasciocutaneous flap for reconstruction of sternal infection. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, J.; Yang, H.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L. Bilateral partial pectoralis major muscle turnover flaps for the management of deep sternal wound infection following cardiac surgery. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6010–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.-H.; Xiang, D.-Y.; Wu, X.-H.; Chen, Y.-B.; Li, R. A neglected problem in the utilization of free anterolateral thigh flap toward reconstructing complicated wounds of extremities: The obliteration of deep dead space. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netscher, D.T.; Eladoumikdachi, F.; Goodman, C.M. Rectus abdominis muscle flaps used successfully for median sternotomy wounds after ipsilateral internal mammary artery ligation. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2001, 47, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morykwas, M.J.; Argenta, L.C.; Shelton-Brown, E.I.; McGuirt, W. Vacuum-assisted closure: A new method for wound control and treatment: Animal studies and basic foundation. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1997, 38, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wu, N.; Yang, T.; Wang, X. Bilateral Pectoralis Major Muscle Flaps in Treating Deep Sternal Wound Infection following CABG in Diabetic Patients: Two Case Reports. Heart Surg. Forum 2023, 26, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, G.; Jing, Z.; Bu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Rong, X.; Li, M. The combined application of antibiotic-loaded bone cement and vacuum sealing drainage for sternal recon-struction in the treatment of deep sternal wound infection. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 17, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, M.; Mekontso-Dessap, A.; Houël, R.; Giroud, E.; Hillion, M.-L.; Loisance, D.Y. Closed drainage using redon catheters for poststernotomy mediastinitis: Results and risk factors for adverse outcome. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2001, 71, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulaxouzidis, G.; Orhun, A.; Stavrakis, T.; Witzel, C. Second intercostal internal mammary artery perforator (IMAP) fasciocutaneous flap as an alternative choice for the treatment of deep sternal wound infections (DSWI. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 68, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeilias, P.; Nenekidis, I.; Tsipas, P.; Hountis, P. Omental versus muscle flaps in the reconstruction of deep sternal wound infection. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 13, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, A.; Tam, D.Y.; Yu, M.; Yanagawa, B.; Gaudino, M.; Lam, T.; Fremes, S.E. Wire Cerclage Versus Cable Closure After Sternotomy for Dehiscence and DSWI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Innovations 2020, 15, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domkowski, P.W.; Smith, M.L.; Gonyon, D.L.; Drye, C.; Wooten, M.K.; Levin, L.; Wolfe, W.G. Evaluation of vacuum-assisted closure in the treatment of poststernotomy mediastinitis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2003, 126, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, M.; Zeitlinger, M.; Hoeferl, M.; Jaeger, W.; Zimpfer, D.; Hiesmayr, J.-M.; Laufer, G.; Hutschala, D. Internal mammary artery harvesting influences antibiotic penetration into presternal tissue. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuura, K.; Okamoto, H.; Morita, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Sawazaki, M.; Seki, A.; Masumoto, H.; Matsuura, A.; Maseki, T.; Torii, S. Results of omental flap transposition for deep sternal wound infection after cardiovascular surgery. Ann. Surg. 1998, 227, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.; Anderson, E.; Harper, J.G. Overview and management of sternal wound infection. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2011, 25, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torto, F.L.; Turriziani, G.; Donato, C.; Marcasciano, M.; Redi, U.; Greco, M.; Miraldi, F.; Ribuffo, D. Deep sternal wound infection following cardiac surgery: A comparison of the monolateral with the bilateral pectoralis major flaps. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, J.; Gustafsson, R.; Nilsson, J.; Lindstedt, S.; Nozohoor, S.; Ingemansson, R. Negative-pressure wound therapy following cardiac surgery: Bleeding complications and 30-day mortality in 176 patients with deep sternal wound infection. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 12, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, K.B.; Thourani, V.H.; Naka, Y.; Grubb, K.J.; Grehan, J.; Patel, N.; Guy, T.S.; Landolfo, K.; Gerdisch, M.; Bonnell, M.; et al. Rigid Plate Fixation Versus Wire Cerclage: Patient-Reported and Economic Outcomes From a Randomized Trial. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, E.D.; Wu, L.; Waljee, J.F.; Momoh, A.O.; Zhong, L.; Chung, K.C. The Impact of Deep Sternal Wound Infection on Mortality and Resource Utilization: A Population-based Study. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

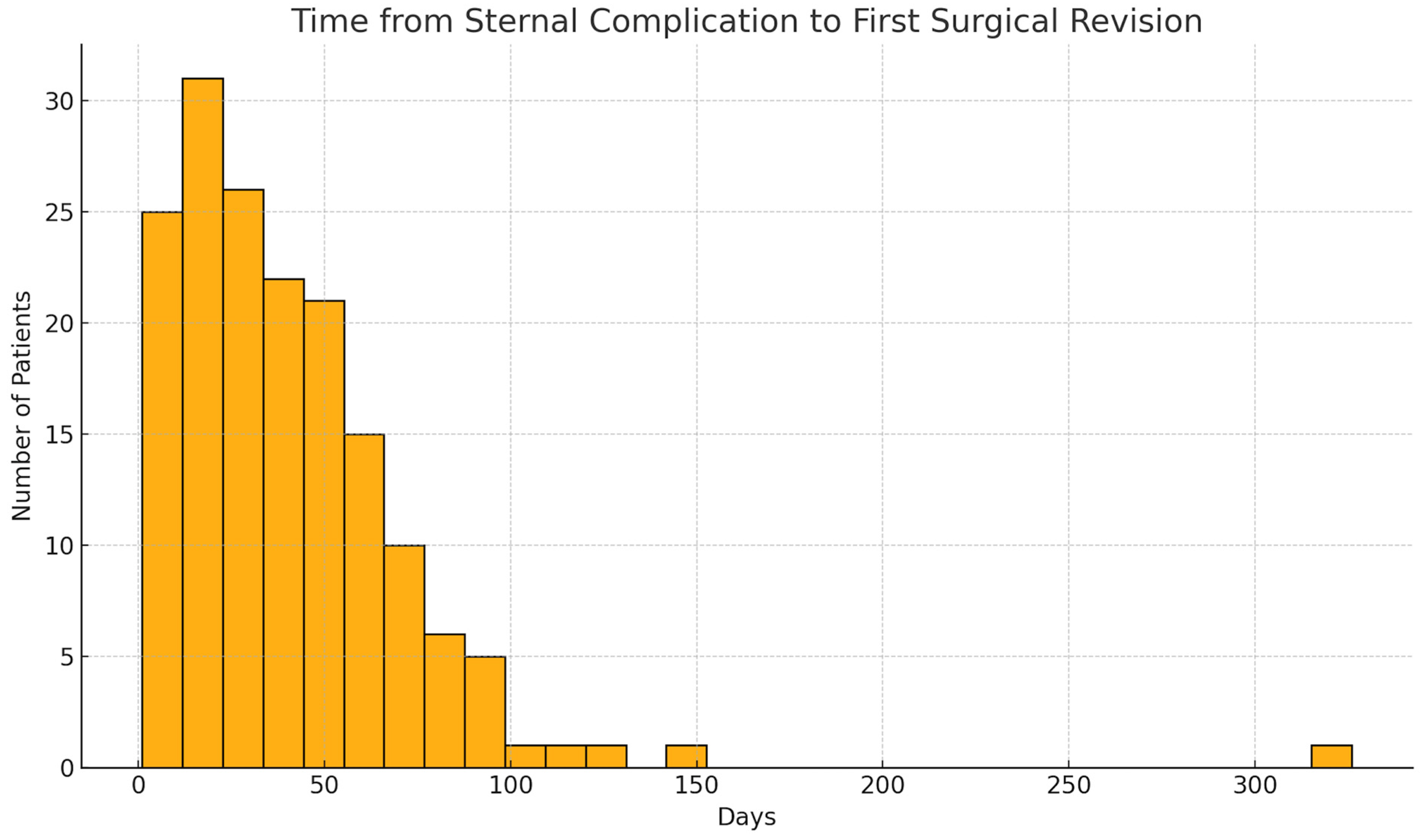
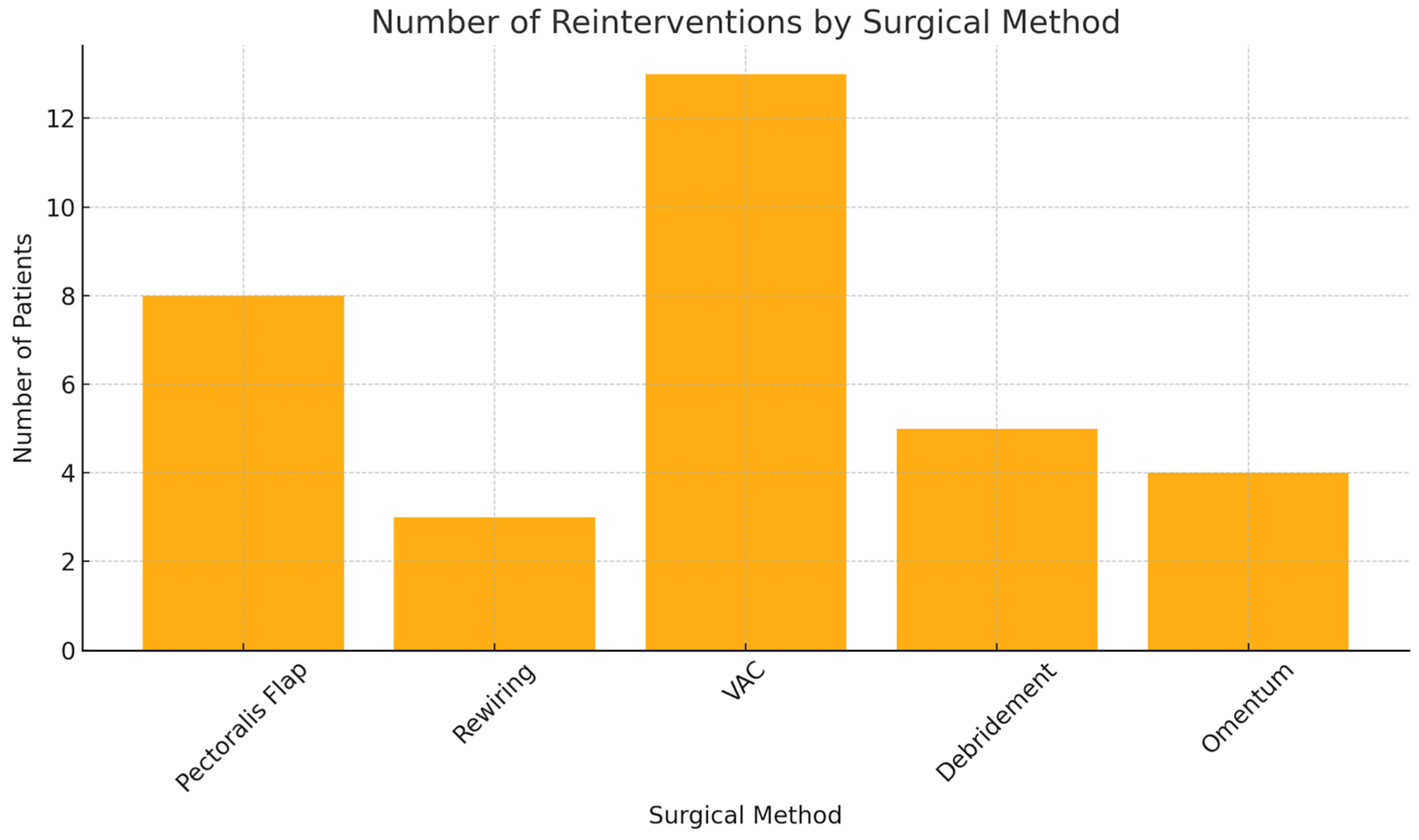
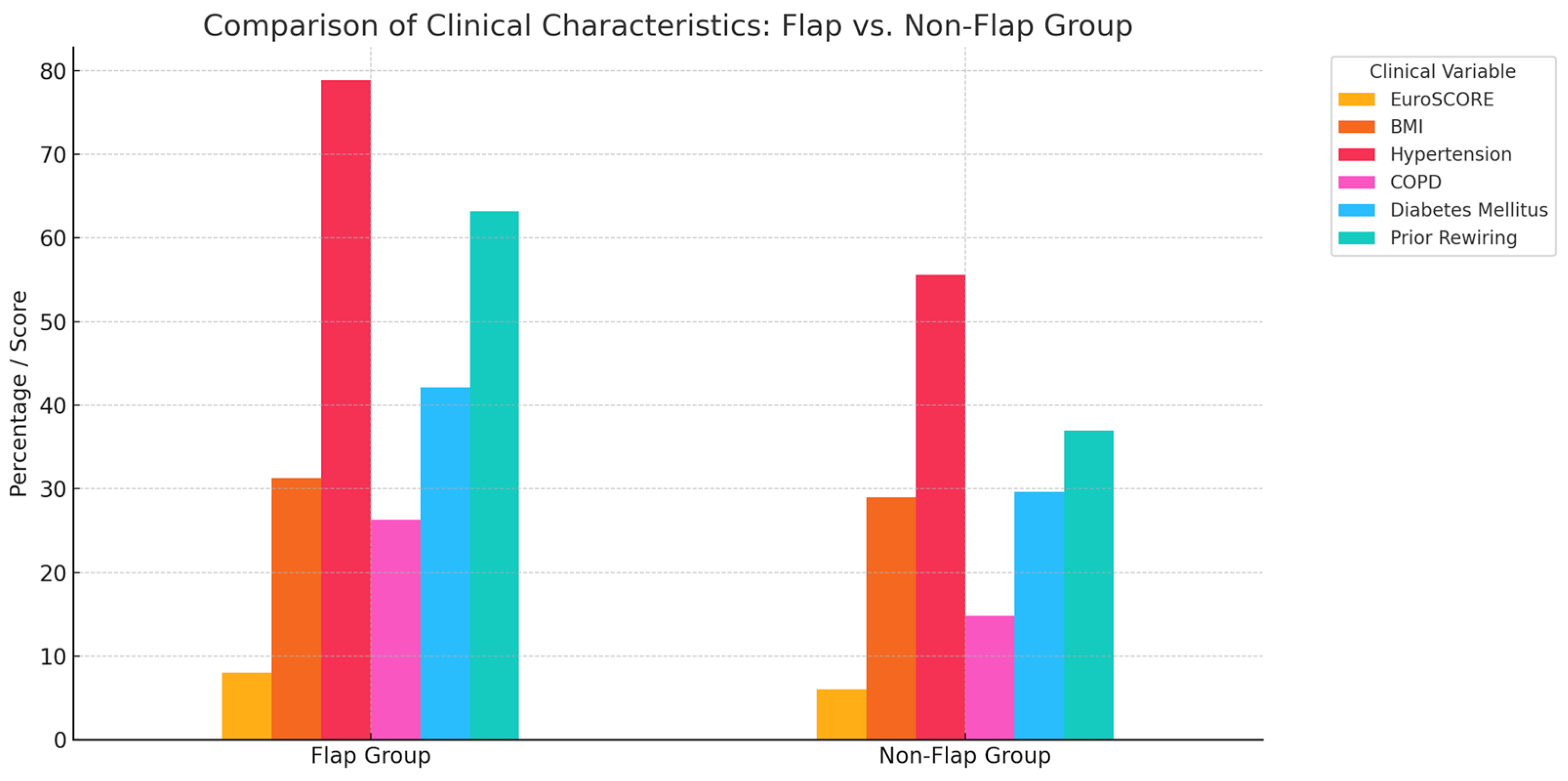
| Parameter | Total | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 64.9 ± 11.9 | 64.0 ± 12.2 | 66.8 ± 11.4 |
| Body weight, kg (mean ± SD) | 89.0 ± 19.8 | 94.5 ± 18.1 | 77.2 ± 18.3 |
| Height, cm (mean ± SD) | 171.3 ± 16.1 | 176.4 ± 6.6 | 160.0 ± 23.6 |
| BMI (body mass index), kg/m2 (mean ± SD) | 29.9 ± 6.2 | 30.3 ± 5.4 | 29.2 ± 7.6 |
| BSA(body surface area), m2 (mean ± SD) | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
| History of smoking | 86 (51.8%) | 64 (56.1%) | 22 (42.3%) |
| Active smokers | 36 (21.7%) | 27 (23.7%) | 9 (17.3%) |
| Arterial hypertension | 153 (92.2%) | 105 (92.1%) | 48 (92.3%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 129 (77.7%) | 88 (77.2%) | 41 (78.8%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 78 (47.0%) | 48 (42.1%) | 30 (57.7%) |
| Coronary heart disease (CHD) | 115 (69.3%) | 84 (73.7%) | 31 (59.6%) |
| Previous myocardial infarction (MI) | 75 (45.2%) | 54 (47.4%) | 21 (40.4%) |
| Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) | 57 (34.3%) | 45 (39.5%) | 12 (23.1%) |
| Atrial fibrillation/flutter | 38 (22.9%) | 26 (22.8%) | 12 (23.1%) |
| Peripheral arterial disease | 40 (24.1%) | 30 (26.3%) | 10 (19.2%) |
| ICD (implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) device | 5 (3.0%) | 5 (4.4%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| Pacemaker | 9 (5.4%) | 7 (6.1%) | 2 (3.8%) |
| Pulmonary disease | 62 (37.3%) | 47 (41.2%) | 15 (28.8%) |
| Chronic lung disease | 60 (36.1%) | 45 (39.5%) | 15 (28.8%) |
| Renal insufficiency | 45 (27.1%) | 30 (26.3%) | 15 (28.8%) |
| Chronic dialysis | 21 (12.7%) | 13 (11.4%) | 8 (15.4%) |
| Parameter | Total | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.7 ± 2.5 | 13.0 ± 2.7 | 11.9 ± 1.8 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 38.2 ± 5.8 | 39.4 ± 5.7 | 35.6 ± 5.0 |
| Platelets (×103/µL) | 225.3 ± 79.7 | 218.4 ± 75.2 | 240.4 ± 87.7 |
| Leukocytes (×103/µL) | 8.9 ± 3.4 | 9.4 ± 3.6 | 7.7 ± 2.3 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 1.8 ± 3.5 | 1.7 ± 3.4 | 2.1 ± 3.6 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 39.6 ± 5.6 | 40.2 ± 5.2 | 38.5 ± 6.4 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.5 ± 1.4 | 1.5 ± 1.4 | 1.4 ± 1.4 |
| LDH (U/L) | 257.5 ± 213.8 | 250.6 ± 205.5 | 272.6 ± 232.1 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 83.0 ± 41.8 | 86.5 ± 42.3 | 75.1 ± 39.8 |
| EuroSCORE (additive) | 7.4 ± 3.7 | 7.0 ± 3.5 | 8.3 ± 4.1 |
| EuroSCORE (logistic) % | 13.7 ± 15.2 | 12.1 ± 12.8 | 17.2 ± 19.1 |
| EuroSCORE II (%) | 7.5 ± 10.6 | 6.1 ± 8.3 | 10.6 ± 14.1 |
| STS mortality (%) | 11.2 ± 104.2 | 2.4 ± 2.6 | 29.3 ± 181.6 |
| STS morbidity and mortality (%) | 133.4 ± 1008.6 | 14.0 ± 10.3 | 377.2 ± 1746.3 |
| Parameter | Total | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) | 108 (65.1%) | 79 (69.3%) | 29 (55.8%) |
| Valve procedures | 33 (19.9%) | 17 (14.9%) | 16 (30.8%) |
| Aortic surgery | 58 (34.9%) | 37 (32.5%) | 21 (40.4%) |
| Concomitant procedures | 42 (25.3%) | 28 (24.6%) | 14 (26.9%) |
| Atrial fibrillation surgery | 12 (7.2%) | 9 (7.9%) | 3 (5.8%) |
| Previous cardiac surgery | 29 (17.5%) | 24 (21.1%) | 5 (9.6%) |
| ECMO required (≤30 days postop) | 18 (10.8%) | 13 (11.4%) | 5 (9.6%) |
| ICU stay (days) | 22.3 ± 37.7 (6.0; 0–253) | 24.0 ± 40.1 (7.0; 0–253) | 18.7 ± 31.9 (5.0; 1–161) |
| Total hospital stay (days) | 67.5 ± 55.4 (50.5; 8–259) | 63.7 ± 53.7 (48.0; 8–259) | 75.7 ± 58.8 (56.0; 12–252) |
| Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) time (min) | 147.7 ± 68.6 (133.5; 0–504) | 152.1 ± 65.5 (138.0; 22–504) | 138.3 ± 74.7 (122.0; 0–411) |
| Aortic cross-clamp (ACC) time (min) | 83.9 ± 45.2 (76.0; 0–305) | 84.8 ± 42.0 (79.0; 0–240) | 81.7 ± 51.9 (71.0; 0–305) |
| Parameter | Rewiring (n = 100) | PMF (n = 56) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 63.2 ± 12.1 | 67.4 ± 11.2 |
| BMI, kg/m2 (mean ± SD) | 29.4 ± 5.8 | 31.1 ± 6.4 |
| EuroSCORE (additive) | 8.0 ± 3.5 | 8.8 ± 3.9 |
| EuroSCORE (logistic) % | 11.3 ± 8.4 | 12.7 ± 8.8 |
| EuroSCORE II (%) | 5.4 ± 4.9 | 5.8 ± 5.7 |
| History of smoking | 49 (49.0%) | 32 (57.1%) |
| Active smokers | 18 (18.0%) | 9 (16.1%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 12 (12.0%) | 19 (33.9%) |
| Renal insufficiency | 9 (9.0%) | 14 (25.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koenig, V.; Christ, A.; Monai, M.; Andreas, M.; Zimpfer, D.; Happak, W.; Werner, P. When Rewiring Fails—The Enduring Role of the Pectoralis Major Flap in Sternal Wound Reconstruction. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238376
Koenig V, Christ A, Monai M, Andreas M, Zimpfer D, Happak W, Werner P. When Rewiring Fails—The Enduring Role of the Pectoralis Major Flap in Sternal Wound Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(23):8376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238376
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoenig, Viktoria, Alexandra Christ, Maximilian Monai, Martin Andreas, Daniel Zimpfer, Wolfgang Happak, and Paul Werner. 2025. "When Rewiring Fails—The Enduring Role of the Pectoralis Major Flap in Sternal Wound Reconstruction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 23: 8376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238376
APA StyleKoenig, V., Christ, A., Monai, M., Andreas, M., Zimpfer, D., Happak, W., & Werner, P. (2025). When Rewiring Fails—The Enduring Role of the Pectoralis Major Flap in Sternal Wound Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(23), 8376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14238376






