Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Versus Autoimmune Encephalitis Using Artificial Intelligence-Based Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
2.3. Model Development and Validation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
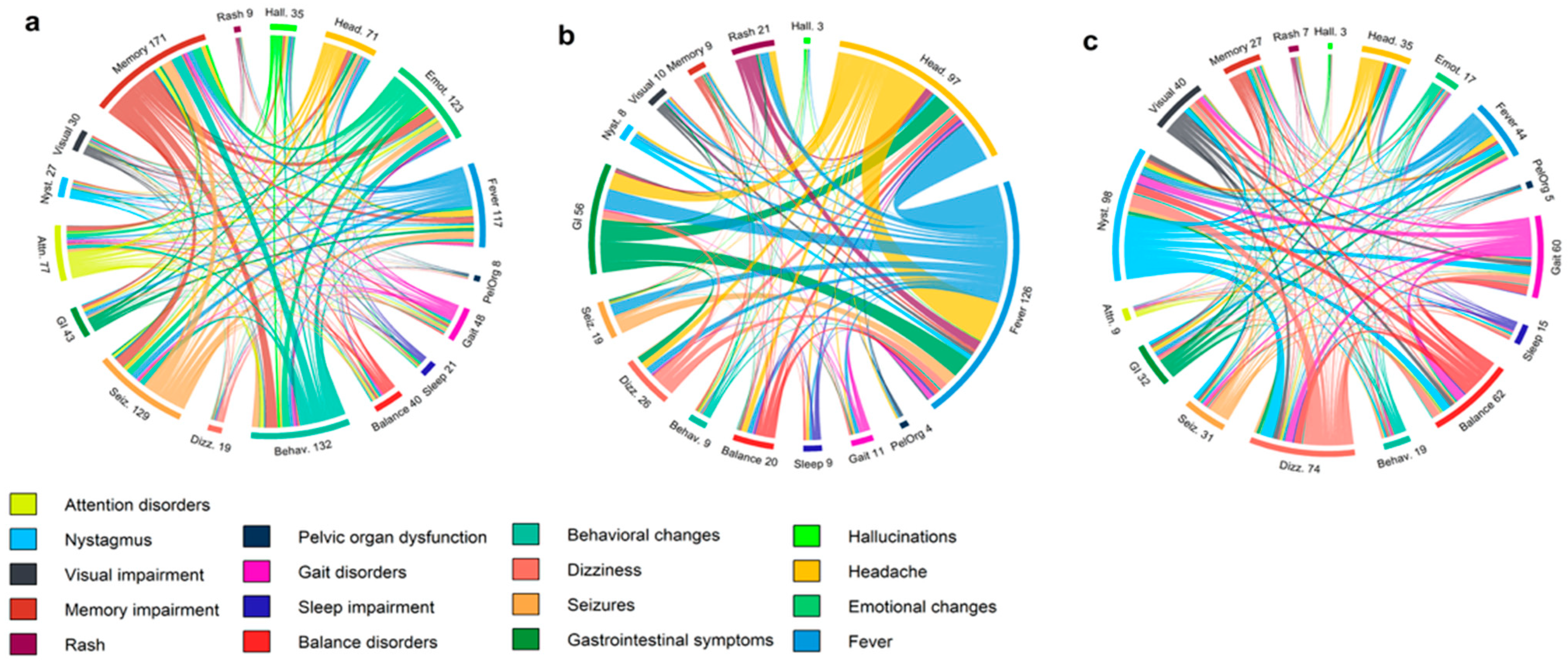
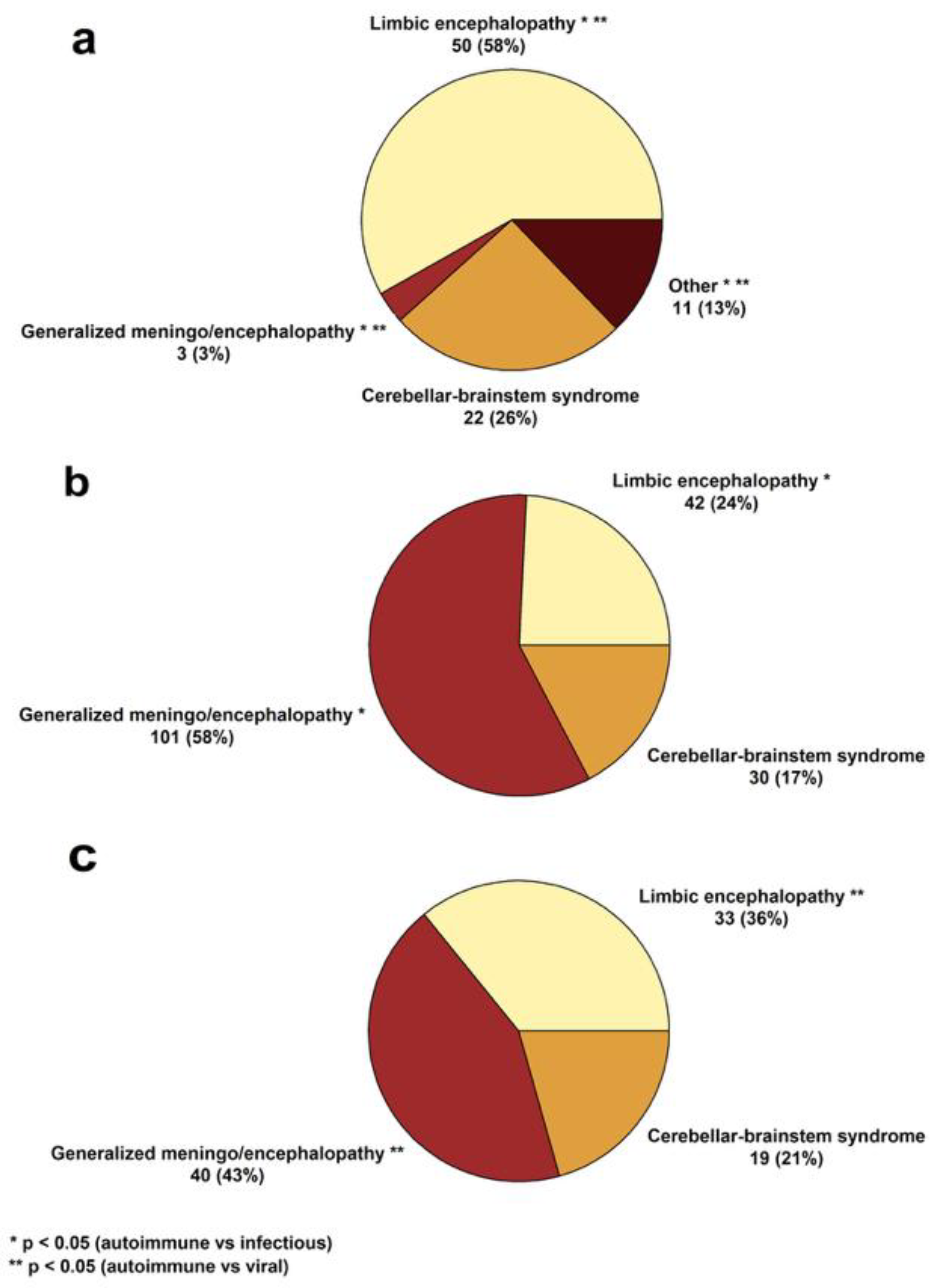
3.1. Clinical and Paraclinical Features of the Cohort
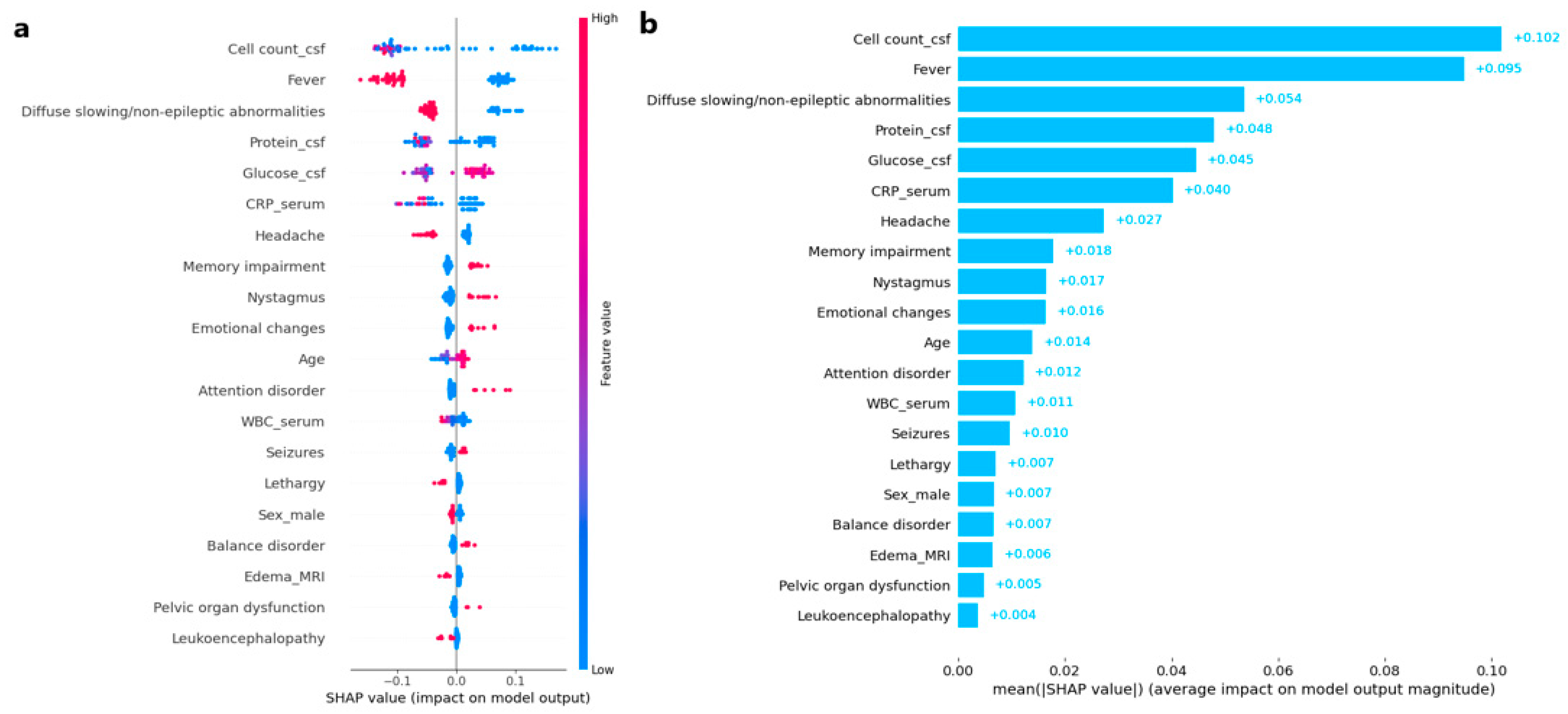
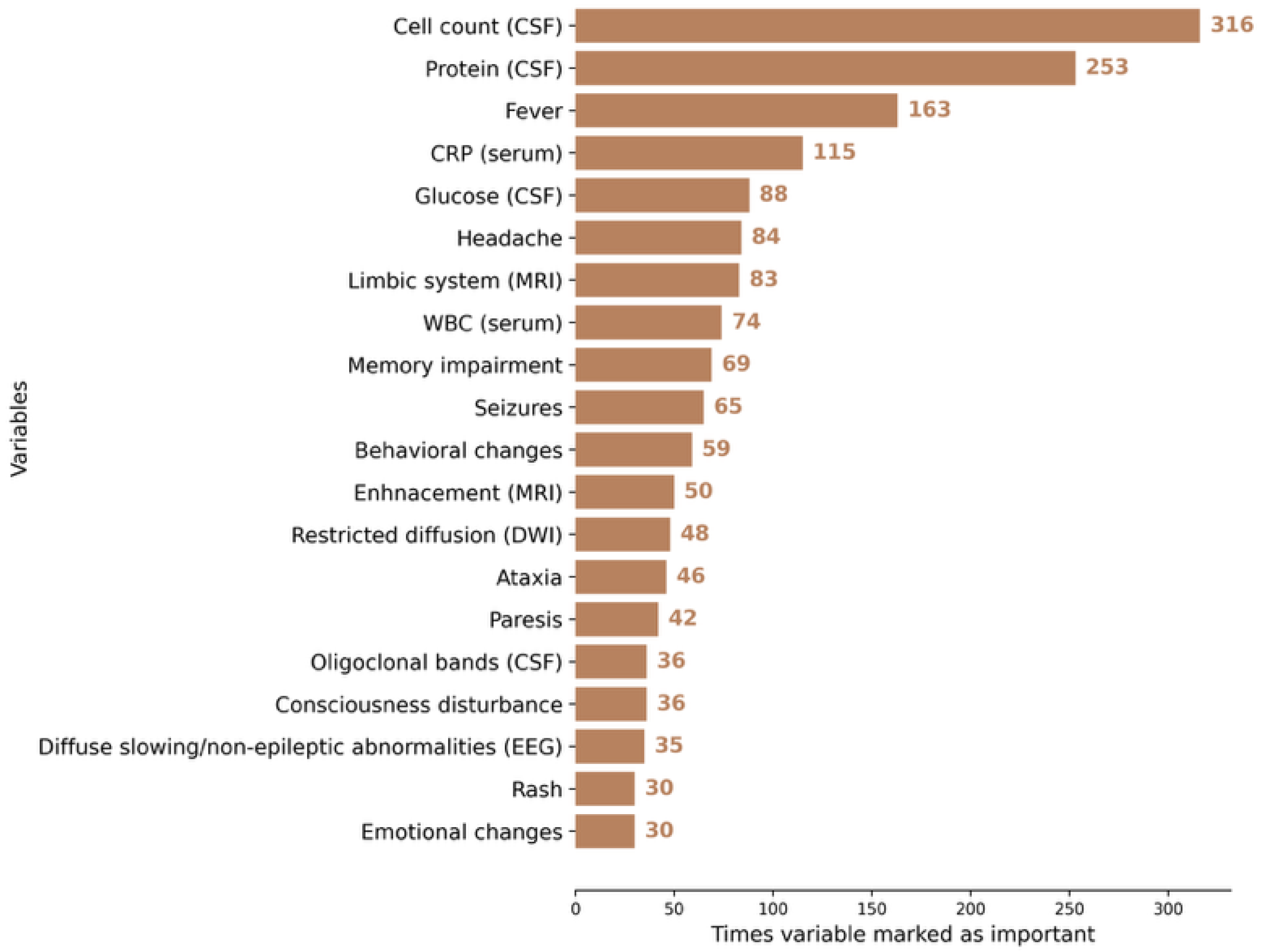
3.2. AI Modeling
3.3. Comparison with Human Controls
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Antibody-Mediated Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Pang, J.; Ma, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y. Global magnitude of encephalitis burden and its evolving pattern over the past 30 years. J. Infect. 2022, 84, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Pittock, S.J.; Kelly, C.R.; McKeon, A.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Lennon, V.A.; Gadoth, A.; Smith, C.Y.; Bryant, S.C.; Klein, C.J.; et al. Autoimmune encephalitis epidemiology and a comparison to infectious encephalitis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.A.; Samannodi, M.S.; Castelblanco, R.L.; Hasbun, R. Clinical Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Encephalitis in Older Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Genrich, G.; Green, A.J.; Tihan, T.; Cree, B.A.C. Encephalitis of Unclear Origin Diagnosed by Brain Biopsy: A Diagnostic Challenge. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, C.A.; Gilliam, S.; Schnurr, D.; Forghani, B.; Honarmand, S.; Khetsuriani, N.; Fischer, M.; Cossen, C.K.; Anderson, L.J. In Search of Encephalitis Etiologies: Diagnostic Challenges in the California Encephalitis Project, 1998–2000. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granerod, J.; Ambrose, H.E.; Davies, N.W.S.; Clewley, J.P.; Walsh, A.L.; Morgan, D.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.J.; Solomon, T.; et al. Causes of encephalitis and differences in their clinical presentations in England: A multicentre, population-based prospective study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang-Orita, N.; Chan-Golston, A.M.; Mitchell, M.; Sivasubramanian, G. 815. False Negative BioFire FilmArray Meningitis/Encephalitis Multiplex PCR Assay in Cryptococcal meningitis: A Single Center Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10 (Suppl. S2), ofad500.860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tiège, X.; Héron, B.; Lebon, P.; Ponsot, G.; Rozenberg, F. Limits of Early Diagnosis of Herpes Simplex Encephalitis in Children: A Retrospective Study of 38 Cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.W.; Sunwoo, J.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W.-J.; Ahn, S.-J.; Lee, S.K.; Chu, K. Clinical significance of Epstein-Barr virus polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid. Encephalitis 2021, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, A.A.; Glaser, C.A.; Amad, Z.; Forghani, B. Patients with Suspected Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: Rethinking an Initial Negative Polymerase Chain Reaction Result. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déchelotte, B.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Joubert, B.; Vogrig, A.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Pinto, A.-L.; Lombard, C.; Desestret, V.; Fabien, N.; et al. Diagnostic yield of commercial immunodots to diagnose paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-García, R.; Muñoz-Sánchez, G.; Naranjo, L.; Guasp, M.; Sabater, L.; Saiz, A.; Dalmau, J.; Graus, F.; Martinez-Hernandez, E. Limitations of a Commercial Assay as Diagnostic Test of Autoimmune Encephalitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, C.; Businaro, P.; Papi, C.; Arlettaz, L.; Marmolejo, L.; Naranjo, L.; Gastaldi, M.; Iorio, R.; Saiz, A.; Planagumà, J.; et al. Assessing Commercial Tissue-Based Assays for Autoimmune Neurologic Disorders (I). Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 12, e200410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papi, C.; Milano, C.; Arlettaz, L.; Businaro, P.; Marmolejo, L.; Naranjo, L.; Planagumà, J.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Armangué, T.; Guasp, M.; et al. Assessing Commercial Tissue-Based Assays for Autoimmune Neurologic Disorders (II). Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 12, e200406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjordside, L.; Nissen, M.S.; Florescu, A.M.; Storgaard, M.; Larsen, L.; Wiese, L.; von Lüttichau, H.R.; Jepsen, M.P.G.; Hansen, B.R.; Andersen, C.Ø.; et al. Validation of a risk score to differentiate autoimmune and viral encephalitis: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Denmark. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 4972–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogrig, A.; Péricart, S.; Pinto, A.-L.; Rogemond, V.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Picard, G.; Selton, M.; Mittelbronn, M.; Lanoiselée, H.-M.; Michenet, P.; et al. Immunopathogenesis and proposed clinical score for identifying Kelch-like protein-11 encephalitis. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuth, S.; Paris, J.; Faddeenkov, I.; De Sèze, J.; Gourraud, P.A. Clinical applications of deep learning in neuroinflammatory diseases: A scoping review. Rev. Neurol. 2025, 181, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Sung, M.; Ha, W.; Chu, M.K.; Kim, W.-J.; Heo, K.; Kim, K.M.; Park, Y.R. Development and validation of an artificial intelligence model for the early classification of the aetiology of meningitis and encephalitis: A retrospective observational study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 61, 102051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Titulaer, M.J.; Balu, R.; Benseler, S.; Bien, C.G.; Cellucci, T.; Cortese, I.; Dale, R.C.; Gelfand, J.M.; Geschwind, M.; et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graus, F.; Vogrig, A.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Antoine, J.-C.G.; Desestret, V.; Dubey, D.; Giometto, B.; Irani, S.R.; Joubert, B.; Leypoldt, F.; et al. Updated Diagnostic Criteria for Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaišvilas, M.; Ciano-Petersen, N.L.; Macarena Villagrán-García, M.D.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Honnorat, J. Paraneoplastic encephalitis: Clinically based approach on diagnosis and management. Postgrad. Med. J. 2023, 99, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, E.; Valencia-Sanchez, C.; Britton, J.; Dubey, D.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lopez-Chiriboga, A.S.; Zalewski, N.; Zekeridou, A.; Pittock, S.J.; McKeon, A. Autoimmune Encephalitis Criteria in Clinical Practice. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, e200151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taieb, G.; Mulero, P.; Psimaras, D.; van Oosten, B.W.; Seebach, J.D.; Marignier, R.; Pico, F.; Rigau, V.; Ueno, Y.; Duflos, C.; et al. CLIPPERS and its mimics: Evaluation of new criteria for the diagnosis of CLIPPERS. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisvilas, M.; Petrosian, D.; Bagdonaite, L.; Taluntiene, V.; Kralikiene, V.; Daugelaviciene, N.; Neniskyte, U.; Kaubrys, G.; Giedraitiene, N. Seroprevalence of neuronal antibodies in diseases mimicking autoimmune encephalitis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Jensen, L.; Zierold, S.; Versluis, J.M.; Boehmerle, W.; Huehnchen, P.; Endres, M.; Mohr, R.; Compter, A.; Blank, C.U.; Hagenacker, T.; et al. Dataset of a retrospective multicenter cohort study on characteristics of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced encephalitis and comparison with HSV-1 and anti-LGI1 encephalitis. Data Brief. 2022, 45, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granillo, A.; Le Maréchal, M.; Diaz-Arias, L.; Probasco, J.; Venkatesan, A.; Hasbun, R. Development and Validation of a Risk Score to Differentiate Viral and Autoimmune Encephalitis in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e1294–e1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, D.; Kothapalli, N.; McKeon, A.; Flanagan, E.P.; Lennon, V.A.; Klein, C.J.; Britton, J.W.; So, E.; Boeve, B.F.; Tillema, J.-M.; et al. Predictors of neural-specific autoantibodies and immunotherapy response in patients with cognitive dysfunction. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 323, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.; Muñiz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Farina, A.; Pinto, A.-L.; Picard, G.; Rogemond, V.; Guery, D.; Alentorn, A.; Psimaras, D.; et al. Early-Stage Contactin-Associated Protein-like 2 Limbic Encephalitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sonderen, A.; Thijs, R.D.; Coenders, E.C.; Jiskoot, L.C.; Sanchez, E.; de Bruijn, M.A.; van Coevorden-Hameete, M.H.; Wirtz, P.W.; Schreurs, M.W.; Smitt, P.A.S.; et al. Anti-LGI1 encephalitis. Neurology 2016, 87, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhram, A.; Sechi, E.; Flanagan, E.P.; Dubey, D.; Zekeridou, A.; Shah, S.S.; Gadoth, A.; Naddaf, E.; McKeon, A.; Pittock, S.J.; et al. Clinical spectrum of high-titre GAD65 antibodies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Moon, J.; Park, K.-I.; Lee, S.K.; Chu, K.; Lee, S.-T. Seronegative autoimmune encephalitis: Clinical characteristics and factors associated with outcomes. Brain 2022, 145, 3509–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmau, J.; Graus, F. Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune encephalitis: Utility and pitfalls for antibody-negative disease. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojžišová, H.; Krýsl, D.; Hanzalová, J.; Dargvainiene, J.; Wandinger, K.-P.; Leypoldt, F.; Elišák, M.; Marusič, P. Antibody-Negative Autoimmune Encephalitis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kherbek, H.; Paramasivan, N.K.; Dasari, S.; Karsten, C.; Thakolwiboon, S.; Gilligan, M.; Knight, A.M.; LaFrance-Corey, R.G.; Losada, V.; McKeon, A.; et al. Exploring autoantigens in autoimmune limbic encephalitis using phage immunoprecipitation sequencing. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Liu, B.; Tan, W.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Han, Y.; Luo, Q.; Gong, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Deep Learning-Enabled Identification of Autoimmune Encephalitis on 3D Multi-Sequence MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musigmann, M.; Spiekers, C.; Stake, J.; Akkurt, B.H.; Mora, N.G.N.; Sartoretti, T.; Heindel, W.; Mannil, M. Detection of antibodies in suspected autoimmune encephalitis diseases using machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, V.; Jacobs, M.A. Radiomics: A new application from established techniques. Expert. Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2016, 1, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Autoimmune Encephalitides (n = 83) | Infectious Encephalitides (n = 150) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Associated Antibody | n (%) | Associated Agent | n (%) |
| Anti-LGI1 | 29 (34.9%) | Viral | 84 (56.0%) |
| Anti-NMDA | 9 (10.8%) | HSV-1/HSV-2 | 34 (22.7%) |
| Anti-AQP4 | 9 (10.8%) | Unidentified | 25 (16.7%) |
| Seronegative | 9 (10.8%) | VZV | 12 (8.0%) |
| Anti-Yo | 7 (8.4%) | TBEV | 10 (6.7%) |
| Anti-GAD65 | 4 (4.8%) | CMV | 1 (0.7%) |
| Anti-CASPR2 | 3 (3.6%) | EBV | 1 (0.7%) |
| Anti-Hu † | 3 (3.6%) | Parvovirus B19 | 1 (0.7%) |
| Anti-AMPAR | 2 (2.4%) | Bacterial | 66 (44.0%) |
| Atypical | 2 (2.4%) | Unidentified | 31 (20.7%) |
| Anti-GABAB | 1 (1.2%) | Streptococcus spp. | 8 (5.3%) |
| Anti-KLHL11 | 1 (1.2%) | L. monocytogenes | 8 (5.3%) |
| Anti-GFAP | 1 (1.2%) | B. burgdorferi | 7 (4.7%) |
| Anti-Ri | 1 (1.2%) | Staphylococcus spp. | 5 (3.3%) |
| Anti-MOG | 1 (1.2%) | N. meningitidis | 3 (2.0%) |
| ANA | 1 (1.2%) | M. tuberculosis | 2 (1.3%) |
| H. influenzae | 1 (0.7%) | ||
| T. pallidum | 1 (0.7%) | ||
| Variable | Autoimmune (n = 83) | Infectious † (n = 150) | Viral (n = 84) | p-Value * | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 59 (41–68.5) | 46.5 (28–63) | 54 (34.25–66) | 0.0108 | 0.2032 |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 38 (45.8%) | 88 (58.7%) | 49 (58.3%) | 0.0588 | 0.1045 |
| Presenting symptoms | |||||
| Headache | 5 (6.0%) | 69 (46.0%) | 42 (50.0%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Disorientation | 26 (31.3%) | 45 (30.0%) | 28 (33.3%) | 0.8333 | 0.7815 |
| Gait disturbance | 17 (20.5%) | 11 (7.3%) | 7 (8.3%) | 0.0031 | 0.0252 |
| Sleep impairment | 7 (8.4%) | 3 (2.0%) | 2 (2.4%) | 0.0370 | 0.0989 |
| Behavioral changes | 28 (33.7%) | 13 (8.7%) | 12 (14.3%) | <0.0001 | 0.0032 |
| Balance disorder | 17 (20.5%) | 10 (6.7%) | 7 (8.3%) | 0.0016 | 0.0252 |
| Fever | 10 (12.0%) | 110 (73.3%) | 62 (73.8%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Impaired consciousness | 22 (26.5%) | 35 (23.3%) | 23 (27.4%) | 0.5895 | 0.8986 |
| Seizures | 42 (50.6%) | 31 (20.7%) | 20 (23.8%) | <0.0001 | 0.0003 |
| Paresthesia | 9 (10.8%) | 12 (8.0%) | 6 (7.1%) | 0.4680 | 0.4030 |
| GI symptoms | 4 (4.8%) | 39 (26.0%) | 22 (26.2%) | <0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| Dizziness | 22 (26.5%) | 14 (9.3%) | 8 (9.5%) | 0.0005 | 0.0043 |
| Ataxia | 27 (32.5%) | 62 (41.3%) | 37 (44.0%) | 0.1854 | 0.1258 |
| Nystagmus | 21 (25.3%) | 13 (8.7%) | 6 (7.1%) | 0.0005 | 0.0014 |
| Vision impairment | 15 (18.1%) | 9 (6.0%) | 4 (4.8%) | 0.0037 | 0.0068 |
| Hearing impairment | 3 (3.6%) | 7 (4.7%) | 2 (2.4%) | 0.7043 | 0.6818 |
| Somnolence | 11 (13.3%) | 20 (13.3%) | 10 (11.9%) | 0.9862 | 0.7928 |
| Tremor | 7 (8.4%) | 22 (14.7%) | 12 (14.3%) | 0.1675 | 0.2337 |
| Speech disturbance | 15 (18.1%) | 37 (24.7%) | 24 (28.6%) | 0.2470 | 0.1088 |
| Memory impairment | 37 (44.6%) | 19 (12.7%) | 16 (19.0%) | <0.0001 | 0.0004 |
| Attention disorder | 14 (16.9%) | 2 (1.3%) | 2 (2.4%) | <0.0001 | 0.0015 |
| Paresis/plegia | 22 (26.5%) | 47 (31.3%) | 29 (34.5%) | 0.4396 | 0.2607 |
| Hallucinations | 9 (10.8%) | 2 (1.3%) | 2 (2.4%) | 0.0019 | 0.0275 |
| Emotional changes | 27 (32.5%) | 5 (3.3%) | 5 (6.0%) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Rash | 1 (1.2%) | 14 (9.3%) | 8 (9.5%) | 0.0155 | 0.0173 |
| Pelvic organ dysfunction | 10 (12.0%) | 5 (3.3%) | 4 (4.8%) | 0.0094 | 0.0894 |
| Laboratory data | |||||
| WBC (×109/L, serum) | 7.88 (5.84–10.30) | 8.98 (6.50–12.85) | 8.38 (6.39–10.22) | 0.0451 | 0.5000 |
| CRP (mg/L, serum) | 2.12 (0.60–5.75) | 11.40 (2.00–85.00) | 4.15 (1.06–21.31) | <0.0001 | 0.0124 |
| Cell count (cells/μL, CSF) | 5 (2–18.75) | 121 (43.75–410.75) | 61 (29.75–126.75) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Protein (g/L, CSF) | 0.46 (0.32–0.71) | 1.02 (0.60–2.07) | 0.73 (0.49–1.15) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose (mmol/L, CSF) | 3.51 (3.31–4.03) | 3.00 (2.45–3.71) | 3.24 (2.82–3.94) | 0.0001 | 0.0300 |
| Oligoclonal bands (CSF) | 15/44 (34.1%) | 14/34 (41.2%) | 10/26 (38.5%) | 0.5208 | 0.7123 |
| EEG data | |||||
| Diffuse slowing/non-epileptic abnormalities | 31/65 (47.7%) | 49/60 (81.7%) | 33/41 (80.5%) | <0.0001 | 0.0008 |
| Epileptic abnormalities | 21/65 (32.3%) | 15/60 (25.0%) | 12/41 (29.3%) | 0.3674 | 0.7421 |
| MRI abnormalities | |||||
| White matter lesions | 4 (4.8%) | 22 (14.7%) | 11 (13.1%) | 0.0294 | 0.0762 |
| Basal ganglia | 6 (4.8%) | 13 (8.7%) | 3 (3.6%) | 0.7799 | 0.3175 |
| Corpus callosum | 1 (1.2%) | 7 (4.7%) | 2 (2.4%) | 0.2684 | 0.5966 |
| Pontine | 2 (2.4%) | 4 (2.7%) | 3 (3.6%) | 0.9515 | 0.7004 |
| Midbrain | 2 (2.4%) | 4 (2.7%) | 3 (3.6%) | 0.9515 | 0.7004 |
| Thalamus | 5 (6.0%) | 10 (6.7%) | 6 (7.1%) | 0.9218 | 0.8360 |
| Corona radiata | 1 (1.2%) | 8 (5.3%) | 3 (3.6%) | 0.1690 | 0.6211 |
| Cortical edema | 4 (4.8%) | 3 (2.0%) | 3 (3.6%) | 0.2375 | 0.7134 |
| Cerebellum | 2 (2.4%) | 6 (4.0%) | 3 (3.6%) | 0.7178 | 0.7004 |
| Limbic system | 29 (34.9%) | 42 (28.0%) | 30 (35.7%) | 0.1756 | 0.8949 |
| Contrast enhancement | 10/74 (13.5%) | 53/113 (46.9%) | 24/71 (33.8%) | <0.0001 | 0.0039 |
| Edema | 9 (10.8%) | 37 (24.7%) | 25 (29.8%) | 0.0172 | 0.0039 |
| Restriction on DWI | 9 (10.8%) | 35 (23.3%) | 14 (16.7%) | 0.0292 | 0.3337 |
| Features | Used by Humans | Selected for AI Model (After RFECV) |
|---|---|---|
| Demographics and clinical | X | |
| Age | X | X |
| Sex_male | X | X |
| Rash | X | |
| Headache | X | X |
| Fatigue | X | |
| Sleep impairment | X | |
| Gait disturbance | X | |
| Behavioral changes | X | |
| Shivering | X | |
| Balance disorder | X | X |
| Catatonia | X | |
| Fever | X | X |
| Consciousness disturbance | X | X |
| Joint/muscle pain | X | |
| Dyspnea | X | |
| Seizures | X | X |
| Drooling | X | |
| Cough | X | |
| Myoclonus | X | |
| Sore throat | X | |
| Disorientation | X | |
| Paresthesia | X | |
| Fainting | X | |
| GI symptoms | X | |
| Back pain | X | |
| Chills | X | |
| Dizziness | X | |
| Ataxia | X | X |
| Nystagmus | X | X |
| Visual impairment | X | X |
| Hearing impairment | X | |
| Lethargy | X | X |
| Somnolence | X | |
| Tremor | X | |
| Delirium | X | |
| Dysphagia | X | |
| Speech disorder | X | |
| Memory impairment | X | X |
| Attention disorder | X | X |
| Paresis | X | X |
| Hallucinations | X | |
| Emotional changes | X | X |
| Olfactory disturbance | X | |
| Pelvic organ dysfunction | X | X |
| Laboratory features | X | |
| WBC_serum | X | X |
| CRP_serum | X | X |
| Cell count_CSF | X | X |
| Protein_CSF | X | X |
| Glucose_CSF | X | X |
| Oligoclonal bands_CSF | X | |
| EEG | ||
| Diffuse slowing/non-epileptic abnormalities | X | X |
| Focal epileptic abnormalities | X | |
| MRI features | ||
| Leukoencephalopathy | X | X |
| Basal ganglia | X | X |
| Cerebellar peduncles | X | |
| Corpus callosum | X | |
| Pontine | X | |
| Midbrain | X | |
| Thalamus | X | |
| Cortical edema | X | |
| Corona radiata | X | |
| Cerebellum | X | |
| Limbic system | X | |
| Enhancement_MRI | X | |
| Enhancement_leptomeningeal | X | |
| Enhancement_pachymeningeal | X | |
| Enhancement_linear | X | |
| Restricted diffusion_DWI | X | X |
| Edema_MRI | X | X |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | AUROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | 0.971 | 1.000 | 0.920 | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.966 |
| XGBoost | 0.943 | 0.957 | 0.880 | 0.978 | 0.917 | 0.940 |
| LightGBM | 0.943 | 0.957 | 0.880 | 0.978 | 0.917 | 0.949 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.943 | 0.920 | 0.920 | 0.956 | 0.920 | 0.964 |
| Naïve Bayes | 0.886 | 0.840 | 0.840 | 0.911 | 0.840 | 0.880 |
| K-nearest Neighbors | 0.871 | 0.833 | 0.800 | 0.911 | 0.816 | 0.865 |
| Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | Specificity | F1-Score | AUROC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI model | 0.971 | 1.000 | 0.920 | 1.000 | 0.958 | 0.966 |
| Neurologist in training 1 | 0.900 | 0.846 | 0.880 | 0.911 | 0.863 | 0.896 |
| Neurologist in training 2 | 0.800 | 0.677 | 0.840 | 0.778 | 0.750 | 0.809 |
| Neurologist in training 3 | 0.757 | 0.618 | 0.840 | 0.711 | 0.712 | 0.776 |
| Attending physician 1 | 0.843 | 0.733 | 0.880 | 0.822 | 0.800 | 0.851 |
| Attending physician 2 | 0.829 | 0.933 | 0.560 | 0.978 | 0.700 | 0.769 |
| Attending physician 3 | 0.871 | 0.864 | 0.760 | 0.933 | 0.809 | 0.847 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrosian, D.; Giedraitienė, N.; Taluntienė, V.; Apynytė, D.; Bikelis, H.; Makarevičius, G.; Jokubaitis, M.; Vaišvilas, M. Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Versus Autoimmune Encephalitis Using Artificial Intelligence-Based Modeling. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 8222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228222
Petrosian D, Giedraitienė N, Taluntienė V, Apynytė D, Bikelis H, Makarevičius G, Jokubaitis M, Vaišvilas M. Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Versus Autoimmune Encephalitis Using Artificial Intelligence-Based Modeling. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(22):8222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228222
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrosian, David, Nataša Giedraitienė, Vera Taluntienė, Dagnė Apynytė, Haroldas Bikelis, Gytis Makarevičius, Mantas Jokubaitis, and Mantas Vaišvilas. 2025. "Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Versus Autoimmune Encephalitis Using Artificial Intelligence-Based Modeling" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 22: 8222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228222
APA StylePetrosian, D., Giedraitienė, N., Taluntienė, V., Apynytė, D., Bikelis, H., Makarevičius, G., Jokubaitis, M., & Vaišvilas, M. (2025). Differential Diagnosis of Infectious Versus Autoimmune Encephalitis Using Artificial Intelligence-Based Modeling. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(22), 8222. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14228222






