Clinical Outcomes Associated with Stellate Ganglion Block Across Multiple Pain Phenotypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection and Variables
2.3. Procedural Details
2.4. Post-Procedural Care and Follow-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Baseline Characteristics
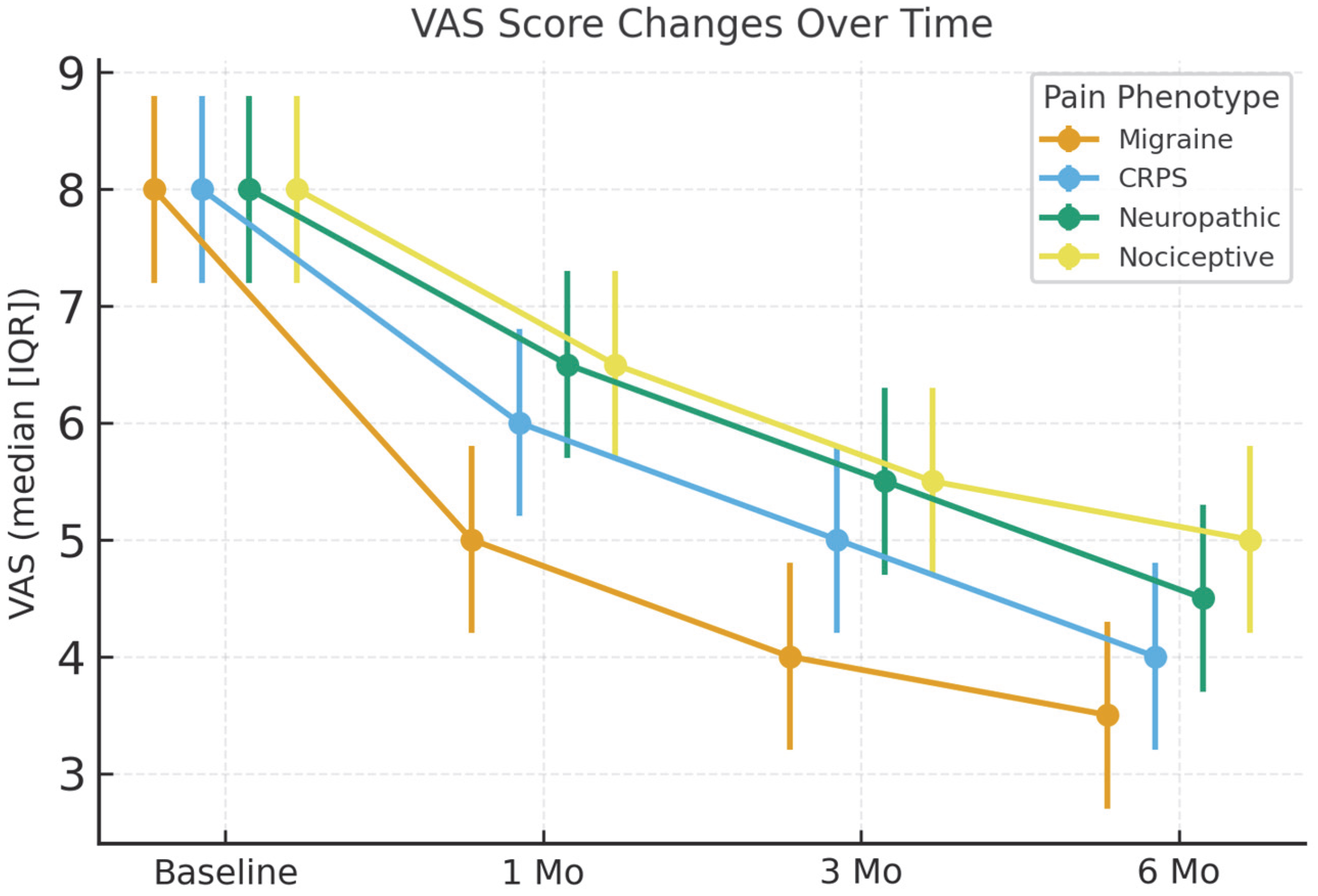
3.2. Primary Outcome: Pain Intensity (VAS)
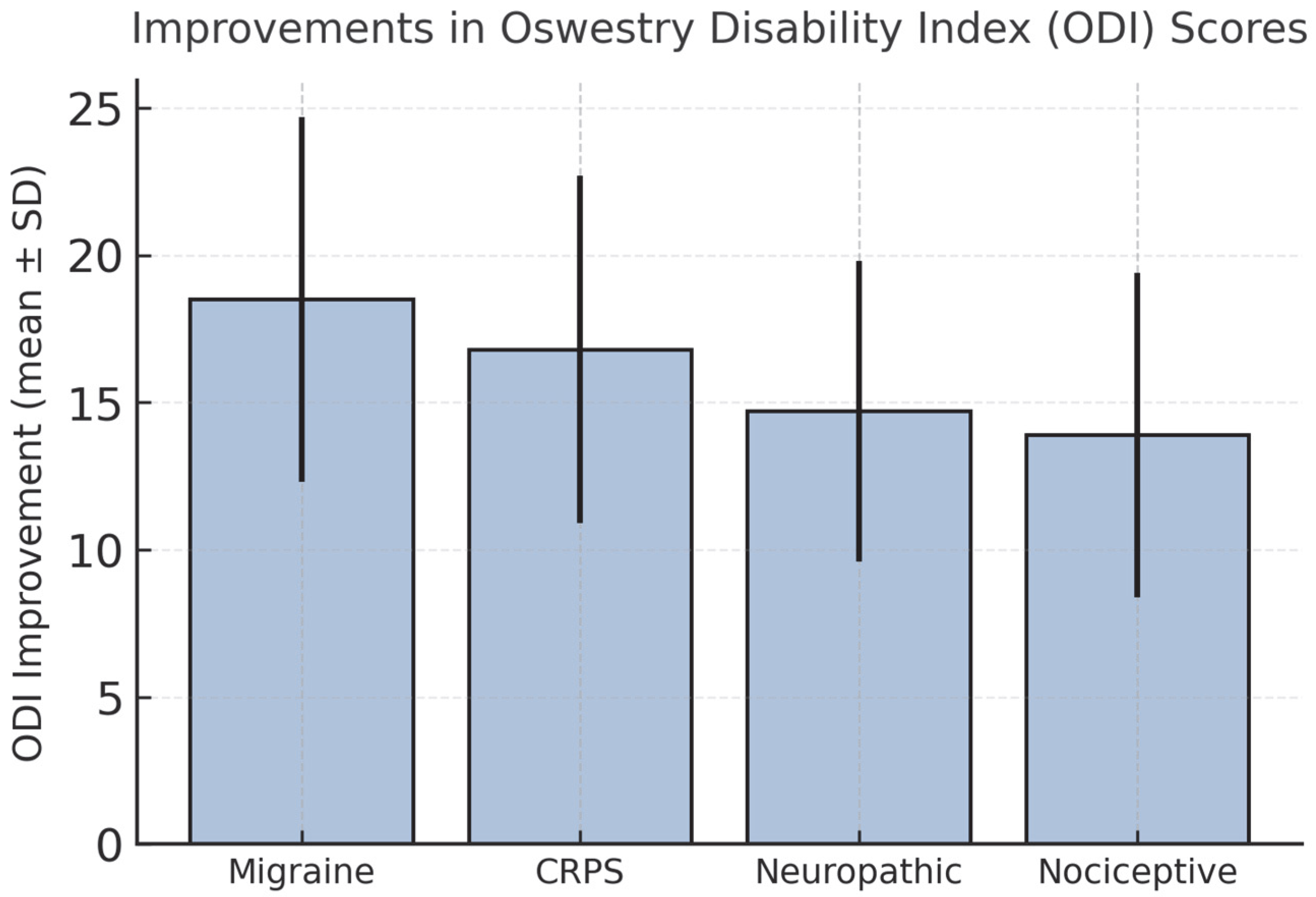
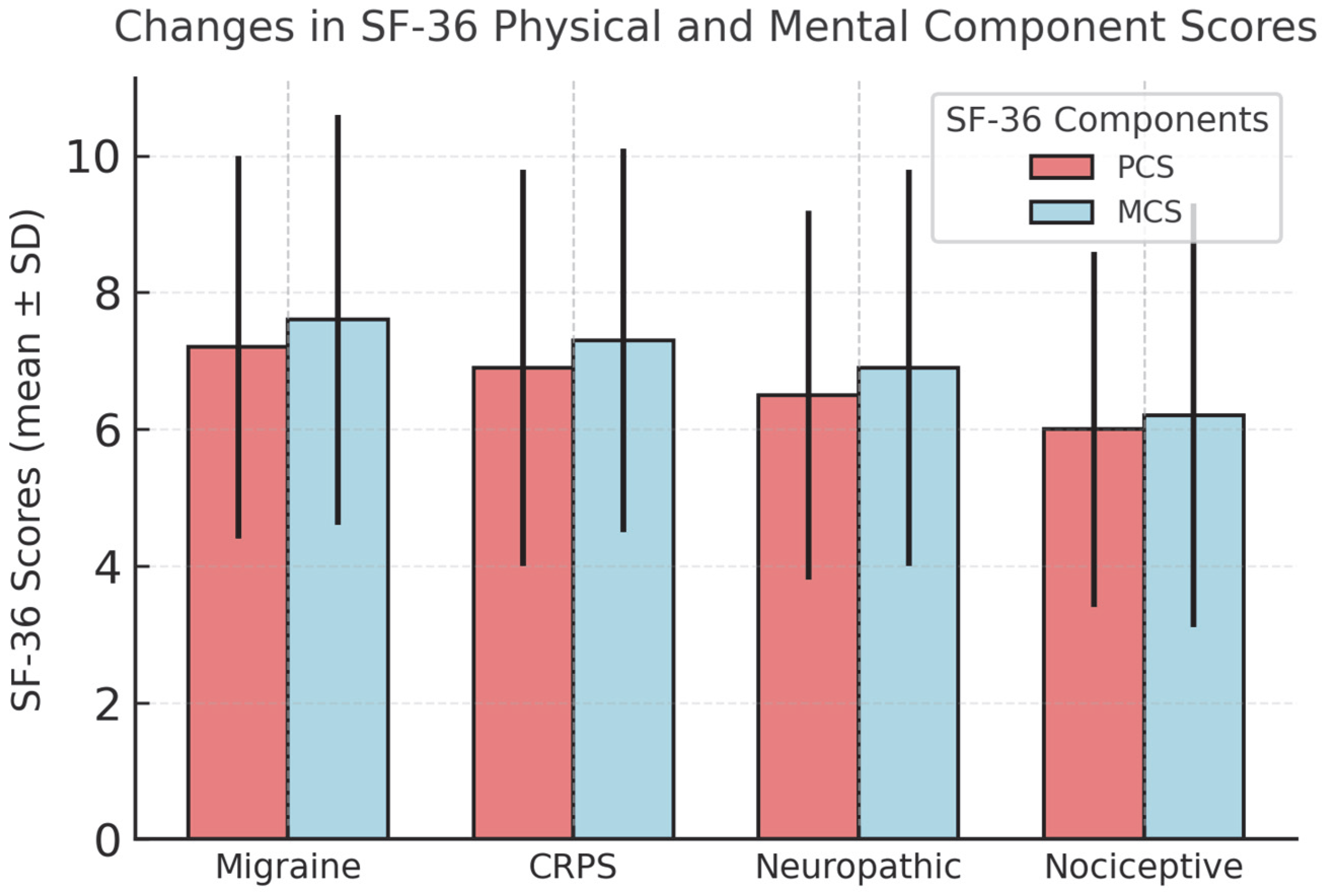
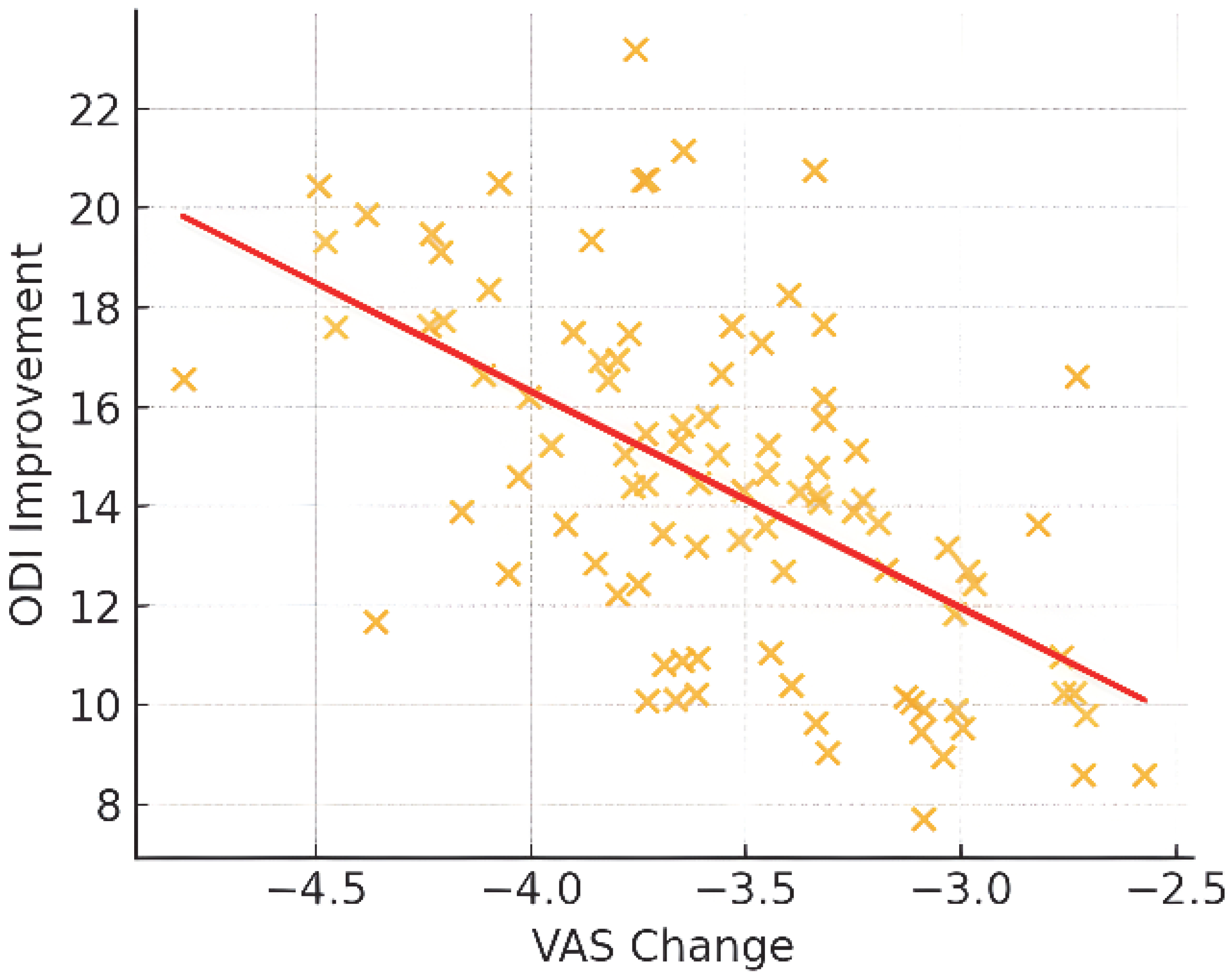
3.3. Secondary Outcomes: Functional Status and Quality of Life
3.4. Multivariate Analysis of Treatment Response
3.5. Safety Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| SGB | Stellate Ganglion Block |
| CRPS | Complex Regional Pain Syndrome |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| ODI | Oswestry Disability Index |
| SF-36 | 36-Item Short Form Health Survey |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| GCP | Good Clinical Practice |
| PCS | Physical Component Score |
| MCS | Mental Component Score |
| MCID | Minimal Clinically Important Difference |
References
- Kirkpatrick, K.; Khan, M.H.; Deng, Y.; Shah, K.B.; Khan, M.; Shah, K. A review of stellate ganglion block as an adjunctive treatment modality. Cureus 2023, 15, e35174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, T.; Liu, T.; An, G.; Li, J.; Xing, J. Stellate ganglion block therapy for complex regional pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain Physician 2024, 27, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Rajarathinam, M. Stellate ganglion block beyond chronic pain: A literature review on its application in painful and non-painful conditions. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 40, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Chen, J.; Xian, L.; Shi, Y. Objective evaluation of stellate ganglion block effects using ultrasound wave intensity technology: A study on hemodynamics. J. Pain Res. 2024, 17, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipov, E.G.; Candido, K.; Ritchie, E.C. Possible reversal of PTSD-related DNA methylation by sympathetic blockade. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 62, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanling, S.R.; Hickey, A.; Lesnik, I.; Hackworth, R.J.; Stedje-Larsen, E.; Drastal, C.A.; McLay, R.N. Stellate ganglion block for the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2016, 41, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zuo, Y. A meta-analysis of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block on the quality of recovery after cancer surgery. Medicine 2024, 103, e39559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.D.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Liou, T.H.; Chen, H.C.; Rau, C.L. Efficacy of noninvasive stellate ganglion blockade performed using physical agent modalities in patients with sympathetic hyperactivity-associated disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, E.D. A prospective, randomized cross-over trial of T2 paravertebral block as a sympathetic block in complex regional pain syndrome. Pain Physician 2019, 22, E417–E424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, S.; Bhoi, D.; Garg, H.; Dehran, M.; Trikha, A.; Ansari, M.T. A Comparison of Analgesic Efficacy and Safety of Clonidine and Methylprednisolone as Additives to 0.25% Ropivacaine in Stellate Ganglion Block for the Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Prospective Randomised Single Blind Study. Korean J. Pain 2023, 36, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.D.; Desai, N.; Patel, A. Stellate ganglion block in post-mastectomy pain syndrome: Emerging interventional strategies. Cureus 2024, 16, e56653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinyes, D.; Rios, J.; López, C. Therapeutic use of low-dose local anesthetics in stellate ganglion block: Implications for agent selection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, V.; Patwardhan, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.; Howe, C.L.; Schultz, D.M.; Shankar, H. Complications associated with stellate ganglion nerve block: A systematic review. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019, 44, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Pu, S.; Xu, X.; Lu, Z.; Wu, J. Real-time ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block for migraine: An observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, C.; Xing, Y.; Meng, L.; Luo, F. Effectiveness, safety, and predictors of response to ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion blockades for the treatment of patients with chronic migraine: A retrospective and observational study. Pain Pract. 2023, 23, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, G.; Bhandari, B.; Kumar, A.; Talawar, P.; Gupta, S.; Atter, P. Efficacy of stellate ganglion interventions for complex regional pain syndrome in the upper limb-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Indian J. Anaesth. 2023, 67, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Yao, P.; Li, H.; Han, Z.; Wang, S.; Hong, T.; Zhao, G. CT-Guided Stellate Ganglion Pulsed Radiofrequency Stimulation for Facial and Upper Limb Postherpetic Neuralgia. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, F.; Cai, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, G.; Zhou, J. Ultrasound-Guided Stellate Ganglion Block Combined with Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy on Postherpetic Neuralgia. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9808994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, V.; Chouhan, R.S.; Pandia, M.P.; Lamsal, R.; Bithal, P.K.; Rath, G.P. Effect of stellate ganglion block on intraoperative propofol and fentanyl consumption in patients with complex regional pain syndrome undergoing surgical repair of brachial plexus injury: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurol. India 2020, 68, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanal, S.; Underwood, M.; Naghdi, S.; Brown, A.; Duncan, C.; Matharu, M.; Mistry, H. A Systematic Review of Economic Evaluations of Pharmacological Treatments for Adults with Chronic Migraine. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Migraine (n = 28) | CRPS (n = 30) | Neuropathic (n = 22) | Nociceptive (n = 16) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 45.9 ± 11.8 | 46.8 ± 12.1 | 47.5 ± 11.2 | 48.1 ± 12.4 |
| Sex (M/F) | 13/15 | 16/14 | 11/11 | 10/6 |
| BMI, mean ± SD | 28.1 ± 3.4 | 27.7 ± 3.3 | 27.9 ± 3.2 | 28.0 ± 3.1 |
| Responders ≥ 30% | 85.7% | 80.0% | 72.7% | 62.5% |
| Responders ≥ 50% | 64.3% | 56.7% | 50.0% | 37.5% |
| Outcome | Migraine | CRPS | Neuropathic | Nociceptive |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODI improvement | +18.5 ± 6.2 | +16.8 ± 5.9 | +14.7 ± 5.1 | +13.9 ± 5.5 |
| SF-36 PCS Δ | +7.2 ± 2.8 | +6.9 ± 2.9 | +6.5 ± 2.7 | +6.0 ± 2.6 |
| SF-36 MCS Δ | +7.6 ± 3.0 | +7.3 ± 2.8 | +6.9 ± 2.9 | +6.2 ± 3.1 |
| Injectate subgroup analysis | No difference | No difference | No difference | No difference |
| Variable | Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.98 | 0.94–1.03 | 0.42 |
| Sex (Female vs. Male) | 1.12 | 0.58–2.17 | 0.74 |
| BMI | 0.97 | 0.88–1.07 | 0.53 |
| Pain phenotype (Ref: Nociceptive) | |||
| Migraine | 2.85 | 1.21–6.71 | 0.016 |
| CRPS | 2.22 | 1.03–4.97 | 0.041 |
| Neuropathic | 1.65 | 0.82–3.28 | 0.15 |
| Injectate type | 1.09 | 0.61–1.93 | 0.76 |
| Complication (Yes vs. No) | 0.89 | 0.38–2.04 | 0.78 |
| Complication | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Transient hoarseness | 6 (6.3%) |
| Conjunctival injection | 3 (3.1%) |
| Major adverse events | 0 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boga, Z.; Kucukbingoz, C.; Yilmaz, A.; Olguner, S.K.; Arslan, A.; Ozer, M.; Sarac, M.E.; Gezercan, Y. Clinical Outcomes Associated with Stellate Ganglion Block Across Multiple Pain Phenotypes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217611
Boga Z, Kucukbingoz C, Yilmaz A, Olguner SK, Arslan A, Ozer M, Sarac ME, Gezercan Y. Clinical Outcomes Associated with Stellate Ganglion Block Across Multiple Pain Phenotypes. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217611
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoga, Zeki, Cagatay Kucukbingoz, Ahmet Yilmaz, Semih Kivanc Olguner, Ali Arslan, Mehmet Ozer, Mustafa Emre Sarac, and Yurdal Gezercan. 2025. "Clinical Outcomes Associated with Stellate Ganglion Block Across Multiple Pain Phenotypes" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217611
APA StyleBoga, Z., Kucukbingoz, C., Yilmaz, A., Olguner, S. K., Arslan, A., Ozer, M., Sarac, M. E., & Gezercan, Y. (2025). Clinical Outcomes Associated with Stellate Ganglion Block Across Multiple Pain Phenotypes. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217611






