Analgesia by Cryotherapy in Patients with Chronic Pain with Analysis of Pain-Modulating and Pro-Inflammatory Parameters—A Clinical Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment
2.2. Population
2.3. Execution of Cryotherapy
2.4. Laboratory Testing
2.5. Pain Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Writing
3. Results
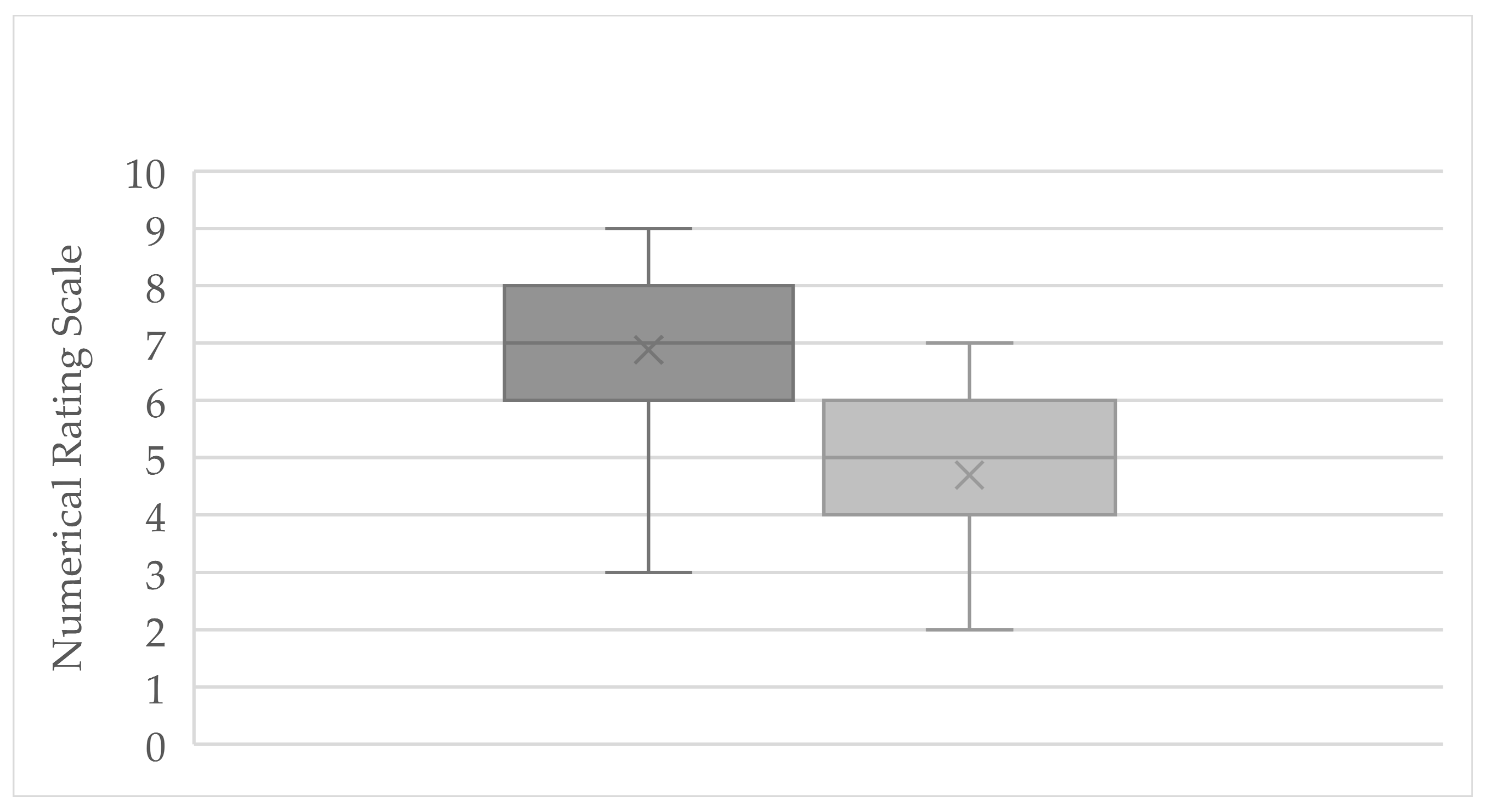
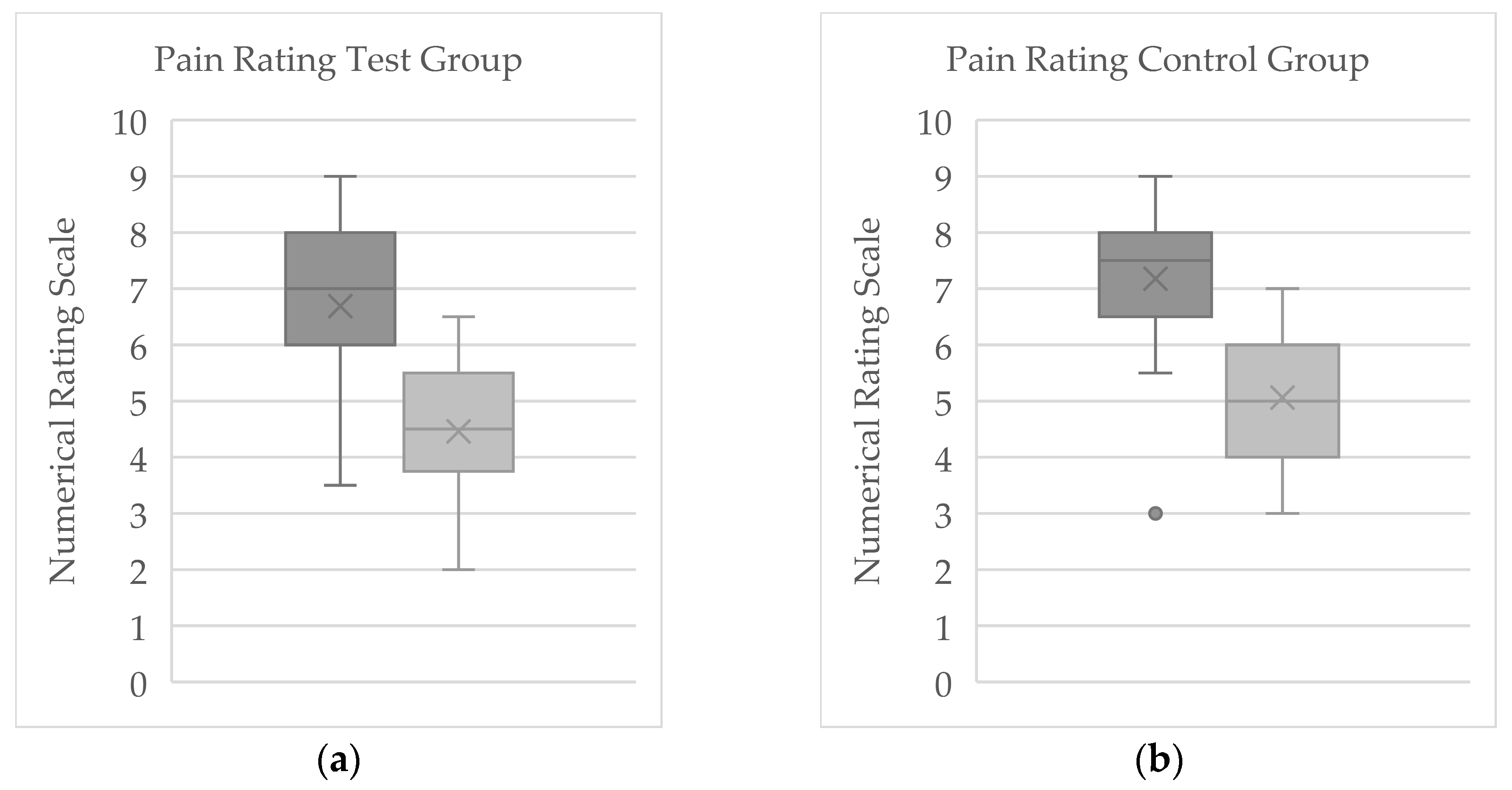
3.1. Numerical Rating Scale
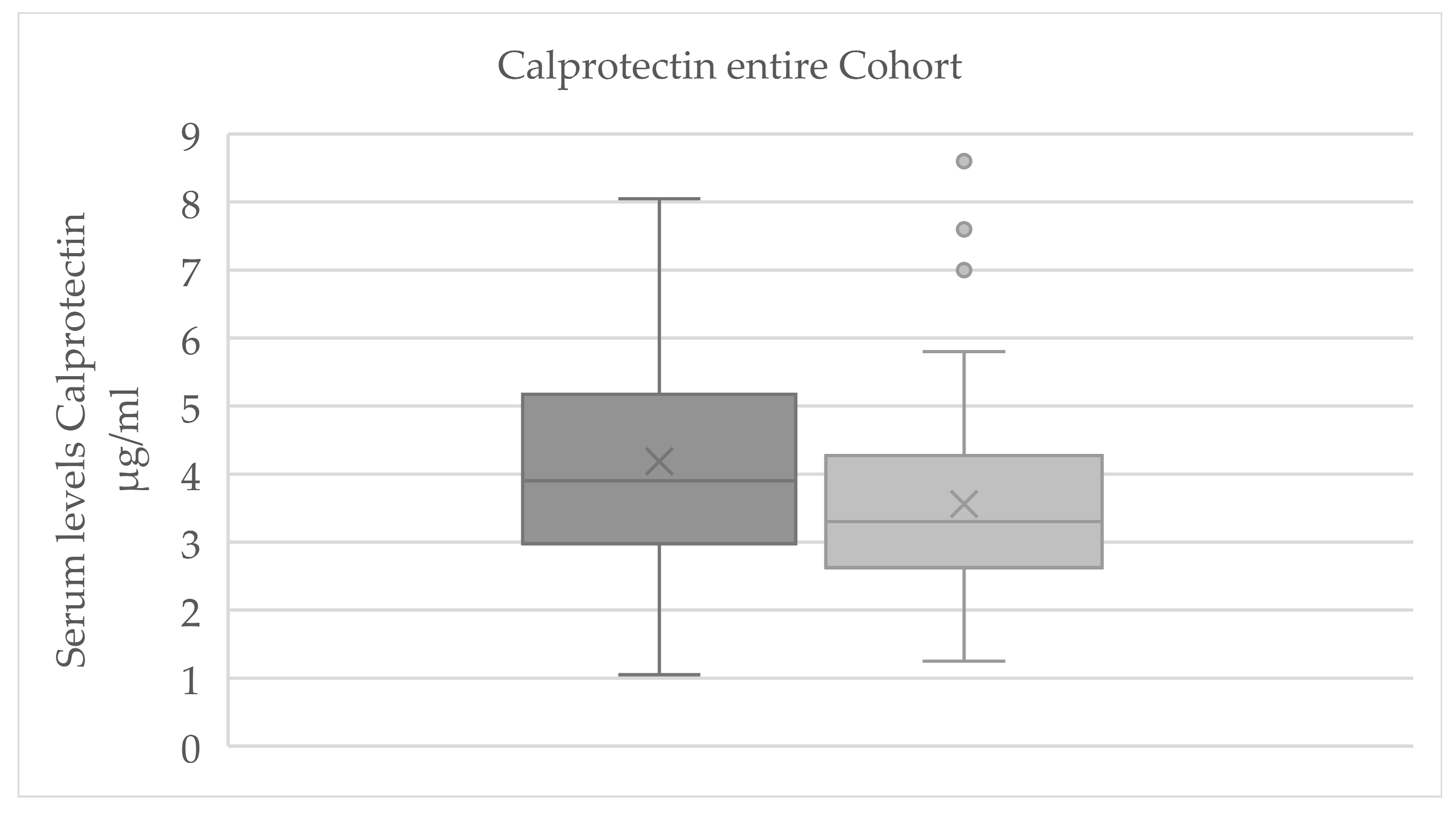
3.2. Evaluation of Serum Parameters
3.2.1. Evaluation of Serum Parameters for Significant Change
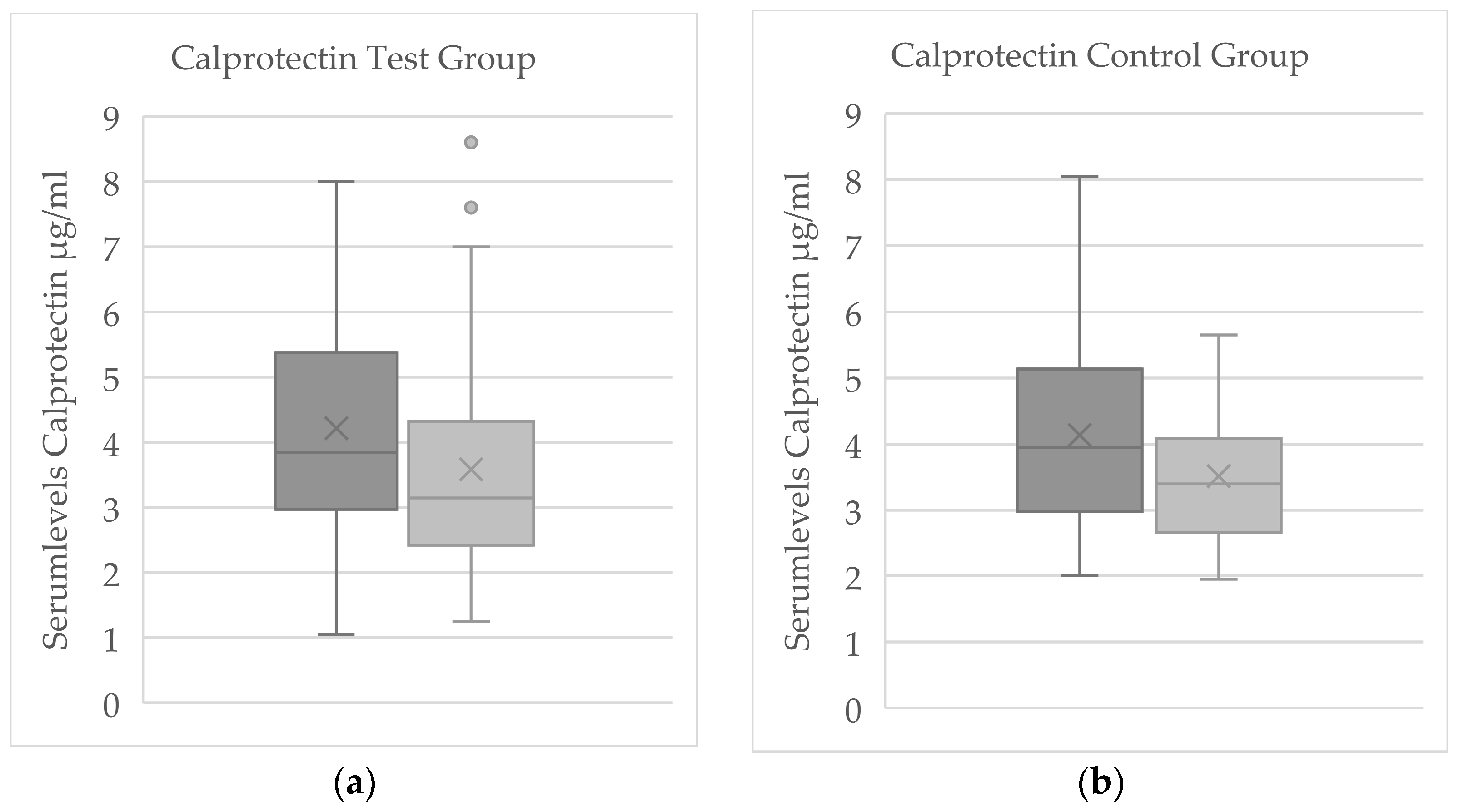
3.2.2. Comparison of Serum Levels Between Test and Control Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| β-NGF | β-nerve growth factor |
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CGRP | Calcitonine-gene-related-peptide |
| CRPS | Chronic regional pain syndrome |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FMS | Fibromyalgia syndrome |
| IL | Interleukin |
| NRS | Numerical rating scale |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| TRP | Transient receptor potential channel |
| TRPV1 | Vanilloid-Receptor 1 transient receptor potential channel |
| WBC | Whole-body-cryotherapy |
Appendix A. Cohort Characterization
| Collective | FMS n = | Chronic Pain Disorder n = | Arthritis n = |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total n = 61 | 32 (52.5%) | 27 (44.3%) | 2 (3.3%) |
| Test group n = 37 | 21 (58.3%) | 15 (41.7%) | 1 (3%) |
| Control group n = 24 | 11 (44%) | 12 (48%) | 1 (8%) |
References
- Wolff, R.; Clar, C.; Lerch, C.; Kleijnen, J. Epidemiologie von Nicht Tumorbedingten Chronischen Schmerzen in Deutschland. Schmerz 2011, 25, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The Revised International Association for the Study of Pain Definition of Pain: Concepts, Challenges, and Compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M. Molecular Pain; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 247–263. ISBN 9780387752686. [Google Scholar]
- Shyu, B.-C.; Tominaga, M. Advances in Pain Research: Mechanisms and Modulation of Chronic Pain; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2018; pp. 13–27. ISBN 978-981-13-1755-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jarlborg, M.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Lamacchia, C.; Martinez Prat, L.; Mahler, M.; Bentow, C.; Finckh, A.; Gabay, C.; Nissen, M.J. Serum Calprotectin: A Promising Biomarker in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stříž, I.; Trebichavský, I. Calprotectin—A Pleiotropic Molecule in Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Physiol. Res. 2004, 53, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, A.B.; Van Den Bosch, M.H.; Blaney Davidson, E.N.; Roth, J.; Vogl, T.; Van De Loo, F.A.; Koenders, M.; Van Der Kraan, P.M.; Geven, E.J.; Van Lent, P.L. The Alarmins S100A8 and S100A9 Mediate Acute Pain in Experimental Synovitis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, M.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S.; Rief, W.; Barke, A.; Aziz, Q.; Benoliel, R.; Cohen, M.; Evers, S.; Giamberardino, M.A.; Goebel, A.; et al. The IASP Classification of Chronic Pain for ICD-11: Chronic Primary Pain. Pain 2019, 160, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, R.; Koppert Michael Strumpf, W.; Willweber-Strumpf, A. (Eds.) Praktische Schmerzmedizin Interdisziplinäre Diagnostik-Multimodale Therapie 4. Auflage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 3–13. ISBN 978-3-662-57486-7. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, J. Schmerz Sucht Ursache Neue Wege in Der Schmerztherapie-Mit Therapieempfehlungen und Begleitenden Übungen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–3, 103–107. ISBN 978-3-662-64903-9. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepańska-Gieracha, J.; Borsuk, P.; Pawik, M.; Rymaszewska, J. Mental State and Quality of Life after 10 Session Whole-Body Cryotherapy. Psychol. Health Med. 2014, 19, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, U.; Dischereit, G.; Klemm, P.M. Pain Reduction through Physical Medicine: Update on the Evidence. Z. Rheumatol. 2022, 81, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenfuß, W. Die Kraft aus der Kälte, 5th ed.; Edition k: Teublitz, Germany, 2022; pp. 12–14. ISBN 978-3-938912-11-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzigon, R.; Grappe, F.; Ravier, G.; Dugue, B. Whole- and Partial-Body Cryostimulation/Cryotherapy: Current Technologies and Practical Applications. J. Therm. Biol. 2016, 61, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizińska, M.; Rutkowski, R.; Romanowski, W.; Lewandowski, J.; Straburzyńska-Lupa, A. Effects of Whole-Body Cryotherapy in Comparison with Other Physical Modalities Used with Kinesitherapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 409174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, P.; Hoffmann, J.; Asendorf, T.; Aykara, I.; Frommer, K.; Dischereit, G.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Neumann, E.; Lange, U.; Klemm, P. Whole-Body Cryotherapy for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Monocentric, Single-Blinded, Randomised Controlled Trial Whole-Body Cryotheraphy in RA. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-Fraire, O.; Rivera-Pérez, J.A.; Guevara-Neri, N.P.; Urrutia-García, K.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, O.A.; Salas-Longoria, K.; Morales-Avalos, R. Efficacy of Whole-Body Cryotherapy in the Treatment of Chronic Low Back Pain: Quasi-Experimental Study. J. Orthop. Sci. 2023, 28, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäluoto, J.; Westerlund, T.; Huttunen, P.; Oksa, J.; Smolander, J.; Dugué, B.; Mikkelsson, M. Effects of Long-Term Whole-Body Cold Exposures on Plasma Concentrations of ACTH, Beta-Endorphin, Cortisol, Catecholamines and Cytokines in Healthy Females. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2008, 68, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Karri, J.; Zacharias, N.A.; Abd-Elsayed, A. Use of Cryotherapy for Managing Chronic Pain: An Evidence-Based Narrative. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzer, C.; Döcke, W.-D.; Volk, H.-D.; Prösch, S. Catecholamines Trigger IL-10 Release in Acute Systemic Stress Reaction by direct Stimulation of Its Promoter/Enhancer Activity in Monocytic Cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 105, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minder, E.I.; Schibli, A.; Mahrer, D.; Nesic, P.; Plüer, K. Effects of Different Centrifugation Conditions on Clinical Chemistry and Immunology Test Results. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2011, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coetzee, J.F.; Lubbers, B.V.; Toerber, S.E.; Gehring, R.; Thomson, D.U.; White, B.J.; Apley, M.D. Plasma Concentrations of Substance P and Cortisol in Beef Calves after Castration or Simulated Castration. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Karoly, P.; Braver, S. The Measurement of Clinical Pain Intensity: A Comparison of Six Methods. Pain 1986, 27, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawker, G.A.; Mian, S.; Kendzerska, T.; French, M. Measures of Adult Pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, S240–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, D.B.; Strout, T.D. The Minimum Clinically Significant Difference in Patient-Assigned Numeric Scores for Pain. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2005, 23, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P.B.; Lamoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, R.M. Clinical Importance of Changes in Chronic Pain Intensity Measured on an 11-Point Numerical Pain Rating Scale. Pain 2001, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, F.D.; Dugué, B.; Costello, J.; Bleakley, C.; Miller, E.; Broatch, J.R.; Polidori, G.; Lubkowska, A.; Louis, J.; Lombardi, G.; et al. Evaluating Safety Risks of Whole-Body Cryotherapy/Cryostimulation (WBC): A Scoping Review from an International Consortium. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inciarte-Mundo, J.; Frade-Sosa, B.; Sanmartí, R. From Bench to Bedside: Calprotectin (S100A8/S100A9) as a Biomarker in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1001025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, A.; Guzel, S.; Sarifakioglu, B.; Guzel, E.C.; Guzelant, A.Y.; Karadag, C.; Kiziler, L. Calprotectin Levels in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis to Assess and Association with Exercise Treatment. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl-Wiesenecker, E.; Galtung, N.; Dickescheid, J.; Prpic, M.; Somasundaram, R.; Kappert, K.; Bauer, W. Blood Calprotectin as a Biomarker for Infection and Sepsis—The Prospective CASCADE Trial. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alito, A.; Verme, F.; Mercati, G.P.; Piterà, P.; Fontana, J.M.; Capodaglio, P. Whole Body Cryostimulation: A New Adjuvant Treatment in Central Sensitization Syndromes? An Expert Opinion. Healthcare 2024, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, A.; Maciak, K.; Miller, E.D.; Starosta, M.; Saluk, J. Targeting Vascular Impairment, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress Dynamics with Whole-Body Cryotherapy in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmann, T.; Moock, J. Diagnostische Verfahren in der Rehabilitation; Bengel, J., Wirtz, M., Zwingmann, C., Eds.; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2008; pp. 329–332. ISBN 9783801720957. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Baseline Mean ± SD Median [95% CI] | End of Study Mean ± SD Median [95% CI] | Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substance P | 3329.3 ± 1075.3 2 | 3273.9 ± 1209.4 2 | −1.267 | 0.205 |
| 3321.1 [3123.5; 3604] 2 | 3188 [2881.6; 3626.8] 2 | |||
| Calprotectin | 4.2 ± 1.7 3 | 3.6 ± 1.4 3 | −2.713 | 0.007 |
| 3.9 [3.25; 4.3] 3 | 3.3 [2.95; 3.8] 3 | |||
| β-NGF | 140.5 ± 693.3 2 | 121.9 ± 572.9 2 | −2.223 | 0.026 1 |
| 0 [0; 0] 2 | 0 [0; 0] 2 | |||
| CGRP | 1424.7 ± 1654.9 2 | 1383.6 ± 1593.7 2 | −0.664 | 0.506 |
| 621.8 [494.1; 820.9] 2 | 594.8 [521.1; 774.9] 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ritter, H.; Beuermann, R.; Unkelbach, V.; Bang, H.; Feist, E. Analgesia by Cryotherapy in Patients with Chronic Pain with Analysis of Pain-Modulating and Pro-Inflammatory Parameters—A Clinical Controlled Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217567
Ritter H, Beuermann R, Unkelbach V, Bang H, Feist E. Analgesia by Cryotherapy in Patients with Chronic Pain with Analysis of Pain-Modulating and Pro-Inflammatory Parameters—A Clinical Controlled Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217567
Chicago/Turabian StyleRitter, Henrike, Ruth Beuermann, Vera Unkelbach, Holger Bang, and Eugen Feist. 2025. "Analgesia by Cryotherapy in Patients with Chronic Pain with Analysis of Pain-Modulating and Pro-Inflammatory Parameters—A Clinical Controlled Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217567
APA StyleRitter, H., Beuermann, R., Unkelbach, V., Bang, H., & Feist, E. (2025). Analgesia by Cryotherapy in Patients with Chronic Pain with Analysis of Pain-Modulating and Pro-Inflammatory Parameters—A Clinical Controlled Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217567






