Effectiveness and Safety of Talc Slurry Pleurodesis in the Treatment of Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion and Low Karnofsky Performance Status Scores
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Talc Slurry Pleurodesis Procedure
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Considerations
2.8. Patient and Public Involvement
3. Results
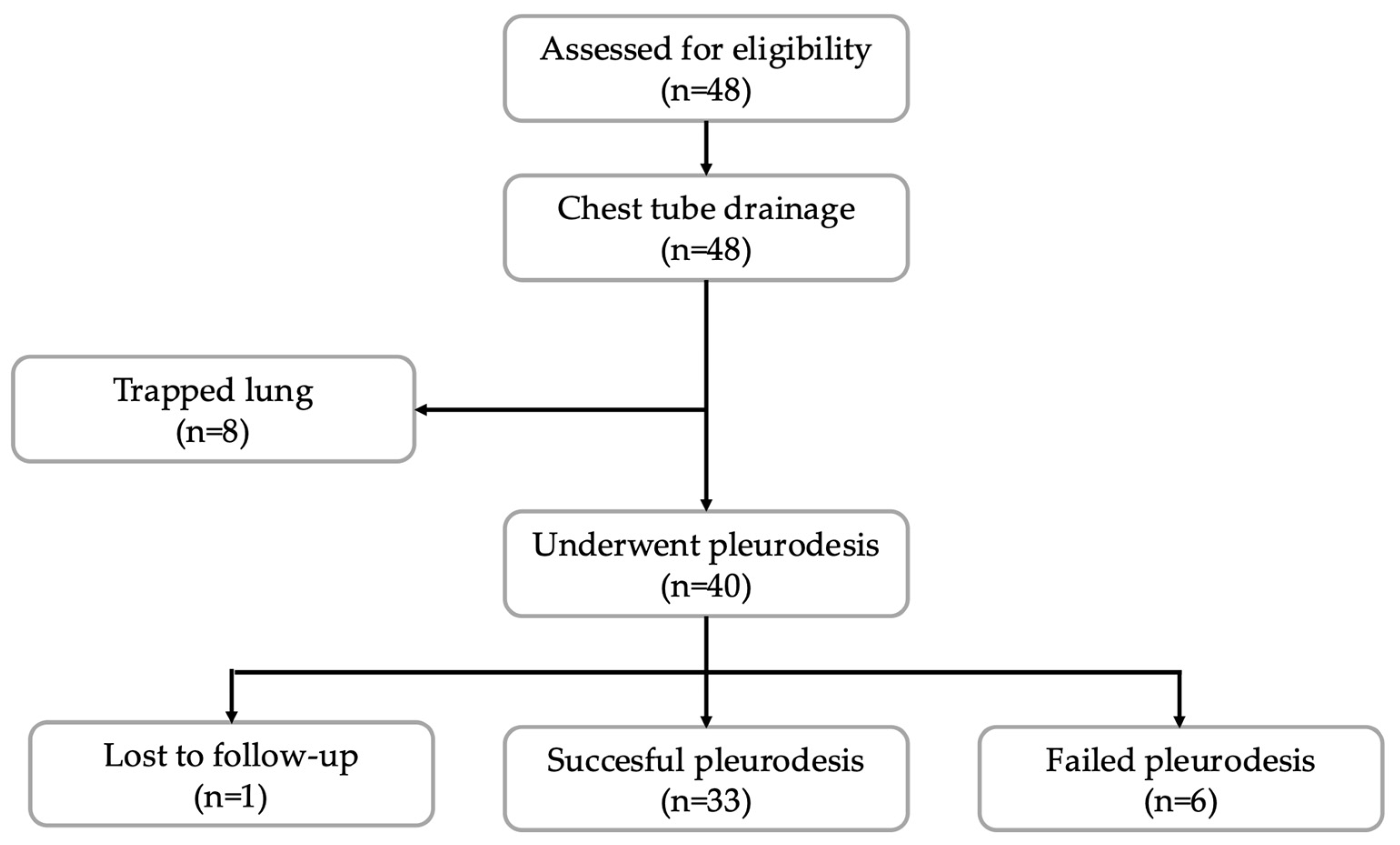
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Baseline Characteristics
3.3. Pleurodesis Outcomes
3.4. Predictors of Success of Pleurodesis
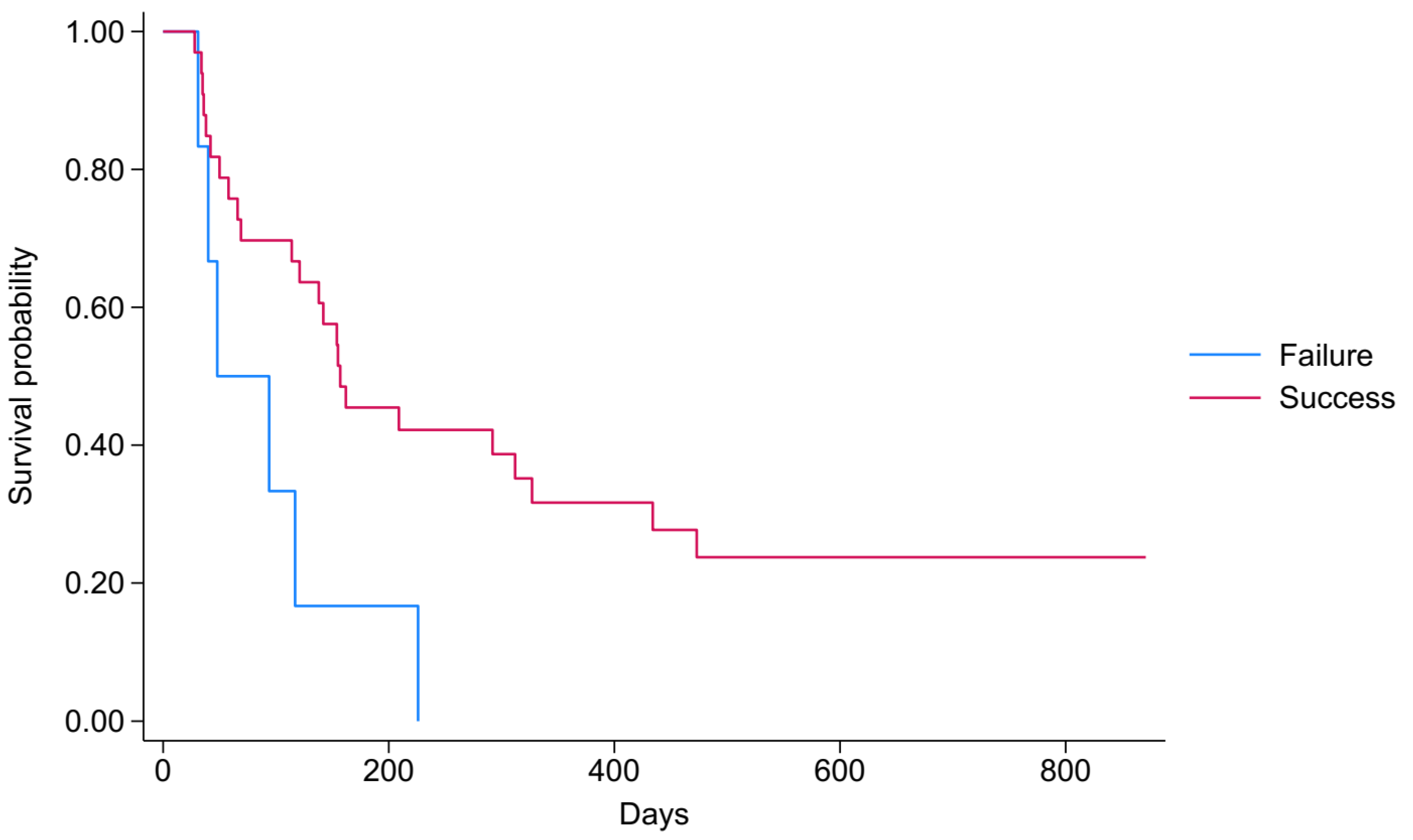
3.5. Survival Analysis
3.6. Predictors of Survival After Pleurodesis
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Results
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
4.3. Comparison with Other Studies
4.4. Clinical and Research Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burgers, J.A.; Kunst, P.W.; Koolen, M.G.; Willems, L.N.; Burgers, J.S.; van den Heuvel, M. Pleural drainage and pleurodesis: Implementation of guidelines in four hospitals. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei, H.; Jabak, S.; Mina, A.; Tfayli, A. Pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions: Outcome and predictors of success. Integr. Cancer Sci. Therap. 2015, 2, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, P.S.; Marques, M.A.; Vargas, F.S. Predictors of talc slurry pleurodesis success in patients with malignant pleural effusion. Pulmonology 2017, 23, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, S.M.; Sileem, A.E.; El-Fakharany, K.M. Pleural fluid CRP, LDH, and pH as predictors of successful pleurodesis in malignant pleural effusions. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2015, 64, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumachi, F.; Mazza, F.; Ermani, M.; Chiara, G.B.; Basso, S.M.M. Talc Pleurodesis as Surgical Palliation of Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion. Analysis of Factors Affecting Survival. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 5071. [Google Scholar]
- Barbetakis, N.; Antoniadis, T.; Tsilikas, C. Results of chemical pleurodesis with mitoxantrone in malignant pleural effusion from breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2004, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.; Souza, M.E.C.; Moraes, F.C.A.; Lima, D.P.; Carvalho, R.L.C. Talc slurry versus thoracoscopic talc insufflation for malignant pleural effusion: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2024, 50, e20240115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, N.R.; Lee, H.J. Diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions: State of the art in 2017. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S1111–S1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffner, J.E. Diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions. Respirology 2008, 13, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, G.; Metintas, M.; Yildirim, H.; Metintas, S.; Dundar, E.; Erginel, S.; Alatas, F. Pleurodesis in follow-up and treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma patients. Tuberk. Toraks 2009, 57, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Mercer, R.M.; Maskell, N.A.; Asciak, R.; McCracken, D.J.; Bedawi, E.O.; Shaarawy, H.; El-Ganady, A.; Psallidas, I.; Miller, R.F.; et al. Survival in patients with malignant pleural effusion undergoing talc pleurodesis. Lung Cancer 2019, 137, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, G.; Neville, E.; Duffy, J.; Ali, N.; Pleural Diseases Group, Standards of Care Committee, British Thoracic Society. BTS guidelines for the management of malignant pleural effusions. Thorax 2003, 58 (Suppl. S2), ii29–ii38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Harriss, E.; Mercer, R.M.; Rahman, N.M. Survival and pleurodesis outcome in patients with malignant pleural effusion—A systematic review. Pleura Peritoneum 2021, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiu, I.; Yevudza, E.; Shrager, J.B. Talc Pleurodesis: A Medical, Medicolegal, and Socioeconomic Review. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 109, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresler, C.M.; Olak, J.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Richards, W.G.; Scalzetti, E.; Fleishman, S.B.; Kernstine, K.H.; Demmy, T.; Jablons, D.M.; Kohman, L.; et al. Phase III intergroup study of talc poudrage vs talc slurry sclerosis for malignant pleural effusion. Chest 2005, 127, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, A.P.; Chan, A.T.; Lee, T.W.; Wan, I.Y.; Ho, J.K. Thoracoscopic talc insufflation versus talc slurry for symptomatic malignant pleural effusion. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1996, 62, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ 2007, 335, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parulekar, W.; Di Primio, G.; Matzinger, F.; Dennie, C.; Bociek, G. Use of small-bore vs large-bore chest tubes for treatment of malignant pleural effusions. Chest 2001, 120, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L.A.; Charnock, G.; Delany, D. Small bore catheter drainage and sclerotherapy for malignant pleural effusions. Cancer 1989, 64, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marom, E.M.; Patz Jr, E.F.; Erasmus, J.J.; McAdams, H.P.; Goodman, P.C.; Herndon, J.E. Malignant pleural effusions: Treatment with small-bore-catheter thoracostomy and talc pleurodesis. Radiology 1999, 210, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller-Kopman, D.J.; Reddy, C.B.; DeCamp, M.M.; Diekemper, R.L.; Gould, M.K.; Henry, T.; Iyer, N.P.; Lee, Y.G.; Lewis, S.Z.; Maskell, N.A.; et al. Management of malignant pleural effusions. An official ATS/STS/STR clinical practice guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, A.C.; Dorn, P.; Psallidas, I.; Porcel, J.M.; Janssen, J.; Froudarakis, M.; Subotic, D.; Astoul, P.; Licht, P.; Schmid, R.; et al. ERS/EACTS statement on the management of malignant pleural effusions. Eur. J. Cardio-Thorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamonsen, M.R.; Lo, A.K.; Ng, A.C.; Bashirzadeh, F.; Wang, W.Y.; Fielding, D.I. Novel use of pleural ultrasound can identify malignant entrapped lung prior to effusion drainage. Chest 2014, 146, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psallidas, I.; Hassan, M.; Yousuf, A.; Duncan, T.; Khan, S.L.; Blyth, K.G.; Evison, M.; Corcoran, J.P.; Barnes, S.; Reddy, R.; et al. Role of thoracic ultrasonography in pleurodesis pathways for malignant pleural effusions (SIMPLE): An open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, H.; Metintas, M.; Ak, G.; Metintas, S.; Erginel, S. Predictors of talc pleurodesis outcome in patients with malignant pleural effusions. Lung Cancer 2008, 62, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, R.M.; Junqueira, J.J.M.; Teixeira, L.R.; Vargas, F.S.; Pego-Fernandes, P.M.; Jatene, F.B. Is full postpleurodesis lung expansion a determinant of a successful outcome after talc pleurodesis? Chest 2009, 136, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viallat, J.R.; Rey, F.; Astoul, P.; Boutin, C. Thoracoscopic talc poudrage pleurodesis for malignant effusions. A review of 360 cases. Chest 1996, 110, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanez, R.C.; Vargas, F.S.; Filomeno, L.B.; Teixeira, L.R.; Fernandez, A.; Jatene, F.; Light, R.W. Intrapleural talc for the treatment of malignant pleural effusions secondary to breast cancer. Cancer 1995, 75, 2688–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, Z.; Ashraf, M. Short comparison of talc poudrage and tetracycline pleurodesis within patients suffering from malignant pleural effusion. Prof. Med. J. 2023, 30, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.E.; Awad, G.; Sanad, M. Chemical pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusion: Which agent is perfect? Cardiothorac. Surg. 2020, 28, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, T.; Morsi, M.; Gomaa, M.; Makled, S. Study of Predictors for Successful Pleurodesis in Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion. Med. J. Cairo Univ. 2020, 85, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Stefani, A.; Natali, P.; Casali, C.; Morandi, U. Talc poudrage versus talc slurry in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion. A prospective comparative study. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2006, 30, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, R.M.; Teixeira, L.R.; Bibas, B.J.; Pego-Fernandes, P.M.; Vargas, F.S.; Jatene, F.B. Effectiveness and safety of outpatient pleurodesis in patients with recurrent malignant pleural effusion and low performance status. Clinics 2011, 66, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Burrows, C.M.; Mathews, W.C.; Colt, H.G. Predicting survival in patients with recurrent symptomatic malignant pleural effusions: An assessment of the prognostic values of physiologic, morphologic, and quality of life measures of extent of disease. Chest 2000, 117, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anevlavis, S.; Kouliatsis, G.; Sotiriou, I.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Archontogeorgis, K.; Karpathiou, G.; Giatromanolaki, A.; Froudarakis, M.E. Prognostic factors in patients presenting with pleural effusion revealing malignancy. Respiration 2014, 87, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, A.; de Dompsure, R.B.; Hagry, O.; Favre, J.P. Early and late mortality after pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusion. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cancer Diagnosis | All (n = 39) | |
|---|---|---|
| n (%) | ||
| Bone cancer | 2 (5.13) | |
| Breast cancer | 13 (33.33) | |
| Gastrointestinal cancer | 2 (5.13) | |
| Gynaecological cancer | 3 (7.69) | |
| Haematological cancer | 2 (5.13) | |
| Lung cancer | 14 (35.90) | |
| Mesothelioma | 2 (5.13) | |
| Renal cell cancer | 1 (2.56) | |
| Characteristics | All (n = 39) | Pleurodesis Failure (n = 6) | Pleurodesis Success (n = 33) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | p Value | |
| Age, years ** | 61 (56–68) | 57 (47–60) | 64 (57–69) | 0.035 |
| Gender, male vs. female | 13 (33.3) | 3 (50.0) | 10 (30.3) | 0.346 |
| The left side is affected | 17 (43.6) | 2 (33.3) | 15 (45.5) | 0.582 |
| KPS score ** | 50 (50–60) | 50 (50–50) | 60 (50–60) | 0.290 |
| Two or less thoracocentesis | 19 (48.7) | 3 (50.0) | 16 (48.5) | 0.946 |
| Number of drainage days pre-pleurodesis, days ** | 8 (6–11) | 8.5 (8–10) | 7 (6–11) | 0.624 |
| Volume of effusion drained before pre-pleurodesis, mL ** | 2600 (1900–4500) | 3150 (1900–5100) | 2550 (1850–4400) | 0.508 |
| Volume of effusion drained post-pleurodesis, mL ** | 200 (100–600) | 725 (100–2000) | 200 (100–550) | 0.308 |
| Time from diagnosis of MPE to chest tube drainage, days ** | 30 (14–60) | 20 (9–43) | 30 (15–60) | 0.284 |
| pH * | 7.43 (0.114) | 7.41 (0.076) | 7.43 (0.120) | 0.497 |
| LDH, U/L ** | 409 (240–774) | 416 (188–1107) | 409 (243–720) | 0.876 |
| Glucose, mmol/L ** | 5.4 (3.4–7.0) | 4.75 (3.3–5.4) | 5.7 (3.6–7.0) | 0.436 |
| Proteins, g/L ** | 38.1 (33.1–43.0) | 34.3 (30.7–41.4) | 38.2 (34.6–43.0) | 0.471 |
| NLR of serum ** | 3.6 (2.8–6.1) | 4.1 (3.5–12.1) | 3.5 (2.8–5.9) | 0.311 |
| NLR of pleural liquid ** | 0.16 (0.06–0.46) | 0.26 (0.19–0.53) | 0.16 (0.05–0.46) | 0.150 |
| Three-Month Mortality | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted * | |||||||
| 95% CI | 95% CI | |||||||
| Characteristics | HR | Lower | Upper | p Value | HR | Lower | Upper | p Value |
| KPS score, >median | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 0.011 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.57 | 0.008 |
| pH, >median | 1.07 | 0.36 | 3.18 | 0.906 | ||||
| LDH, >median | 0.34 | 0.09 | 1.24 | 0.103 | 0.47 | 0.13 | 1.74 | 0.256 |
| Glucose, >median | 1.08 | 0.36 | 3.20 | 0.895 | ||||
| Proteins, >median | 0.86 | 0.29 | 2.55 | 0.781 | ||||
| NLR of serum, >median | 5.04 | 1.38 | 18.44 | 0.014 | 4.82 | 1.25 | 18.62 | 0.023 |
| NLR of liquid, >median | 1.99 | 0.65 | 6.08 | 0.229 | ||||
| End of Study Period Mortality | ||||||||
| Unadjusted | Adjusted * | |||||||
| 95% CI | 95% CI | |||||||
| Characteristics | HR | Lower | Upper | pValue | HR | Lower | Upper | pValue |
| KPS score, >median | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.74 | 0.006 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.55 | 0.001 |
| pH, >median | 1.16 | 0.56 | 2.41 | 0.681 | ||||
| LDH, >median | 0.55 | 0.26 | 1.15 | 0.110 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 1.83 | 0.657 |
| Glucose, >median | 0.79 | 0.38 | 1.63 | 0.522 | ||||
| Proteins, >median | 0.81 | 0.39 | 1.68 | 0.572 | ||||
| NLR of serum, >median | 4.00 | 1.85 | 8.68 | <0.001 | 5.48 | 2.25 | 13.33 | <0.001 |
| NLR of liquid, >median | 1.46 | 0.71 | 3.00 | 0.306 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kastrati, E.; Hasani, A.; Gradica, F.; Isufaj Haliti, T.; Bolat, A.; Hoxha, I. Effectiveness and Safety of Talc Slurry Pleurodesis in the Treatment of Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion and Low Karnofsky Performance Status Scores. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217527
Kastrati E, Hasani A, Gradica F, Isufaj Haliti T, Bolat A, Hoxha I. Effectiveness and Safety of Talc Slurry Pleurodesis in the Treatment of Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion and Low Karnofsky Performance Status Scores. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217527
Chicago/Turabian StyleKastrati, Eliza, Antigona Hasani, Fadil Gradica, Tefta Isufaj Haliti, Aidana Bolat, and Ilir Hoxha. 2025. "Effectiveness and Safety of Talc Slurry Pleurodesis in the Treatment of Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion and Low Karnofsky Performance Status Scores" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217527
APA StyleKastrati, E., Hasani, A., Gradica, F., Isufaj Haliti, T., Bolat, A., & Hoxha, I. (2025). Effectiveness and Safety of Talc Slurry Pleurodesis in the Treatment of Patients with Malignant Pleural Effusion and Low Karnofsky Performance Status Scores. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217527






