Perioperative Outcomes of Ureteroscopy in Patients with Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract and Neurogenic Bladder: A Retrospective Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUA | American Urological Association |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| CHUV | Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| EAU | European Association of Urology |
| JJ | Double J ureteral stent |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| SFR | Stone Free Rate |
| URS | Ureteroscopy |
| UTI | Urinary Tract Infection |
| UPJ | Ureteropelvic Junction |
References
- Türk, C.; Petřík, A.; Sarica, K.; Seitz, C.; Skolarikos, A.; Straub, M.; Knoll, T. EAU Guidelines on Diagnosis and Conservative Management of Urolithiasis. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimos, D.; Krambeck, A.; Miller, N.L.; Monga, M.; Murad, M.H.; Nelson, C.P.; Pace, K.T.; Pais, V.M., Jr.; Pearle, M.S.; Preminger, G.M. Surgical Management of Stones: AUA/Endourology Society Guideline. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, B.K.; Giusti, G.; Sun, Y.; Osther, P.J.; Frank, M.; De Sio, M.; Turna, B.; de la Rosette, J. Complications associated with ureterorenoscopy (URS) related to treatment of urolithiasis: The Clinical Research Office of Endourological Society URS Global study. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, S.; Knoll, T.; Giusti, G. Contemporary ureteroscopic management of renal stones. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 36, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, J.; OuYang, J. Risk Factors of Infectious Complications following Ureteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Urol. Int. 2020, 104, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Lee, M.W. Treatment of stones associated with complex or anomalous renal anatomy. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 34, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhojani, N.; Miller, L.E.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Cutone, B.; Chew, B.H. Risk Factors for Urosepsis After Ureteroscopy for Stone Disease: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampel, A.; Hohenfellner, M.; Schultz-Lampel, D.; Lazica, M.; Bohnen, K.; Thürof, J.W. Urolithiasis in horseshoe kidneys: Therapeutic management. Urology 1996, 47, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, J.N.; Fowler, C.J.; Kessler, T.M. Lower urinary tract dysfunction in the neurological patient: Clinical assessment and management. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, M.S.; Kalmus, A.; Casale, P. Morbidity and efficacy of ureteroscopic stone treatment in patients with neurogenic bladder. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Ren, Y.; Xie, T.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Study on the diagnostic efficacy of the computerized tomography attenuation value of renal pelvis urine in true bacteriuria secondary to renal and ureteral stones. Ren. Fail. 2025, 16, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ost, M.C.; Lee, B.R. Urolithiasis in patients with spinal cord injuries: Risk factors, management, and outcomes. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2006, 16, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerwein, D. Urinary tract infection in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2002, 19, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.; Telang, J.; Kim, T.K.; Swarna, K.; Qi, J.; Dauw, C.; Seifman, B.; Abdelhady, M.; Roberts, W.; Hollingsworth, J.; et al. Infection-related hospitalization following ureteroscopic stone treatment: Results from a surgical collaborative. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khusid, J.A.; Hordines, J.C.; Sadiq, A.S.; Atallah, W.M.; Gupta, M. Prevention and Management of Infectious Complications of Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 718583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAU Guidelines Panel on Urolithiasis. EAU Guidelines; EAU Guidelines Panel on Urolithiasis: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Martov, A.; Gravas, S.; Etemadian, M.; Unsal, A.; Barusso, G.; D’Addessi, A.; Krambeck, A.; de la Rosette, J.; Clinical Research Office of the Endourological Society Ureteroscopy Study Group. Postoperative infection rates in patients with a negative baseline urine culture undergoing ureteroscopic stone removal: A matched case-control analysis on antibiotic prophylaxis from the CROES URS global study. J. Endourol. 2015, 29, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.G.; Jairath, A.; Balaji, S.S.; Tak, G.; Ganpule, A.P.; Vijayakumar, M.; Sabnis, R.B.; Desai, M.R. Changing trends in the endourological management of urolithiasis in anomalous kidneys. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonebrook, E.; Hoff, M.; Spencer, J.D. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract: A Clinical Review. Curr. Treat. Options Pediatr. 2019, 5, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornic, J.; Wöllner, J.; Leitner, L.; Mehnert, U.; Bachmann, L.M.; Kessler, T.M. The Challenge of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria and Symptomatic Urinary Tract Infections in Patients with Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKibben, M.J.; Seed, P.; Ross, S.S.; Borawski, K.M. Urinary Tract Infection and Neurogenic Bladder. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 42, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambyah, P.A.; Oon, J. Catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, J.; Gory, A.; Bernard, L.; Ruffion, A.; Denys, P.; Chartier-Kastler, E. Infection urinaire et vessie neurologique [Urinary tract infection and neurogenic bladder]. Prog. Urol. 2007, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Pearle, M.S. Complications of ureteroscopy. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 31, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rosette, J.; Denstedt, J.; Geavlete, P.; Keeley, F.; Matsuda, T.; Pearle, M.; Preminger, G.; Traxer, O.; CROES URS Study Group. The clinical research office of the endourological society ureteroscopy global study: Indications, complications, and outcomes in 11,885 patients. J. Endourol. 2014, 28, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, J.; Bartoletti, R.; Bruyère, F.; Cai, T.; Geerlings, S.; Köves, B.; Schubert, S.; Pilatz, A.; Veeratterapillay, R.; Wagenlehner, F.M.E.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Urological Infections: Summary of the 2024 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.J.; Wymer, K.; Sanchez, J.; Kavoussi, L. Best Practice Statement on Urologic Procedures and Antimicrobial Prophylaxis. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association of Urology. EAU Guidelines; EAU Guidelines Office: Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2024; ISBN 978-94-92671-24-5. Available online: https://uroweb.org/guidelines (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Stritt, K.; Roth, B.; Masnada, A.; Hammann, F.; Jacot, D.; Domingos-Pereira, S.; Crettenand, F.; Bohner, P.; Sommer, I.; Bréat, E.; et al. UROPOT: Study protocol for a randomized, double-blind phase I/II trial for metabolism-based potentiation of antimicrobial prophylaxis in the urological tract. Trials 2024, 25, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.P. Struvite stones. Kidney Int. 1978, 13, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Gupta, G.; Velu, V.; Awasthi, R.; Dua, K.; Malipeddi, H. Formation of struvite urinary stones and approaches towards the inhibition-A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract | Total (n = 23) |
|---|---|
| Ureteral stenosis/UPJ obstruction–no. (%) | 12 (52.2) |
| Anatomic/malposition–no. (%) | 3 (13.0) |
| Post-cystectomie/urinary diversion–no. (%) | 3 (13.0) |
| Renal transplant | 2 (8.7) |
| Reflux–no. (%) | 1 (4.3) |
| Other–(%) | 2 (8.7) |
| Neurogenic Bladder | Total (n = 30) |
|---|---|
| Cerebrovascular disease (Stroke)–no. (%) | 8 (26.7) |
| Neurodegenerative disease–no. (%) | 8 (26.7) |
| Spinal cord injury/paraplegia–no. (%) | 4 (13.3) |
| Diabetic or toxic neuropathy–no. (%) | 3 (10.0) |
| Congenital disorder–no. (%) | 2 (3.7) |
| Other–no. (%) | 5 (16.7) |
| Type of LUTS | |
| Urinary retention–no. (%) | 4 (13.3) |
| Overactive bladder/incontinence–no. (%) | 7 (23.3) |
| Mixed symptoms–no. (%) | 6 (20.0) |
| Use of urinary catheter–no. (%) | 13 (43.3) |
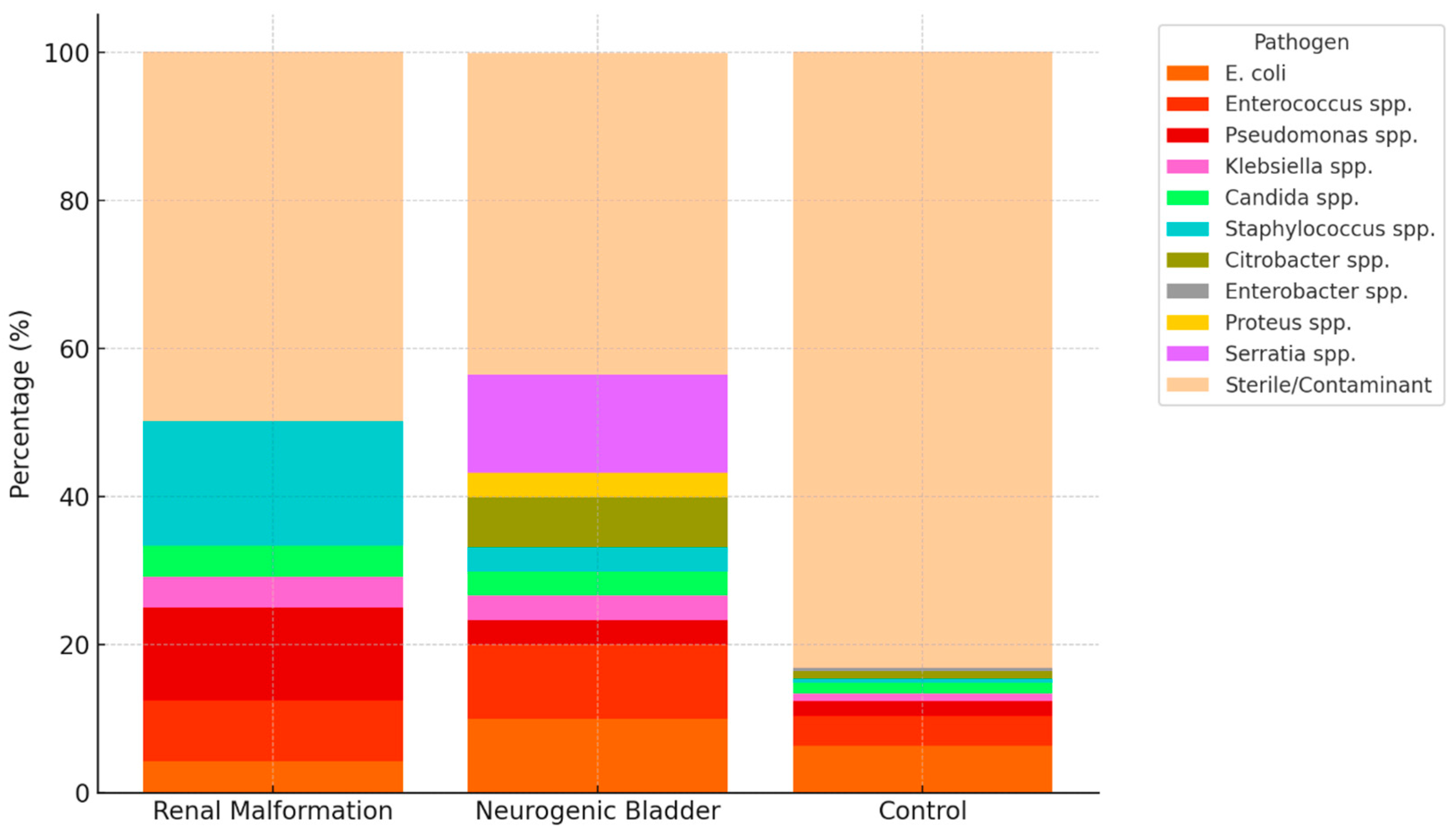
| Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract (n = 23) | Neurogenic Bladder (n = 30) | Control (n = 202) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogens | |||
| Escherichia coli | 1 (4.2) | 3 (10.0) | 13 (6.4) |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 2 (8.3) | 3 (10.0) | 8 (4.0) |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 3 (12.5) | 1 (3.3) | 4 (2.0) |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 1 (4.2) | 1 (3.3) | 2 (1.0) |
| Candida albicans/glabrata | 1 (4.2) | 1 (3.3) | 3 (1.5) |
| Staphylococcus aureus/lugdunensis | 4 (16.7) | 1 (3.3) | 1 (0.5) |
| Citrobacter freundii/koseri | - | 2 (6.7) | 2 (1.0) |
| Enterobacter cloacae | - | - | 1 (0.5) |
| Proteus mirabilis | - | 1 (3.3) | - |
| Serratia marcescens | - | 4 (13.3) | - |
| Sterile/Contaminant flora | 11 (50.0) | 13 (43.3) | 168 (83.2) |
| Renal Malformation (n = 23) | Neurogenic Bladder (n = 30) | Control (n = 297) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | ||||
| Median age–yr (IQR) | 67.0 (20–86) | 68.5 (29–86) | 54.0 (11–96) | <0.001 |
| Sex, male–no (%) | 12 (52.2) | 27 (90.0) | 205 (69.0) | 0.01 |
| Sex, female–no (%) | 11 (47.8) | 3 (10.0) | 92 (31.0) | - |
| Median BMI–kg/m2 (IQR) | 24.9 (18–36) | 25.5 (18–62) | 27.1 (16–52) | 0.064 |
| ASA score ≥ 3–no (%) | 8 (34.8) | 23 (76.7) | 58 (19.5) | <0.001 |
| Median Creatinine-mmol/l (IQR) | 95 (50–364) | 84 (34–183) | 86 (39–348) | 0.938 |
| Intervention Details | ||||
| Positive urine culture–no (%) | 12 (52.2) | 17 (56.7) | 34 (11.5) | <0.001 |
| Indications for URS | ||||
| Urolithiasis–no (%) | 21 (91.3) | 28 (93.3) | 274 (92.3) | 0.353 |
| Urogenital cancer–no (%) | 2 (8.7) | 2 (6.7) | 23 (7.7) | - |
| JJ stent in situ–no (%) | 14 (60.9) | 27 (90.0) | 248 (83.5) | 0.012 |
| Median JJ dwell time–day (IQR) | 28.0 (8–65) | 36.0 (6–133) | 32.0 (2–365) | 0.591 |
| Median operative time–min (IQR) | 48.0 (9–113) | 52.0 (6–83) | 43.0 (7–138) | 0.789 |
| Infectious complication | ||||
| Infectious complication–no (%) | 7 (30.4) | 10 (33.3) | 12 (4.0) | <0.001 |
| Odds Ratio (OR) | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | |||
| Age (per year) | 0.98 | 0.96–1.01 | 0.159 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.49 | 0.13–1.26 | 0.488 |
| ASA score ≥ 3 | 1.36 | 0.40–3.82 | 0.634 |
| Urinary catheter | 13.3 | 4.1–17.0 | <0.001 |
| Positive urine culture | 0.50 | 0.26–0.87 | 0.008 |
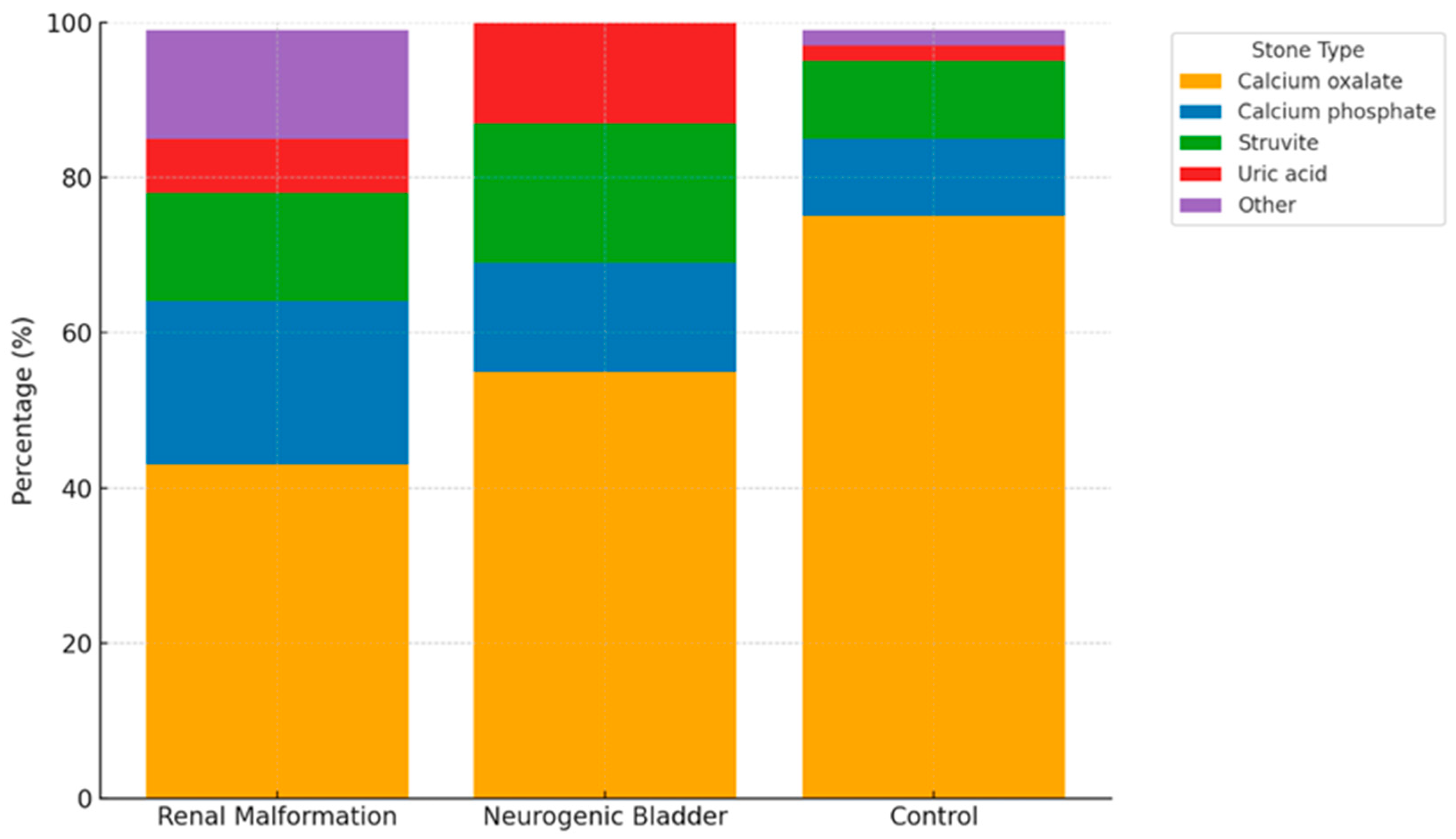
| Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract (n = 14) | Neurogenic Bladder (n = 22) | Control (n = 290) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kidney Stone Composition | |||
| Calcium oxalate–no (%) | 6 (43) | 12 (55) | 220 (75) |
| Calcium phosphate–no (%) | 3 (21) | 3 (14) | 30 (10) |
| Struvite–no (%) | 2 (14) | 4 (18) | 30 (10) |
| Uric acid–no (%) | 1 (7) | 3 (14) | 5 (2) |
| Other–no (%) | 2 (14) | 0 | 5 (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breu, B.; Ortolini, M.; Masnada, A.; Crettenand, F.; Grilo, N.; Stritt, K. Perioperative Outcomes of Ureteroscopy in Patients with Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract and Neurogenic Bladder: A Retrospective Comparative Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217508
Breu B, Ortolini M, Masnada A, Crettenand F, Grilo N, Stritt K. Perioperative Outcomes of Ureteroscopy in Patients with Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract and Neurogenic Bladder: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217508
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreu, Beatrice, Matteo Ortolini, Audrey Masnada, François Crettenand, Nuno Grilo, and Kevin Stritt. 2025. "Perioperative Outcomes of Ureteroscopy in Patients with Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract and Neurogenic Bladder: A Retrospective Comparative Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217508
APA StyleBreu, B., Ortolini, M., Masnada, A., Crettenand, F., Grilo, N., & Stritt, K. (2025). Perioperative Outcomes of Ureteroscopy in Patients with Anatomical Anomalies of the Urinary Tract and Neurogenic Bladder: A Retrospective Comparative Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7508. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217508






