The Impact of the Oral and Esophageal Microbiota in EoE and Achalasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Oral and Esophageal Microbiota
1.2. The Pathologies
1.2.1. Eosinophilic Esophagitis
1.2.2. Esophageal Achalasia
1.3. Rationale and Aim
2. Materials and Methods
3. Interactions Between the Esophageal Microbiota and Esophageal Diseases
3.1. Microbiota and EoE
3.2. Microbiota and Achalasia
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ullah, H.; Arbab, S.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, Q.; Li, K. Crosstalk between gut microbiota and host immune system and its response to traumatic injury. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1413485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, K.E.; Pfaffinger, J.M.; Ryznar, R. The interplay between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and implications for host health and disease. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2393270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Cong, Y. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Ng, S.C. The gut microbiota in the pathogenesis and therapeutics of inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, G.; Guarnaccia, A.; Fancello, G.; Agrillo, C.; Iannarelli, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Masucci, L. Fecal microbiota transplantation and other gut microbiota manipulation strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Song, Z. The oral microbiota: Community composition, influencing factors, pathogenesis, and interventions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 895537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contaldo, M.; Fusco, A.; Stiuso, P.; Lama, S.; Gravina, A.G.; Itro, A.; Federico, A.; Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, F.; Serpico, R.; et al. Oral microbiota and salivary levels of oral pathogens in gastrointestinal diseases: Current knowledge and exploratory study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T. Gut microbiota dysbiosis: Triggers, consequences, diagnostic and therapeutic options. Microorganisms. 2022, 10, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhi, M. The involvement of oral bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2024, 12, goae076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliarakis, I.; Messaritakis, I.; Nikolouzakis, T.K.; Hamilos, G.; Souglakos, J.; Tsiaoussis, J. Oral bacteria and intestinal dysbiosis in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.N.; Ganeshkumar, N.; Kolenbrander, P.E. Helicobacter pylori adheres selectively to Fusobacterium spp. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 13, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Feng, L.; Cai, X.; Qian, Y.; Xu, L. Esophageal microflora in esophageal diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1145791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, D.; Makihara, S.; Corsi, P.R.; Viana, A.T.; Wiczer, M.V.; Nakakubo, S.; Mimica, L.M. Microbial flora of the normal esophagus. Dis. Esophagus 1998, 11, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Bini, E.J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M.; Francois, F.; Blaser, M.J. Bacterial biota in the human distal esophagus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4250–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plat, V.D.; van Rossen, T.M.; Daams, F.; de Boer, N.K.; de Meij, T.G.J.; Budding, A.E.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; van der Peet, D.L. Esophageal microbiota composition and outcome of esophageal cancer treatment: A systematic review. Dis. Esophagus 2022, 35, doab076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landres, R.T.; Kuster, G.G.; Strum, W.B. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology 1978, 74, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhowaiter, S. Eosinophilic esophagitis. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, D.; Marella, S.; Idelman, G.; Chang, J.W.; Chehade, M.; Hogan, S.P. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Immune mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 1142–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schizas, D.; Syllaios, A.; Vailas, M.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Triantafyllou, T.; Tsapralis, D.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Theodorou, D. Eosinophilic esophagitis and achalasia: Two distinct nosologic entities or a possible etiopathogenic association? Dig. Dis. 2021, 39, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; Christos, P.J.; Reisacher, W.R. Airborne and food sensitization patterns in children and adults with eosinophilic esophagitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.A.; Allen-Brady, K.; Uchida, A.M.; Peterson, K.A.; Hoffman, A.M.; Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Achalasia is strongly associated with eosinophilic esophagitis and other allergic disorders. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 34–41.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, A.F.; Rake, G.W. Achalasia of the cardia: So-called cardiospasm. QJM 1930, 23, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Brina, A.L.P.; Palmieri, O.; Cannarozzi, A.L.; Tavano, F.; Guerra, M.; Bossa, F.; Gentile, M.; Merla, A.; Biscaglia, G.; Cuttitta, A.; et al. Focus on achalasia in the omics era. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrilas, P.J.; Boeckxstaens, G. The spectrum of achalasia: Lessons from studies of pathophysiology and high-resolution manometry. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, U.C.; Daschakraborty, S.B.; Singh, R. Pathogenesis of achalasia cardia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3050–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.B.; Ketchem, C.J.; Dougherty, M.K.; Eluri, S.; Dellon, E.S. Association between eosinophilic esophagitis and esophageal dysmotility: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder Grusell, E.; Dahlén, G.; Ruth, M.; Bergquist, H.; Bove, M. The cultivable bacterial flora of the esophagus in subjects with esophagitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, G.; Shilts, M.H.; Boone, H.H.; Correa, H.; Acra, S.; Tovchigrechko, A.; Rajagopala, S.V.; Das, S.R. The salivary microbiome is altered in children with eosinophilic esophagitis and correlates with disease activity. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitch, T.C.A.; Bisdorf, K.; Afrizal, A.; Riedel, T.; Overmann, J.; Strowig, T.; Clavel, T. A taxonomic note on the genus Prevotella: Description of four novel genera and emended description of the genera Hallella and Xylanibacter. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 45, 126354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasahira, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Go, T.T.; Yo, S.; Monden, S.; Ninomiya, T.; Oosawa, M.; Handa, O.; Umegaki, E.; Inoue, R.; et al. The relationship between bacterial flora in saliva and esophageal mucus and endoscopic severity in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.K.; Fang, R.; Wagner, B.D.; Choe, H.N.; Kelly, C.J.; Schroeder, S.; Moore, W.; Stevens, M.J.; Yeckes, A.; Amsden, K.; et al. Esophageal microbiome in eosinophilic esophagitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, B.L.; Abonia, J.P.; Abud, E.M.; Aceves, S.S.; Ackerman, S.J.; Braskett, M.; Chang, J.W.; Chehade, M.; Constantine, G.M.; Davis, C.M.; et al. Advances and ongoing challenges in eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders presented at the CEGIR/TIGERs symposium at the 2024 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology meeting. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, S.; Calgaro, M.; Pandolfo, M.; Caldart, F.; Ghisa, M.; Greco, E.; Sattin, E.; Valle, G.; Dellon, E.S.; Vitulo, N.; et al. Salivary microbiota composition may discriminate between patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) and non-EoE subjects. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchin, S.; Bonazzi, E.; Tomasulo, A.; Bertin, L.; Lorenzon, G.; Maniero, D.; Zingone, F.; Cardin, R.; Barberio, B.; Ghisa, M.; et al. Could modulating the esophageal microbiome be the answer for eosinophilic esophagitis treatment? Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, N.; Khademian, M.; Momen, T.; Saneian, H.; Nasri, P.; Famouri, F.; Ebrahimi, G. The effectiveness of synbiotic on the improvement of clinical symptoms in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Int. J. Pediatr. 2022, 2022, 4211626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvoet, S.; Doucet-Ladevèze, R.; Perrot, M.; Barretto, C.; Nutten, S.; Blanchard, C. Beneficial effect of Lactococcus lactis NCC 2287 in a murine model of eosinophilic esophagitis. Allergy 2016, 71, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, W.F.; Fu, P.Y.; Xu, J.Q.; Wang, T.Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, Z.C.; et al. The role of type II esophageal microbiota in achalasia: Activation of macrophages and degeneration of myenteric neurons. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 276, 127470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Duda, K.A.; Lanzetta, R.; Silipo, A.; De Castro, C.; Molinaro, A. A journey from structure to function of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15767–15821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tume, R.; El Sherbiny, S.; Bono, R.; Gautier, T.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Meroño, T. The balance between proinflammatory “bad” and immunomodulatory “good” lipopolysaccharide for understanding gut-derived systemic inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1588129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Youn, Y.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lim, C.H.; Lim, H.S.; Moon, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.; Hong, S.J. Esophageal microbiota and nutritional intakes in patients with achalasia before and after peroral endoscopic myotomy. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 28, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Sato, H.; Mizusawa, T.; Tominaga, K.; Ikarashi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Mizuno, K.I.; Hashimoto, S.; Yokoyama, J.; Terai, S. Comparison of oral and esophageal microbiota in patients with achalasia before and after peroral endoscopic myotomy. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 32, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, H.; Ihara, E.; Takeya, K.; Mukai, K.; Onimaru, M.; Ouchida, K.; Hata, Y.; Bai, X.; Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, T.; et al. The interplay between alterations in esophageal microbiota associated with Th17 immune response and impaired LC20 phosphorylation in achalasia. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
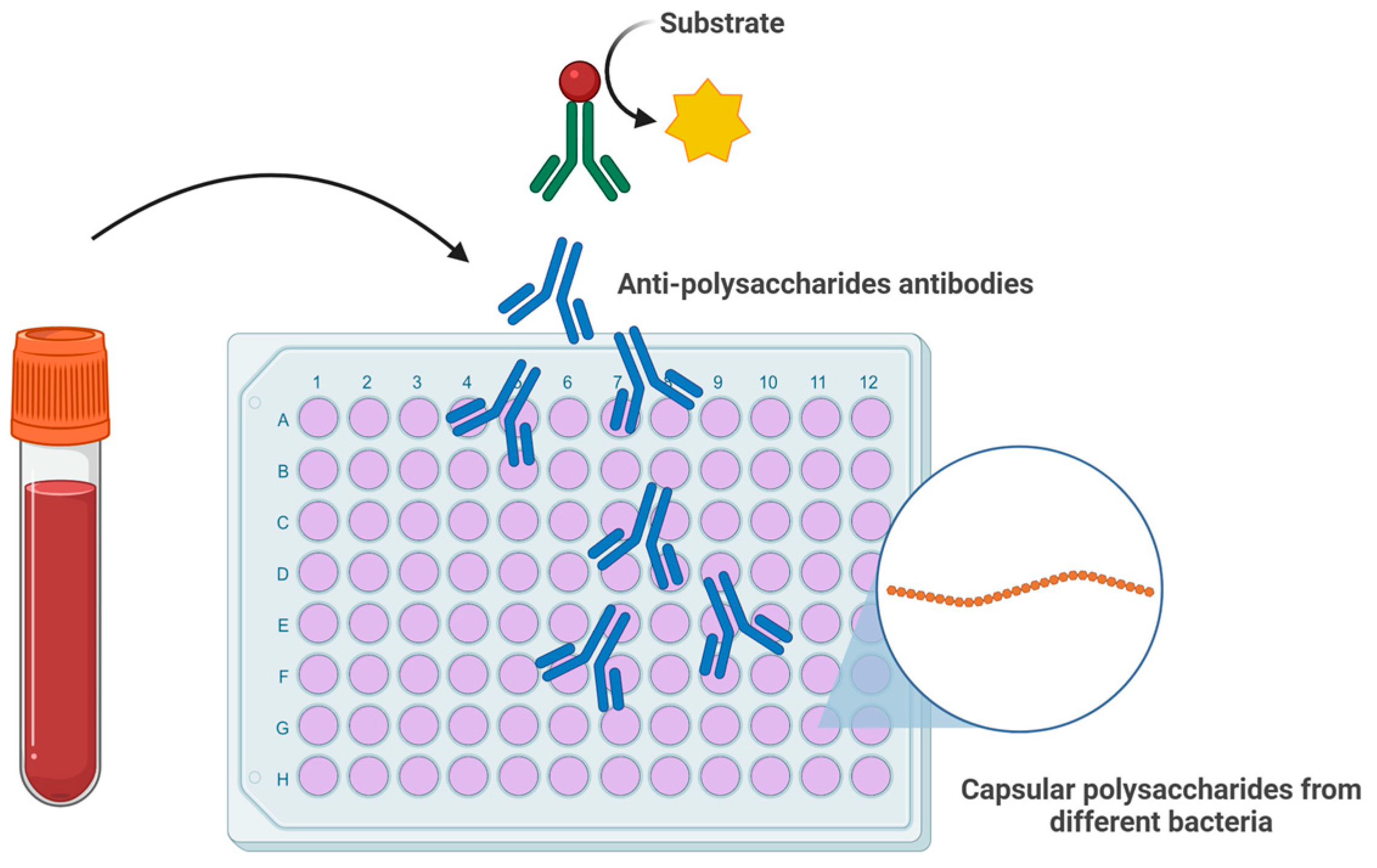
- Temme, J.S.; Butler, D.L.; Gildersleeve, J.C. Anti-glycan antibodies: Roles in human disease. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 1485–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
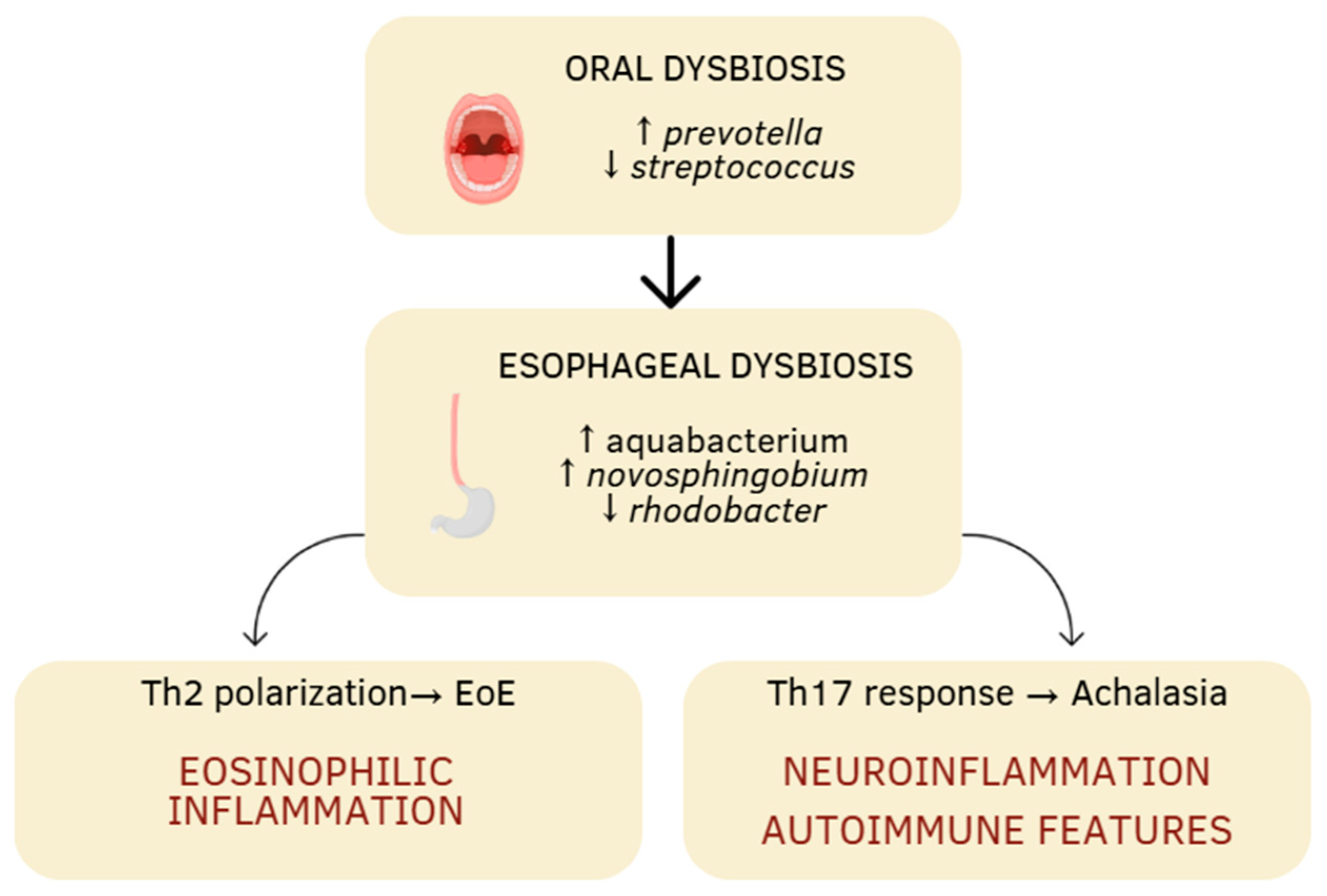
| Aspect | Eosinophilic Esophagitis | Achalasia |
|---|---|---|
| Microbial diversity | Increased | Reduced |
| Altered dominant flora | ↑ prevotella, ↑ haemophilus, ↑ aggregatibacter, ↓ streptococcus | ↑ aquabacterium, ↑ novosphingobium, ↑ lactobacillus, ↓ rhodobacter |
| Type of immune response | prevalence Th2 (↑ IL-4, IL-5, IL-13) | prevalence Th17 (↑ IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22, IL-23A) Activation TLR4-MYD88-NF-κB |
| Physiopathological consequences | epithelial barrier dysfunction, eosinophilic inflammation | neuronal loss of the myenteric plexus, esophageal motor dysfunction |
| Persistence of dysbiosis after treatment | not clearly documented (but possible) | persistent even after POEM 1 |
| Therapeutic prospects | probiotics in experimental phase to restore the barrier and modulate inflammation | probiotics or targeted interventions to limit immune activation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manente, R.; De Caro, G.; Paris, D.; Tramice, A.; Boccia, G.; Zeppa, P.; Chiodo, F.; Iovino, P. The Impact of the Oral and Esophageal Microbiota in EoE and Achalasia. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217502
Manente R, De Caro G, Paris D, Tramice A, Boccia G, Zeppa P, Chiodo F, Iovino P. The Impact of the Oral and Esophageal Microbiota in EoE and Achalasia. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(21):7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217502
Chicago/Turabian StyleManente, Roberta, Gianluca De Caro, Debora Paris, Annabella Tramice, Giovanni Boccia, Pio Zeppa, Fabrizio Chiodo, and Paola Iovino. 2025. "The Impact of the Oral and Esophageal Microbiota in EoE and Achalasia" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 21: 7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217502
APA StyleManente, R., De Caro, G., Paris, D., Tramice, A., Boccia, G., Zeppa, P., Chiodo, F., & Iovino, P. (2025). The Impact of the Oral and Esophageal Microbiota in EoE and Achalasia. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(21), 7502. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14217502








